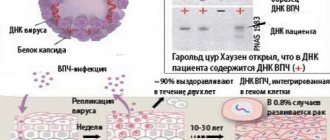
One of the most common papillomaviruses is HPV 16, which manifests itself differently in people and is transmitted sexually from a partner. The human body is able to cope with the infection on its own: within a few months after infection, HPV is destroyed or begins to manifest itself. Treatment of HPV type 16 should include antiviral and immunostimulating drugs.
What it is?
HPV is a virus that can enter the body of a healthy person from the external environment. Depending on the route of transmission, it infects the carrier with one or several strains of varying degrees of cancer danger. The virus usually lies dormant in the body. Its activation is associated with moments of weakening of the immune system, which ceases to stop the development of viral particles.
Results table
When conducting an HPV analysis, the results are summarized in a table, which includes information about quantitative and qualitative indicators.
This table provides general information about possible indicators based on PCR analysis.
| Expected result | HPV viral load | Decoding of indicators. |
| Negative reaction. Clinically insignificant. | less than 3 Lg | The virus was not detected in the body. Refers to the norm of indicators. |
| Doubtful information. Clinically significant indicators. | 3 – 5 Lg | The concentration of the virus is at the limit values (slightly exceeds the normal limit). Additional research, including screening, is required. |
| Positive | more than 5 Lg | The viral concentration is at a high level. |
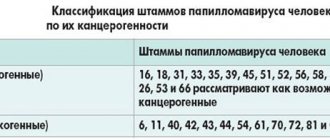
The laboratory sheet indicates all types of HPV for the presence of which the test was carried out. In most cases, these are 12 types - 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 of medium and high oncogenic degree.
O and a viral load of less than 3 Lg indicates the complete absence of the virus or its insignificant amount. No treatment required. The infection may be present in the human body, but does not produce any effect. No growths are observed.
A concentration of 3–5 indicates the presence of a small amount of the virus. Women in whose body papillomavirus is detected must undergo additional examination to exclude the presence of cervical dysplasia. Patients receive general immune-strengthening treatment. If condylomas are present, removal is performed.
A positive test result at a concentration above 5 indicates a danger to humans. The body is infected with a virus. The likelihood of developing cervical dysplasia in women is increased. Additional analyzes are being carried out. Treatment consists of removal of growths, large-scale antiviral and immunostimulating therapy. You may need to consult an oncologist.
Features of manifestation
The main feature of the infection is the formation of neoplasms located on the skin or mucous membranes. They can be single or multiple, have different shapes and sizes.
Such growths do not pose a danger in themselves, but their trauma against the background of constantly reduced immunity can lead to the degeneration of cells into a malignant form. As a result, a destructive process is launched, affecting both the site of growth formation and the entire organism as a whole.
How does this manifest itself in gynecology?
It is the presence of 16 and 18 strains of papillomavirus in the patient that in most cases leads to the development of cervical cancer. First, changes in the epithelium manifest themselves in the form of dysplasia, and after some time cancer formations appear. This process can affect not only the cervix, but also affect the external genitalia, vagina and anal area.
Typically, the time required to transition from a benign tumor to a malignant one takes more than 10 years. However, there are factors under the influence of which oncological processes manifest themselves faster.
PCR - diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection type 16.18
Research method
Real-time polymerase chain reaction. What biomaterial can be used for research? Throat (oropharynx) smear, urogenital smear, rectal smear, urogenital scraping (PCR).
3-4 hours before taking swabs from the oropharynx (throat), do not eat, drink, brush your teeth, rinse your mouth/throat, chew gum, or smoke. 3-4 hours before taking nasal swabs, do not instill drops/sprays or rinse your nose. It is best to take smears in the morning, immediately after a night's sleep.
For women, it is recommended to take a urogenital smear before menstruation or 2 days after its end.
Men should not urinate for 3 hours before taking a urogenital smear.
General information about the study
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a collection of about 100 related viruses. Some types cause skin warts, while others can cause sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and genital warts.
Genital HPV is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases in the world.
The incubation period can last from 2 months to 2-10 years.
A latent course of the disease is characteristic, in which there are no clinical manifestations, and colposcopic, cytological and histological examination reveals the norm. In 30% of cases, the virus can be cleared within 6-12 months.
Important!
Agapov Nikolai Konstantinovich
Dermatologist of the highest category
Ask a Question
It is most common in young women and men, with the main route of spread being oral, anal or vaginal sex. Although most viruses from this group are not very dangerous to health, there are, however, several types of papilloma (for example, HPV-16, 18) that can be dangerous to health. They usually do not cause visible changes, but when present in the epithelium, they can cause cervical cancer, as well as other less common tumors, such as cancer of the vagina, mouth, throat, penis and anus. The HPV test detects the DNA of specific viruses associated with a high risk of cancer. The combination of papillomavirus DNA with the cell gene leads to dysplasia/neoplasia (most often in the transition zone of the cervix). Infection with them leads to relatively benign bowenoid papulosis or squamous intraepithelial neoplasia of the cervix.
Diagnosis of latent HPV infection is carried out only by PCR. It allows you to find HPV DNA in the biomaterial being studied. The principle of the method is based on the amplification (multiple increase in the copy number) of a DNA region specific for a given pathogen.
What is the research used for?
As a way to determine the risk of cervical cancer (to diagnose cervical cancer itself, cytological examination is used, when atypical epithelial cells are detected, which may be a herald of the development of cervical cancer).
When is the study scheduled?
Women over the age of 30 who are at risk of HPV infection, as well as women over 21 years of age who are at risk for HPV infection and have cytologically detected atypical squamous cells of unknown significance (positive ASC-US test).
Men who are at risk of contracting HPV can also be tested.
What do the results mean?
Reference values:
- HPV DNA type 16, Ig not detected.
- HPV DNA type 18, Ig not detected.
- When viral DNA is detected, the amount is indicated and an interpretation of the viral load (clinically significant/insignificant) is given.
- A positive result indicates the presence of genetic material of HPV types 16 and 18 in the test sample.
- The absence of genetic material for HPV types 16 and 18 in the test sample means that the presence of HPV infection is unlikely.
If the smear shows cytological changes and the PCR result is negative, then further monitoring is required, as in the case of a negative cytological examination and a positive PCR test.
Symptoms of infection
Until the virus begins to actively spread, it is almost impossible to track its presence. Therefore, symptoms of infection become visible only some time after infection. The main sign of the presence of HPV is the appearance of various growths that arise due to changes in the structure of tissue cells.
Possible neoplasms include:
- warts;
- papillomas;
- genital warts.
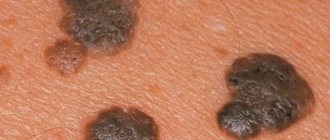
Strains 16 and 18 are characterized by the development of condylomas that appear exclusively in the genital area. They are considered the most dangerous type of neoplasm, since it is precisely such growths that subsequently change into cancerous tumors. Due to their elongated shape ending in a rounded end, condylomas are called genital warts.
Genital warts are flesh-colored
Subsequently, symptoms such as:
- burning;
- constant itching;
- pain;
- weight loss.
All this manifests itself at the location of the condyloma and is caused by its presence. When tumors begin to grow and multiply, this indicates an exacerbation of the virus and a low level of immune defense.
Dangers during pregnancy
Types 16 and 18 of papillomavirus are more threatening to the life and health of the mother, not her fetus. The unborn child develops in the same way as other children; there are no obstacles to the formation of internal organs. Intrauterine development of the fetus proceeds in accordance with the norm.
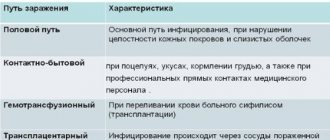
However, the presence of genital warts on the genitals of a pregnant woman can affect the health of the child after birth. While passing through the natural birth canal, the baby comes into contact with a viral growth, which causes it to become infected. And from birth, the child will become a carrier of a highly oncogenic type of virus, which can contribute to the development of a cancerous tumor.
Therefore, a pregnant woman must be diagnosed for the presence of papillomavirus and take timely treatment to avoid risks. If the problem is detected late, a cesarean section is usually recommended. This operation will help avoid unwanted consequences for the child and reduce the risk of infection.
How is it transmitted?
The main route of transmission of the virus is sexual. A less common method of transmission is household contact and vertical (birth) transmission. Most often, people who are just entering into sexual relations are infected. The first two years of sexual life account for a greater percentage of papillomavirus infection.
Transmission of the virus from a carrier to a healthy person occurs through damaged skin or mucous membranes. Virus particles penetrate deep into the epidermis due to damage to the natural barrier. Sexual intercourse is characterized by microtraumas through which the virus enters the woman’s body.
How to live fully if you have a virus in your body
If an oncogenic type of HPV is identified, the patient can live a full life. You should be careful about your own health.
The recommendations of gynecologists are as follows:
- Come for an appointment 2 times a year even without signs of inflammation or cancer.
- Colposcopy and scraping for atypical cells – once every 2 years.
- Force or persuade the male partner who caused the appearance of HPV to undergo treatment. Such strains cause cancer of the tongue and penis in representatives of the stronger half of humanity.
- Carry out all treatment measures.
- Eliminate factors that contribute to the activation of type 16 of the virus.
- It is allowed to give birth. The type of birth is chosen by the doctor based on the patient’s diagnosis and the condition of the cervical canal.
- Avoid transmitting the virus to other partners.
The prognosis for type 16 HPV is favorable. The patient, together with the gynecologist, must make every effort to prevent malignancy and relapse of the disease.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures are aimed not only at identifying papillomavirus strains, but also at monitoring the consequences of its activity. Without this, it is impossible to prescribe further treatment.
The following methods are used to diagnose HPV:
- Polymerase chain reaction allows you to evaluate the presence of viral DNA and identify a specific strain.
- Digene test aimed at identifying highly oncogenic HPV types.
- A biopsy is used to assess the patient's condition and determine the malignancy of the tumor.
- Colposcopy is a detailed examination that helps identify various pathologies in the internal genital organs.
Diagnostics helps to distinguish between similar diseases, assess the degree of impact of the virus on the body and track changes that occur.
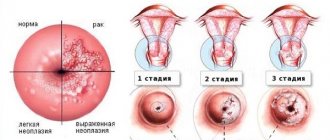
Stages of disease development
Gynecologists distinguish 4 main stages that the disease goes through during its development in the carrier’s body:
- Incubation period. The virus enters the body and begins to gradually adapt to new conditions. At this time, the immune defense can stop the activity of the infection, after which the virus finds itself in a “dormant” state.
- Manifestation of symptoms. After some time (from several months to several years), the first symptoms appear. The growth of genital warts begins, pathogenic activity affects different parts of the body.
- The occurrence of dysplasia. Dysplastic changes. Mucosal dysplasia occurs due to the deep penetration of viruses into the DNA of healthy cells, which gradually atrophies the normal function of the epidermal layers. Against this background, pathological growths develop in the form of papillomas, condylomas, and wart structures.
- Oncology. The development of cancer occurs with irreversible consequences for the skin or mucous membranes. As a result, healthy tissues are suppressed, and the cancerous tumor grows and deepens.
Analyzes
Any tests for HPV involve the collection of biomaterial obtained from the cervical canal. As a result of the analysis, the presence of the virus is detected, its strain and the level of viral load are determined. An HPV test is recommended for every sexually active woman at least once a year for prevention. After diagnosing papillomavirus, tests for infection must be taken every six months.
The primary test that women undergo is a Pap smear. This cytological study allows you to diagnose the presence of atypical cells in the body in the cervical area and suspect a viral effect.
The most common test aimed at diagnosing HPV is the PCR test. This is the widest range of diagnostic measures that allows you to identify the viral pathogen, its concentration and thereby select the optimal method of treatment.
The cost of such an examination will be from 700 to 2000 rubles, depending on the number of strains tested. The results are provided to the patient within 3 days after taking the biomaterial. For diagnostic reliability, the study must be carried out approximately in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
In this case, a contraindication for analysis is:
- menstruation period;
- recent sexual intercourse (less than 2 days ago);
- douching;
- recent colposcopy;
- use of antibacterial drugs (only after 2 weeks).
The results will be deciphered as follows:
Lg<3.0 – infection is absent in the body;
Lg 3.0-5.0 – viral particles are present, medium concentration level;
Lg>5.0 – the virus has a strong effect on the body, the concentration is high.
After receiving this data, it is possible not only to prescribe the correct treatment, but also to monitor the effectiveness of the therapy.
Is it possible to cure papillomavirus type 16 forever?
The immune system in men is capable of destroying an infection that affects DNA (this will take from six months to 1 year); infected individuals turn to doctors for help, wanting to be treated immediately. Rarely in women, HPV on the cervix is removed naturally and leaves the body during menstruation. With a normal menstrual cycle, after three months the papilloma virus disappears from the surface of the cervix. After the initial detection of the disease, doctors advise retaking the test; if the result remains positive, treatment is prescribed, which is aimed at:
- reducing the risk of cancer;
- removal of papillomas and condylomas;
- prevention of active cell division;
- strengthening the immune system.
Modern medicine, with timely treatment of the patient, diagnosis and therapeutic actions aimed at destroying the virus, can save a person from the manifestations of infection. There is no absolute guarantee that HPV 16 will leave the body forever. It all depends on the functioning of the immune system. People under 25 years of age are usually stronger than people whose age has exceeded 40 years, and the likelihood of complete recovery is higher among young people.
It is almost impossible to cure HPV type 16: the virus can live in the epithelial layer, suppressed by the immune system. Treatment in this case includes taking medications for life.
Treatment and removal methods
All HPV treatment comes down to conservative and radical methods. The former are designed to help strengthen the immune system and restore the normal state of immune defense. The second relate directly to the removal of manifestations of the virus, that is, genital warts.
Possible drugs for treatment include:
- antiviral agents (Allokin-alpha, Panovir, etc.);
- immunomodulators (Interferon, Viferon, etc.).
Both of these groups of drugs help not only boost natural immunity, but also inhibit the virus, so that the growths stop reproducing.
Surgical methods for removing tumors are as follows:
- radio wave destruction;
- laser removal;
- cryotherapy;
- electrocoagulation.
[Show slideshow]
Both methods must be used together to achieve the best therapeutic effect.
Review of modern methods for removing papillomas
The development of medicine allows you to choose one of the methods for removing papillomas and condylomas. The size of the area that is removed depends on the course of the disease, the area of the growths, and the degree of development of the disease.
After surgery, the doctor evaluates the condition of the mucous membranes in order to detect whether there are any distant, invisible lesions. Colposcopy is used for this. The excised tissue is sent for analysis to determine the type of virus - this will allow the doctor to understand which antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs will be optimal to cure the disease.
Removal of papillomas is mandatory; their accumulation leads to the virus changing the course of processes in the epithelial cells.
In modern medicine, the following surgical methods are used to remove papillomas:
- laser surgery;
- chemotherapy;
- cryodestruction;
- surgical removal;
- radio wave surgery;
- diathermoelectrocoagulation.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Laser removal has two advantages - no burned edges and minimal risk of inflammation after surgery. After completing the procedure, the doctor treats the wounds with potassium permanganate: which promotes rapid healing, within a week the wounds disappear, and in their place a dry crust forms, which subsequently disappears. The scar that appears at the site of the former growth is invisible, and after a few weeks it completely disappears. The disadvantages of the technique are the impossibility of removing large growths and long recovery after the intervention.
Chemodestruction involves treating papillomavirus formations with an alkali or acid solution. It is used to heal females; it can only get rid of single formations. It is difficult for the doctor to control the depth and strength of the effect.
Cryodestruction is the destruction of growths using ultra-low temperature. After the procedure, the cells of the formations die. This technique carries the risk of touching healthy areas and destroying living skin cells.
Radio wave and electrocoagulation techniques are effective for getting rid of single condylomas, but have a high efficiency of about 80%. They involve exposing the growths to high-frequency current, which destroys the formations. Minus – 55% chance of relapse in men.
Is it possible to fully recover?
The human papillomavirus, once it enters the body, remains there forever. Today there is no way by which he can be completely cured. The key to the health of patients with HPV is timely administration of medications and proper surgical treatment.
Thanks to such measures, it is possible to ensure reliable prevention of the development of cancer, protect your life, and also have healthy children in the future.
Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist about the dangers of oncogenic HPV:
Methods of treating papillomavirus with drugs
Drug treatment is prescribed by the attending physician and consists of taking drugs with a certain spectrum of action.
Immunomodulators. Helps strengthen the immune system and improve the body's protective functions. It is forbidden to take medications of this type for a long time: in this case, the immune system may simply weaken. A specific drug is prescribed only by a doctor (each case is unique, and the disease can occur with different intensity in different individuals). The dosage is calculated by the immunologist for each patient individually. You can purchase the drugs at any pharmacy.