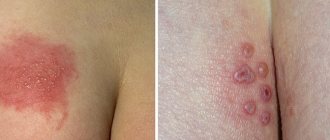
About relapses
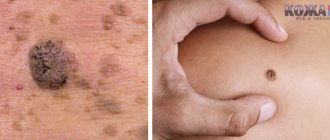
Relapses are something that a person who has once contracted basal cell carcinoma, including superficial one, should always be wary of. It is important not to miss the next initial stage shown in the photo, and for this you should regularly carefully examine the skin for suspicious changes and not neglect examinations by a doctor.
WE RECOMMEND YOU TO WATCH:
Basalioma - symptoms and treatment
For skin cancer in the early stages, surgical treatment is preferable. Doctors completely remove the tumor and a small area of surrounding skin (within 5 mm of the visible border of the tumor). This is necessary to ensure that the tumor does not continue to grow.
Mohs micrographic surgery (MOHS) is considered one of the standard of care for basal cell carcinoma. This method allows you to remove tumors located in hard-to-reach places. This operation eliminates the need for the surgeon to make a wide indentation, thereby allowing less tissue to be removed than with other operations. This gives the best aesthetic result (for example, when the skin around the eyes is damaged). The operation takes place under local anesthesia. The surgeon, examining the edges of the tumor under a microscope for the presence of cancer cells, removes the visible tumor layer by layer along with a thin layer of surrounding tissue. Each removed layer is sent to the laboratory for analysis. The operation is completed when data from tissue sections indicate that the surgeon has reached healthy tissue.
Adjuvant (postoperative) radiation therapy is indicated when the patient has undergone surgery to remove regional lymph nodes affected by the tumor. Therapy is applied to the area of the lymph nodes in order to achieve remission and inhibit the growth of metastases. Radiation therapy is also used as an independent treatment when surgery is contraindicated or when it is impossible to remove the tumor due to its location (for example, in the corner of the eye) [12].
One of the alternative options for removing basal cell carcinoma is cryotherapy , or cryodestruction, which is the destruction of the tumor using low temperatures. It is suitable for the treatment of skin cancer in the early stages, before metastasis.
Chemotherapy is prescribed for metastatic skin cancer. In this case, the goal of treatment is not to rid the patient of a malignant neoplasm, but to prolong his life, reduce symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease [12].
There are new classes of drugs that help control the tumor process longer and improve survival among patients. First of all, these are targeted drugs . They are used to treat rare forms of basal cell carcinoma, when the cancer metastasizes deep into the skin, reaching muscle and bone tissue. Targeted drugs act specifically on cancer cells. They block oxygen from the molecules that feed the tumor, thereby disrupting the mechanism of cancer cell reproduction.
New and more promising drugs include immunodrugs from the group of checkpoint inhibitors .
They block molecules that prevent the human immune system from recognizing and destroying malignant cells [13].
Features of photo classification of basal cell carcinoma.
The presented photos show basal cell carcinoma in each of its main variants. Attempts have been made to classify basal cell carcinomas based on growth pattern or differentiation patterns, but such methods have not achieved universal acceptance. Thus, there is no generally accepted classification for basal cell carcinomas; about 26 different varieties have been described. The most common types are: 1) nodular, 2) pigmentary, 3) cystic, 4) ulcerative, 5) superficial, 6) fibrosing (scleroderma-like), 7) basosquamous (also known as metatypical cancer), and Pincus fibroepithelioma. Most often, basal cell carcinoma comes in one of three subtypes: nodular, superficial, or ulcerative. You will also see in the photo how basalioma has signs of several varieties at once.
Attempts have been made to classify basal cell carcinomas based on growth pattern or differentiation patterns, but such methods have not achieved universal acceptance. Thus, there is no generally accepted classification for basal cell carcinomas; about 26 different varieties have been described. The most common types are: 1) nodular, 2) pigmentary, 3) cystic, 4) ulcerative, 5) superficial, 6) fibrosing (scleroderma-like), 7) basosquamous (also known as metatypical cancer), and Pincus fibroepithelioma. Most often, basal cell carcinoma comes in one of three subtypes: nodular, superficial, or ulcerative. You will also see in the photo how basalioma has signs of several varieties at once.
Wound after removal of basal cell carcinoma. Postoperative care.
After removal of the basal cell carcinoma, the wound can be sutured or left open to heal on its own. In case of closure with flaps, it is necessary to apply pressure to the area of the flaps for 1-2 days. For this purpose, special tampons, rollers applied over the bandage, or elastic bandages can be used. If you have time, you can use cold compresses to reduce the severity of swelling for 10 minutes every 2 hours. It is necessary to wash the sutured or open wound daily with soap and water after removing basal cell carcinoma 2 times a day. In the case of open wounds, large unsutured wound defects, infection with microbes and the formation of crusts are avoided; for this, use baneocin, erythromycin ointments, silver sulfadiazine (Ebermin, Dermazin), lincomycin ointment 2 times a day. Applying dressings can help maintain moisture in unsutured wounds and speed up the healing of basal cell carcinoma after removal. Antibacterial solutions such as miramistin, prontosan are used for washing instead of soap if suppuration is suspected. An additional intake of multivitamin preparations is required for rapid healing (Vitrum, Multitabs), which is especially important for older people. One percent povidone iodine, 3% hydrogen peroxide and 0.5% chlorhexidine solution, alcohol solutions are harmful to proliferating skin cells and delay healing. Taking glucocorticoids orally or applying ointments based on them (prednisolone, hydrocortisone, triamcinolone) also reduces healing and does not in any way contribute to a more complete removal of basal cell carcinoma. Poor nutrition with a lack of protein and vitamins also slows down healing.
Causes
As in many other cases associated with cancer, clear and unambiguous reasons for the development of the disease have not yet been identified. But there are a number of factors that, according to doctors, contribute to this disease.
So, the probable causes of basal cell carcinoma include the following:
- prolonged exposure of the skin to sunlight, abuse of solarium;
- regular interaction with substances containing arsenic;
- consumption of liquids that contain a high content of arsenic and heavy metals;
- xeroderma pigmentosum virus;
- skin damage associated with burns, scar development, etc.;
- precancerous diseases that are not treated in time and are left to chance;
- predisposition to the disease due to light skin and hair color, mature age, etc.;
- serious immune disorders.
Obviously, none of these reasons is decisive, but each of them individually or several in combination can contribute to the development of basal cell carcinoma.
How to diagnose skin basal cell carcinoma
It is very difficult to recognize basal cell carcinoma among other skin diseases. After all, basal cell carcinoma is similar to psoriasis, seborrhea and other skin ailments. In order for a specialist to detect basal cell carcinoma in a patient and make the correct diagnosis, determining its stage and form, he conducts the following studies:
- cytological;
- histological;
- differential diagnosis.
During a cytological examination, a scarified smear is taken from the patient’s affected area of skin, which allows the diagnosis to be immediately verified and the accumulation of cancer cells to be identified. During histological examination of the tumor, the result can be unpredictable. Therefore, to obtain accurate results, the doctor uses microspectrophotometric diagnostics. According to the indicators of this study, not only the accuracy of histological conclusions increases, but also the effectiveness of appropriate therapeutic measures increases.
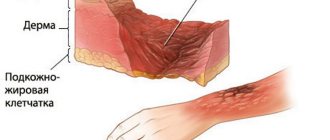
What is basalioma?
Basalioma (or basal cell carcinoma) is a malignant neoplasm that develops from the basal layer of the epidermis. In other words, this pathology is one of the variations of skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma primarily affects elderly people, but can be observed in children. People with pale skin that is not prone to tanning are most susceptible to this disease. The most typical places of localization are the wings of the nose, nasolabial triangle, neck, and scalp.
One of the characteristic features of the pathology is the long-term progression of the disease. Often, the transition of basal cell carcinoma from the initial stage to the fourth stage takes 10-15 years. In addition, this type of skin cancer does not cause metastases, but can spread to other organs. The frequency of occurrence in women and men is the same.
What education looks like at the initial stage, photo
At the very beginning of the disease, basalioma appears as a small red spot or painless nodule on the skin. Then the formation begins to increase in size, peel off and become covered with ulcers. Over time, the tumor takes the form of a plaque covered with scales and peeling.
Diagnostic methods
During the diagnostic process, it is important to differentiate basal cell carcinoma from other diseases. This pathology has similar symptoms to diseases such as psoriasis, microsporia, systemic lupus erythematosus and melanoma.
How is diagnosis carried out?
- An oncologist or dermatologist will collect an anamnesis of the disease and listen to the patient’s complaints.
- Next, histological and cytological examinations will be prescribed. To do this, a scraping will be made from the surface of the tumor.
- In some cases, a lymph node biopsy is prescribed.
Prognosis and necessary measures to prevent cancer
This disease is not accompanied by metastases, so its prognosis is quite favorable. It is necessary to undergo timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment according to the identified stage of tumor development. This is the only way the patient can avoid the irreversible consequences that occur with an advanced form of basal cell carcinoma. However, after applying effective treatment methods, certain cosmetic defects may be visible on the healed areas of the skin.
It is practically impossible to limit or protect yourself from the occurrence of this cancer, but you can reduce the risk of its occurrence. To do this you need to follow simple rules:
- Avoid exposure of the skin to direct sunlight from the scorching sun;
- try to eat foods containing animal proteins as little as possible;
- avoid direct contact with chemicals or toxic substances;
- in case of doubtful neoplasms, do not resort to self-medication, but immediately consult a doctor.
Thanks to these simple rules and timely treatment, you can not only eliminate risk factors, but also overcome basal cell carcinoma.
How to identify basalioma at the initial stage, its symptoms
Symptoms of the disease depend on the stage and type:
- The most obvious signs include the appearance of a red or pink nodule in a place typical for the localization of basal cell carcinoma.
- At the beginning of the disease, the nodule is small and does not cause discomfort.
- In addition, new formations may appear next to the nodule, which eventually combine into one plaque.
- This plaque begins to become covered with ulcers, bleed and cause pain.
- The vessels in the affected area become deformed and cause petechiae (spider veins) to appear on the surface of the skin.
- Next, the plaque enters the scarring stage.