Every person who encounters any formation on the skin and worries about their health begins to worry, especially if the tumor appears suddenly.
Not everyone can independently determine what exactly the disease is and how dangerous it is to health. After all, any of the formations, be it a wart, mole or papilloma, can develop into skin cancer.
General information
Warts, as well as papilloma, occur in children and adults. The formation of growths can occur on any part of the body, and in appearance they look more than “unattractive”, which is why they cause a feeling of discomfort in the patient. But it is much more important that the pathology can be contagious and transmitted to a healthy person as a result of household or sexual contact.
The cause of development in most cases is the human papillomavirus (HPV), characterized by the activity of microorganisms that provoke the formation of abnormal formations of a benign type on tissues.
Due to the fact that both forms of tissue surface deformation are similar in general characteristics, there is a misconception that a wart and a papilloma are the same thing, but there is a big difference between them.
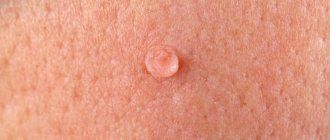
Papilloma
A neoplasm in the form of a papilloma is a pathological growth of epithelial cells of the dermis with a soft surface. Initially, the size of the formation is microscopic (0.2 mm), but gradually it can increase to 2 cm. The papilloma is oval in shape and light brown in color. The texture of the tumor is loose, and its outline is uneven. It is attached to the upper layer of the epithelium on a wide stalk.
The location is mainly in the armpits, neck, face and groin. The growth can be single or multiple. In most cases, in one area there are from 5 to 20 neoplasms measuring 0.2 - 0.5 cm. In many ways, the prevalence of the pathological process depends on the state of the immune system, which resists the virus.
How to distinguish a wart from a papilloma
The growths on the body are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV). Depending on the strain of the virus (there are more than 100 of them), either warts or papillomas with a high or low oncogenic risk are formed.
It is difficult for a person who does not have special knowledge to distinguish them visually. The following table provides comparative characteristics of warts and papillomas:
| At the wart | Have papilloma | |
| Color | Grayish or brown | From nude to black |
| Form | Round or oval | Globular, filiform, pointed, flat, elongated, chicken comb-shaped |
| Circuit | Clear | "Ragged" edges |
| Localization | 1. Open areas of the body. 2. Only on the skin. 3. Single or several around the maternal wart | 1) Mainly in the folds of the skin, where it is damp. 2) On mucous membranes. 3) In the intimate area. 4) Often grow in colonies |
| Surface | Dry, rough | Soft or dense, lumpy |
An accurate diagnosis can only be made by a doctor after an examination or laboratory tests.
Characteristic features of development
When considering how a wart differs from a papilloma, you should pay attention not only to the external signs of neoplasms, but also to the features of their development.
Common features include:
- formation on the surface of the epithelium;
- the cause of development is HPV;
- route of infection – contact and household;
- benign nature;
- influence of the state of immunity on development.
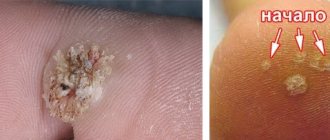
Warts
The size of the wart can range from 2 to 10 mm. Their surface is characterized by a rough surface and clear boundaries. The color of warts varies widely from a color indistinguishable from skin color to light gray and black. These benign neoplasms appear on open and hairy parts of the body: fingers, head, back, legs. Also, experts distinguish several subtypes of warts: flat, simple and plantar.
Medical diagnostics
Although it is possible to distinguish a wart from a papilloma even by external signs, medical diagnosis is still required. It should be borne in mind that in addition to the two main forms of tumors, humans often develop other types of growths, for example, a mole or condyloma, which are also considered pathological neoplasms that can cause serious diseases.
Diagnosis begins with a visit to the doctor, who, as a result of examination, establishes a preliminary diagnosis. To definitively confirm which form of growth is progressing in a person, a differential diagnosis (examination that takes into account differences between pathologies) may be required.
In medicine, a modern device is used to make a diagnosis - a dermoscope, with the help of which a specialist examines the body of the growth in all its layers.
In addition to making a diagnosis, examination is necessary to determine the presence of human papillomavirus, the state of the immune system and the presence of cancer cells.
Why are neoplasms dangerous?
The main danger that warts and papillomas pose is the threat of degeneration into a malignant form. The degree of their danger depends on the type of papillomavirus:
- high (oncogenic) – 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 52, 58, 59, 68;
- low (non-oncogenic) – 6, 11, 26, 41, 42, 50, 61, 73, 82, etc.;
- absent – 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
There is a high probability of malignancy if warts and papillomas are constantly injured (rubbed against clothing, touched by something, etc.). In this case, infection with harmful bacteria may occur. To prevent the degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one, it is necessary to regularly visit a dermatologist and not hesitate to detect suspicious symptoms. Particularly dangerous are genital warts that affect the internal genital organs of a woman, since they can cause serious diseases: pseudo-erosion of the cervix, ectopia of the columnar epithelium, and cervical cancer. In addition, their presence is manifested by a number of unpleasant symptoms: burning and itching in the vagina, unpleasant odor, pain in the lower abdomen, pain and discharge of ichor during sexual intercourse. In men, the lack of treatment for papillomas leads to decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and infertility. It can also provoke dangerous diseases: adenocarcinoma, anal cancer, diseases of the penis, oral cavity or larynx.
Many varieties are not dangerous, but ignoring the treatment of warts and papillomas will provoke an increase in their number. And the constant attack of the body by viruses will ultimately lead to a deterioration in the overall health of a person.
Prevention
The human papillomavirus, which is the main cause of formations, according to statistics, is present in the body of 80% of people. However, it does not manifest itself until the immune system is fully functioning.
To prevent the appearance of warts or papillomas on the skin, it is recommended to follow several preventive measures:
- strengthen immunity;
- do not have promiscuous sex life;
- maintain hygiene;
- try to avoid contact with infected people.
Despite all the differences between papillomas and warts, both neoplasms can cause the development of serious diseases.
You should not self-medicate. It is better to contact specialists in time and prevent complications that will subsequently require long-term treatment.
What types of HPV cause papillomas and warts?
Differences in the types of growths that appear on the skin and mucous membrane of the human body are associated with the strain of the virus that caused it.
| Warts | Papillomas | ||
| View | HPV strain | View | HPV strain |
| Plantar growths (spikes) | 1,2,4 | Flat, affecting the arms, chest, neck. | 5,8,12,14,15,17,19,20,36,37,46,47,50 |
| Simple | 2,4,26,27,29,57 | Filiform | 6,11,53,54,55 |
| Flat | 3,10,28,49 | Growths of the mouth and respiratory tract | 6,7,11,16,32 |
| Epidermodysplasia veruciformis | 2,4,3,5,8,9,10,12,14,15,17,19,20,36,37,46,47,50 | Bowenoid papulosis | 6,18 |
| Butcher's wart | 7 | Carcinoma verrucous | 11,61 |
Often the same strain of human papillomavirus infection provokes the appearance of different types of growths. It may be associated with the presence of low oncogenic strains in the body. An increase or change in color signals possible cell degeneration. If such growths occur, it is necessary to undergo a diagnostic examination to determine the type of virus.
Warts, papillomas, condylomas are the result of a viral infection that suppresses immune defense and can significantly affect the full functioning of a person. You should not ignore the appearance of symptoms of the disease and clearly distinguish them from other ailments. Lack of treatment can lead to unpleasant consequences and sometimes life-threatening complications.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
conclusions
Warts and papillomas, depending on the location, require observation by a doctor: a dermatologist, gynecologist, urologist or oncologist, as they can become inflamed, degenerate into malignant tumors and simply spoil the appearance. Dangerous tumors must be removed with a laser or radio knife.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Methods for removing tumors
Treatment of warts and papillomas should only be performed under the guidance of a qualified specialist. There should be no self-medication, since the pathology will not only not be eliminated, but will also significantly worsen, and serious complications may arise. Under no circumstances should you resort to your grandmother’s methods of tying the growth with thread or sealing it with tape in order to deprive it of blood flow. This can only injure the neoplasm, which will inevitably lead to the appearance of new growths and increase the risk of malignancy. Treatment of warts can be carried out medicinally using the following drugs:
- Viferon;
- Salicylic and Oxolinic ointments;
- Clareol;
- Antipapillomas;
- Cryopharma;
- Panavir;
- Isoprinosine.
The main goal of therapy is to increase the patient’s immunity, so the doctor may prescribe Echinacea, Immunal, Eleutherococcus and Aloe extract, Ribomunil, Lykopid, Imudon, Anaferon, Actovegin, FiBSA, multivitamins and others.
However, the high infectivity and autoacculation of warts are arguments in favor of their removal. Papillomas can only be removed. Today, the most common methods for removing warts and papillomas are:
- cryodestruction - freezing with liquid nitrogen, after which after a while the growth disappears. It is characterized by the absence of pain and a small number of complications. Practically ineffective in the fight against genital warts;
- removal with a radio knife - cutting off not only the growth itself, but also the epithelium underneath it. The device does not come into contact with the tumor, but acts on it from a distance. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and lasts no more than 30 minutes;
- laser removal - excision of the growth with a laser beam. During the procedure, healthy tissue is not affected, the blood vessels are sealed, which eliminates bleeding, inflammation and scarring. Removal is painless and quick;
- electrocoagulation – removal of tumors using alternating current. Rare relapses occur after this procedure;
- surgical method - indicated in the case of large and deep tumors. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. It has significant disadvantages: it causes relapses, leaves scars and scars.
Removal with a radio knife is one of the most popular procedures. It involves cutting off the growth using high-frequency radio waves. The procedure has many advantages:
- does not require special training;
- carried out quickly and painlessly;
- guarantees the absence of side effects in the future if all doctor’s recommendations are followed (relapses, scars, etc.);
- is particularly accurate and efficient;
- does not damage healthy tissue;
- bloodless and safe removal: the radio knife makes a cut, cauterizes blood vessels and disinfects;
- fast healing;
- affordable cost of the procedure.
As a rule, medical procedures are complemented by the use of measures to strengthen the immune system and destroy the human papilloma virus.