Chickenpox or varicella zoster virus is most often observed in children, however, it also happens that the disease affects an adult. As a rule, children experience the disease before the age of 12 years. The infection has no particular complications and occurs with classic symptoms. U
Adults suffer from chickenpox much more seriously, and in some situations the viral disease can be fatal. However, the immune system is designed in such a way that if a person has already suffered from this disease in childhood and his body has learned to produce antibodies to chickenpox, the likelihood of re-infection will be minimal.
Unfortunately, chickenpox is not the flu or ARVI. It is impossible to find out immediately that a child or adult has become infected. As a rule, the first symptoms of infection appear only 2-3 days after contact with a sick person. Once the pathogen enters the body, it does not manifest itself for a long time, and only after a few days does a person find out that he is infected with the chickenpox virus.
Experts say that the incubation period for chickenpox ranges from 11 to 23 days. In other words, a child can be infected with the chickenpox virus for almost a month, be a carrier of the infection and not know about it. As a result, sometimes it is not even possible to determine where the patient became infected and who could become a carrier of the infection. In the case where a child is infected with chickenpox, it is quite simple to find out the source of the virus. Most often this happens in places where children have direct contact: in kindergartens and schools. If we are talking about an adult, then the options may be different.
general information
The danger of contracting chickenpox in adulthood is its severe course, the possible transition of the rash into a hemorrhagic or bullous form (when ulcers appear on internal organs).
In addition, an adult may experience serious complications in the form of encephalitis, disruption of the cardiovascular system, pyoderma or lymphadenitis.
Fun fact: “wind parties” were popular in the early 20th century. Parents deliberately brought their children to those who were already infected with chickenpox so that the child could easily transfer the disease.
Ways to get rid of marks after chickenpox
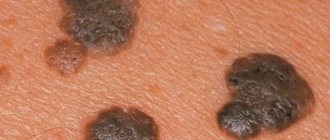
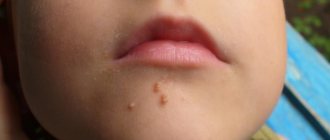
Often, after all the elements of the rash have passed, areas of hypopigmentation, small scars or depressions remain on the skin. The lighter areas of the epidermis will become completely invisible after the first tanning sessions in late spring - early summer.
Scars that form when vesicles open or form pustules, although absolutely harmless, can create a cosmetic defect. They can be eliminated with a laser or significantly reduced in size by applying hydrocortisone ointment in the first 2-3 weeks from the moment they appear.
Specific dimples at the site of burst vesicles cannot always be completely removed. Cosmetic procedures in the form of photo-exposure, laser procedures and deep peelings can have a certain effect. Unfortunately, there may be no result at all, regardless of the volume and quality of the procedures performed.
Infection and stages of the disease
Chickenpox is transmitted by airborne droplets, which, interestingly, is the only virus to which susceptibility in humans is 100%. The pathogen enters the body through the respiratory system and penetrates the mucous epithelium. After the virus enters the bloodstream, a skin reaction begins: itching, swelling and the appearance of a rash.
Conventionally, the stages of the disease can be divided into several periods:
- Incubation – for adults from 11 days to 3 weeks, for children 2 weeks. At this time, chickenpox practically does not manifest itself; fever or weakness may appear.
- Prodromal – characterized by elevated body temperature, lower back pain, migraine, lasts 2-3 days.
- The period of appearance of the rash - in people over 30 years of age is accompanied by high fever, nausea, general weakness, and radiating pain throughout the body. Lasts from a week to 10 days.
After the crusts dry, the recovery stage begins, and the virus becomes no longer dangerous to others.
Does immunity appear?
Having once had chickenpox in a mild form, a person receives lasting immunity to it. But the disease virus settles permanently in the body and, under favorable conditions, can become active. Repeated cases of mild chickenpox are rarely encountered in medical practice; In them, the disease occurs in an erased form, there are few acne and they almost do not bother the patient. A person may not even know that he is sick and continue to communicate with healthy people, risking infecting them.
Shingles is another sign that the chickenpox virus has become active. It is characterized by unbearable pain and burning, and can also occur repeatedly.
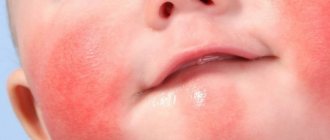
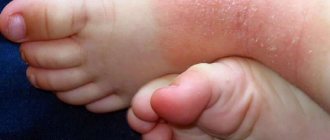
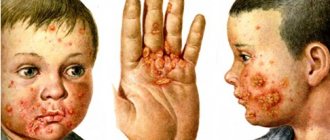
The nature of the rash with chickenpox
In adults, this virus causes massive rashes throughout the body, often accompanied by additional unpleasant symptoms. At first, the rash looks like small pinkish spots, about 2 mm in size. A few hours after their appearance, they enter the papules stage, then crusts appear on them, which disappear over time.
Rashes can also develop on the mucous membranes; they take the form of small ulcers and disappear together with the main symptoms of smallpox.
Relapses
Once contracted, the disease provides lifelong immunity. Chickenpox scars, like in the photo, are a kind of payback for this. At the same time, relapses are not excluded. So, in the future, chickenpox may return in the form of shingles, photographs of which you can see on a separate page.
WE RECOMMEND YOU TO WATCH:
Features of the course in pregnant women
Herpes virus type 3 is incredibly dangerous when carrying a child, in the last stages of pregnancy. Small risks of developing complications exist in the first weeks; in the middle of the perinatal period, chickenpox does not pose a danger to the fetus.
If the infection occurs immediately before childbirth (a week or later), complications in the form of congenital chickenpox are possible. In such cases, the baby may experience breathing problems, inflammation of the bronchi, diarrhea and damage to internal organs. About 30% of cases end in death.
Varieties of chickenpox
All cases of chickenpox are conditionally classified based on the following indicators:
- according to the mechanism of disease development: congenital or acquired virus;
- by form: typical, atypical, rudimentary, gangrenous, hemorrhagic, visceral;
- by severity: mild, moderate, severe;
- according to the characteristics of the course: smooth, with complications, together with a mixed infection.
Each type of chickenpox has its own symptoms and specific treatment. This is also why you should not diagnose the disease yourself or take various medications, since this can be dangerous for both adults and children.
The rudimentary form of chickenpox is considered the mildest. This is what most often occurs in children. The most severe form is the hemorrhagic form, since it involves bleeding into the internal organs of the sick person.
Signs of chickenpox
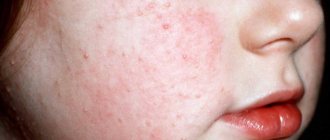
The first symptoms of chickenpox in an adult appear like a typical cold. There may be weakness, muscle aches, nagging pain in the sacral area, and sore throat.
As a rule, in the first days the patient attributes his condition to food poisoning or flu. In addition, before the first papules appear, health can improve and deteriorate within 2-3 weeks. It depends on the age of the patient and his immune system.
If a rash appears, it is better not to take risks and look online for photos of what chickenpox looks like in adults. If your fears are confirmed, do not panic, because not every case of this virus ends in complications in people over 30.
The rash is the main symptom of chickenpox, the rest can manifest themselves to varying degrees as the disease progresses:
- dizziness;
- ulcers of the mucous membranes of the mouth and genital organs;
- migraine;
- fever;
- vomit;
- nagging pain in the joints.
When confirming the diagnosis, it is advisable for the patient to consult a doctor, despite the fact that there is no specific treatment for the disease, everyone should know how to behave correctly with chickenpox.
Firstly, this concerns limiting your social circle, you need to warn everyone about your condition and cancel your appointments. Next, stock up on everything you need, get separate towels, dishes and bed linen.
It is better to send people away who have never had chickenpox before. It is advisable not to limit sweet and fried foods as much as possible.
Differential diagnosis
The disease must be differentiated from other infections with skin rashes. These include the following conditions:
- Herpes simplex (generalized form).
- Bullous dermatoses.
- True eczema.
- Congenital syphilis.
- Pyoderma.
This is the main thing that can be confused with chickenpox in a child. Smallpox, which is now considered defeated, is no longer relevant as an element of differential diagnosis.
Herpes simplex
A generalized infection caused by the herpes simplex virus may resemble chickenpox in its intoxication syndrome, vesicular rash, and widespread lesions. However, this case is characterized by high fever, which occurs after the rash. And the latter are most often grouped in certain areas of the body (around the mouth and nose, on the genitals). The condition with typical chickenpox is much easier.
Bullous dermatoses
Skin diseases in which blisters appear are called bullous dermatoses. These include pemphigus, Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis, and Lyell's syndrome. They are also accompanied by fever, intoxication and damage to the mucous membranes. But bullous dermatoses also have significant differences:
- Large blisters are present against the background of a small rash.
- There are usually no rashes on the face.
- Nikolsky's symptom is characteristic (peeling of the epidermis when sliding with a finger).
- The blisters quickly burst, revealing weeping erosions.
Some conditions, especially Lyell's syndrome, are characterized by severe patient condition, dehydration and dysfunction of internal organs.
It is much easier to confuse chickenpox, especially the atypical form, with bullous dermatoses. But the doctor will always be able to distinguish between these conditions.
True eczema
Diagnostic errors are also possible with true eczema, which is accompanied by blistering rashes and the formation of crusts. Its differences from chickenpox are as follows:
- No epidemic prevalence.
- Most often professional in nature.
- Normal body temperature.
- Grouped rashes are localized on open areas of the body.
- Large wet surfaces quickly form.
- Severe skin itching.
Eczema is caused not by viruses, but by bacteria or as a result of contact with allergens. It never becomes widespread.
Congenital syphilis
Another condition with which it is necessary to differentiate chickenpox in young children is congenital syphilis. It has the following differences:
- The rash is usually macular or bullous.
- The elements are most often localized on the palms and soles, around the mouth.
- Many children develop a runny nose with bloody discharge.
A laboratory test allows you to accurately make a diagnosis - when scraping from pathological foci, a specific causative agent of the disease is identified - Treponema pallidum.
Pyoderma
Chickenpox, complicated by the addition of bacterial flora, should also be distinguished from primary staphylococcal pyoderma. In such cases, the pustules are located mainly on open areas of the skin; the disease is not accompanied by intoxication and often has a persistent long-term course.
The conditions with which chickenpox is confused in children are quite varied. But making a diagnosis is the doctor’s task. Only a specialist knows all the features of the disease and is able to distinguish it from other pathologies.
Therapeutic measures
Conventionally, there are 2 stages of treatment for chickenpox in adults:
- relief of symptoms;
- dealing with the consequences.
During the course of chickenpox, all measures are aimed at improving the condition. For this purpose, antipyretic drugs (paracetamol, ibuprofen) and analgesics (analgin) are taken. To reduce itching, you can take antihistamine tablets (suprastin, diazolin), but as a rule, they do not help much.
At the second stage, the main problem is papules; if the patient scratches them, it is necessary to use antibacterial agents (brilliant, hydrogen peroxide). The oral cavity can be rinsed with furatsilin solution.
If there are scars left after chickenpox, you can use creams with bodyaga or mumiyo.
Despite the fact that the disease is of viral etiology, proper treatment of chickenpox in adults does not involve taking antiviral drugs or interferon analogues. In the case of this pathogen, they are ineffective.
Treatment of mild chickenpox
Mild chickenpox can be treated at home. Treatment of the disease should be aimed at preventing the transition of chickenpox to more severe forms, in which cardiovascular, neurological and purulent complications are possible, as well as at relieving intoxication, relieving itching and reducing temperature.
For a patient with mild chickenpox, it is recommended:
- drinking plenty of fluids to quickly remove the chickenpox virus from the body;
- avoiding sweating, because it increases itching;
- frequent hand washing to avoid infection in papules when scratching;
- limiting physical activity;
- easily digestible food rich in vitamins;
- exclusion of sweets from the diet, as they contribute to the proliferation of microbes on the skin;
- washing the body in the shower without using a washcloth, which helps maintain the integrity of the vesicles;
- isolation from healthy people for the entire period of illness.
Diagnostics
If there are few rashes and it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis, then laboratory tests are performed:
- Microscopy of vesicular contents.
- General urine and blood tests. The appearance of deviations from the norm in them indicates the presence of an infectious process in the body.
- Detection of antibodies to the virus in the patient’s blood. With a dynamic increase in their number, the diagnosis of chickenpox is beyond doubt.
With typical clinical symptoms, diagnosing chickenpox does not cause difficulties for an infectious disease specialist, especially if the patient indicates recent contact with the patient.
If there are few rashes and it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis, then laboratory tests are performed.
Drugs
The advisability of using medications for mild chickenpox and their dosage for each patient is determined by the doctor. Medicines are prescribed for oral administration, injection and local treatment.
Their examples are presented in the following table.
| Drugs | Group | Action |
| Acetylsalicylic acid; Ibuprofen; Paracetamol. | Antipyretics | Normalize the temperature; prescribed at body temperature +38.5°C and above |
| Kagocel; Acyclovir (tablets or ointment); Gerpevir (ointment); Valacyclovir; Valtrex; Amiksin; Cycloferon; Famciclovir. | Antiviral | Blocks the replication of the chickenpox virus |
| Diazolin; Suprastin; Loratadine; Tavegil. | Antihistamines | stop allergic reactions; have a calming and weak hypnotic effect; reduce itching. |
| Oxacillin; Cefazolin. | Antibiotics | Prevents the proliferation of bacteria, prescribed in case of secondary infection |
| Zostevir | Immunoglobulins | binds Varicella Zoster virus; relieves chickenpox; reduces the stage of rashes. |
| Reopoliglyukin | Detoxification | Cleanses the blood of toxins, quickly removes them from the body |
| Fenistil (gel); Calamine (lotion); Zinc ointment; Delaxin (cream or powder); Tsindol. | Antipruritic | When applied topically, they reduce itching, relieve irritation, and soothe inflamed skin. |
| Fukortsin; brilliant green. | Disinfectants | Dries and disinfects chickenpox pimples |
| Furacilin; Miramistin; potassium permanganate. | Used in the form of a weak solution for washing the mucous membranes of the mouth or genitals; destroy pathogenic microorganisms. |
It should be remembered that self-treatment with local remedies is fraught with the appearance of cosmetic defects on the skin, so they are also used only as prescribed by a doctor.