Many people do not know when they hear about the diagnosis of HPV type 33 in women, what is it? Papillomavirus 33 strains are included in the dangerous group. If it is not treated promptly, there is a high risk of developing a cancerous tumor. The problem is that diagnosis is difficult; moreover, this virus is almost impossible to completely remove from the body. The infection manifests itself and progresses mainly in women. Men are its carriers, since their immunity more often suppresses the virus.
Features of HPV 33, how dangerous it is
HPV type 33 is an easily transmitted aggressive agent of the internal environment. It quickly passes from one state to another (from dormant to reactive) and colonizes the mucous membranes and skin of a sick person.
Its main distinguishing feature and danger is its high degree of oncogenicity. Although, there are also more loyal types of strain 33 - of average oncogenicity, in which the probability of the formation and development of cancer cells is 35–50% out of 100.
HPV genotyping
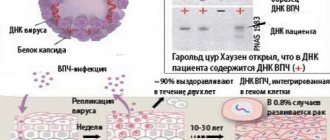
HPV genotyping provides additional opportunities to determine the prognosis of the disease.
HPV genotyping provides additional opportunities to determine the prognosis of the disease. The need for genotyping can be justified because:
- detection of several genotypes of the virus is associated with a less favorable prognosis of the disease and a higher risk of persistence;
- The degree of oncogenicity of different high-risk genotypes is not the same. HPV types 16 and 18 have the greatest oncogenicity; there are recommendations for determining these two genotypes of the virus after testing for a wide range of types in order to more aggressive patient management tactics: when genotypes 16 and 18 are identified, it is recommended to immediately conduct a colposcopic examination; when other high-risk types are identified - perform cytology first, and only if the cytology result is positive, perform colposcopy;
- Genotyping makes it possible to distinguish reinfection from persistent infection during the patient’s return visit. P
It is all the more important to obtain such information, since it is the chronic persistent form of infection that poses the danger, while recent infection is most likely to resolve spontaneously.Reinfection is indicated by a change in the spectrum of genotypes; persistent infection is indicated by the persistence of the virus genotype a year after the first testing; re-infection with the same genotype of the virus after self-cure is almost impossible.
Testing for HPV types 31 and 33 is prescribed by a gynecologist or oncologist
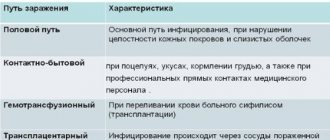
Mechanism and routes of infection
The mechanism of transmission of the papilloma virus is represented by a standard picture of contact spread: through blood, through saliva, through sweat, through the skin during microtrauma, as a result of sexual contact, in a household way.
The main routes of infection are represented by the following accession options:
- As a result of a kiss. Saliva, as a biologically active waste product, can be a carrier of dangerous pathogenic bacteria. When kissing mouth to mouth or when saliva comes into contact with the skin, the virus is transported from a sick person to a healthy person. Clear signs of oral HPV infection are: redness of the oral mucosa, the appearance of a red rash in the corners of the mouth and on the soft palate, and the appearance of a seizure.
- Through touch, hugs. Sweat is also one of the biological carriers of DNA. It consists of water, urea and cellular structures. Clothing, bedding, upholstery and many other fabric products can be breeding grounds for infection.
- Important: HPV strain 33 is very resistant to chemicals and dies only when boiled. Dishes, hygiene products, and bedding of a sick person must be subjected to heat treatment. The sick person must be isolated from other family members.
- Transmission by external means (through the skin). Microtraumas, cuts, and picked papillomas are one of the most likely factors in the occurrence of infection. Since the affected area is a direct source of infection. Upon contact with door handles, dishes, personal hygiene items, and other people (shaking hands, hugging, passing an infected object), the virus moves freely from a sick person to a healthy person.
- Infection through sexual contact. HPV 33 strains can be found in seminal fluid and semen. Some bacteria are also located on the head of the penis in a dormant (anabiotic) state. Unprotected sexual intercourse is the first and most common route of transmission.
- Household transmission route. Sharing personal hygiene products, dishes, underwear and bedding leads to mass infection of all family members (neighbors) living in the same area as the sick person.
Prevention of human papillomavirus infection and its relapses
The key to health is a correct lifestyle. Simple actions will help prevent HPV 33 infection and its relapses, in particular, completely giving up bad habits that reduce immunity (smoking, alcohol). Basically, HPV infection occurs through unprotected sexual intercourse, therefore, the use of contraceptives is mandatory. It is not recommended to start sexual activity too early, since the risk of infection with the virus and the formation of genital warts increases significantly.
After removing an existing growth, a woman should undergo regular preventive examinations.
At-risk groups
The risk group for the occurrence of a viral infection, with its further progression and destructive effect on the body (crystallization), includes the following categories of citizens:
- Teenagers from 13–17 years old. Early puberty, neglect of the rules of contraception, extreme vulnerability of the body - can become serious prerequisites for the occurrence of various kinds of diseases, their rapid progression into the most complex forms of the course.
- People suffering from immunodeficiency (HIV).
- Often sick. This is a special medical category, which includes patients suffering from acute respiratory viral diseases more than three times a year. They have a low ability to resist external attacks.
- Men and women who tend to lead a hectic lifestyle. This group can also include those who tend to drink large amounts of alcohol and are dependent on drugs.
- Children under 3 years of age. Living in the same area as an infected person, children and the elderly are the first to suffer. Their immune system is the most susceptible, and the ability to resist is almost non-existent.
How does papillomavirus manifest itself in women?
Infectious, viral, fungal infections have three stages of development. For each of them, the symptoms will be completely different.
There are 33 types of HPV in women, manifested as follows:
- First stage. Threefold increase in epithelial cells. More than 1/3 of the body is damaged by the papilloma virus. The patient complains of mild malaise, frequent bouts of fatigue, weakened immunity, and discharge from the vaginal area.
- Second stage. Further spread of the virus. More than 2/3 of the body is affected by keratinized epithelium. Small red growths appear in the lumens of the cervix. They hurt, itch and are the root cause of multiple erosions.
- Third stage. Viral infection is obvious. The patient experiences high fever, weakness, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Red spots appear on the mucous membranes. The cervix is inflamed. There is an exacerbation of chronic diseases, a general deterioration of immune processes.
Symptoms
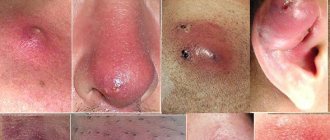
The process can cause irregular growth of abnormal cervical cells. This pathology develops in three stages. Severe neoplasia is already intraepithelial cancer. Often one disease develops against the background of another, so the appearance of pointed and flat warts on the labia minora and majora, on the vaginal mucosa or around the anus should force every woman to undergo a full diagnostic examination.
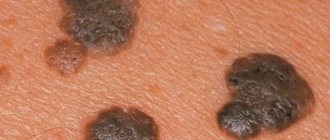
The size of warts may vary. They can have different shapes and look like a head of cauliflower or a rooster's comb. Women can easily detect them by feeling the labia minora, labia majora, and vaginal walls. If there are many condylomas and they are inconveniently located, minor bleeding may occur during sex. Also, the growth of papillomas may be accompanied by itching.
Diagnosis of human papillomavirus
The set of diagnostic measures for identifying Human Papillomavirus type 33 is divided into two categories:
- Standardized techniques - examination, basic tests.
- Special research tools - hardware diagnostics, visits to highly specialized specialists, laboratory tests to detect infections.
Standard Methods
At your first visit to a gynecologist, a routine examination is scheduled. It includes palpation, collection of anamnestic data (patient complaints), as well as taking basic smears to study the microfloat, and ordering general urine and blood tests.
Specialized research tools
Most of them involve studying the problem using medical equipment.
- Colposcopy. A colposcope is a device for identifying pathological changes in the mucous membrane of the cervix. It is inserted into the vagina. The total duration of the study is no more than 5 minutes. The technique is absolutely painless.
- Scraping Using microtweezers, doctors separate the damaged area of skin (mucous membrane) and examine it under a magnifying device, adding various reagents.
- Biopsy. In the acute course of the disease, the patient is prescribed a biopsy - the collection of biomaterial for a comprehensive study. This test allows you to determine the type of virus, its characteristics, the degree of impact on the body, the speed of spread, and so on.
- DNA test. Specialists in oncology laboratories use certain reagents to determine the mobility of the viral base, its aggressiveness and the degree of impact on healthy cells. A DNA test is performed if cancer is suspected.
- Blood test for hidden infections. Allows you to determine for certain the strain of the reagent introduced into the blood.
Symptoms and diagnosis of papillomavirus type 33
Symptoms of HPV type 33 in women against the background of the spread of infection are manifested by the following signs:
- Unnatural discharge from the genitals with bloody admixture and an unpleasant odor.
- During sexual intercourse, discomfort is felt, pain is felt due to damage to the warts.
- Periodic pain in the lower abdomen becomes frequent and more intense.
If such symptoms appear, it is necessary to be examined in the near future at a medical institution, where the disease will be diagnosed for the presence of HPV 33:
- Visual inspection by a specialist.
- Colposcopy is a detailed examination of the cervix in women who suspect the presence of a virus in the body. A special device allows the doctor to examine the organ in an enlarged form and conduct the necessary tests. The woman may feel slight discomfort.
- Cytological analysis. It consists of preliminary taking a scraping directly from the cervical canal and cervix. If HPV 33 is present in a woman’s body, the analysis will show this.
- The Digene test makes it possible to determine the HPV strain with maximum accuracy and determine the tendency to degenerate into cancer.
- The polymerase chain reaction method makes it possible to detect HPV type 33 DNA. A significant drawback of the method is that the result may not always be correct.
- During the biopsy, local anesthesia is used, and when examining the cervix, surface tissue is collected for examination. Such an analysis helps to establish an accurate diagnosis and determine the degree of development of spread 33 in a woman.
If genital warts form in the form of condylomas, you should not neglect them, but immediately seek help. In addition, virus 33 papillomas can appear on the skin of the arms, legs and other parts of the body.
Drug treatment for the virus
Traditional treatments for strain 33 include:
- Taking immunomodulators.
- Prescription of a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
- Use of a multivitamin complex.
- Getting rid of warts using ointments, gels, and hardware techniques.
Folk recipes
Traditional medicine is a supportive, additional therapy for an existing disease. Their use is advisable in the form of oils, herbal preparations and tinctures.
The most effective herbs and oils for fighting inflammation are:
- Chamomile.
- Sage.
- Myrrh.
- Eucalyptus.
- A series.
- Cranberry.
- Celandine.
- Garlic.
- Juniper.
Effective methods for removing papilloma in intimate places
Papillomas are common warts that appear uncontrollably in any accessible location.
Their removal on sensitive areas of the skin is carried out using pedal-assisted means. Their main parameters are: low acidity, natural composition, no age restrictions.
However, there are also hardware methods for removing keratinized areas of the epidermis. Their use is advisable in case of warts appearing on the inner surface of the labia, in the anal area.
- Radio wave excision - using a special knife, an unwanted tumor is removed. To relieve pain, local anesthesia is prescribed.
- Laser therapy. Aimed at cauterizing papilloma.
- Surgical removal. Indicated in cases of low effectiveness of other methods. In other words, it is used when a wart “takes root”, touching the microcapillary network.
Can papillomas be removed during pregnancy?
HPV type 33 in pregnant women is subject to mandatory treatment in the early stages of virus detection. Without specialized drug treatment, there is a possibility of giving birth to a sick, disfigured baby with mental retardation.
Therapy for pregnant women is carried out with the help of local antibiotics, vitamin supplements, agents that strengthen the placental barrier, and medications aimed at preventing multiple developmental disorders in the child.
Important!
Removal of papilloma during pregnancy and lactation is carried out only on open skin areas. Intimate intervention and hardware methods of elimination are strictly prohibited.
Consequences and danger: how to live, what to do
Many men and women ignore the first signs of the disease, believing that nothing bad is happening. By attributing everything to a cold, overwork, or poor diet, a person himself allows the infection to gain a foothold in the body and begin to destroy it.
Thanks to this, the human papillomavirus, spreading deeper and further, involves several basic systems of the body: urinary, reproductive, cardiovascular. It is they who begin to suffer in the first place and, accordingly, the problems arising as a result of infection concern them.
- Infertility. Cervical cancer and male infertility are the most common complications caused by the presence of HPV type 33.
- Exacerbation of latent cardiovascular diseases.
- Extensive inflammation of the urinary tract.
- Impaired blood supply.
- Ulcerative changes in the mucous membranes.
- Re-infection with another type of bacteria.
HPV type 33 affects mainly irresponsible citizens who do not care about their own health, lead an immoral lifestyle and do not undergo preventive examinations by a gynecologist (urologist). Accidental infection is also possible, but the risk of getting an infection through contact and household contact is extremely low.
Characteristics of 31 types of virus
Papillomavirus type 31 has a lot of differences from HPV-33, and above all this concerns its DNA. Infection usually occurs during sexual contact. The virus poses a serious threat to human health and can be localized both on the epidermis and on the mucous membranes of various organs.
Although HPV type 31 can pass from a carrier to a healthy person almost immediately after direct contact, it may still remain silent for one or several months. However, as soon as the immune system of an infected person begins to weaken, the virus in his blood is activated, which entails the development of one or another pathology.
Human papillomavirus type 31 can cause the development of cancerous tumors. After entering the body, it begins to gradually modify its cells, which can result in various diseases of the genital organs in men and women.
Human papillomavirus type 31 can be transmitted through kissing, as well as hematogenously.
That is, if a healthy person has a wound on his body, and he somehow came into contact with an HPV carrier, then the guarantee that infection with this virus will occur is almost one hundred percent. Children become infected with this type of papillomatosis through household contact or the so-called “vertical” method (that is, during intrauterine development or the process of delivery).
Causes and development factors
Of course, human papillomavirus type 31 is an infection that is transmitted through sexual contact, household contact, and perinatal contact. However, its entry into the body does not always cause serious illness, since certain conditions are necessary for HPV to be activated. In particular, such as:
- unprotected sex;
having promiscuous sex life;- problems in the gastrointestinal tract;
- significant weakening of the immune system (seasonal or permanent);
- frequent ARVI;
- failure to comply with safety measures in public places;
- alcoholism;
- smoking;
- long and frequent stays in rooms with high air humidity;
- neglect of hygiene rules.
Any acute processes occurring in the body can cause activation of HPV-31 DNA. Virus type 31 in women can “wake up” under the influence of bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis, colpitis, etc. In men it can be prostatitis, prostate diseases, urogenital diseases of various etiologies.
Clinical picture
A symptom of HPV-31 is the formation of benign growths on the skin of an infected person - papillomas. They can have different locations, sizes and colors. However, papillomatosis is not the most terrible disease.
A more severe pathology that this virus can cause is bowenoid papulosis. This disease, due to the action of the type 31 virus in men, causes the formation of papillomas on the head of the penis, but the infection may well spread to neighboring areas of the skin. In women, type 31 provokes the development of neoplasms that are localized in the vagina, so they can only be detected during examination in a gynecological chair.
How to treat 31 papilloma viruses depends on the results of PCR. This diagnostic method gives almost 100% correct results, and with its help it is possible to detect DNA of various genotypes of papillomavirus in human blood. Only after the diagnosis is confirmed can further steps be taken.
How to treat?
To treat diseases that develop due to infection with this type of papillomavirus, several approaches are used:
Complete removal of growths by removal (surgery, laser therapy, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation).- The use of immunomodulatory drugs (Immunal, Timalin).
- Using ointments or other medications to get rid of benign tumors on the skin (Superchistotel, Acyclovir).
Important to remember! People who have been infected with HPV once have a high risk of relapse of the disease. To prevent this from happening, you should not self-medicate. Therapy should be prescribed exclusively by the attending physician and carried out under his close supervision.
If it is not possible to cure papillomavirus infection with conservative or traditional methods, then the patient is prescribed surgical excision or instrumental removal of warts and other growths. This is the only way to avoid re-development of the disease, although even the most highly qualified dermatologist cannot give a 100% guarantee that papillomatosis will not return.