Herpes type 3 is a common viral disease, ranking third after influenza and acute respiratory infections. It provokes diseases such as chickenpox and shingles, which have a high likelihood of developing complications. Therefore, the disease requires treatment and medical supervision from the first days of symptoms.
Herpes type 3 is a common viral disease, ranking third after influenza and acute respiratory infections.
Features and types of herpes
Among the variety of herpes viruses, there are 8 main types:
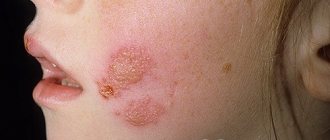
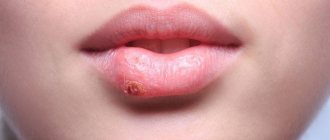
- Type 1 – the simplest and most well-known to everyone. It is characterized by a rash on the lips, cheeks, and nasal mucosa and appears in the form of blisters with liquid. Accompanied by itching, swelling, malaise, muscle pain, headache, and sometimes fever.
- 2 types – “genital”. The symptoms are the same as those of herpes simplex, with localization on the genitals and buttocks. Women get sick more often. They experience exacerbation mainly at the beginning of the menstrual cycle.
- Type 3 – Varicella Zoster virus – chicken pox. Herpes type 3 often causes shingles. Having been ill once, a strong immunity is developed.
- Type 4 – Epstein-Barr virus causes mononucleosis. Infection by contact, sexual and airborne routes. It affects the nasopharynx, lymph nodes, kidneys, and spleen. Young people under the age of 25 often suffer from this disease.
- Type 5 – cytomegalovirus. “Target organs” – liver, kidneys, eyes. It is dangerous when pregnant women are infected, causing death or pathology of the fetus.
- Type 6 - there are two types: 6a (causes multiple sclerosis), 6b (pseudo-rubella in children, which most often affects children under 2 years of age). It appears as pink rashes and high fever.
- Type 7 – affects monocytes and t-lymphocytes (promotes cancer of lymph nodes). May cause chronic fatigue and negative effects on the brain. Characterized by sleep disturbances, depression, decreased memory and attention.
- Type 8 - affecting blood cells, can cause Kaposi's sarcoma and other cancers.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of chickenpox is made by specific rashes and characteristic clinical manifestations.
Laboratory diagnosis of chickenpox before the rash appears is difficult. Immunoglobulins type M can be produced over time, and even in the first four days from the onset of the rash they are negative. Ig M usually appears in the blood on the fifth day after the first wave of rashes. After 2-4 weeks from the onset of the disease, type G immunoglobulins are fixed in the blood. Having appeared once, they circulate in the lymph and bloodstream throughout their lives. The Ig G titer will increase as the virus transitions from a latent state to an active one.
The second type of herpes of the third type is herpes zoster. It is diagnosed mainly by characteristic signs. In case of a blurred clinical picture, in order to differentiate from intercostal neuralgia, it is recommended to study the titer of G antibodies with an interval of 7-10 days. If the amount of Ig G increases, it means that the herpes virus type 3 is spreading.
Signs of herpes type 3 and its symptoms
Chickenpox is common in childhood. A child becomes infected through contact with peers in kindergarten, school, and other institutions. The greatest chance of infection occurs before the age of 10 years.
The herpes virus Varicella Zoster is transmitted in the following ways:
- by air (airborne);
- upon contact with a patient;
- household (through household items).
When an adult is infected with chickenpox, the disease is much more severe than in childhood, which is expressed by a prolonged febrile state, damage to internal organs, and the late appearance of a rash.
Chickenpox has a long incubation period, lasting up to 21 days.
Chickenpox symptoms
The disease progresses in stages:
- fever up to 38-39 degrees, weakness, malaise;
- a rash appears in the form of pink tubercles (papules) all over the body, which turn into itchy blisters with liquid;
- blisters (vesicles) when scratched can rot and turn into another form of rash - pustules;
- then they burst and become covered with a crust, which subsequently falls off.
The rash leaves no trace.
This disease is characterized by rapid spread with simultaneous various stages of development described above.
Thus, papules, pustules and small erosions (after scratching) can be immediately seen on the child’s body.
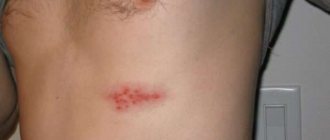
For adults, there is a high probability that the herpes virus type 3 can cause shingles if the immune system is low.
Shingles
The following factors contribute to its appearance:
- stress;
- physical overload;
- various infections;
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs;
- endocrine diseases;
- oncology;
- organ transplantation;
- radiation and chemotherapy;
- HIV infection;
- taking certain medications (hormones, immunosuppressants, cytostatics);
- introduction of the vaccine.
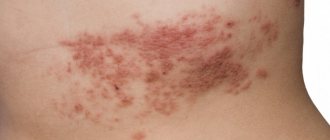
Clinical manifestations of herpes zoster
The symptoms of herpes zoster are similar to those of chickenpox, since the causative agent is the same - herpes virus type 3. Just as with chickenpox, it is characterized by an acute onset with increased temperature, aching bones, weakness, intoxication, and enlarged lymph nodes.
Its distinctive feature is the appearance of pain in the area of the affected nerve, manifested by neuritis and neuralgia. A burning sensation and numbness of the skin are felt over the affected nerve.
Then a blistering rash appears, which is most often located in one half of the body. Vesicles can fuse.
There are atypical forms of herpes zoster:
- Ocular – manifested by the appearance of a rash on the face, on the mucous membranes of the mouth and eyes along the location of the trigeminal nerve.
- Auricular – with it the process develops in the ear canals and auricles.
- Necrotic – occurs in patients with immunodeficiency conditions caused by various reasons (HIV, blood diseases, various infections, tumors, etc.). In this form, a bacterial infection is associated with herpes, causing necrosis of tissues and mucous membranes.
- Meningoencephalic – very rare. Characterized by damage to the nerves located in the intercostal space. After 2 weeks, the spread passes to the brain, leading to a severe coma.
- In the abortive form, there is an absence of the rash characteristic of herpes.
- The appearance of blisters with hemorrhagic fluid in the hemorrhagic form of the disease.
The disease lasts up to 3 weeks.
Having had type 3 herpes, a person becomes a lifelong carrier.
Causes and route of entry of the virus into the body
Herpes type 3 (Varicella Zoster) belongs to the Alphaherpesviruses subfamily. Viral particles have a similar structure to herpes viruses types 1 and 2 and are highly contagious. Herpes infection usually occurs during preschool or school age. Virus particles are transmitted by airborne droplets or household contact from a sick person to a healthy person.
Important! It is impossible to avoid infection with the herpes zoster virus during contact with an infected person.
Primary infection of children leads to the development of chickenpox. After eliminating the symptoms of the disease, viral particles remain in the human body for life, localizing in the nerve ganglia and roots of the spinal cord. However, exposure to provoking factors leads to activation of herpes. Therefore, a relapse of the infection develops, manifested in the form of herpes zoster.
Doctors identify the following factors that can cause exacerbation of herpes:
- infectious diseases;
- the presence of chronic infectious and inflammatory processes;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- autoimmune diseases;
- frequent stressful situations;
- chronic pathologies of internal organs;
- nervous and physical stress;
- pathologies of the hematopoietic organs;
- carrying out radiation or chemotherapy;
- severe injuries;
- carrying out an organ transplantation operation, after which the patient requires taking immunosuppressants;
- overheating and hypothermia;
- immunodeficiency states;
- various oncopathologies;
- taking hormonal drugs, cytostatics;
- vaccination.
At risk are the elderly, patients with HIV or AIDS, pregnant women, and young children.
Treatment of the disease
There is no specific algorithm in this case, only based on symptoms.
The following methods are used:
- Treatment of bubbles with antiseptics.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain.
- If the temperature rises, use antipyretic drugs.
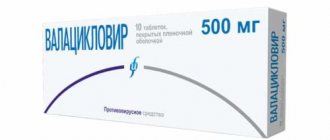
- Prescription of antiviral drugs: valacyclovir, famaciclovir, acyclovir, etc.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures: magnetotherapy, reflexology, etc.
- If a bacterial infection occurs, treat with antibiotics.
- Immunostimulants to activate the immune system.
- Antihistamines, hormones for severe itching.
Necessarily! Consuming large amounts of liquid in the form of water, compotes, fruit drinks, tea with lemons, etc. to reduce intoxication caused by viruses. Bed rest.
Features of therapy
At the moment, there are no drugs that can cure herpes virus infection. Therefore, when chickenpox or herpes zoster occurs, symptomatic therapy is indicated. It is aimed at reducing the intensity of pain, accelerating reparative processes, preventing the development of complications, and strengthening the immune system.
As part of the treatment of herpes type 3, antiviral agents (Acyclovir, Famciclovir, Valaciclovir) are widely used. They block the proliferation of viral particles, therefore facilitating the course of the infection and preventing the occurrence of neuralgia. Medicines are available in the form of cream for external use and tablets for oral administration. For herpetic eye infections, antiviral drops (Interferon) and ophthalmic ointments (Acyclovir, Zovirax) are prescribed.
Important! The simultaneous use of systemic and local antiviral drugs significantly increases the effectiveness of drug treatment.
For severe pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Meloxicam, Ibuprofen) are indicated. When muscle cramps develop, Gabapeptin, Carbamazepine, and Pregabalin are prescribed. To prevent the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, it is recommended to regularly treat the rash elements with antiseptic solutions or ointments.
To increase immunity, immunostimulating drugs (Cycloferon, Genferon) are widely used. They help reduce the concentration of viral particles in the bloodstream and activate the body's defenses. If a bacterial infection occurs, then antibiotic therapy is indicated. To eliminate burning and itching in severe forms of herpesvirus infection, corticosteroids and antihistamines are prescribed.
Impact of infection during pregnancy
During pregnancy, infection with herpes type 3 is dangerous because, both during short and long periods of pregnancy, it can lead to pathology of fetal development.
Possible complications
- Chicken pox can occur in complicated forms.
- With hemorrhagic, vesicles appear and hemorrhages occur on the skin and mucous membranes. There may be bleeding from internal organs: uterus, stomach, etc.
- When bullous, large blisters with purulent contents form.
- With gangrenous, necrosis of areas of the skin and mucous membranes occurs.
- Generalized causes damage to the nervous system and internal organs.
- With herpes zoster of the ocular form, the development of glaucoma, keratitis, and ear infection is possible - facial nerve paralysis often occurs.
- Complications from chickenpox and lichen have a varied picture: myocarditis, pneumonia, abscess, phlegmon, nephritis, arthritis, meningitis, encephalitis.
Complications
When pregnant women are infected with herpes, intrauterine damage to the fetus, fetal death, the development of multiple congenital defects, and the development of congenital chickenpox are possible.
The most common complication of chickenpox in adults is the addition of a secondary tank. infections. Also possible:
- damage to internal organs (generalized chickenpox),
- development of bleeding and hemorrhages in organs (hemorrhagic chickenpox),
- development of chickenpox pneumonia, meningitis, meningoencephalitis.
With herpes zoster, chronic pain due to postherpetic neuralgia and the development of meningoencephalitis and meningitis are possible.
Prevention
In order for the virus to be in remission, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system:
- Diet enriched with vitamins and minerals, taking multivitamins.
- Hardening the body.
Upon contact with a sick person:
- Provide him with separate dishes.
- Clean and ventilate the room where the infected person is located more often (since the virus is transmitted by airborne droplets).
- Wash your hands after interacting with a sick person.
- Do not touch blisters on the skin.
To protect against infection, the population is vaccinated.
Indications for vaccination:
- preschoolers;
- aged people;
- people with weakened immune systems.
- Related Posts
- Herpes virus type 8: what kind of virus it is, symptoms and treatment
- Herpes type 6 in children: what are the symptoms, how to treat the virus?
- Herpes types 1 and 2 - what is it: symptoms, treatment
« Previous entry
The danger of herpes during pregnancy
The greatest danger is the manifestation of the acute form of the third type of herpes during pregnancy. A woman's hormonal system undergoes serious changes during this period. This contributes to the active reproduction of the virus. This process can be aggravated by poor nutrition, hypothermia, prolonged exposure to heat and some other factors.
The manifestation of chickenpox during pregnancy is fraught with the following consequences:
- polyhydramnios;
- premature birth;
- delays in fetal development;
- miscarriage.
The baby is susceptible to herperviruses at any time during intrauterine development. The infection easily penetrates the placental barrier. Infection in the first trimester is fraught with congenital deformities or malformations. Herpes is also dangerous in late pregnancy. Infection of a child leads to damage to the nervous system. In especially severe cases, the baby dies.
Treatment of the disease in such a situation should be carried out under the strict supervision of a gynecologist and an infectious disease specialist. If the infection affects the eyes, an ophthalmologist is involved. A woman must strictly follow all instructions. Medicines are prescribed in minimal dosages so as not to harm the baby. The most commonly used are Acyclovir and Viferon. If the disease is not accompanied by excruciating pain, then it is better to refuse painkillers.