Papillomas are formations that appear on various parts of the body as a result of infection of the body with papillomavirus (HPV).
Growths can form on the skin and mucous membranes.
Papillomas on the pubis and anogenital area pose a great danger, as they can provoke the development of dangerous complications.
Formations may appear in:
- on the external and internal genitalia of women
- on the penis and scrotum - in men
- on the pubis
- in the groin and perineum area
- in the anus area
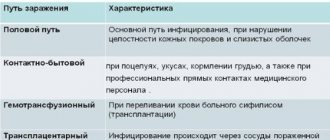
Methods of infection with papillomas
If a papilloma appears on the pubis, most likely the infection occurred through sexual contact.
Human papillomavirus infection is a disease with a predominantly sexual transmission method.
Although it can also infect humans through close household contact.
But it is obvious that in everyday life people do not touch each other’s pubis or genitals.
Therefore, taking into account localization, if you find papillomas in yourself, this is a “gift” from your sexual partner.
Moreover, the infection could have occurred quite a long time ago.
It is likely that it took place several months ago.
For this reason, it is often not possible to determine the source of infection.
Incubation period of papillomas
The incubation period of human papillomavirus infection can be long and lasts several months.
The infectious process develops in two stages.
The initial stage is after the virus enters the body.
It is characterized by the persistence of HPV in episomal form.
During this period, the infected cell can produce viral particles.
Therefore, this stage is called reproductive.
During this process, the virus accumulates in the body.
Next comes the integrative stage.
The DNA of the virus is inserted into the genome of infected cells.
At the initial stage, the pathology is reversible.
Many go into remission.
Papillomas do not appear on the pubis, and malignant tumors do not develop.
If the disease enters the integrative stage, various skin formations begin to appear.
Prevention of the development of dangerous complications
If you follow preventive measures, papillomas will not appear. Main recommendations:
- healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition;
- permanent sexual partner;
- genital hygiene;
- avoiding stress and nervous disorders.
Papillomas on the pubic area tend to spread throughout the body, but if taken correctly, they do not cause harm to health. Delayed treatment will lead to complications. Following the recommendations will prevent the appearance of new formations.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
How contagious is the papilloma virus?
HPV is a highly contagious infection.
The risk of infection with one contact reaches 70%.
It penetrates through microdamages of the skin and mucous membranes.
Even a condom does not protect against the virus.
Because it can enter the body, for example, through the skin on the pubis.
Due to its high contagiousness, there is a high percentage of people infected with HPV at a young age.
Those infected in the age category of 15-30 years are about 20-25% of the general population.
After 30 years, the number of virus carriers decreases to 8-9%.
HPV persists in the body for a long time.
But for most people it does not cause symptoms.
After a few months or years, it is eliminated on its own.
Papillomas on the pubis appear only if a person has a weak immune system.
Then the virus actively multiplies and causes mutations in skin cells.
Benign and sometimes malignant oncological formations appear.
Features of diagnostics of formations
Diagnosing HPV does not cause difficulties when contacting a specialist. It is necessary to undergo examination and tests. Laboratory tests are used:
- histology of biological material;
- cytological examination;
- DNA screening for detection of papillomavirus.
A biomaterial (a piece of tissue) is collected, which is sent for testing to the laboratory. Based on the result, it is concluded whether the formation is malignant.
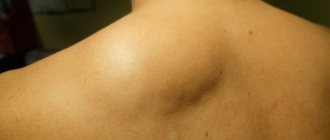
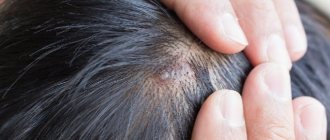
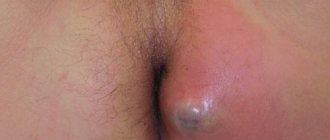
Symptoms and types of papillomas
The signs of papillomas are quite obvious.
Small pedunculated formations appear on the skin.
They rise significantly above the level of the skin.
The color may be red or flesh-colored.
Blood vessels are visible in them.
Types of skin lesions due to human papillomavirus infection:
- genital warts (the most common variant)
- spots
- papules
- bowenoid papulosis
- giant condyloma
In addition to the formation on the skin itself, other symptoms are possible.
Patients may complain of itching and pain.
Sometimes there is a tingling or crawling sensation.
Painful cracks in the skin may occur.
Features of papillomas in the intimate area
Papillomas in the intimate area
The patient can independently recognize the neoplasm, which is located on the upper layer of the epidermis, without much difficulty. But it is quite difficult to determine the presence of growths on the cervix, vagina or urethra.
There are several types of neoplasms that differ not only in external signs, but also have different areas of localization. Acute ones can be sexually transmitted. They are placed in intimate places in the form of small tubercles. Also, growths can attach to the surface of the skin or mucous membrane with the help of a stalk. They appear in both single and multiple quantities.
Papillomas formed on the pubis and other areas of the intimate area are small in size and have a flesh-colored or whitish color. They can develop into malignant neoplasms. At the same time, they begin to rapidly increase in size and spread to healthy areas of the skin.
Tests for diagnosing papillomavirus
The very fact of detection of papillomas may be sufficient grounds for their removal.
It doesn't matter how dangerous they are.
The main thing is that these formations look ugly and can interfere with the quality of sexual life.
But still, a person who comes in with pubic papillomas is usually examined.
First of all, in order to find out what type of HPV affected his skin.
It can be low-, medium-, or highly oncogenic.
If oncogenic types are detected, the patient is monitored dynamically.
Because the risk of cancer remains even after papillomas are removed.
PCR is used to determine the type.
A scraping of the pubic skin is taken.
It is then examined to identify a fragment of the virus's DNA.
Women are also recommended to undergo smears for oncocytology.
Sometimes your doctor will order testing for other STDs.
Because in the presence of papillomavirus, they are detected quite often - in approximately 50% of patients.
The person himself is often unaware of them.
Because sexually transmitted infections may not be accompanied by symptoms.
Should they be removed?
Treatment of intimate warts is a whole complex of measures, part of which is their removal. But the most important thing in this process is the reduction of HPV activity. The process of getting rid of genital papillomas is divided into 3 stages:
- Preventing the virus from multiplying by taking antiviral drugs.
- Strengthening immunity with immunomodulatory drugs.
- Removal of papilloma.
No one is immune from the appearance of intimate warts. But since they can be a symptom of unpleasant diseases, you should not delay a visit to the doctor when they appear. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chances of avoiding unpleasant consequences.
Tests for an immunologist and an immunogram for pubic papillomas
Papillomas almost always appear against a background of reduced immunity.
Therefore, patients need to consult an immunologist and conduct a study of the activity of the immune system.
This is necessary because:
- allows us to predict the development of the disease
- makes it possible to select immunomodulatory therapy
A person with poor immunity suffers not only from papillomas.
He exposes himself to the risk of dangerous infectious diseases.
Nonspecific inflammatory processes may occur in the body.
Therefore, even after removal of papillomas, it is worth adjusting the immune system.
This will help avoid recurrence of the formation of anogenital warts.
It will also prevent other diseases of infectious origin.
Causes
Diabetes
The formation of papillomas is provoked by human papillomavirus. It is found in the body of many people and is activated only under the influence of external factors. These include:
- Lack of hygiene.
- Allergic reactions.
- Unfavorable living or working conditions.
- Infectious diseases that cause decreased immunity.
- Great physical activity.
- Poor nutrition.
- Diabetes.
- Stress and neuroses.
- Long-term use of medications.
- Being in a room with a humid environment.
- Bad habits.
- Pregnancy.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Use of hormonal contraception.
- Hormonal disorders.
There are many reasons for the activation of the HPV virus. Most often, they have a complex effect, increasing the risk of papillomas.
Histology and oncocytology for papillomas
HPV is dangerous for the body.
Especially for women.
In them, the presence of papillomas can result in cervical cancer.
But the virus is dangerous in men too.
In both sexes, HPV causes squamous cell carcinoma.
In total, about 180 types of virus are known.
Of these, 29 have oncogenic potential.
Therefore, it is advisable to examine women with identified papillomas.
They need regular monitoring while the virus is in the body.
Even if the papillomas are removed, the risk of cancer remains.
To avoid pathology, it is worth taking a smear for oncocytology once every six months.
It is taken from the cervix.
The doctor checks whether there are atypical cells in it.
If necessary, if the result of an oncocytology test is unfavorable, clarifying studies are prescribed.
The doctor performs a colposcopy.
Using a special device, he examines the vaginal part of the cervix under a magnification of several tens of times.
This way the doctor can see pathologically changed areas of the epithelium.
Before developing into cancer, the papilloma virus causes dysplasia.
At first it has the first degree, then the second.
Both are reversible.
The first degree regresses on its own in most women, the second - only in 30%.
With the third degree, the risk of degeneration into cancer reaches 80%.
Therefore, grade 2-3 dysplasia is an indication for surgical treatment.
Pathological areas of the altered epithelium are “cauterized.”
This helps prevent cancer.
Timely performance of oncocytology is of utmost importance in the early detection of dysplasia.
A woman who is not lazy to visit a gynecologist once every six months can prevent cervical cancer with almost 100% success.
Sometimes, at the time of removal, papillomas already look suspicious.
In unfavorable cases, they can degenerate into squamous cell carcinoma.
Then they are sent for histological examination after removal.
The doctor examines the structure of the tissue and looks for signs of malignancy.
Histological diagnosis is also used if it is necessary to distinguish papilloma from other benign skin tumors.
If signs of malignancy are detected, the scope of the operation can be expanded.
Next, we will consider what methods are used to remove papillomas, what advantages and disadvantages they have.
Signs of defeat
The first symptom of infection is the appearance of warts in the pubic area.
This mainly occurs through sexual intercourse, the virus is transmitted from an infected partner to a healthy one. A person becomes infected with one of the types of virus - pointed or filamentous papillomas, as in the photo. They differ in their natural origin, shape and color. Pointed growths look like small flesh-colored or pink papillae and affect the pubic area in several places at the same time. They are particularly dangerous for women as they can lead to cervical cancer.
Thread-like, cone-shaped papillomas are pale yellow in color. They have the ability to grow, enlarge and merge with each other over time. This pathology is typical for women approaching menopause.
Symptoms of the disease:
- warts appear on the inside of the genitals;
- formations inside the vagina, on the internal membranes;
- In case of injury, bleeding and pain are noted;
- strong growth;
- the growths acquire a flesh-colored, pale brown color;
- constant feeling of discomfort in the pubic and genital area;
- sexual intercourse causes pain;
- frequent infectious pathologies;
- unpleasant smell.
In women, against the background of papillomavirus, it is possible to develop pelvic cancer. Timely diagnosis and removal of warts will help prevent the further development of pathology.
Diagnostics
If there are tumors on the pubis, women should visit a gynecologist, men a urologist. A dermatologist can consult patients.
An examination is necessary to establish the correct treatment and determine the type of papillomavirus that provoked the pathology. Diagnostics is very important, because the results will show how dangerous the virus is to human life and will help create the correct treatment regimen.
There are several categories of papillomavirus:
- The first group – there is no oncogenicity (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 28, 49).
- The second group is rare oncogenicity (6, 11, 13, 32, 34, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 51, 72).
- The third group is medium oncogenicity (26, 30, 35, 52, 53, 56, 58, 65).
- The fourth group is increased oncogenicity (16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 45, 50, 59, 61, 62, 64, 68, 70, 73).
Diagnostics consists of conducting a PCR analysis, which is necessary to determine the strain of the virus and its concentration. The test is so accurate that no further laboratory procedures are required. The doctor may prescribe a biopsy or cytological examination.
Removal of papillomas with liquid nitrogen
Cryodestruction is one of the oldest methods in dermatology.
It is also the most accessible.
Any dermatologist, including a public clinic, can remove pubic papillomas with liquid nitrogen.
Because this does not require special equipment.
You just need to take a stick with cotton wool, dip it in liquid nitrogen and press it onto the papilloma for a few seconds.
This is how tissue is frozen.
And frozen tissue subsequently dies.
The method has both advantages and disadvantages.
Its advantages:
- no anesthesia is required, since removing pubic papillomas with nitrogen is almost painless
- low costs for the procedure itself
- no need to buy anesthetics or pay for an anesthetic injection
- You can remove papillomas with nitrogen from any doctor - it’s a simple and affordable procedure
But there are also disadvantages.
After the procedure, an inflammatory reaction is observed and the patient experiences pain.
Only the smallest papillomas can be removed.
And if they are large, there is a risk of freezing the tissue too deeply.
In this case, scars will appear on the skin.
They can also form if a person's skin is too thin and vulnerable.
Then even the usual time of exposure to liquid nitrogen on the papilloma may become excessive for the patient.
Once the formation is frozen, it will not be possible to send it for histological examination.
This is another disadvantage of this procedure.
But it still remains one of the tools for removing papillomas for dermatologists.
Because it makes it possible to quickly and effectively remove many small formations on the pubis.
Electrocoagulation of pubic papillomas
The method of electrocoagulation of pubic papillomas in women and men allows the papillomas to be cauterized or separated from the body due to temperature exposure.
The tissues become very hot and are destroyed.
Using electrocoagulation, you can both “burn” the papilloma and separate it from the body.
This makes it possible to send the formation for histological examination.
Other advantages of the method:
- possibility of removing even large pubic papillomas
- absence of bleeding, as simultaneous coagulation of blood vessels occurs
- low risk of relapse
Electrocoagulation also has disadvantages.
The method has a greater risk of scarring than other methods, which will be discussed below.
When removing pubic papillomas using electrocoagulation, the doctor needs to use anesthesia.
Because this procedure is painful.
After it, pain may occur.
Because nearby tissues also heat up and become damaged.
Clinical picture
Papillomas occur more often in men than in women. They are usually located in groups. When located on the pubis, they cause itching and burning. They are also subject to constant injury when wearing underwear and sexual contact. Once damaged, they begin to bleed and cause pain.
If the growths are located on the pubis, they should be removed, as they can transform into malignant neoplasms.
Signs of degeneration of papillomas are:
- Soreness.
- Bleeding.
- Itching.
- Burning.
- Change in color or shape.
- Rapid growth.
If these signs occur, you should contact a doctor who will conduct the necessary diagnostics and determine the possibility of surgical excision of the growth.
Laser vaporization of pubic papillomas
A laser is used to destroy pubic papillomas.
With short pulses, the tissues are heated to such an extent that they simply evaporate.
In this case, the areas of skin located next to the papilloma are not affected.
The laser allows you to evaporate papilloma with maximum precision.
There is a risk of scarring, but it is small.
Less than when using electrocoagulation.
The laser coagulates blood vessels more effectively.
This is a non-contact technique.
Therefore, there is not the slightest risk of wound infection during the procedure.
If the infection gets into the skin, this can only happen after removal, if the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations.
But there are also disadvantages.
Only small or medium-sized papillomas can be removed.
Large formations are usually not removed with a laser, preferring other methods.
Plus, there is no material left for histological examination.
If it is necessary, then preference is given to other methods of combating pubic papillomas.
Radio wave removal of papillomas
For medium and large papillomas, radio wave removal is often used.
It has a number of advantages compared to other methods.
The doctor can control the depth of exposure.
Therefore, if removed correctly, scars usually do not appear.
After this procedure, there is a minimal risk of relapse.
The resulting tissue can be sent for histological examination.
Removal of pubic papillomas is performed under local anesthesia.
Application or infiltration anesthesia can be used.
More often it is infiltrative.
The doctor uses a syringe with a thin needle to inject anesthetics into the skin.
He punctures the base of the papilloma.
Then, during its removal, the person does not feel anything.
Keloid and hypertrophic scars after removal of papillomas
Sometimes scars form after removal of papillomas.
More often they occur if the removal was carried out at home or by an incompetent specialist.
A greater risk of scarring occurs when using folk remedies or chemical cauterization.
Correct implementation of destructive procedures reduces the risk of scar formation to a minimum.
But still, in a certain percentage of patients they appear.
Even if the most modern methods are used and the papilloma is removed by an experienced doctor, scars may appear.
This occurs when the deep layers of the skin are damaged.
Subsequently, such scars can also be removed.
There are also drugs that significantly reduce their size.
How is the virus transmitted?
Warts can be transmitted sexually , through tactile touch or household objects.
The papilloma virus lives on the surface of wet objects for quite a long time.
This could be someone else's wet towels, floors in public showers, saunas and swimming pools, toothbrushes and other personal hygiene products.
To avoid becoming infected with the papilloma virus, you must refrain from tactile contact with people who have warts. Read more about the causes of warts here.
You should also be careful when visiting public places and always use only personal hygiene products, underwear and towels.
It is necessary to lead a correct lifestyle and maintain the immune system so that the papilloma virus does not worsen and manifest itself in the form of skin growths.
- Common warts are lumps on the skin that have a dark tint. They may form dark, raised constellations on the patient's skin;
- Chicken growths that form on the feet and soles. They can appear in places where the skin rubs against uncomfortable and tight shoes. They have a grayish color, are dense to the touch, and cause discomfort when walking;
- Flat skin growths, most often on the forehead. Most often, such warts appear in children and young people;
- Genital condylomas , which form on the mucous membranes, armpits and intimate places.
Women, like men, can also have senile or filiform warts.
The papilloma virus often provokes the appearance of unpleasant condylomas in intimate places of the female body: on the chest, nipples and genital area.
Women who have regular sexual contact with carriers of the virus and pregnant women experiencing stress .
The HPV virus can provoke the appearance of papillomas on a woman’s chest. Often a wart appears on the nipple . The reason may be:
- Mechanical damage to the mammary gland, especially during feeding;
- Microscopic cracks on the surface of the nipples;
- Failure to comply with hygiene requirements;
- Uncomfortable, synthetic bra.
The formation of a wart on the nipple is accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the chest area: burning, tingling. The sensitivity of the nipple becomes worse, and whitish or milky discharge may appear from the ducts of the mammary gland.
Based on the results of the examination, the mammologist or oncologist makes a diagnosis: intrastream papilloma. The disease may occur without symptoms at the initial stage, but later its manifestations worsen and become painful.
Viral warts often affect a woman’s intimate area. Factors contributing to their occurrence include:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse, as a result of which the papilloma virus came into contact with the mucous membranes of the skin;
- Reduced immunity and disturbed microflora of the genitals;
- Other viral diseases: chlamydia, gonorrhea, thrush, herpes;
- Poor hygiene;
- Pregnancy, lactation and stress.
Intimate skin growths can be removed using a laser, liquid nitrogen or radio waves, or removed at home.
Treatment of skin growths in the clinic in the chest and nipple area comes in several types:
- Removal of skin epithelium using laser . The laser does not cause bleeding or inflammation, and does not leave scars or scars. It is used to remove simple types of papillomas;
- Therapy is carried out using liquid nitrogen and exposing the formation to low temperature. Sometimes there are negative consequences after cryotherapy;
- Exposure of skin growths to current and high temperature - radio waves ;
- Surgical removal of excess epithelium.
The most effective ways to remove warts are laser and cryodestructive methods. But which is better to choose? The pros and cons of each method are described in detail here.
If a growth has appeared on your body, you should know exactly which doctor treats warts and when you should contact him. Our articles will help you find out what will happen if a wart:
You still don't know:
We have given answers to all these questions in our other articles. You need to know this if you are worried about warts.
Chemical coagulation of papillomas
Chemical coagulation is one of the methods for removing pubic papillomas.
Concentrated solutions of acids or alkalis are used.
They cause a chemical burn to the skin at the site of application.
After this, the damaged tissues die.
The drugs Feresol and Solcoderm are used.
These methods are effective, but sometimes they can be quite traumatic.
Patients often use these drugs on their own.
In this case, the solutions enter the surrounding tissues, causing their necrosis.
In the future, scarring is possible if the impact was too deep.
Methods for eliminating pathology
Treatment of papillomatosis in men with anogenital lesions is aimed at destroying foci of the virus and stimulating the body's immune resistance. To achieve the desired result, destructive methods and treatment with immunomodulators (Amiksin, Likopid, Inosiplex) are used. To destroy HPV foci, liquid nitrogen, some acids, a radio knife, a surgical scalpel, and a laser are used. When using any methods of destructive therapy, local treatment is first performed, which is aimed at eliminating condylomas. No one guarantees that such treatment will provide 100% results, and that after some time you will not again encounter the problem of papillomas in the intimate area.
Chemical destruction methods
To remove papillomas, doctors use a variety of solutions of acids, alkalis and salts. Good results are obtained by using essential oils of thuja and celandine herb juice. These products are not very effective and often leave burns, after which initiation begins. As you can see, treatment of papillomatosis with chemicals is ineffective; moreover, if used incorrectly, they can cause tissue necrosis.
Physical methods for removing condylomas
Cryotherapy is the treatment of HPV by freezing small tumors with liquid nitrogen. When treating condylomas in the perianal area, a special technique is used, as a result of which all tumors are removed in several sessions. This procedure is completely painless, which allows you to remove all tumors on the genitals in men.
Radio wave therapy
Radio wave treatment involves the use of a special device “Surgitron”, which is used to cauterize condylomas on the penis, mucous membranes, tissues, and scrotum. All manipulations are carried out after pain relief. Radio wave treatment is a fairly effective method of therapy, but there is always the possibility of relapses.
Electrocoagulation
To remove papillomas using this method, an electric current is used to cauterize the tumors. Treatment with this method is painless and does not require anesthesia. The photodynamic therapy method is actively used to destroy anogenital warts.
Laser therapy and surgical removal of tumors
Laser therapy is effectively used to destroy condylomas. The laser destroys the tumor tissue, and a drying crust remains in its place. The healing process is fast, but scars may remain. Surgical removal of condylomas is carried out under local anesthesia. This method is recommended for large genital warts.
Immunological methods
The presented method of treatment is aimed at increasing the immunological resistance of the body. After immunotherapy, the patient’s body must independently suppress the papillovirus infection.
Folk remedies for removing pubic papillomas
The use of folk remedies is ineffective in most cases.
Often folk recipes are not pathogenetically justified.
They are based on conspiracies, ineffective plants, etc.
Sometimes such methods work, because in 15% of cases papillomas disappear on their own.
Usually, no result can be achieved.
The exception is when plants that have a cytotoxic effect or can cause a chemical burn to the skin are used.
The fight against papillomas can be effective if you use:
- thuja juice
- celandine
Podophyllotoxin used in medicine is also of plant origin.
But the plant from which it is made grows in North America.
Pubic papillomas: immunological treatment and antiviral drugs
After papillomas are removed, doctors often prescribe treatment to suppress the virus.
Applicable:
- means for stimulating the immune system
- general antiviral drugs
Interferons are most often prescribed.
They simultaneously stimulate the immune system, kill viruses and have antiproliferative activity.
Used locally and systemically.
Local interferons have low effectiveness against HPV.
Therefore, they are rarely used in monotherapy.
Mostly prescribed in addition to systemic medications.
For pubic papillomas, alpha interferon is prescribed intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
It is used in a dose of 1.5 to 3 million IU, every other day.
The course of treatment is 1 month.
After such a course, papillomas sometimes disappear even without their physical removal.
Local therapy is also used.
The drugs are injected into the lesions or applied in the form of a gel.
Cytokine inducers are also used.
Imiquimod is prescribed as a 5% cream at night.
It is used in a course of several months.
Warts disappear in 50-60% of cases.
Without treatment, over the same period they disappear in only 15% of patients.
For the treatment of HPV, inducers of endogenous interferon synthesis can be prescribed.
They are mainly used in combination with the destruction of pubic warts.
The drug Gepon is used.
Mechanisms of action:
- increased interferon production
- suppression of HPV replication
- increased macrophage activity
- decreased cytokine production and decreased inflammatory response
- increased antibody production
- increased nonspecific resistance of the body
The drug is prescribed orally at a dose of 2 mg, 3 times a week.
Other medicines that may also be used include:
Isoprinosine - a course of 5 days, 50 mg per kg per day in three doses, a total of 3 courses are needed.
Panavir - after one injection increases the level of leukocyte interferon by 3 times.
Glycyrrhizic acid – activates local immunity, blocks the introduction of the virus into the cell.
There are many other drugs that destroy viruses or enhance immunity.
Which of them should be prescribed is decided by the immunologist.
The decision is made based on the results of the immunogram.
Manifestations of intimate warts
Papillomas that appear in the genital area have their own name - genital warts. These are growths on a thin stalk that look like cauliflower or rooster combs. More often there are multiple clusters of condylomas, less often single formations. Due to their location, such warts often become wet and covered with a whitish coating. If inflammation occurs, purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor is observed in their folds. It is extremely rare to have a flat wart on the pubis.
Condyloma is easily damaged, resulting in bright pink erosion and bleeding areas on its surface.
Genital warts do not appear just like that; often this is facilitated by concomitant diseases, usually sexually transmitted, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and others.
Side effects of immunomodulators for papillomas
Flu-like conditions often develop when interferons are used.
Body temperature rises, signs of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract appear.
There is a headache.
The higher the dose, the greater the risk of side effects.
They can be relieved by using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
When using cytokine inducers, local reactions may occur.
This is redness, swelling, and the formation of erosions on the skin.
Control tests after treatment of papillomas
After treatment of pubic papillomas, laboratory monitoring is needed.
It is required for:
- viral load estimates
- prevention of recurrence of papillomas (by timely administration of a course of antiviral therapy)
- determining the likelihood of malignant oncological diseases
Control involves performing quantitative studies for human papillomavirus infection.
If it decreases, the virus is likely to be eliminated soon.
In the future, papillomas will not appear.
An increase in the number of papillomavirus DNA copies indicates the need for further antiviral therapy.
Recurrence of skin formations is possible.
In this case, they will have to be deleted again.
In addition, women regularly undergo smears for oncocytology.
This is required if oncogenic HPV types are detected during PCR.
Symptoms of the pathological condition
It should be borne in mind that papillomatosis, which manifests itself in the pubic area, is characterized by vague symptoms:
- if the pubic area is damaged in representatives of the stronger sex, then in addition to neoplasms, red spots are formed in this area of the body, as well as a sensation of pain and burning;
- if the vagina is damaged, then painful sensations occur during sexual intercourse, groundless tingling, as well as so-called “lumbago”, which make themselves felt during menstrual bleeding;
- if papillomas are injured, short-term bleeding is possible;
- in a situation where condylomas appear in the urethra, urination problems may occur;
- If an infection has penetrated the papillomas tissue, a repulsive odor appears.