Herpes type 7 is a little-studied representative of the herpesvirus group. The genetic structure and some other characteristics of this virus are similar to other representatives of the group; quite often herpes viruses of different types are found in the blood of the same person. Experts believe that the causative agent of type 7 infection contributes to the activation of the previous type and the development of various complications.
Experts believe that the causative agent of type 7 infection contributes to the activation of the previous type and the development of various complications.
Features of herpes type 7
HHV-7 is a virus that can infect T lymphocytes and monocytes. In the body, such an infection can be present for a long time in a dormant state, skillfully hiding from the immune system.
For the most part, herpes virus type 7 is transmitted by airborne droplets, but spread through blood and its components is possible. This type of herpes virus, unlike HHV-6, is not transmitted from mother to fetus during intrauterine development.
Mostly, infection occurs in childhood, therefore, in most cases, it is possible to identify antibodies to such an infection. At the same time, the presence of antibodies in the body does not always indicate that the pathology is in an active stage. When an infection first enters the body, it remains there throughout life. When the immune system is malfunctioning, its reactivation is noted.
Risk subgroups
An increased risk of infection with the herpes virus or activation of latent HHV-7 is observed in people who have a weakened immune system.
People at risk include:
- suffering from immunodeficiency conditions (AIDS or HIV),
- having cancer,
- have undergone chemotherapy,
- in the treatment of which immunosuppressive drugs were used,
- have undergone blood transfusions and organ transplants,
- drug abusers,
- whose professions involve daily contact with a large number of people,
- having promiscuous love relationships.
Symptoms and signs
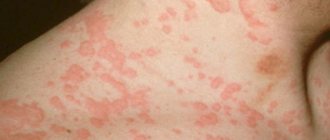
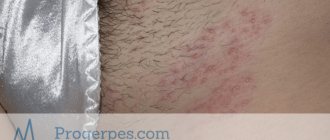
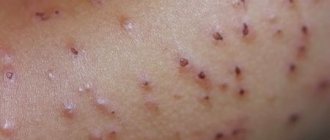
With herpes virus type 7, the symptoms develop the same as with type 6 virus. Children 2-3 years old are especially susceptible to the disease, and doctors often confuse their manifestations. Penetrating into a weakened body, the infection begins to develop rapidly and provokes the occurrence of such severe pathologies as roseola and exanthema. Characteristic manifestations of such pathologies are considered to be a rise in body temperature and the appearance of a rash throughout the body.
Children may experience inflammation of the throat mucosa and enlarged lymph nodes in the back of the head. In addition, type 7 virus can cause dangerous lesions such as meningoencephalitis, which is characterized by damage to the membranes of the brain and spinal cord.
With herpes type 7, symptoms of infection may be as follows:
- mental retardation and memory gaps;
- increased fatigue and decreased performance;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- inflammation in the throat;
- headaches;
- disturbing sleep;
- prolonged depression and nervous tension.
People with a progressive type 7 infection have an elevated body temperature for a long time and it is quite problematic to bring it down. Against the background of general inflammation, disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system and loss of appetite may occur, which can lead to weight loss and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
The insidiousness of the infection lies in the fact that the virus can affect the genitourinary system and cause kidney atrophy. In some cases, disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system that provoke arrhythmia may be of concern.
Clinical picture
There are no specific primary symptoms of infection with herpesvirus type 7. You can suspect the development of chronic fatigue syndrome in adults based on the following symptoms:
- a significant decline in performance for no apparent reason;
- lethargy and fatigue;
- headache;
- decreased cognitive function;
- chronic pharyngitis;
- difficulty falling asleep;
- pain and enlargement of lymph nodes;
- low-grade fever for no apparent reason for 6 months;
- pain in the joints;
- feeling of anxiety;
- muscle pain after minor exercise;
- depression and tearfulness;
- feeling of lethargy after sleep.
The listed clinical picture can also develop against the background of pathologies of the central nervous system, HIV infection, anemia, and hypofunction of the endocrine glands. Therefore, only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment after a thorough diagnosis.
In young children, herpesvirus type 7 leads to the development of sudden exanthema. The incubation period of the disease usually does not exceed 2 weeks. The infection begins acutely with a sharp rise in temperature to 390 C, against the background of which there are no catarrhal symptoms.
The high temperature lasts 4-5 days, normalizes after the appearance of a specific rash - pink spots that turn pale when pressed. Initially, the elements of the rash are localized in the back and abdomen, but they quickly spread throughout the body. The general state of health does not change. The rash does not require treatment and disappears on its own 2-3 days after its appearance.
Diagnostics
Treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist, and it is best to avoid taking medications on your own.
The infection can be diagnosed using the following types of studies:
- ELISA analysis. This method reveals the amount of antibodies that the body can produce to fight infection. This procedure makes it possible to identify the initial or aggravated form of pathology.
- Virological culture. This test is aimed at diagnosing the presence of viruses in the body, and blood, urine, mucus, saliva or feces are taken for analysis. The taken material is placed in a special environment favorable for the propagation of infection. After some time, the specialist assesses the rapid growth of the herpes infection.
- PCR diagnostics. This research method reveals the type of herpes virus by polymer chain reaction even before the appearance of characteristic symptoms. Analysis at the molecular level makes it possible to detect the DNA of the herpes pathogen in human cells.
The most common method for diagnosing infection is an immunogram, which reveals the state of the body's immune system.
HHV-7 and pregnancy
There are still no scientifically substantiated facts about the effect of herpes virus type seven on the course and outcome of pregnancy. Considering that, according to statistical data, specific antibodies to this type of herpesvirus are detected in the vast majority of adults, primary infection during pregnancy is unlikely.
However, if HHV-7 infection does occur during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, in a small number of cases complications typical of herpes infection in general may develop (termination of pregnancy, primary immunodeficiency in the child, etc.).
Treatment options
A doctor can determine type 7 herpes virus by external signs or other data obtained from interviewing the patient.
Unfortunately, today there are no drugs that could suppress the reproduction of HHV-7. It is for this reason that there are no antiviral therapy regimens for such an infection, and all medical care is aimed at symptomatic treatment.
Doctors say that treatment should be carried out when the virus is in the active stage, and this can be determined based on laboratory parameters. The latent stage, in which the infection occurs in an active form, cannot be treated, but it should not be left to chance. The patient must make every effort so that the pathology does not progress to the stage of exacerbation.
Important: in addition to taking medications, treatment of the virus requires normalization of lifestyle, that is, the patient will have to give up bad habits. In addition, a balanced diet and moderate physical activity are required.
Treatment for type 7 herpes includes massage, physiotherapy and therapeutic showers, as well as mental relaxation. Eliminating the infection requires taking nootropic drugs and conducting autogenic training.
Diagnostic measures
A neurologist or psychiatrist can identify chronic fatigue syndrome. To detect herpesvirus type 7, doctors prescribe the following examinations:
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction). The method involves identifying the DNA of herpes virus type 7, quantitative determination of viral particles;
- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). The serological technique is aimed at identifying the pathogen;
- consultation with a psychoneurologist, which involves analyzing the patient’s personality;
- electron microscopy.
If sudden exanthema is suspected, the child needs differential diagnosis with other infections that lead to the development of fever and skin rash (scarlet fever, allergies, measles, rubella). Additionally, a consultation with a pediatrician, an infectious disease specialist, and an immunogram are prescribed.
Remedies for herpes type 7
Treatment for herpes type 7 is carried out with the participation of a psychiatrist, neurologist and other specialists. This is determined by which organs and systems are infected. Basically, the treatment regimen includes taking systemic antiviral drugs, immunostimulants and immunomodulators. Prescribing such medications can reduce the activity of the virus and increase the body's defenses. For herpes type 7 in adults, symptoms and treatment depend on the symptoms caused by the infection.
Studies have shown that the pathogen is insensitive to a large number of nucleoside analogue drugs, which are mainly used for the treatment of herpes. Viral particles have variable sensitivity only to medications of this group, such as Foscarnet and Ganciclovir.
Elimination of herpes type 7 in children does not require specific treatment. At the same time, to normalize the condition of the child’s body, symptomatic therapy is selected, which involves the selection of antihistamines and antipyretics. In order to eliminate signs of intoxication in the body, drinking plenty of fluids is recommended.
Important: symptomatic treatment includes taking immunostimulating drugs such as Immunal, Interferon, Immunoglobulin, Viferon and Genferon.
The following medications can be used to reduce fever:
- Aspirin;
- Paracetamol;
- Nise;
- Ibuprofen;
- Nurofen.
Treatment of the herpes virus can be carried out using traditional medicine. For this purpose, medicinal herbs are used, which have a pronounced antiviral and immunomodulatory effect.
- Melissa infusion. It is necessary to chop the fresh plant and pour 2 tablespoons of this mass into 500 ml of boiling water. The resulting mixture should be left for 1-2 hours, after which drink ½ glass several times a day.
- Infusion of lungwort. To prepare the medicine, you need to pour 2 teaspoons of dry herb with a glass of boiling water and leave the mixture for 1 hour, wrapped in a warm blanket. This infusion should be taken instead of tea 2 times a day for 1-2 weeks.
- Sweet clover decoction. It is necessary to pour a tablespoon of dry herb with a glass of boiling water and leave for several hours to infuse. This remedy should be drunk ½ glass several times a day before meals.
Treatment of the herpes virus should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, since improper therapy can cause the development of various complications.
If you suspect type 7 herpes, you need to find out what kind of infection it is and how to fight it from a doctor. It is necessary to treat the type of virus only during the period of its activation, when pronounced symptoms appear.
To prevent the activation of a dormant infection, you should follow some simple preventive measures:
- increasing the body's defenses;
- organization of proper and balanced nutrition;
- giving up good habits;
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- strengthening the nervous system and normalizing its functioning;
- proper organization of work and rest schedules;
- timely treatment of pathologies arising in the body;
- You should also undergo regular medical examinations.
It is important to remember that when the first signs of type 7 virus appear, you should seek advice from a specialist as soon as possible. To date, there is no special method of treating herpes, but with the help of some methods it is possible to prevent the development of complications by sending the infection into a dormant state.
- Related Posts
- Herpes virus type 2: what are the modes of transmission, symptoms and treatment of the virus, photo
- Herpes type 6 in children: what are the symptoms, how to treat the virus?
- Herpes type 5: causes of the disease, main symptoms, treatment and prevention
« Previous entry
Types of herpesvirus infection
Important ! Medical specialists have identified more than 150 types of herpes, but a person at any age is susceptible to only 8 types.
Each of them penetrates the nerve cells of the human body and contributes to the development of complex pathologies. Moreover, the infection can spread in a latent form, affecting internal organs.
Herpes virus type 7
All types of herpesvirus infection differ in their characteristic symptoms and the degree of damage to the human body:
- Herpes simplex type 1 is the most common type of infection. It is activated and progresses in blood cells after hypothermia, overheating, stress or exhaustion of the body. During exacerbations, it manifests itself only in the upper layers of the skin of the face and on the mucous membranes. It begins with itching, burning and tingling at the site of localization, then redness appears, turning into small tubercles. These tubercles turn into bubbles filled with liquid. After a few days, the bubbles dry out and form crusts. Treatment of this type consists of restoring the immune system and taking vitamin complexes. An ointment containing zinc is applied externally. In advanced forms, antiviral drugs are taken as prescribed by a doctor.
- Herpes type 2 - mainly affects the mucous membranes of the genital organs, anus, and inner thighs. Often transmitted sexually. The main symptoms are burning pain and itching at the sites of occurrence, followed by blistering rashes, the healing period of which reaches 20 days. Along with the rash, the patient feels weakness, aching joints, and pain when urinating. If a pregnant woman does not get rid of relapses of herpes before giving birth, then there is a risk of infection of the newborn baby. Treatment is successful when taking the drug Acyclovir, vitamins C and E - against intoxication of the body.
- Herpes type 3 - manifests itself in the form of chickenpox and after treatment settles permanently in the body. At an older age, the causative agent of herpes type 3 (varicella-zoster virus) can recur with herpes zoster. Since the disease affects nerve cells, the sites of infection are accompanied by severe pain. Along with antiviral medications, if necessary, the doctor prescribes painkillers.
- Herpes type 4 (caused by the Epstein-Barr virus) - affects the lymphatic system, causing inflammation of the lymph nodes. Transmitted by airborne droplets. It starts from the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and penetrates the blood, spreading throughout the body. In the initial stage, the disease causes a slight malaise, reminiscent of a cold. In its acute form, the disease manifests itself as mononucleosis (the main patients are children). Type 4 herpesvirus is treated with immunostimulating drugs and, if necessary, antibiotics are included in the therapy. At high temperatures, medications are prescribed to “bring down” the temperature.
- Herpes type 5 (cytomegalovirus) is a severe type of herpes that affects all internal organs. Foreign microorganisms enter the body through contact and sexual contact. Having “settled” in the mucous membrane of the cervix and salivary glands, the virus remains in a latent state and is activated after the body is weakened. At the first opportunity, herpes begins to destroy the cells of the carrier, which leads to inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, cervix and vagina. For treatment, a whole range of therapeutic measures is used, such as restoring immunity, taking vitamins and antiviral drugs.
- Herpes type 6 - this type of herpevirus is rare and therefore not well studied. It is divided into 2 subtypes - 6A and 6B. The first type destroys the immune system, leads to chronic fatigue and contributes to the development of multiple sclerosis. The second type leads to inflammation of the meninges and the development of epilepsy. It is transmitted by airborne droplets and settles in the oral mucosa. Antiviral drugs such as interferons (protein compounds of natural origin), ganciclovir (sodium salt compounds), and immunoglobulins (immune serum from blood plasma) are used to treat the infection.
- Herpes type 7 is found in the salivary glands of patients. The main symptom is chronic fatigue and decreased performance. The main method of treatment is to suppress symptoms.
- Herpes type 8 - by destroying T-lymphocytes, it reduces the body's ability to resist, which entails dangerous consequences. The patient's body is not able to resist any viruses. Therefore, this type of herpes occurs in HIV-infected people and is the cause of such pathologies as lymphoma, Castleman's disease, Kaposi's sarcoma. Treatment includes taking antiviral drugs, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Locally – retinoic acid, which eliminates dermatological pathologies.
Lymphoproliferative and skin diseases
Herpes infection is associated with the development of this group of diseases. Diseases corresponding to lymphoproliferative characteristics have been little studied. These are neoplasms arising from lymphoid tissue - lymphomas, which, according to the international classifier, are classified as diseases of the blood system. This also includes leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, reticulosarcoma and other aggressive malignant tumors.
Dermatologists associate lichen - pink and flat - with type 7 of the virus. With lichen, small blisters appear on the skin, which are very itchy, and inflammatory spots or papules. Such skin manifestations last up to six months, pass spontaneously and arise again according to their own laws of development.
The virus poses a danger to the fetus. In the adult population of the planet, this virus occurs with a frequency of 60 to 95%, so by default it is better to assume that a pregnant woman is a carrier of the virus. After the fact of pregnancy is established, the woman must be tested for herpes types 6 and 7. It has been proven that in some cases, reactivation of the virus leads to miscarriage and fetal development defects. All measures must be taken to support the immunity of a pregnant woman.