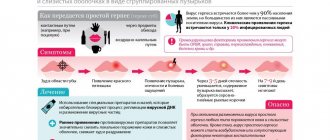
What is HSV
The abbreviation stands for “herpes simplex virus.” HSV types 1 and 2 are a viral disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes and manifests itself as focal inflammation in the form of blisters grouped in clusters. This process is called ballooning degeneration. In the English version, the abbreviation looks like HSV (Herpes Simplex Virus). The disease is divided into 2 main, more common types:
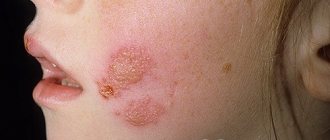
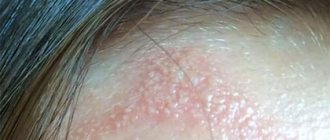
- HSV-1, herpes type 1 or labial. Bubbles are localized in the corners or along the edges of the lips. Often occur after hypothermia of the body due to drafts. In common parlance it is called a “cold.” The problem causes both physical and moral discomfort.
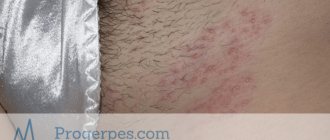
- HSV-2, HSV type 2, or genital herpes. This form affects the mucous membrane of the genital organs and the anal area. Papules are localized on the penis, prostate, vagina, perineum and rectum.
The causative agent of the disease
HSV types 1 and 2 - what kind of disease this is is known to many. The cause is the DNA-containing pathogen Herpes simplex (herpes simplex, HSV). It is a member of the Herpesviridae family. Its shape is round and its diameter reaches 150-300 nm. When exposed to unfavorable factors, such as sunlight, drying, high and low temperatures, it dies. Main properties of the pathogen:
- the presence of an antiviral link that suppresses the immune system of the human body;
- the ability to persist for a long time in intracellular structures, transferring genetic material to daughter cells (this is called persistence);
- virus types 1 and 2 differ in the favorite location of pathological rashes;
- There is HSV type 3, which causes herpes zoster and chickenpox, and type 4, which causes infectious mononucleosis.
Source of the disease
The virus carrier or patient is the source of the disease. The pathogen can enter the body at an early age. Children 3-6 years old are especially prone to infection. At this age, the antibodies that were transferred from the mother at birth stop acting, so the susceptibility to HSV increases. The microorganism penetrates the body and settles on epithelial cells, where a host cell suitable for it is located.
Then it enters the blood, nerve fibers, plexuses and ganglia. The pathogen remains in the body forever, going deep into the nerve nodes. There it assumes a latent state until activated by unfavorable factors that reduce immune defense. An infected person may contain viral cells:
- nasopharyngeal mucus;
- discharge from ulcers and erosions;
- blood during menstruation;
- conjunctival secretion;
- vesicle contents;
- sperm;
- vaginal and cervical secretions.
Transmission of infection
Most often, herpes is transmitted only through direct contact with damaged tissues of a sick person, as well as through the body fluids of the carrier. When the bubbles containing the pathogen are opened, the virus enters the external environment. At room temperature it remains viable for 24 hours. At this point, you can become infected by sharing utensils, cosmetics, and even by passing metal coins to each other.
Self-infection with type 2 virus is common. For example, contact lens wearers can introduce the herpes virus into their eyes when they wet their lenses with saliva rather than a special solution.
How is the herpes virus transmitted?
The pathogen is not able to remain in environmental conditions for a long time, so it can be transmitted in numerous ways. This results in a high risk of infection and widespread pathology. It is transmitted in such ways as:
- Direct contact. Transmission occurs through contact with the skin or mucous membranes of a virus carrier or a sick person.
- Indirect (indirect). The microorganism gets on personal or intimate hygiene items, dishes, after which the skin or mucous membranes of a healthy person come into contact with them. Since the pathogen has low resistance to the environment, the transmission condition is a short period of time. For this reason, this route of transmission is rarely observed.
- Transplacental. The pathogen is transmitted from mother to child through the placenta.
- Sexual transmission of HSV type 2. The genital form is infected directly during sexual intercourse due to contact of the mucous structures of the urogenital tract. This is a type of direct transmission.
- Airborne. Through exhaled air and tiny droplets, the microorganism is transmitted to a healthy person when he inhales.
- Vertical. It is the transmission of the virus from mother to fetus during childbirth.
Preventive measures
Following good personal hygiene will help you avoid getting infected with herpes. After visiting public places, you must wash your hands with soap. Even members of the same family are recommended to have separate dishes. A person who has discovered that he has a herpetic infection must temporarily refuse tactile contact with others.
Protected sex reduces the risk of contracting herpes. However, it is not recommended to enter into casual relationships or frequently change partners. If symptoms of the disease appear, sexual activity should be avoided for the period of treatment. Sexual relations can be resumed after signs of herpes are eliminated. If the virus is in a passive state, its transmission is virtually impossible.
Carriers of herpes can reduce the number of relapses of the disease if they avoid stress and hypothermia. Strengthening the immune system is the main preventive measure. Proper nutrition and giving up bad habits will help support the immune system. Playing sports has a positive effect on the body. The patient is recommended to take vitamin complexes twice a year.
Features of the HSV virus types 1 and 2
Both forms of the virus are characterized by lifelong infection, when the pathogen cannot be completely eliminated. The difference between them is the age when infection occurs more often:
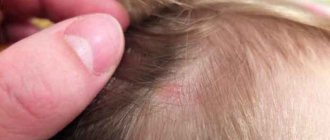
- Herpes virus type 1 (labial) affects a person between 3 and 5 years. This is due to the fact that during this period the baby becomes more independent, and the antibodies received from the mother cease to function. The result is that the child’s body becomes more susceptible to bacteria and viruses.
- The development of HSV type 2 (genital) occurs when a person has already reached puberty. This is explained by the fact that this form of pathology is sexually transmitted.
What diseases does it cause?
HSV causes disease only under certain conditions. The main one is the weakened immunity of the virus carrier. The infection rate of the human population under favorable conditions for the virus is about 90%. HSV type 1 is observed in 60% of cases, and type 2 in 30%. Each form causes certain diseases:
| Virus type | Type of virus | What diseases does it lead to? |
| 1 | HSV | labial herpes (“cold” on the lips); herpetic infection of the skin and mucous membranes; herpetic keratitis. |
| 2 | herpes of newborns; genital HSV. |
Risk factors
Penetrating into the human body through mucous membranes or microcracks in the skin, HSV is localized in the nerve ganglia, where it enters a latent state. This means that the pathogen remains in the human body forever, which is why it is not possible to completely recover from it. Under favorable conditions, the virus is activated, resulting in the appearance of vesicles. Factors that lead to this are:
- excessive alcohol intake;
- hypothermia;
- visits to the solarium;
- overheating of the body (“solar” HSV, which develops due to a lack of melanin);
- physical or mental injuries;
- hormonal changes;
- medical procedures, including abortions;
- weakening of the immune system.
In children
Do not think that herpes does not pose a danger to a child. The rash will go away, but traces will remain in the body. The virus can infect internal organs, the nervous system and cause many more complications.
In the first months of life, the body of a newborn baby is protected by the mother’s immunity.
Along with breast milk, he also takes in antibodies produced by the mother’s body. But if a woman is infected with herpes, then the presence of herpes virus in the baby is possible.
Herpes is often diagnosed in children at 2 years of age. By this time, the mother’s protection is no longer there, and the body has not yet produced its own antibodies. But by the age of 5, the body is able to resist the virus, as it begins to produce substances necessary for protection.
How does herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 affect the body?
The development of HSV is a long process that includes several stages. The first is infection that occurs through direct, airborne, vertical, sexual or indirect routes. The virus then goes through the following phases:
- Transition to a latent state. After entering the body through one of the routes, the infection takes on an inactive form, in which there are no symptoms. This does not mean that the pathogen is not in the body. It is simply “waiting” for favorable conditions to manifest itself.
- Activation of HSV. Occurs under the influence of triggers, i.e. factors that trigger certain processes in the body.
- Development of antibodies to the virus. After an infection enters the body, the immune system produces antibodies to it. This is the name of a special type of proteins in blood cells - immunoglobulins, designated by the Latin letters ig. There are 5 types of antibodies that characterize the disease in their own way:
- IgM – appears first after infection;
- IgG – detected several days after the previous one, the most common class of antibodies (75%);
- IgA – produced in mucous membranes, found in saliva and breast milk;
- IgE – indicates the presence of an allergy, is present in the blood in small quantities;
- IgD - produced in the embryo during gestation; in adults only minor traces are observed.
Stages of development
This form of virus is called labial. This pathology is familiar to many; it is more common. The incubation period of primary infection is 1-8 days. The rash may appear on the lips, cheeks, and other areas of the face. The entire process of infection development goes through 4 main stages:
- Itching and tingling in the lips. More often the virus is localized in their corners. A person feels how they itch very much. Against this background, redness of the lesion appears. The peculiarity of this stage is that if you start treatment, you will be able to prevent the virus from moving to the next stages. Effective here are Acyclovir, Gerpevir, Herperax, Ribavirin, Oxolinic ointment.
- The appearance of small bubbles. Their contents are transparent. Over time it becomes cloudy. The itching persists against this background.
- Ulceration of vesicles in areas of epithelial erosion. A serous exudate is released from them, which contains millions of viral particles. At this stage, the person is especially contagious to others. If an antibody test is performed, it shows the presence of IgG.
- Crust formation. Comes in 3-5 days. It is important not to disturb the integrity of the crusts, otherwise the lesion will bleed and hurt. Symptoms disappear completely 7-9 days after the appearance of itching on the lips.
Herpes simplex type 2
The course of this form is similar to the development of the labial one. The difference is that the bubbles are localized not on the face, but on the skin and mucous membrane of the genital organs. They can be found on the clitoris, labia, pubis, buttocks, sacrum, and glans penis. Skin hyperemia occurs first, then blisters form. Gradually they turn into ulcers, which become covered with crusts when ulcerated.
In some patients, the pathology manifests itself as small individual spots, similar to insect bites. For this reason, a person does not always recognize the presence of HSV. The following factors can provoke activation of the genital form:
- overwork;
- emotional stressful situations;
- flu;
- angina;
- ARVI;
- surgical operations;
- sexual contact;
- frequent drinking of alcohol.
Treatment
Treatment tactics depend on the severity of the course, the prevalence of the rash, and the form of the disease. In any process when bubbles form, antiviral therapy is prescribed (acyclovir, Zovirax, cytovir, erazaban). The drug is taken orally for 7-10 days.
Acyclovir ointment is used topically on the affected area, which is applied throughout the period of blistering.
After discontinuation of etiotropic drugs, therapy with immunomodulators is carried out to improve the antiviral response of the immune system. Used: cycloferon, lykopid, immunomax.
When an acute condition develops, antihistamines are prescribed to reduce allergization of the body by a foreign agent (virus).
Locally, as a prevention of secondary infection, especially with extensive lesions, treatment is carried out with antiseptic solutions: an aqueous solution of methylene blue, a solution of brilliant green, fucarcin, miramistin.
To improve regeneration processes and speed up recovery, take Wobenzym.
For viral conjunctivitis, ophthalmoferon and virgan are instilled into the eyes. The frequency of instillations depends on the intensity of inflammation.
For severe, widespread herpes and specific lesions of the central nervous system, antiviral therapy is administered intravenously.
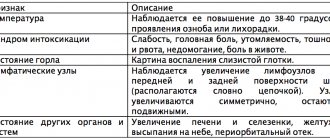
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of the disease may vary depending on the location, strain of the herpes rash and the individual characteristics of the person. A characteristic symptom is a rash of vesicles. Labial herpetic infection is characterized by sores on the lips, nose, and facial skin. Vesicles are observed at the entrance to the vagina with vaginal herpes in women, on the penis with HSV type 2 in men. In addition to the appearance of ulcers, the following symptoms are possible:
- General signs of intoxication. Possible increased temperature, fever, lymphadenitis (enlarged lymph nodes), malaise. Sometimes numbness occurs at the site of inflammation.
- The appearance of a rash on the palate, tongue, tonsils, oropharynx, and inner surface of the cheeks. In this case, HSV proceeds like a respiratory disease.
- Pain syndrome. With genital herpes, there is pain in the lower abdomen and in the genital area. There may be purulent discharge from the vagina. In men with the genital form, burning and pain in the urethra occur when urinating. In this case, medications are often prescribed in the form of suppositories.
Diagnosis of herpes simplex virus
The diagnosis is made by a dermatovenerologist. Sometimes a consultation with an ophthalmologist, gynecologist, or urologist is necessary. If a person has ever suffered from type 1 HSV, it does not mean that he will never suffer from its second form. It is especially dangerous due to the possible development of tumors and necrosis, and even blindness if the eyes are affected. A common complication is herpetic vesicular dermatitis. During pregnancy, it can lead to its termination. The most dangerous consequence is infertility.
Due to dangerous complications, for some categories of patients, a dermatovenerologist prescribes diagnostics without fail. It is necessary for:
- pregnancy planning;
- normal course of pregnancy;
- patients with immunodeficiency;
- patients with suspected urogenital infections;
- patients with blistering skin rashes;
- pregnant women with suspected intrauterine infections.
Diagnostic methods
The entire diagnostic process involves more than just a visual examination. Due to the difference in symptoms in certain patients, additional laboratory and instrumental studies are required. Today there are the following methods for diagnosing HSV:
- Virological research. It consists of isolating the pathogen in the culture of sensitive tissues. This method is considered the “gold standard” in detecting viral infections. The sensitivity of the study is 95-100%. Its use is limited by high cost, technical complexity, and duration of the study.
- Cytological examination. It is a light microscopy of specially stained smears of biological material. HSV is confirmed by giant cells and intranuclear inclusions. The method is inexpensive, fast, but has only 60% sensitivity.
- Biological method. If the material is applied to scarify the cornea of a rabbit, then if HSV is present, it will develop keratiat. In newborn mice, a neuroinfection called encephalitis occurs in the brain using this diagnostic method.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Determines the presence of antibodies to the pathogen in the blood.
- PCR of cerebrospinal fluid is a polymerase type of chain reaction. The molecular biological method detects DNA particles of the causative agent of herpes infection. The technique is capable of identifying even one viral cell in the taken biomaterial.
- DIY plasticine crafts for children
- Back exercises in the gym photos and videos. The best exercises to strengthen a girl's back
- What does the histology of the cervix, glands and moles show?
Enzyme immunoassay for herpes virus
To carry out an enzyme immunoassay, blood, cerebrospinal fluid, amniotic fluid, saliva or breast milk are taken. The procedure is carried out in two stages. First, the collected material is first combined with an antigen, after which the immune complex is monitored. Second, a chromogen is added to determine the level of pathogenic microflora in the body based on the intensity of the staining. There are 2 types of ELISA:
- Qualitative analysis. Of the 5 main classes of immunoglobulins, IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, IgDI detects only the first 3. The analysis determines the type of infection and the presence of relapses in the past.
- Quantitative analysis. Determines the amount of immunoglobulins in the blood. Roughly assesses the state of the immune system.
The marker of primary penetration is anti hsv IgM antibodies. Anti hsv IgG is also important in diagnosis. They appear in the blood a few days after infection. To decipher the result, reference values are used. These may vary from laboratory to laboratory, but are always indicated on the form. The result of the analysis is one of the diagnoses:
- Seropositivity. Antibody levels are below the threshold.
- Seronegativity. Antibody levels are above the threshold.
Decoding the results
The detected antibodies and their quantity make it possible to judge whether a person has had a herpes infection in the past or has recently appeared. The primary marker is IgM. It is an indicator of infection. An IgG antibody indicates infection of the body with HSV type 1 or 2. The analysis is described in detail in the table:
| Index | Decoding |
| IgM- IgG- | The person has no immunity. The risk of primary infection is high. |
| IgM- IgG+ | Having immunity to herpes. There is no risk of primary infection. Secondary exacerbation depends on the state of immunity. Prevention is possible. |
| IgM+ IgG- | Primary infection, the patient requires treatment. |
| IgM+ IgG+ | Secondary exacerbation, the patient needs therapy. |
Preparing for analysis
To ensure that the analysis results are accurate and reliable, follow a number of simple rules:
- Blood is donated to the laboratory only on an empty stomach.
- Minimize any physical activity one hour before your test.
- During the day, you should exclude fatty and fried foods, alcohol, and do not smoke from your diet.
- Also, avoid taking any drugs or medications the day before.
- Children under 5 years old are given a glass of warm water to drink half an hour before the test.
Herpes simplex types 1 and 2 during pregnancy
Due to herpes infection, the fetus develops deformities in the womb. In infants, HSV can cause congenital pathologies. The genital form is especially dangerous for pregnant women. It leads to mental and physical disorders in the child much more often. In the early stages, miscarriages or fetal death in the womb are noted. In pregnant women, the disease is more severe. In addition to the classic symptoms, the following appear:
- copious light-colored vaginal discharge;
- swollen genitals, their soreness;
- heat;
- painful and frequent urination.
For this reason, pregnant women are tested for antibodies igM and iGG. The analysis is carried out several times throughout the entire period of gestation. The results of the study are deciphered as follows:
| Index | Decoding |
| IgM- IgG- | If the readings are negative, the woman is healthy and has never had the disease. Due to the fetus's lack of immune protection, there is a risk of infection. |
| IgM- IgG+ | There are 3 decryption options:
|
| IgM+ IgG- | The initial stage of the disease, there is a risk for the child. |
| IgM+ IgG+ | The first half of the primary acute infection requires antiviral treatment. |
Clinical picture of genital herpes
Herpes simplex type 2 is detected in adults who are sexually active. Protected sexual contact (using a condom) does not always prevent infection - the rash may be located around the genitals. The chronic relapsing form of the disease worsens the quality of life and makes sexual intercourse difficult. Recurrences of herpes virus types 1 and 2 more than 3 times a year indicate immunosuppression and require specific treatment of the disease.
Symptoms of herpes simplex virus type 2:
- prodromal period - headache, drowsiness, disability, pain in the perineum, lumbago in the vagina, thigh, anus, burning and itching of the skin of the external genitalia, fever up to 38 degrees, chills;
- period of active infection - swelling and redness of the labia majora and minora, perianal area, skin in the thighs and groin area, formation of itchy grouped blisters with transparent contents, rash diameter 2-4 mm, opened blisters are painful to the touch and when moving, sexual intercourse is not possible due to pain;
- recovery period - brown crusts form in place of the opened blisters, which are rejected without scarring or pigmentation, normalization of the general condition.
With normal functioning of the immune system, herpes simplex type 2 does not recur or worsens rarely, sometimes it is asymptomatic. During the period of carriage, a person can infect the sexual partner, but the highest probability of infection is characteristic of the active phase of the disease.
Treatment of HSV types 1 and 2
It is immediately worth noting that HSV cannot be cured completely. Treatment only helps to stop the exacerbation and prevent the development of infection in the future. Basic principles of therapy:
- Herpes is a viral microorganism, so antibacterial drugs do not work on it. Levomekol, Tetracycline and other antibiotic ointments will not be effective. Antiviral drugs become the basis of etiotropic therapy.
- The use of medications is irrational if the labial form manifests itself in a mild degree.
- There are no medications for prevention - you cannot protect yourself from the occurrence of herpes in the future with the help of medications.
- Physiotherapy with infrared or ultraviolet radiation may be used. In some cases, antiviral chemotherapy is used.
Use of antiherpetic antiviral drugs
Inactivation of the pathogen is carried out only with antiviral agents. The approach to treatment is complex, so therapy includes both systemic and local drugs. First group:
- Acyclovir. A drug from the group of acyclic nucleosides that inhibits the replication of viral cells. You need to take 5 tablets of 200 mg daily for 5-10 days. Contraindications: hypersensitivity, breastfeeding, pregnancy, age under 2 years. The medicine can cause multiple adverse reactions.
- Famciclovir. Blocks the synthesis of viral DNA of cells, prevents the replication of viruses. For genital herpes - 3 times daily, 250 mg for 5 days, for labial herpes - 1 time per day, 1500 mg. After taking, nausea, allergies, and headache are possible. The drug should not be taken in childhood.
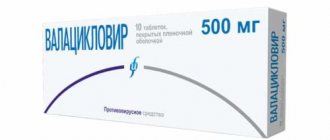
- Valaciclovir. Inhibits the activity of DNA polymerase of herpes viruses. Once a day you need to take 1000 mg, divided into 2 doses. Cannot be used by HIV-positive people under 18 years of age, after bone marrow or kidney transplantation. Almost all potential adverse reactions are possible. An analogue is Valtrex.
The immediate site of the lesion can be treated with ointments. They must also contain antiviral components. The following drugs are commonly used:
- Zovirax. Based on acyclovir, which inhibits the replication of herpes simplex viruses. Use a cotton swab to apply the cream to the affected area up to 5 times a day. treatment lasts 4 days. Zovirax is prohibited if you are allergic to acyclovir. After use, itching, angioedema, dermatitis, redness, and burning are possible.
- Acyclovir Hexal. Stops viral DNA synthesis. The drug is prohibited during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and renal impairment. You need to apply the cream 4-6 times a day. Treatment lasts 5-10 days. After application, redness and itching may occur.
Immunostimulating therapy
Herpes is activated against the background of a general weakening of the immune system. For this reason, complex treatment of the virus additionally includes immunomodulators:
- Kagocel. Has antiviral and immunomodulatory effects. For herpes, you need to take 2 tablets three times a day for 5 days.
- Neovir. Effective against viruses, helps strengthen the immune system. You need to take 750 mg per day. The course of treatment is 5-7 doses with breaks of 2 days. An analogue is Reaferon.
Symptomatic treatment
While being treated with antiviral drugs, the doctor prescribes some patients medications that relieve certain signs of infection. The following medications may be used for specific herpes symptoms:
- For fever and aches. Antipyretics Ibuprofen and Paracetamol are indicated.
- From itching, pain, burning. Local analgesics such as Benzocaine and Lidocaine are effective.
- To prevent bacterial infection. To disinfect the lesion, after taking a bath and drying the skin, each element of the rash is lubricated with a solution of brilliant green, Fucarcin, Miramistin or 2% silver nitrate.
Adaptogens
This group of drugs consists of herbal products. They are able to activate the internal resources of the body, increase tone and immunity. Against this background, the body copes with herpes faster. Each drug indicated must be used according to the instructions. Useful for herpes are fir and sea buckthorn oil, as well as tinctures:
- propolis;
- Schisandra chinensis;
- aralia;
- aloe vera;
- Eleutherococcus;
- ginseng.
Vitamins and microelements
Vitamin therapy can increase immunity and restore the body weakened after suffering from a virus. To help cope with the disease:
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C);
- zinc preparations;
- vitamin E capsules;
- vitamin A;
- vitamin B1 (thiamine).
Therapeutic measures
Medicine cannot yet destroy the virus that has settled inside the cells of the donor’s body. Modern treatment is only capable of:
- reduce the relapse rate,
- reduce the duration of attacks of exacerbation of herpes simplex,
- help a sick person cope with illness,
- prevent complications from occurring.
To do this, the therapeutic regimen includes:
- Antiviral drugs - Acyclovir, Famciclovir, Valacyclovir. The use of such medications is especially effective when carrying out therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating the symptoms of facial herpes.
- Analgesics - Paracetamol, Ibuprofen. They reduce pain and fever symptoms.
- Anesthetics are topical preparations.
- Disinfecting solutions - Zinc ointment, Acyclovir cream, Doconazole, which relieve inflammation, disinfect wounds formed after opening of the blisters, dry them, accelerate regeneration processes.
Much attention is paid to strengthening the immune system. The patient is advised to follow the principles of proper nutrition, actively engage in sports and harden himself.
How to treat HSV types 1 and 2 with folk remedies
You should not completely rely on folk recipes. The herpes virus is very dangerous under certain conditions, and in the absence of adequate treatment it becomes recurrent. During treatment with medications, you can use the following recipes:
- Apply crushed garlic to the problem area 2 times a day.
- Wipe the area of inflammation with freshly squeezed celandine juice up to 3 times a day using a cotton swab.
- Brew 200 ml boiling water 1 tbsp. l. lemon balm. Cover with a towel and leave until cool. Drink the strained infusion 100 ml before meals. At the same time, lubricate the rash with raw egg white.
- Take a piece of ice from the refrigerator, wrap it in a thin napkin and apply it to the area of inflammation for a couple of minutes. In the early stages this method is very effective.
Pathogen
The herpes simplex virus has double-stranded linear DNA. The active action of the virus occurs in the nucleus of the affected cells. Herpes pathogens have pronounced cytopathic properties, due to which they kill the affected cells, but if they enter certain types of cells (for example, neurons), replication does not occur and the affected cell does not die.
Neuronal cells are capable of exerting a unique inhibitory effect, transferring the disease to the latent phase of the course, during which the virus exists together with a physiologically active cell. After an indefinite period of time, the awakening of the viral genome may occur, which will become an impetus for the replication of the virus.
The herpes simplex virus tolerates drying and freezing quite well. When heated to 50-52 degrees, inactivation occurs within 30 minutes. The protective shell of the herpes virus dissolves under the influence of alcohols and acids. Treatment with disinfectant solutions will not have a significant effect on the virus, which cannot be said about UV radiation, which destroys herpes the fastest.
Prevention of herpes
A vaccine against herpes has not yet been developed. There are no medications that would definitely protect against such an unpleasant virus. For this reason, for prevention, you can only perform the following actions:
- treat all chronic diseases;
- provide adequate nutrition and sleep;
- to harden;
- observe the correct work and rest schedule;
- often be in the fresh air;
- exercise;
- take multivitamin complexes;
- protect yourself with condoms.