Herpes in children is one of the most common chronic viral infections, during exacerbation of which characteristic blistering rashes appear on the skin and mucous membranes.
Source: agushkin.ru
Many parents believe that the appearance of herpes on a child’s lips is just a symptom of a common cold and do not consult a doctor. Actually this is not true. Indeed, a herpes infection can remain latent for a long time and manifest itself as episodic rashes of blisters on the skin. However, a significant decrease in the activity of the cellular component of immunity, due to a variety of reasons, can lead to dissemination of the pathogen with damage to internal organs, the peripheral and central nervous systems.
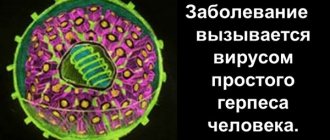
The term “herpetic infection” is traditionally applied to infectious processes caused by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 (HSV, lichen simplex virus, herpes simplex virus).
Causes and risk factors
The causative agents of herpes simplex in children are viruses of the herpevirus family (Herpetoviridae). About 100 types of herpes virus are described in the medical literature, but only 8 types of them are pathogenic for humans:
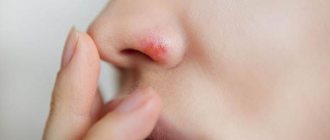
- The most common type of virus. Causes the appearance of blistering rashes on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, around the mouth and wings of the nose.
- It is somewhat less common than herpes virus type 1. Affects the mucous membranes of the genitals. In some cases, it causes the development of herpetic stomatitis and herpetic sore throat.
- Another name for this type is Varicella Zoster. During primary infection, the child develops chickenpox. In adolescents and adults who have previously had chickenpox, this type of virus causes shingles.
- Another name is Epstein-Barr virus. It can cause infectious mononucleosis (Filatov's disease). In addition, infection with this type of herpevirus leads to a significant weakening of the immune system, as a result of which the child becomes susceptible to infectious diseases, as well as exacerbations of chronic somatic pathologies. In addition, there is evidence of the oncogenic activity of the Epstein-Barr virus, in particular, the development of certain types of lymphomas is associated with it.
- Another name is cytomegalovirus. This type of herpes virus causes the development of cytomegalovirus infection, which poses a particular danger to pregnant women, as it can cause serious abnormalities in the development of the fetus.
- This type of herpes in children causes sudden exanthema (pseudo-rubella, roseola), the main symptom of which is the appearance of small pink papules on the skin. The rash may be preceded by an increase in body temperature, but without any respiratory symptoms.
Herpes viruses type 7 and 8 were discovered relatively recently and have not yet been well studied. Virologists suggest that they can provoke the development of depression, chronic fatigue syndrome, and, possibly, some malignant neoplasms.
The term “herpetic infection” is traditionally applied to infectious processes caused by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 (HSV, lichen simplex virus, herpes simplex virus).
Herpetic infection is a typical anthroponosis, that is, an infectious disease, the causative agent of which in natural conditions parasitizes exclusively in the human body.
The source of infection is a sick (infected) person. Most often, herpes in children is transmitted by airborne droplets. Contact-household and transplacental transmission of infection are less common.
Susceptibility to herpes in children is very high. According to statistics published by WHO, in European countries and the United States, over 80% of children over the age of 5 years are infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 or 2.
Source: alphr.com
Strengthening the immune system
An important point in the treatment of herpes infection in children is the correction of immunity. The use of the drug VIFERON® for herpes infection leads to the restoration of the production of all types of endogenous interferon, activation of the production of antibodies, macrophages and natural killer cells. Nonspecific defense factors and the body's ability to resist infection increase. Viferon Ointment for herpes can be prescribed to children over 1 year old, Viferon Suppositories can be used from the first day of life, and in pregnant women from 14 weeks.
Based on materials: 1. “New aspects in the therapy of herpes simplex”, A. A. Khaldin, O.V. Chistik, D. V. Ignatiev. 2. “Modern aspects of perinatal herpesvirus infections: clinical picture, diagnosis, new approaches to therapy,” V.V. Ivanova, M.V. Ivanova, A.S. Levina, A.A. Zakina, O.V. Tikhomirova, G.F. Zheleznikova, O.A. Aksenov, E.V. Komeleva.
Loading...
Take other surveys
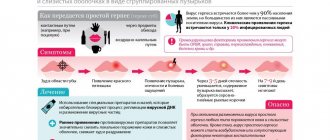
Symptoms of herpes in children
Herpes in children is chronic and recurrent. Exacerbations occur with varying frequency, but usually occur 1-3 times a year. Factors that provoke relapses are any diseases and conditions that weaken the child’s immunity (ARVI, otitis media, pneumonia, increased insolation, hypothermia, etc.).
The clinical picture of an infectious disease caused by a herpevirus is determined by its form. In the latent form, there are no symptoms of herpes in children; the presence of infection can only be detected by the results of laboratory tests.
With the local form of herpes in children, the following lesions are observed in children:
- skin (herpetic dermatitis, Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis, zosteriform herpes, ulcerative necrotizing dermatitis);
- mucous membranes of the oropharynx (gingivostomatitis, herpetic sore throat);
- mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract (respiratory tract catarrh, laryngitis, pharyngitis);
- eye (conjunctivitis, keratitis, iridocyclitis, chorioretinitis, uveitis, optic neuritis);
- genital organs (urethritis, balanoposthitis, vulvovaginitis).
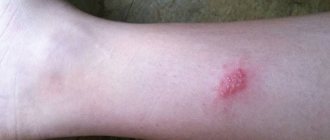
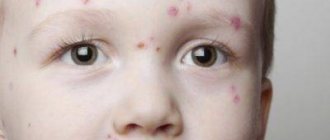
Herpetic skin rashes are mainly localized on the red border of the lips, cheeks, and wings of the nose. Their appearance is usually preceded by prodromal phenomena:
- slight general malaise;
- slight chills;
- itching, burning in the area of the future rash.
Foci of erythema appear on the skin, and then in their place small blisters appear, filled with transparent contents, which gradually become cloudy or become hemorrhagic in nature. After the blisters open, a painful erosion forms in their place, which is subsequently covered with crusts that fall off after a few days.
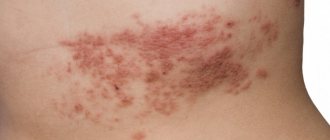
Herpes rashes on a child’s body can be located along the peripheral nerves. In this case, a disease called herpes zoster or herpes zoster develops. It should be noted that in children, especially young children, such a course of herpetic infection is extremely rare and occurs only in those who have previously had chickenpox.
Source: herpes911.ru
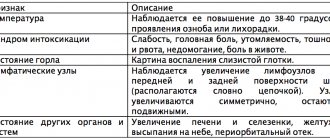
Lesions of the oral mucosa manifest themselves as symptoms of recurrent herpetic stomatitis. During exacerbation, the disease is often accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication (weakness, headache, increased body temperature). Multiple vesicles appear on the oral mucosa, after opening which sharply painful and long-term (up to 15 days) healing erosions remain.
Many parents believe that the appearance of herpes on a child’s lips is just a symptom of a common cold and do not consult a doctor. Actually this is not true.
The appearance of herpes in a child’s throat (on the back of the throat and tonsils) indicates the development of herpetic sore throat.
Herpes in children can also occur as an acute respiratory infection. In this case, there are no characteristic rashes on the skin and mucous membranes, and the disease proceeds with a clinical picture typical of ARVI.
Genital herpes in children and adolescents manifests itself as general (regional lymphadenitis, intoxication, increased body temperature) and local (appearance of vesicles on the surface of the genital organs) symptoms.
Herpetic eye infection most often manifests as conjunctivitis and/or keratitis. Damage to the posterior parts of the eyeball is rare.
Herpetic infection of the central nervous system can occur either as encephalitis or as serous meningitis.
With visceral forms of herpes in children, a clinical picture develops that is characteristic of an inflammatory disease of the affected organ (nephritis, enterocolitis, esophagitis, pneumonia, hepatitis).
Disseminated (generalized) herpetic infection occurs with damage to the nervous system and internal organs.
Against the background of an immunodeficiency state, for example, in children with HIV infection, a toxic-septic condition may develop due to generalized multiple organ pathology.
A little about disease prevention↑
Some healers claim that a herpetic infection on the stomach can only be cured with folk remedies. For example, a decoction of herbs with a sedative effect. But doctors adhere to a slightly different point of view - prescriptions for medicinal infusions must be combined with taking pharmacological drugs. Otherwise, the infection will have a lot of adverse reactions.
Prevention of herpes specifically on the stomach can be called adherence to the principles of basic personal hygiene when visiting swimming pools, baths, public locker rooms, etc. But the most important rule is maintaining a healthy lifestyle, taking care of your immune system and maintaining a sleep and rest schedule. Timely contacting a medical facility when the first symptoms of illness of any origin appear will save a lot of time and shorten the duration of the disease several times. After making a correct diagnosis, specialists will develop an effective treatment regimen for herpes on any part of the body, including the abdominal area.
Herpetic infection of newborns
As a special variant of the course of the infectious process, herpetic infection of newborns is identified as a separate form. Infection of newborn children with herpes occurs at the time of their passage through the infected birth canal of the mother (80%) and transplacentally (20%). The risk of developing clinically manifest forms increases with a long anhydrous period and the use of instruments for delivery that violate the integrity of the skin. About 70% of all registered neonatal herpes infections come from mothers with a latent form of herpes. The child is at greatest risk of infection if the mother is initially infected during pregnancy (one month before birth).
Manifestation of herpetic infection of a newborn occurs during the first month of life, usually in the first two weeks, in one of the following clinical forms:
- Severe disseminated infection. The pathological process involves the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth and eyes, the central nervous system, lungs, and liver. Thrombohemorrhagic syndrome is added. The lethality of this form is 50–80%.
- Widespread mucocutaneous changes (keratitis, stomatitis, dermatitis). The prognosis for this form of herpes in children in the first month of life is determined by the severity of bacterial superinfection. Mortality can reach 30%.
- Damage to the central nervous system. Manifests itself with symptoms of viral encephalitis. Mortality reaches 80%.
Intrauterine infection of the fetus with the herpes virus can lead to the formation of congenital malformations associated with the development of residual phenomena of a previous herpes infection (hydrocephalus, microcephaly, porencephaly).
Source: netderm.ru
Description and features
In addition to the listed places, this disease sometimes manifests itself in the form of blistering accumulations on:
- fingers, toes;
- nerve endings;
- mucous surface of the genitals, oral, nasal cavities;
- cornea and conjunctiva.
This virus is characterized by several features. It has:
- neurotropism, that is, nerve cells are mainly affected due to the presence or formation of receptors in them that are complementary to viral infections;
- neurovirulence, possibly causing diseases associated with the functionality of the nervous system;
- suppression of phagocytosis (one of the links in the protective mechanism of immunity) to an incomplete level.
Because of these abilities, type 1 herpes is not susceptible to the effects of immunity, which allows it to exist latently in the tissues of the nervous structures and spread as much as possible throughout the population.
The virus can be present in the human body in two forms:
- Latent - the main form of existence after infection;
- Manifestation - can appear up to three times during the year. The increased activity lasts for about a week, followed by the disappearance of all symptoms. Also, recurrent manifestations depend on the general condition of the immune system.
Diagnostics
In the process of diagnosing herpes in children, the following laboratory tests are used:
- traditional virus isolation in cell culture;
- accelerated method of virus cultivation followed by the use of monoclonal antibodies to indicate antigens;
- methods of molecular hybridization and PCR (detection of herpes virus DNA in the studied culture);
- detection of antibodies to the herpes virus (ELISA, immunoblotting).
In some cases, herpes in children requires differential diagnosis with the following diseases:
- shingles;
- genital ulcers and gingivostomatitis of other etiologies;
- drug dermatitis;
- dermatitis herpetiformis;
- chicken pox.
According to statistics published by WHO, in European countries and the United States, over 80% of children over the age of 5 years are infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 or 2.
Distinctive features of herpes on the stomach↑
Herpes itself is an infection that, once it enters the human body, remains there forever. The disease can be muffled by minimizing the negative manifestations of the viral attack. Any stressful situations, temperature factors (both hypothermia and overheating of the body), and a general decrease in immunity can “awaken” herpes cells.
Herpes on the abdomen is caused by viral pathogens classified as type 3 in the herpetic classification. The causative agent is varicella zoster, also called shingles virus or chickenpox virus. The disease manifests itself with the same symptoms in both adults and younger patients. Depending on whether the virus entered the body for the first time or repeatedly, there are 2 types of herpes infection in the abdominal area:
- The primary lesion occurs in the form of chickenpox;
- Secondary infection and each subsequent infection spreads along the nerve fibers, called shingles by doctors.
The Zoster virus is present in the body of every 8 out of 10 children under 13 years of age, so chickenpox is usually classified as a childhood disease. It is noteworthy that adolescents who have chickenpox do not have immunity against re-infection with the herpes virus.
Treatment of herpes in children
Modern methods of drug treatment of herpes in children do not allow achieving complete recovery. Therefore, the main goal of therapy is to eliminate the clinical manifestations of the disease, suppress the activity of the virus and increase immunity, which allows for long-term remission. For this purpose, antiviral agents, interferons, and immunostimulants are used. For severe pain and/or increased body temperature, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Acyclovir (Gerpevir) is most often used as an antiviral drug for herpes in children. It can be used both locally (in the form of an ointment), and systemically (tablets, injections), and in combination (local and systemic treatment simultaneously).
Interferons not only suppress the activity of viruses, but also prevent the further spread of infection, preventing the virus from infecting new areas of the skin and mucous membranes, and internal organs.
Immunostimulating drugs strengthen the immune system and thereby contribute to the transition of the infection into latency and the achievement of long-term remission.
With frequent exacerbations of herpes in children, the child is referred for consultation to an immunologist, since this is evidence of a dysfunction of the immune system.
Complications and consequences
It is more difficult for a child’s body to fight the virus than for an adult. In the absence of timely treatment, herpes located in the nerve ganglia in a child can have consequences in the form of complications on the central nervous system, resulting in depressive disorders and schizophrenia. Disturbances in the functioning of internal organs become serious consequences.
Herpes on the eye (ophthalmoherpes) with complications leads to iridocyclitis, keratitis and other eye diseases.
When herpes affects the ENT organs in children, hearing decreases or deafness occurs, and herpetic sore throat may occur. The virus is also dangerous for the reproductive system. In the future, it can lead to infertility.
Causes of infection
Factors that provoke exacerbation of the disease are present in more than 90% of the world's population. However, they do not appear until favorable conditions arise for their activation, namely:
- colds, viral and bacterial pathologies;
- hypothermia;
- stressful situations and overwork;
- injury;
- exhaustion associated with frequent dieting;
- menstrual cycle;
- oncological diseases;
- long-term hormonal therapy;
- overheating (exposure to sunlight for a long time);
- avitaminosis.
All this leads to weakened immunity, which increases the likelihood of infection.
The herpes virus is quite easily transmitted through:
- saliva, for example, during kissing;
- toys;
- cosmetical tools;
- dishes;
- personal hygiene items.
Often, the infection can enter a healthy body, penetrating into microcracks in the skin, and it can also be acquired congenitally during intrauterine development when a woman is infected with a virus during pregnancy.
conclusions
The first type of herpes is the most common of all varieties. Most often it manifests itself in childhood, but infection is also possible in adulthood, and women suffer from it to a greater extent, unlike men.
The disease has certain signs that make it possible to determine whether there was an infection or not. After their detection, it is necessary to seek medical help for diagnostic procedures, which will confirm or refute the diagnosis. When infected with herpes, the doctor will prescribe the use of medications that will help get rid of the acute form of the pathology.
Unfortunately, this virus has a high adaptive capacity, so it is impossible to achieve a complete cure for it.