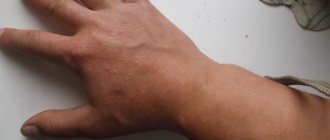
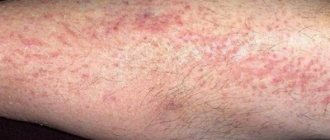
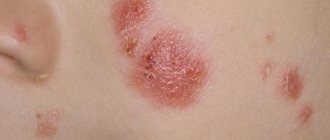
Psoriasis on the legs appears quite often. The disease refers to recurrent inflammatory dermatitis. The main sign of the development of psoriasis on the legs in women and men is the formation of psoriatic rashes of various types. The spots can be round, oval or teardrop-shaped. The shade of the plaques also differs. Depending on the type and course of the disease, they may be pale or, conversely, bright scarlet in color.
It should also be noted that psoriasis is an incurable disease. Periods of remission are sooner or later replaced by relapse. This happens under the influence of some factors, which we will discuss later in the article. Damage to the nail plates is also common with this disease. Toenail psoriasis can act as an independent disease, or it can develop against the background of damage to other parts of the body.
Causes of the disease and risk factors
The etiology of psoriasis has not yet been fully studied, so the exact cause that gives rise to the manifestation of dermatosis is still unknown. The rash may appear as a result of one or more triggering factors.
The main reasons include:
- emotional breakdowns. This is the most common cause of dermatosis: the body reacts to stress by damaging the skin;
- metabolic disorder (lipid);
- food poisoning;
- hormonal imbalances;
- infectious diseases, focal infections or vaccinations.
Among the most likely risk factors are:
- genetic predisposition. Often the disease is transmitted from parents to children;
- skin damage. This may include cuts or bruises to the legs as a result of a fall;
- intoxication as a result of long-term use of certain medications. Often, exacerbation of psoriasis is caused by antibiotics, beta blockers or vitamins C and B;
- alcoholism. The generalization of the process is more active against the background of intoxication. Treatment of such patients is difficult due to addiction to alcohol;
- hypothermia;
- acclimatization process.
Psoriasis is an external manifestation of internal problems in the patient’s body.
Causes
Many years of research into psoriasis by world scientists to date have not been able to formulate a clear answer to the question of what are the causes of the disease.
Photo of psoriasis on the legs
In modern medical practice, there are several theories suggesting possible provoking factors of the disease. These include:
- disruption of the body's metabolic processes, mainly lipid;
- emotional overstrain, stress, psychological stress;
- disruptions in the body's hormonal balance;
- heredity;
- frequent viral and bacterial diseases;
- injuries and damage to the dermis;
- hypothermia, excessive amounts of ultraviolet radiation.
Important! Psoriasis often occurs in people who abuse alcohol, cigarettes and other bad habits.
How the disease begins: symptoms and signs
The onset of the disease has symptoms common to all cases:
- A small reddish lump (papule) appears on the skin of the legs. It has clear edges and rises above the healthy dermis. Then there are more and more lesions. They grow and merge with each other, forming large plaques. These rashes are clearly visible on the legs;
- Each hearth is covered on top with whitish-grayish scales. They are easy to scrape off, and the harder you comb them, the more exfoliation occurs;
- if you continue to scrape the plaque, thin red skin will be exposed, which will begin to bleed;
- The initial stage is characterized by the following feature: when healthy skin is damaged, new papules form on it (after 10-14 days);
- the rashes are itchy and itchy.
Psoriasis is often localized on the legs, most often in the bend areas: above or below the kneecap. Papular rashes may appear on the thighs (usually on the inside).
Psoriatic papules on the soles of the feet and heels are bright red in color. The skin in the area of the rash becomes thick, rough and often cracks. Pustules (pustules) may appear.
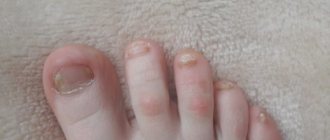
The nail plates are severely affected. They become deformed, thicken, and become lumpy. If the process is not stopped, the nails will begin to peel off and crumble.
What does psoriasis look like on the legs?
Psoriasis of the legs has the same symptoms as rashes in the arms or abdomen. However, it can cause slight swelling of the knee and ankle joints. In addition, there is a high probability of skin infection in the event of any (even minor) lesion. The skin of the feet is most susceptible to fungus.
Psoriasis of the legs in children is somewhat different:
- The baby's entire foot turns red. It hurts to hurt her;
- holes appear on the nails (as if pricked by a needle);
- rashes are noted in the folds of the skin: on the legs or thighs;
- the baby suffers from itching. When scratching the lesions, bleeding is observed.
Lesions on the soles and toes
Complicating the course of the disease on the legs is the release of sweat. Due to it, the itching intensifies. This is especially true for psoriasis that has developed on the fingers and between them. Formations can appear not only on the skin, but also on the nails. Their deformation and thinning are observed.
Psoriasis between the toes
Like papules on the foot, lesions on the toes cause discomfort. From the photo you can determine the initial stage of the disease, because the affected nails look approximately the same. Lack of proper treatment leads to roughening of the skin on the soles, followed by cracking. This is a very painful condition.
Types of pathology and what they look like
The affected areas look different depending on the type of dermatosis.
Spotted (common)
Vulgar psoriasis is the most common form of the disease. The symptoms are:
- numerous plaques are red. They are convex and covered on top with whitish-grayish scales;
- over time, the affected area expands, turning into one large plate;
- It is painful to touch the skin in the affected area. It itches and bleeds when scratched;
- nails are cracking.
This type of dermatosis is observed mainly in the knee area.
Pustular
The manifestations are:
- the skin is very hyperemic and strewn with blisters filled with pus;
- boils are very painful;
- localization: soles of feet.
Since the pustules constantly burst as a result of friction with shoes or clothing, weeping lesions are formed that are easily accessible to infection.
Onychodystrophy
This type of psoriasis destroys the structure of the nail plates.
The symptoms are as follows:
- the appearance of small pinpoint depressions or grooves, as well as psoriatic plaques;
- the affected nail is surrounded by inflamed and dry skin;
- the nail plate thickens and becomes fragile.
Psoriatic arthritis
It manifests itself as damage to the joints (their bone and cartilage tissue) against the background of the patient’s existing skin lesions (10% of cases).
Symptoms of psoriatic arthritis:
- swelling of the joints accompanied by severe pain;
- redness of the skin at the site of inflammation;
- joint deformation;
- pain when flexing and extending a limb.
Localization: knees, heel area (as a result of inflammation of the tendon), sole of the foot.
Clinical picture of psoriasis of the feet
Psoriasis of the feet is common. This is a chronic disease with a recurrent wave-like course, which is difficult to respond to even symptomatic drug correction. Typically, patients are diagnosed with so-called vulgar (simple, common) psoriasis on the feet.
Its main symptoms are, at first, single, and then multiple, inflamed reddish-pink spots, which increase in size over time and merge into monolithic lesions. The surface of such loose elements is strewn with silver-gray scales, which easily fall off at the slightest mechanical impact on the plaques.
Psoriasis on the feet is accompanied by:
- Intense itching and peeling of affected areas of the skin;
- Hyperemia (redness) and swelling;
- Deterioration of general well-being - weakness, decreased performance, neuroses, apathy;
- During periods of exacerbation - increased body temperature;
- Hypertrophied dryness, emaciation of the skin.
Psoriasis of the feet can also occur in the pustular form. In this case, limited areas of erythema (redness) initially appear on the feet, on the territory of which pustules grow over time - bubbles of different sizes filled with exudate - a clear liquid.
Due to the fact that psoriasis on the feet is associated with a high risk of traumatization (damage to the integrity) of the eruptive elements, it is often accompanied by secondary infection of pustules. In this case, the liquid filling them acquires a grayish-yellow tint (pus), and when such elements are opened, an unpleasant putrefactive odor is felt.
Psoriasis of the feet occurs in three stages:
- The progressive phase of the disease is accompanied by a massive proliferation of plaques and pronounced local symptoms of psoriasis - itching, hyperemia, peeling, pain;
- At the stationary stage of the disease, the existing elements of the rash dry out, the inflammatory process subsides, and new plaques do not form;
- The regression stage is a period characterized by a decrease in the intensity of the manifestation of all the signs that cause psoriasis on the feet. Pustules (if any) disappear, in their place characteristic dry crusts first appear, after removal of which hyperpigmented areas of the skin are noticeable.
Diagnostic methods
It is very important to recognize the disease in time and begin its treatment. First step: visit a dermatologist. He will conduct a visual examination of the affected areas and find out the patient’s symptoms. All this will allow the doctor to differentiate psoriasis from similar diseases.
The following will help confirm your analysis:
- Analysis of urine;
- potassium oxide test (detects fungus in lesions);
- blood test for biochemistry;
- bac sowing
Additionally, a biopsy with histological analysis and an x-ray of the affected joint (in the case of psoriatic arthritis) may be prescribed.
Pregnant women are advised to do a prolactin test. His goal is to find out what triggered the dermatosis: genetics or stress.
Preventive measures
By following preventive measures, you can prevent the occurrence and development of the disease.
Prevention recommendations:
- lead an active lifestyle, play sports;
- sunbathing;
- wear comfortable, loose shoes, be sure to walk barefoot (at home, in the garden);
- monitor the condition of your nails: keep them clean, treat them with products that prevent the development of fungus;
- treat feet with antiseptic agents;
- follow a diet (no smoked meats, sweets and alcohol).
If psoriasis has become your problem, do not despair, because, knowing the symptoms and causes of the disease, you can begin treatment on time. But only an attentive attitude to the pathology and patiently going through all the procedures will help curb its unpleasant symptoms. Hello!
How to treat psoriasis on the legs at home?
Many of us, having noticed the first symptoms of psoriasis, do not rush to see a doctor, but try to be treated at home.
It starts with self-discipline:
- quit smoking and alcohol;
- stop taking medications that cause dermatosis;
- exclude chronic infections.
Ointments and creams for topical skin treatment
Psoriasis responds well to treatment with ointments with the addition of tar or a solution of salicylic acid, solid oil or zinc . These drugs belong to the class of non-steroidal drugs.
They are completely natural, and their action is not as fast as that of hormonal agents, but the ointments can be used for a long time. They help quickly exfoliate scales and stop the growth of new papules.
However, the penetration of the active substance is prevented by dry and dense skin with psoriasis. Therefore, to achieve the greatest effect, ointments should be combined with gels.
Effective hormonal agents include: Fluocortolone, Hydrocortisone and Prednidazole. But it should be remembered that their long-term use is undesirable due to possible side effects.
Leg psoriasis is dangerous due to fungal infection. In this case, it is recommended to use Clotrimazole, Levomekol (ointment), Lamisil (cream).
Hormonal drugs can only be used with the permission of a doctor.
Systemic drugs
They are used in cases where local therapy has not brought the desired result.
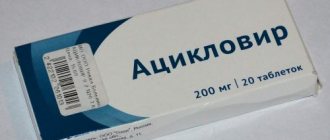
The drug Cyclosporine
Systemic medications for psoriasis of the legs:
- Cyclosporine (to suppress the immune system response);
- Methotrexate (suspends the cell cycle);
- Retinoids (low doses). Effective for extensive skin lesions.
Treatment with folk remedies
It should be remembered that traditional therapy for psoriasis is designed for a long time and only in the initial phase of dermatosis.
Popular recipes:
- homemade ointments with birch tar . Apply with a cotton swab to the affected area. After a few minutes, wash off with water. With each subsequent day, the procedure time must be increased, but not more than 40 minutes per session;
- decoction from the string . Proportion: 4 tbsp. herbs per liter of boiling water. The product should sit for 60-90 minutes. Use for oral administration (100 g for adults and 25 g for children) before meals. Or add to the bath;
- decoction of birch buds . Take 2 tbsp. means and brew 1 tbsp. boiling water The finished composition can be drunk or made as compresses for the legs;
- burdock leaves . They cover the affected area and tie it with a bandage for 30 minutes.
Systemic drugs
For moderate and severe disease, systemic medications are prescribed in the form of tablets and injection solutions.
It is recommended to treat psoriasis on the legs under the supervision of a doctor using the following medications:
- Antihistamines help cope with itching and reduce the inflammatory process (Zyrtec, Suprastin, Telfast, Claritin, Diazolin, etc.).
- If suppuration is present, antibiotics from the group of penicillins or cephalosporins are prescribed.
- Enterosgel, Filtrum-sti, Polysorb, activated or white carbon and other enterosorbents have a detoxifying effect.
- Diprospan in the form of an injection solution is used to treat severe forms of the disease. This is a hormonal drug that has a rapid therapeutic effect, but at the same time causes many side effects.
- Sandimmune is an immunosuppressant that helps quickly eliminate inflammation. The drug is highly toxic, so it is used only in a hospital setting under the watchful supervision of doctors.
- Methotrexate in the form of tablets and injection solutions is an analogue of folic acid that stops cell division and the spread of the psoriatic process. The drug cannot be used for pathologies of the kidneys and liver.
- Infliximab is indicated for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis.
- A solution of sodium thiosulfate cleanses the body of waste and toxins, has an anti-inflammatory effect, and restores immune defense.
Physiotherapy to help get rid of the disease
Treatment of psoriasis should be comprehensive and supplemented by such physical treatment methods as:
- Ural Federal District . It can be wideband, narrowband or combined. Irradiation has a local effect. There are special devices for treating feet. In 80% of cases, stable remission is achieved;
- PUVA therapy . Recommended for extensive skin lesions. A very effective method. The essence is a combination of UV irradiation and the use of special ointments and solutions. Efficiency: up to 96%.;
- cryotherapy . The effect of this technique is based on a sharp cooling of the patient’s body by 1-2 degrees. As a result of hypothermic stress, the body mobilizes its entire reserve;
- laser therapy . Helps normalize cellular growth and does not destroy the structure of skin cells.
The latest medical technologies, combined with drug treatment, effectively fight psoriasis, prolonging the time of remission.
Pathology
Psoriasis is a systemic pathology that affects up to 5% of the world's population. The disease involves the skin, joints and a number of internal organs. Scientists point to several concepts for the development of the disease:
- infectious-immunological;
- genetic;
- neuroendocrine;
- exchange.
They argue that changes during the course of the disease occur in the gastrointestinal tract, nervous, cardiovascular and urinary systems. The musculoskeletal system is most negatively affected.
The pathology is characterized by a violation of the “structure of the dermis, cellular activation and local infiltration of the skin by inflammatory cells.”
In general, the disease significantly changes a person’s quality of life: productivity and the desire to communicate in society decrease, and apathy and stress often set in. From a medical disease it develops into a social problem.
Is it possible to cure leg psoriasis permanently?
Unfortunately, this disease cannot be completely cured.
However, with proper therapy, you are guaranteed a stable (for many years) remission. Modern medical advances and procedures can eliminate unsightly external manifestations. The main thing is to prevent aggravation.
And to do this, you just need to eat right and don’t forget about foot prevention and, in particular, foot hygiene.
conclusions
The effectiveness of treatment for psoriasis on the legs is no different from therapy on other parts of the body. If treatment is started in the early stages, then the chances of complete or long-term remission are much higher. According to experts, ignoring the symptoms of the disease can cause the pathology to spread to the joints and develop psoriatic arthritis.
To exclude such a scenario, it is worth visiting a dermatologist at the first signs of the disease and conducting an examination to find out the reasons. Then it will be possible to get by only with external treatment and physiotherapy instead of systemic drugs - tablets and injections.