Doctors call HPV (human papillomavirus) the scourge of the 21st century. It is spreading across the planet very quickly. Currently, it ranks first among sexually transmitted infections. Over the past 10 years, the number of people infected with this virus has increased 10-fold, and the epidemic is only gaining momentum.
The number of people infected with HPV is growing rapidly
Understanding HPV
Human papillomavirus belongs to the family of DNA papillomaviruses. The genome of the virus is enclosed in a protein shell. More than 200 serotypes of the virus (different sequence of nucleotide combinations) have been studied. Of these, about 30 have been identified in humans.
HPV has the ability to infect the epithelium of the skin and mucous membranes. When it enters a cell, it changes its normal life cycle: instead of dying, the cell begins to divide uncontrollably. Due to excessive cell division, various hypertrophic formations occur on the skin and mucous membranes. They can be either benign or malignant.
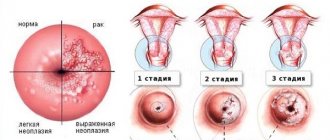
Depending on the serotype, the virus has a high and low oncogenic risk
Depending on the effect on the number of mitoses, serotypes of high oncogenic risk (HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 49, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68) and low oncogenic risk (6,11, 42) are distinguished ,43,44). Thus, HPV 31, upon penetration into the epithelium, is capable of causing malignant neoplasms.
HPV type 31 can cause cancer
In men, up to 90% of anal cancers, up to 40% of penile cancers, and up to 80% of head, mouth and pharynx cancers are caused by oncogenic types of HPV.
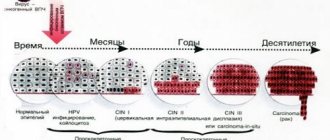
Developmental mechanism and genotyping
Papillomavirus type 31 in women and men can remain in a passive phase for a long period. There are several risk factors for its activation: poor nutrition, pregnancy or childbirth, stress, diet, bad habits, unprotected sexual intercourse, exposure to sunlight, pathologies of the stomach and intestines. More often, the virus is transmitted sexually during unprotected sex, less often through contact with the mucous membrane.
The virus manifests itself by the appearance of papilloma. The danger of a benign formation lies in the likelihood of transition to a cancerous process. Bowenoid papulosis is considered the main manifestation of HPV in men and women. The disease is diagnosed by plaques that rise above the skin. They may have a pink or yellow tint.
To determine the prognosis of the disease, genotyping is used. The need for its use is justified, since the detection of certain HPV genotypes is associated with a less favorable outcome of the pathology and a higher risk of persistence. To confirm or refute the cancer process, cytology is prescribed. If the test result is positive, then colposcopy is performed.
Using genotyping, it is possible to distinguish reinfection from viral persistence. Reinfection is indicated by a change in the spectrum of genotypes. Recurrence of the same genotype of the virus after recovery is impossible.
How does HPV 31 become infected?
The penetration of the virus into epithelial cells occurs from an infected person through microdamages and cracks in the skin and mucous membranes. The contact must be quite close, so the main route of transmission of HPV is sexual.
The everyday route of transmission without sexual contact cannot be ruled out (the virus remains viable in the environment, in swimming pool water), however, this route of transmission is much less common and does not play a significant role in the rapid spread of the virus.
The incubation period (the time from the moment the virus enters the body until the appearance of symptoms) for HPV 31 is usually from 2 to 11 months, but can last for many years.
After a virus enters a cell, several outcomes are possible:
- HPV can eliminate itself from the body along with the constantly dying epithelium.
- The virus can persist (exist without causing disease) in cells without causing any clinical manifestations. The man is the carrier of the virus.
- HPV 31 causes cell proliferation, resulting in the formation of benign neoplasms - warts, papillomas.
- HPV 31 can initially or against the background of existing benign formations cause oncogenic cell mutations, in which case cancer develops.
The main source of infection with human papillomavirus, incl. and HPV 31 - sexual contact
What to do next
After completion of therapy, it is important to maintain a positive result, and since the activity of HPV directly depends on the state of the immune system, it is necessary to regularly take measures to strengthen it. A diet rich in vitamins, hardening, physical exercise, giving up bad habits and timely treatment of diseases - this is what is needed to maintain immunity.
In addition, if you have previously been diagnosed with HPV 31, be sure to undergo PCR diagnostics at least twice a year, visit a gynecologist (urologist) and do not forget about safe sex.
What is the insidiousness of HPV?
- HPV infects up to 70-80% of the sexually active population, but in only 1-1.5% it manifests itself clinically. The percentage seems small, but this is the only virus with reliably proven oncogenic properties.
- It primarily affects young people aged 17 to 28 years. It has been proven that early onset of sexual activity increases the risk of infection by 22 times.
- After infection, it can “dormant” in the body from several months to tens of years.
- In most cases, sexual partners do not know that they are infected.
- Even if a man does not show any symptoms of the disease, he can be a source of infection for a woman (and in women, cervical cancer is caused by HPV in 100% of cases).
- A complete cure for HPV is almost impossible.
- HPV does not penetrate the blood, but persists at the site of introduction. On the one hand, this is good. On the other hand, immunity is practically not formed after an infection; a person is able to become infected with the virus again.
- Men do not undergo annual examinations like women, so the initial manifestations of even malignant tumors are usually missed. Taking into account also the psychological characteristics of men, they usually go to the doctor with an advanced form of cancer.
Who is susceptible to infection?
Everyone is susceptible to infection, but to a greater extent:
- Women aged 16-25 years who have become sexually active.
- Girls who began sexual activity at an early age (before 16 years).
- Young and middle-aged women who do not have a permanent partner.
- Men who are promiscuous.
- Children born from an infected mother.
- Carriers of STIs and chronic diseases of the genital organs.
- People who already have a different strain of HPV in their body.
- All people with various immunodeficiencies are infected with HIV.
What symptoms can HPV 31 cause in men?
So, the virus entered the epithelial cells. Why does it cause diseases in some, while in others it simply “dormants” or is eliminated from the body itself? There is no exact answer to this question.
It is assumed that several factors that weaken the immune system contribute to the manifestation of disease symptoms:
- accompanying illnesses;
- other infections, especially viral ones;
- hypothermia;
- smoking;
- stress.
Subclinical manifestations of HPV
Subclinical manifestations are conditions when there is an infection, there are changes in the epithelium, but the patient himself does not notice or feel anything. These include neoplasia and dysplasia of the epithelium of the penis, anal canal, and oral cavity. This change in the structure of normal tissue is considered a precancerous condition.
Theoretically, they can be diagnosed by scraping microscopy, but in practice such conditions in men are simply missed.
Clinical forms of HPV
These are the conditions for which a man already consults a doctor.
- Anogenital warts
Warts appear at the site of HPV infection
After some time, compactions, papules, plaques, and condylomas begin to form at the site of virus penetration. The size of the neoplasms can range from barely noticeable microscopic to quite large growths (giant Buschke-Levenstein condyloma).
These are, as a rule, benign formations, but their degeneration into cancer cannot be ruled out.
Warts cause inconvenience, are injured during sexual intercourse, and bleed.
- Penile cancer
It develops gradually and can grow both outward (exophytic form) and inward (endophytic form). Any non-healing ulcer, any lump, or growth on the penis should be examined for the presence of malignant cells.
- Anal cancer
The incidence of this type of cancer is increasing. Oncogenic viruses, including HPV 31, are found in 70% of patients. Homosexual men and HIV-infected men are more susceptible to anal cancer. Symptoms: compactions in the anus, ulcerations, growing and bleeding papillomas, bleeding.
- Cancer of the oral cavity, tonsils, pharynx, larynx
There is a trend toward an increase in the number of these HPV-related cancers, particularly in men. HPV infection with this localization is caused by appropriate sexual behavior.
Risk factors
Factors contributing to virus activation:
- gastritis,
- gastric ulcer,
- inflammation of the pancreas,
- frequent colds,
- severe nervous shock, stress,
- chronic metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus),
- kidney diseases,
- immune deficiency (organ transplant, HIV),
- hormonal disbalance,
- menopause.
Immunity is reduced by smoking, alcohol, and an unbalanced diet. Older people often experience exacerbations.
Gastritis can provoke activation of the disease
Diagnostics
There are no screening examinations of the genital organs for men, similar to the medical examination for women. Therefore, a man himself should show interest and periodically examine his anogenital area. For any changes - the appearance of spots, warts, changes in skin color, ulcers - it is advisable to undergo an examination, including for HPV.
You can contact a urologist, andrologist or dermatovenerologist.
Basic examination methods for suspected HPV:
- cytological examination of a smear or print;
- molecular biological research using PCR for the presence of HPV and determination of its genotype;
The PCR method accurately determines the type of HPV infection - histological examination of a biopsy specimen for suspected malignancy.
Therapeutic measures
If tests have confirmed the presence of HPV 31 in the patient’s body, treatment cannot be delayed - every day of delay increases the risk of malignancy of the growths. Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely eradicate the virus - therapy is aimed at suppressing its activity and eliminating the visible manifestations of the disease (papillomas).
You can deactivate HPV by taking the following medications:
- Medicines with antiviral activity - Groprinosin, Isoprinosine, Cycloferon;
- Cytostatics (drugs are prescribed for high risk of malignancy of growths) - Podophyllin, Vinblastine, 5-Fluorouracil;
- Immune stimulants that enhance the production of one’s own interferon (necessary to strengthen the immune system) - Panavir, Immunomax, Lykopid;
- The complex of vitamins Aevit, Alphabet or others also helps to increase the body's defenses.
Destructive methods for getting rid of genital tumors - laser, radio wave removal, electrocoagulation. Excision with a scalpel is carried out only in case of malignancy (degeneration) of growths.
Cryotherapy and necrotizing drugs are not recommended for use in relation to papillomas caused by type 31 of HPV.
Treatment of HPV 31
Treatment of HPV is currently aimed at eliminating clinical manifestations and improving quality of life.
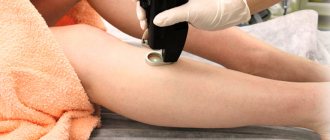
Exposure to liquid nitrogen is one of the methods for removing papillomas
If anogenital warts are present, they are removed surgically or by other methods: laser, liquid nitrogen, cauterized with acids and cytotoxic drugs.
In almost half of the cases the disease recurs.
There are no methods that can completely rid a person of the papilloma virus. However, there are studies showing that the use of drugs that stimulate antiviral immunity greatly reduces the number of relapses. These are interferon preparations, interferon inducers and other immunomodulators . The search and development of such drugs is very active.
When a malignant process is detected, radical treatment is carried out in all possible ways: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy.
Significance of Research
The unit of measurement here is viruses per 100,000 epithelial human cells - genome equivalent. It is abbreviated as Lg. When removing biological material, the doctor must take this into account and obtain at least 10,000 epithelial cells for analysis.
When reading a PCR study, everything is simple: the virus is detected at all or not. If yes, then its type is determined. When reading the analysis of the Daijin test, the inscription “DNA not detected” does not mean anything.
If the value indicated is less than
- 3Lg – the patient has a low concentration of the virus;
- 3-5 Lg – clinically high concentrations
- More than 5Lg - very high
“reference value” means the average of static studies in any one age group, or simply the norm. In particular, for HPV, reference values have a negative value, which means their presence in the analysis is a deviation.
Treatment of HPV type 31:
- Removal of all clinical manifestations from the skin surface. For this, the following technologies are used: laser removal, radio wave, surgical (using a scalpel), removal with an electric knife, liquid nitrogen, the use of drugs that cause local tissue necrosis (duofilm, solcoderm, collomac, feresol, condiline)
- Taking antiviral drugs: isoprinosine, allokin-alpha, epigen intimspray, Aldara cream 5%, panavir.
- Strengthening the immune system. Immunal, reaferon, and polyoxidonium are widely used. Self-medication is unacceptable.
If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with HPV, she must:
- Be under the supervision of a competent gynecologist throughout your pregnancy.
- The doctor’s actions will depend on the manifestations of the virus.
- The virus does not have a teratogenic effect.
- Skin manifestations should not be urgently rushed out and removed. This can be done after childbirth.
- During this period, use the minimum amount of drugs to treat it.
- During a natural birth, the baby can sometimes become infected with a virus.
- In case of serious pathology of the cervix, a caesarean section is indicated (this happens very rarely).