Quincke's edema is an acute allergic reaction in which extensive swelling of the skin, subcutaneous tissue and muscles appears.
It can develop at any age, including children. About 10% of the population have experienced a similar pathology.
In young children, Quincke's edema appears very rarely (about 2% of all cases). The disease requires immediate medical intervention, as it is life-threatening and can lead to death.
Causes
In 30% of cases, it is not possible to determine the cause of Quincke's edema in a child.
The most common are allergic reactions, which can be triggered by the following factors:
| Food allergens | Nuts, chocolate, citrus fruits, seafood, cheese. |
| Plant pollen | Wormwood, ragweed, birch, poplar. |
| Medications | Antibiotics, vaccines, anticonvulsants, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, sulfonamides. |
| Preservatives, dyes and food additives | Tartranisine, sulfides, monosodium glutamate (most often they are added to sausages, juices, carbonated drinks, cheeses) |
| Insect bites | Wasps, bees, mosquitoes. |
| Household chemicals | Washing powders, cosmetics and detergents. |
| Down or wool | Dogs, cats, rabbits. |
Also, a number of factors include a number of factors that cause the appearance of Quincke's edema.
The main ones:
- pseudo-allergic reactions that occur when the digestive system is upset;
- neoplasms and blood diseases;
- viral infections (hepatitis);
- parasitic infections (giardiasis);
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- a hereditary factor in which the body produces insufficient amounts of certain enzymes.
Diagnostic methods
The patient is diagnosed based on the clinical manifestations of the disease.
Use the following facts as additional information:
- Do you have any relatives with a tendency to allergies?
- the body's reaction to medications;
- presence of infection in the body;
Not every patient is diagnosed the same way. There are cases when there is none of the above, but the patient suffers from Quincke's edema. You can find out the reasons for this after taking tests and researching them.
What happens in the body
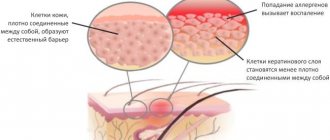
Quincke's edema occurs in the same way as a regular allergy with a more pronounced vascular component.
Under the influence of allergy mediators, the functioning of nerve trunks and blood vessels is disrupted. The vessels dilate and their permeability increases.
The consequence of this is the penetration of plasma into the intercellular space and the occurrence of local edema.
The functioning of nerve cells is disrupted, which leads to paralysis of the nerve trunks. The tone of blood vessels is disrupted, which further relaxes their walls.
Why does this symptom appear?
Medications can provoke a negative reaction. The use of excessive dosages of medications leads to serious consequences.
Therefore, self-medication is strictly prohibited! The group of provoking drugs includes antibiotics, anticonvulsants and B vitamins.
Quincke's edema occurs when using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. This is due to the ability of medications to release histamine.
This substance provokes the development of acute allergic reactions. This group of drugs is very dangerous for children.
Adverse reactions include bronchial asthma, dermatitis and angioedema.
Foods containing excessive amounts of dyes and additives can also provoke a reaction.
They are found in sausages, cheeses, marinades, dried fruits and juices. Children under three years of age should not be introduced to this food.
Swelling is caused by:
- seafood;
- animal hair;
- medications;
- plant pollen;
- cosmetical tools;
- household dust.
The allergen may not be so dangerous in its characteristics. It all depends on the general state of the immune system and the susceptibility of the child’s body.
Even harmless plant pollen can lead to a severe reaction. Unusual symptoms also appear after contact with insects.
How does the disease begin?
The first signs of the disease are the rapid development of swelling. Quincke's edema develops in those parts of the body where there is a layer of subcutaneous fat.
It begins rapidly within a few minutes (in rare cases it can occur over a longer period of time).
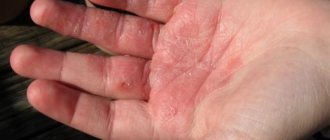
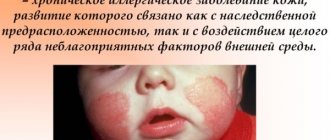
Tissue swelling develops very rapidly, while the color of the skin does not change. Lips quickly swell, the skin around the eyes swells, and the face becomes puffy. May also appear in the neck or palms of the hands.
Characteristic signs
Quincke's edema can develop in various parts of the child's body. Depending on this, the clinical manifestations of the pathology vary.
| Damage area | Clinical manifestations |
| Mucous membranes, subcutaneous fat |
|
| Larynx |
|
| Gastrointestinal organs |
|
| Brain |
|
| Other organs |
|
The clinical picture of the pathology is always well defined, so diagnosing the pathology is not difficult. If you notice the first symptoms, you must urgently call a doctor . Otherwise, dangerous symptoms of the disease can lead to death, especially if laryngeal edema occurs.
Photos of Quincke's edema in children:
Symptoms
Symptoms of Quincke's edema in children:
- if the swelling spreads to the pharynx, trachea or larynx, the child’s breathing becomes hoarse, heavy, and intermittent. The face acquires a bluish tint, then quickly turns pale. This swelling may persist for 24 hours. The voice becomes hoarse, a barking cough appears;
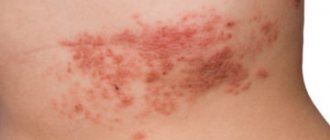
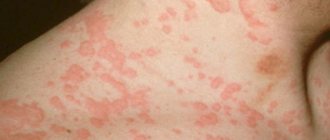
- In about half of the cases, swelling can be combined with urticaria. In this case, itchy red blisters appear on the child’s skin. Despite the fact that they look scary, the main danger is not this reaction, but swelling of the larynx;
- Quincke's edema may be accompanied by a reaction from the nervous system. The child may be overly excited, scared, and anxious. Lethargy and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness may also occur;
- if the swelling spreads to the internal organs, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting, acute abdominal pain may occur, and in some cases signs of peritonitis appear;
- with cerebral edema, symptoms begin in the form of seizures and confusion;
- if the swelling affects the genitourinary system, urinary retention and signs of acute cystitis appear.
Photo: Swelling of the oral mucosa
Symptoms of the disease
The reaction develops rapidly; signs of angioedema in children are swollen lips, neck, and face. The upper torso, hands, feet, and genital area are often affected. Quincke's edema is visible in the eyes of a child - the eyelids swell on one or both sides.
- When the tonsils are affected, the picture is similar to a sore throat.
- Edema of the larynx is indicated by a hoarse voice, difficulty breathing, a gusty cough, blue discoloration and then gradual paleness of the skin.
- Swelling that appears in one area may occur in another. This mainly applies to large-scale swelling.
- When the mouth and tongue swell, speech becomes difficult.
- If the process is localized in the gastrointestinal tract, the child may complain of tingling of the tongue, followed by diarrhea and vomiting, and sharp pain in the intestinal area.
- Rarely, swelling of the meninges occurs. With it, the child cannot fully tilt his head forward, complains of a headache, and behaves inhibited. Convulsions and vomiting may occur.
- If only the skin is affected, joint pain, fever may appear, and the child may lose consciousness.
The pathological condition can last from an hour to several days.
How does angioedema begin in a child?
Immediately after contact with the allergen, the listed symptoms increase sharply. This happens in a matter of minutes. Source: G. I. Smirnova. Urticaria and Quincke's edema // Allergic diseases in children. Ed. M.Ya. Studenikina, I.I. Balabolkina. M.: Medicine, 1998: 279-287 If you press on the swollen area, the child will not experience pain, but you will feel a dense swelling, on which, after pressing, there will be no characteristic depression.
Diagnostics
In the case of acute angioedema, the cause can be identified without special studies based on a visual examination.
If it is suspected that the swelling was caused by a food allergy, skin tests are performed in order to further eliminate the risk of anaphylaxis.
Diagnostic methods:
- visual examination, identifying a rash on the torso and limbs;
- determination of swelling of the hands, feet, oral cavity, nasopharynx and nasal passages;
- collecting anamnesis and identifying connections with the allergen;
- general blood analysis;
- determination of cryoglobulins;
- ESR analysis;
- determination of antinuclear and antithyroid autoantibodies;
- Analysis of urine.
Other forms of the disease
The disease is not always easy to recognize.
Often its symptoms can visually remind the patient of completely different diseases:
- swelling of the brain. The symptoms of angioedema with swelling of the brain will be the same as with meningitis. Feelings of dizziness are common. Convulsions and severe pain in the head may occur;
- swelling of the genitourinary system. The general clinical picture will be exactly the same as with cystitis. When going to the toilet, you will feel severe pain and stinging;
- articular form. There is swelling of the joints, but fortunately there is no inflammation. The body may be very itchy;
All these varieties of quinque are fortunately rare. But regardless of the form of the disease, it poses a great danger to life. After the first manifestations, you should consult a doctor and take appropriate medications.
Find out why angioedema is dangerous in children. What does Dr. Komarovsky think about food allergies? Details in the article.
Treatment of Quincke's edema in children
In order to relieve swelling, medications from different groups are used. The name of the drugs, dosage and method of administration must be prescribed by a doctor.
Under no circumstances is it recommended to self-medicate, as this is very dangerous and can worsen the child’s condition, even leading to death.
Medicines
In case of swelling of the larynx, against the background of low blood pressure, emergency care is provided:
- The child is laid down, his legs are raised, and he is turned to his side. If possible, give humidified oxygen;
- in this case, a 0.1% solution of Adrenaline is administered, 0.1 ml for each year of life. Injections are carried out every 10 to 15 minutes until the child’s condition improves;
- if the allergen enters the body through the eyes or nose, they are washed and instilled with a 1% solution of Prednisolone and a 0.1% solution of Adrenaline;
- Prednisolone 2 – 4 mg/kg body weight is administered intravenously, repeat after an hour if necessary;
- a 2.5% solution of Tavegil or a 2% solution of Suprastin is administered intravenously, 0.1 ml for each year of life;
- for heart failure, a 0.06% solution of Korglykon 0.01 mg/kg body weight per 10 ml of 10% Glucose is slowly administered intravenously. Lasix 1 mg/kg is prescribed intramuscularly;
- if necessary, a Reopoliglucin solution is administered intravenously as a dropper;
- if drug treatment is ineffective, tracheal intubation is performed.
In the future, treatment continues in the hospital, and the following drugs are prescribed:
| Glucocorticoids | Prednisolone, Dexamethasone. |
| Antihistamines | Erius, Suprastin, Fenstill. |
| Infusion therapy | Glucose solution 5%, Reopoliglucin. |
| Forced diuresis | Lasix, Furosemide. |
| Reduced vascular fragility | Ascorutin. |
| Enterosorption | Activated carbon, Polyphepan, Enterosgel. |
Folk recipes
It is quite difficult to get rid of Quincke's edema using traditional medicine methods, especially if the disease develops rapidly.
- In order to quickly relieve the symptoms of the disease, nettle leaves are used. 3 g of dry leaves are poured with 200 ml of boiling water and left in a sealed container for an hour. Strain and give the child a teaspoon three times a day;
- If the baby is not allergic to milk, in order to quickly get rid of the disease, he is given warm milk with soda. A glass of milk needs to be boiled, and after it has cooled to a comfortable temperature, add baking soda on the tip of a knife. You need to drink this remedy once a day.
Read how a spirogram is performed for bronchial asthma. How is Strelnikova breathing exercises done for bronchial asthma? The answer is in the article.
What is Quincke's edema
The cause is a reaction to a strong allergen. According to statistics, angioedema affects mainly girls. Particular attention is paid to children who have a hereditary predisposition.
Often the disease is inherited, but there is also an acquired form. In this case, doctors talk about the presence of pseudo-hereditary angioedema in the body.
First aid
If symptoms of Quincke's edema appear, you should immediately call an ambulance.
First aid for Quincke's edema in children consists of a number of rules.
Here they are:
- it is necessary to limit the child’s contact with the allergen (if a bee stings, remove the sting);
- you need to provide the child with free breathing, remove clothes or unbutton the collar;
- lying down can aggravate the situation, so until the ambulance arrives, the child must be carried vertically in his arms or sat down, not allowing him to lie down;
- drip your nose with any vasoconstrictor drops that are in the house;
- give any antihistamine in the appropriate dosage, preferably under the tongue, so it will begin to act faster. The most effective in this case are injections;
- apply cold to the site of swelling, this can be a towel soaked in cold water or a heating pad with ice;
- Give plenty of water at room temperature in order to remove the allergen from the body as quickly as possible. For more successful removal, use an alkaline drink (Borjomi, Narzan, Polyana Kvasovaya); in extreme cases, you can prepare it yourself by adding 1 g of baking soda to 1 liter of water;
- if the child has lost consciousness, we perform artificial respiration;
- Even if the child feels a little better, under no circumstances cancel the call for an ambulance, since without the use of the necessary medications, the condition may worsen at any time.
Treatment
When treating children admitted with signs of giant urticaria, the doctor prescribes drugs (tavegil, diazolin, suprastin) to stop the swelling. After assistance is provided, the sick child is sent to the hospital department. If anaphylactic shock develops, the victim is sent to intensive care. If symptoms of suffocation occur, hospitalize the patient in the surgical department.
The main part of the treatment is aimed at providing first aid for angioedema:
- Administration of prednisolone or dexamethasone injections;
- Detoxification therapy;
- Taking diuretic drugs.
To prevent swelling from spreading throughout the larynx and trachea, the acute allergic process is stopped with special medications. The drug dexamethasone copes well with the symptoms of edema.
Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is prescribed when urticaria is associated with angioedema. Dexamethasone is a glucosteroid, one of the most effective hormonal therapy for stopping angioedema and anaphylactic shock. Can be administered intravenously in an emergency to raise blood pressure. Dexamethasone is used in the treatment of allergies due to chronic diseases.
For allergic type
- Avoiding contact with possible allergens (dust, allergenic products, wool, medications, drinks);
- Diet;
- The use of new generation antihistamines that do not depress the central nervous system (loratadine, cetirizine, acrivastine) in combination with additional H2 receptor antagonists (famotidine, ranitidine, cimetidine);
- First generation drugs (suprastin, fenkarol, diazolin, dexamethasone, etc.) for the relief of giant urticaria.
For pseudoallergic
- Identifying the cause of the disease after a thorough diagnosis;
- Treatment of concomitant pathologies that cause allergies;
- Diet with a restriction of foods containing large amounts of tyranium and histamine;
- In the acute stage, frozen plasma and intravenous tranexamic acid are administered;
- Diuretics.
For swelling of the larynx
For laryngeal edema, prednisolone is administered - an antiallergic, decongestant glucocorticosteroid drug , prescribed primarily in the treatment of Quincke's edema. When administered intravenously, it helps relieve swelling, reduce vascular permeability, and increase blood pressure.
Prevention
In order to avoid the appearance of Quincke's edema in a child, it is necessary to use prevention methods
Here they are:
- avoid contact with allergens;
- adhere to a hypoallergenic diet. Especially control over nutrition should be strengthened during the period of exacerbation of seasonal allergies, since cross-reactions to food products may occur.
- Before using medicinal antibiotics, be sure to do a test. And completely eliminate penicillin antibiotics, since they are the most common cause of edema;
- Vaccinate with caution. After the injection, the child must remain near the treatment room for at least half an hour, so that in the event of an allergic reaction, he can receive timely medical assistance;
- in the spring-autumn period, avoid places with large concentrations of insects;
- In everyday life you need to use hypoallergenic detergents and cosmetics. For young children with allergies, it is better to use baby or brown laundry soap, without fragrances or fragrances, to wash clothes.
- children prone to allergic reactions should wear clothes made from natural fabrics;
- If the cause of swelling is plant pollen, it is necessary to wet clean the room as often as possible during the flowering season, keep the window closed, and cover the window left for ventilation with damp gauze.
- If the swelling can be caused by an allergy to wool, before going to visit, you need to check with the owners if they have pets.
- At the first signs of allergy, it is necessary to show the child to a dermatologist or allergist in order to prescribe the correct treatment to further prevent the development of Quincke's edema.
Find out the principles of the diet for hay fever. What are the symptoms of seasonal hay fever? Full description here.
What are the causes of bronchial asthma? Details below.
Useful tips
- if children often develop allergic reactions, mothers need to learn how to provide first aid, including artificial respiration and chest compressions;
if Quincke's edema develops not for the first time, it is necessary to have ampoules of Adrenaline 0.1%, Suprastin and syringes in the house. Also in the first aid kit should be antihistamines in tablets and vasoconstrictor drops;
- In the future, you need to teach the child to help himself independently, as well as warn teachers in kindergarten, and later teachers at school, that an allergic reaction in the form of Quincke's edema to certain allergens may occur.
- Children who may have a similar reaction to food products should prepare their food at home, and when visiting public catering establishments, warn the staff about the allergy.
Expectant mothers need to remember that a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy and breastfeeding, in most cases, prevents the risk of developing allergies in the baby. Thus, preventing the appearance of Quincke's edema.
Previous article: Food allergy Komarovsky Next article: Food allergy in infants
Complications
It has already been said above that a dangerous complication is asphyxia, which contributes to the patient falling into a coma. But the worst thing is that it is not always possible to get out of it and the patient dies.
The occurrence of swelling in the stomach threatens a complication in the form of peritonitis.
But doctors are most concerned about facial swelling. After all, complications can spread to the brain. Each symptom is dangerous in its own way, some pose a lesser threat, some more. But with each of them you need to contact specialists.