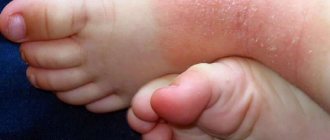
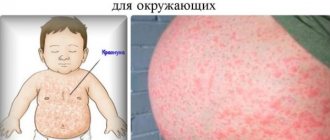
A rash can appear not only in a child, but also in an adult and cause reasonable concern, because it may not only be a cosmetic problem.
The skin is the largest human organ, which reacts acutely to internal changes in the body. Doctors call skin rashes rash or exanthema. It has many morphological types, but papular rash is the most common in medical practice.
The rashes are described as lumpy, clearly defined new growths - papules or nodules that can be easily felt under the fingers and, as a rule, do not cause pain.
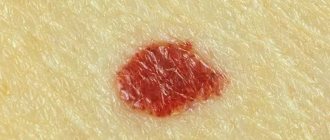
As a rule, papules are inflamed tubercles of a dome-shaped, oval or flattened shape. Their size can vary from 1 mm to several tens of millimeters; large ones are already called plaques. Unlike vesicles containing infiltrate, papules have no content.
Causes
There are many causes of papular rashes:
- various infections are the most common cause. There are many ways of infection with them, from airborne droplets to an insect bite or communication with an infected person;
- sexually transmitted diseases - such as syphilis and HIV, which are contracted through unprotected sex and insufficient sanitary treatment of reusable needles, and even through blood transfusions;
- bacterial, viral and fungal infections;
- diseases of nonspecific etymology;
- allergic reactions;
- pathologies of the immune system;
- parasitic infestations.
The range of diseases in which various papular rashes are one of the defining signs or a successive stage is great.
Types of papular rashes
Modern medicine divides papular rashes into three main categories:
- Miliary – the smallest, up to 2 mm in diameter, cone-shaped, located near the hair.
- Lenticular - medium in size (up to 5 mm), can be flat or convex, and also have a variety of shapes.
- Numular - formed by the fusion of flat eruptions and can reach up to 20 mm in diameter, ultimately taking on the appearance of a coin.
With a papular rash, the skin may often change color, but generally, when the rash goes away, no scars or pigment spots remain on the skin.
Based on the factor that provoked the rash, as well as the scale and location of the lesion and other symptoms (the presence of peeling and itching), the disease is divided into the following types:
- maculopapular;
- maculopapular;
- erythematous.
To classify rashes, the following symptoms are taken into account: location, color of nodules and adjacent skin, presence of itching, type of lesions (single or already merged), cause of the rash.
As the disease progresses, not only the size of the rash, but also their nature may change, so when contacting a doctor, it is necessary to describe in detail: when and what kind of rash appeared and what symptoms were accompanied.
Types and classification
Papules and pustules have different locations, sizes, shapes, and colors. This allows them to be classified into certain types. Assigning a formation to a specific type allows the dermatologist to select an effective treatment regimen.
Depending on the depth of occurrence of papules, there are:
- epidermal (superficial);
- dermal (in the papillary layer);
- epidermodermal (mixed).
By size:
- lenticular (0.5x0.5 cm);
- plaques (diameter larger than a large coin)
- miliary (with a pinhead);
- numular (5-kopeck size).
The shape of papules is:
- flat;
- hemispherical;
- polygonal;
- cone-shaped (follicular).
Based on the color of the formation, they are classified into:
- pink;
- brown;
- white;
- red;
- purple.
According to the presence of an inflammatory process:
- inflamed;
- uninflamed.
Other types of papules:
- lichenoid (flaky, characteristic of lichen);
- syphilitic (round red formations on the skin and mucous membrane, capable of merging and ulcerating);
- bowenoid (red spots, related to precancerous conditions of the dermis);
- Gottron's papules (nodules located in the area of the proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints);
- fibrous (formed in single numbers, localized on the nose);
- erythematous (localized on the extensor surfaces of the joints, characteristic of vasculitis and lupus erythematosus);
- piezogenic (slightly protruding round formations the color of the epidermis, formed in the heel area).
Pustules are classified according to the following criteria:
- by localization into follicular, intradermal and subcorneal;
- by pathogenesis into autoimmune, infectious;
- by the number of cameras into single-chamber and multi-chamber.
Based on size, they are divided into miliary, lenticular and numular elements. When making a diagnosis, the color of the attributes, the localization of the affected area of the skin, the symmetry of the growths, and the presence of additional symptoms are taken into account.
Maculopapular
The rashes are small in size - from 1 to 10 mm and the nature of their location on the skin. They are localized on the face, spread throughout the body, and have pink and brown shades.
Causes of macular papular rashes:
- measles is a disease accompanied by high fever. Gradually a fusion of elements occurs;
- entero- and rotavirus – bulges appear on the face and move to the body;
- papular urticaria - an allergic reaction that causes itching, rash - medium-sized blisters;
- exudative form of erythema - attributes are localized on the flexor surfaces;
- mononucleosis - formations on the skin up to 1.5 cm of irregular proportions;
- chickenpox, scarlet fever, meningitis, felinitis - are accompanied by the appearance of growths that go through the stages of development from papule to vesicle, expulsion of the contents of the capsule, healing of the wound;
- syphilis - a rash forms in the second stage of the disease, the appearance of nodules is accompanied by severe itching. The elements are red, brown, localized on the neck, upper body, and head. The temperature does not increase during the secondary stage of the disease;
- rubella - the elements are small, point-like, and do not merge.
Maculopapular
The macular type of rash is characterized by the formation of vesicles with a dense, pastel-colored consistency. Elements can appear on any part of the body, on the palms and soles.
Causes of unpleasant symptoms:
- infectious diseases - measles, mononucleosis, rubella;
- allergies to medications, waste products of staphylococcus, streptococcus provoke the appearance of papules;
- helminthic infestation - swellings on the skin can merge with each other;
- action of viruses, HIV infection.
After identifying a rash, consult a doctor for a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Erythematous
Bulging with the erythematous type of dermal lesions appears on the knees, elbows, and spreads to the body and limbs. Papules up to 1 cm in size are red in color with a dark center; the elements can merge.
Causes of the pathological process:
- autoimmune diseases - lupus, vasculitis provoke rashes;
- syphilis in adults, newborns;
- atopic dermatitis can cause the formation of papules;
- scabies;
- diathesis;
- hormonal imbalance - pregnancy in women, adolescence.
Nodules can appear on the penis of men. The attributes do not cause discomfort or pain, and are considered a cosmetic defect that is not sexually transmitted.
Papular urticaria
Insect bites can cause allergies in some people in the form of severely itchy reddish rashes, which are called papular urticaria or acute prurigo. Children under 10 years of age are at risk.
It is based on an acute reaction to the saliva released during a bite. Accordingly, the peak of the disease occurs in spring and summer.
Most often, the rash affects the extremities; hard, bright red papules about 5-10 mm in size appear. Urticaria does not have a tendency to merge, but with a long-term persistent course, old papules take on an erythrematous appearance and swell.
By and large, the disease can go away on its own, without medical intervention, and even chronic forms completely disappear by the age of seven.
Papular urticaria should be distinguished from pigmented pox, chickenpox, scabies and other similar diseases. To do this, a patient examination, skin tests and allergy tests are carried out. Histology is prescribed in extremely rare cases to identify spongiotic vesicles.
Papular syphilide
Often, secondary, and especially recurrent syphilis is characterized by the appearance of a papular rash of various sizes, upon which the patient experiences pain when pressed. They are smooth, dark red in color and dense in consistency; over time they begin to peel off and do not itch. Without medical intervention, the rash can last for weeks.
Papules appear randomly not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes. Favorite places are still the genitals, anus, feet and palms. Miliary papules are often located in groups in the hairline area. And in patients with recurrent secondary syphilis, lenticular nodules can appear in the shape of a ring.
Rashes of papular syphilide must be distinguished from some types of lichen and psoriasis, condylomas, hemorrhoids, vasculitis and pseudosyphilitic papules. The latter do not contain Treponema pallidum in their fluid and give a negative reaction to syphilis.
Diseases with papules
Rashes on the epidermis are characterized by the morphological elements of the rash, which include papules, vesicles, pustules, blisters, spots and tubercles.
A papule is a nodular formation with a diameter of 0.1 to 2 cm. Such elements often leave behind pigmentation and peeling. A vesicle is a small spherical vesicle that rises above the surface of the epidermis. Inside contains a clear, colorless or cloudy liquid. The element is located in the superficial layers of the skin.
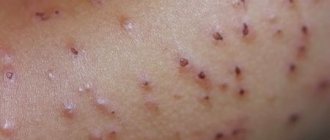
Papule (left) and pustule (right)
The pustule looks like a small yellow ball with a white spot on top and purulent contents. Over time, the formation bursts. Such elements hurt when touched. The skin around the pustule is hyperemic and swollen. After opening the abscess, a crust forms, which disappears after a while.
People often turn to dermatologists with the problem of acne and warts on the body. These formations look like papules. A wart is a keratinized solid formation with a diameter of 0.1 to 1 cm. It can be located in the papillary layer, on the surface of the dermis.
Warts
Warts do not form inflammation around themselves, do not hurt or cause itching. At first they do not differ from the color of the skin, but over time they can darken, become brown or black.
Acne papules, unlike warts, are characterized by an inflammatory process and are painful to the touch. There are pimples without inflammation - comedones.
Rashes are characteristic of the following pathologies: psoriasis, measles, scabies, anthrax, syphilis, atopic dermatitis, herpes, typhus, eczema, Kaposi's sarcoma, streptococcal impetigo.
The diseases differ in the appearance of the papules, their location and other associated symptoms:
psoriasis. It is an autoimmune chronic disease that affects the skin. Manifested by weakness, fatigue, depression. The main symptom is spots that rise slightly above the surface of the skin. Red psoriasis papules vary in size and shape: teardrop-shaped, coin-shaped, and dotted. Initially, the size of the formation is 3-4 mm, but as the disease progresses, the papules increase to 10 or more centimeters. Morphological elements affect the entire body and can merge;- eczema. This is a neuro-allergic recurrent pathology that manifests itself in the upper layers of the dermis. This disease is characterized by a rash that causes itching and burning. At first the skin turns red. Then small pink-red papules form. As inflammation progresses, they transform into vesicles and pustules. After opening the formation, weeping eczema occurs. When the inflammatory process subsides, the skin turns pale, erosion becomes crusty;
- scabies. The disease is contagious and is caused by parasitic scabies mites on the skin. Elements of the rash are represented by scabies. They look like dirty gray lines of a straight or curved shape. Elongated papules and pustules can form under them. The formations cause severe itching. When scratching, erosions occur;
- Kaposi's sarcoma. These are multiple malignant neoplasms on the skin. First, papules form, similar to rashes caused by lichen ruber. Places of localization are the arms, legs, and feet. Papules peel, increase in size (can reach 5 cm), and are painful. After resorption, the nodules leave pigmented impressions. Kaposi's sarcomatosis can metastasize to the lungs, bones, and liver. In this case, the person experiences a bloody cough and diarrhea, and a high fever;
syphilis. This is a sexually transmitted systemic disease of an infectious nature that affects the mucous membranes, skin, nervous system, bones, and internal organs. Papular syphilides appear during the period of exacerbation of the disease. They can be meliar, lenticular, numular, plaque. In primary syphilis, the formation looks like a round ulcer with a smooth bottom and even edges. Erosion is painful. Small ulcers appear on the mucous membranes. Chancres up to 5 cm in diameter are observed in the abdomen, thighs, chin, forearms and hands. Secondary syphilis manifests itself as nodules, spots, papular-pustular rash, and vesicles. Formations can occur on any part of the body; they do not merge. Their color and shape vary. The skin around the syphilides does not swell or become inflamed;
- streptococcal impetigo. This is a contagious pathology of streptococcal nature. Initially, bluish-red papules appear on the skin, which can be eroded. Then they transform into vesicles with an edematous and hyperemic base. Localized in the area of the buttocks, thighs, back and abdomen;
- atopic dermatitis. This is a non-contagious, chronic inflammatory skin disease. It manifests itself as follicular papules and plaques on the extensor surface of the limbs and trunk. In adults, atopic dermatitis is characterized by pigmentation, secondary leukoderma. Whitish spots form in the cheek area.
Papular necklace
It is also called a mother-of-pearl ring. In this case, the papules are small, all the same size, do not increase and gradually lose their bright color. This nonspecific rash is localized near the head of the penis, along the length of the coronary sulcus, and less often on the foreskin. They are formed from connective and vascular tissue and are essentially angiofibromas. Papular necklace as a normal variant occurs in 10-20% of adult men. This is more of a cosmetic defect - the rash is not contagious and does not cause any discomfort.
Localization on the body
Pustules can be located on the skin of the neck, head and torso. In men, they can be localized in the penis area. There are pustules on the lips, genitals, arms and legs, back and abdomen, heels, face, tongue.
Skin papules occur as a result of hormonal imbalance and a tumor process. The rash on the genitals is called pearlescent papule. It appears in the form of small pimples that do not cause discomfort.
Localized around the head of the penis. Develops due to blockage of the sebaceous glands.
Features of papular rash in HIV
Papular rash is one of the main signs of HIV and is accompanied by the following:
- prolonged increase in body temperature;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- prolonged diarrhea and corresponding weight loss;
- thrush and mouth ulcers;
- weakness, dizziness;
- increased sweating;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle and thrush in women.
The above symptoms are similar to the flu and may mislead the doctor
If these symptoms occur together, you should consult a doctor who will conduct an appropriate analysis and, if necessary, prescribe a course of treatment for HIV. If left untreated, it will develop into AIDS with all the ensuing complications.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
Exanthema itself is a sign of various diseases. Different types of rash differ in shape, size, color, location and duration of manifestation. The most unpleasant symptom accompanying the rash is itching and peeling. In some cases, an increase in body temperature may occur. Often after recovery there are no traces left on the body.
It is impossible to identify the causes of the rash at home. Only a highly specialized doctor can diagnose and prescribe adequate treatment.
Since a papular rash can be a sign of a serious illness, the physician is required to conduct some mandatory studies:
- draw up a general clinical picture of the disease:
- conduct a visual inspection and palpation of the affected areas;
- order skin tests and other laboratory tests.
Treatment
It must be borne in mind that rashes are only an external expression of the underlying ailment. And initially, treatment is aimed at eliminating the root cause and relieving symptoms.
It happens according to the following scheme:
- in case of allergic origin, it is necessary to eliminate the source of the allergy and start taking antiallergic drugs ( Diazolin, Claritin, Citrine , etc.);
- if the rash is infectious in nature, then antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed;
- treatment of affected areas with ointments and compresses to relieve itching;
- a special diet that excludes preservatives, dyes and irritating foods;
- cleansing droppers or various sorbents are prescribed: Polysorb or Enterosgel .
The latter has good reviews:
Enterosgel gave results that exceeded all expectations. The skin became significantly cleaner, the rashes decreased, and there was lightness throughout the body. Very pleased.
Olga, 35 years old.
Doctors recommend being more careful when taking sorbents:
Polysorb can cause constipation with long-term use. It should also be taken at least an hour after meals, since in addition to toxins, it also removes all nutrients.
Dermatologist Ilyenko I.L.
To relieve itching, you can use the widely known Fenistil-gel . For the most part it has excellent reviews:
My daughter turned out to have a terrible allergy to the antipyretic. You just need to apply this transparent gel 2-3 times a day and the itching will gradually go away. Helps even with mosquito bites. A must have in every home medicine cabinet
Ekaterina, 26 years old.
I lubricated the child’s pimple once a day, the itching began to go away and gradually dry out. And it helped my husband. The only drawback is the price.
Larisa, 45 years old.
To eliminate rashes, you can also use folk remedies . This is especially true for pregnant and lactating women, for whom many medications are not available.
For example, to eliminate itching, you need to rub the lesions with a solution of salicylic acid with diphenhydramine and a few drops of menthol .
Herbs such as:
- licorice root - take 2 times a day;
- make a bath infusion with marjoram;
- Brew 1 tablespoon of stinging nettle and drink as tea.
But even traditional methods of treatment should not be used without first consulting a doctor, since many herbs can also cause an allergic reaction.
Treatment of papular acne and pimples
Treatment of papular acne should be carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist. Therapy can be difficult and lengthy, even lasting several years.
Treatment of follicular lesions begins with proper hygiene and facial skin care. The skin should be cleansed daily with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory face wash gels and micellar makeup remover lotions. Using scrubs and cleansing masks will help.
It is important to prevent the skin from drying out and systematically moisturize and lubricate it. Well-hydrated skin does not produce excess sebum.
Cosmetics used to care for a face with papular acne should be professional, purchased at a pharmacy, have natural ingredients and a light formula that does not overload the skin. Proper care of acne-affected skin inhibits the development of the disease and brings a feeling of relief.
Facial skin care
Treatment of papular acne should be supported by a proper diet, avoidance of alcohol and smoking.
Skin care is carried out in parallel with the use of local medications. Their task is to reduce excessive sebum production, exfoliate the epidermis, unclog pores and reduce inflammation, swelling and redness. Topical creams and gels containing vitamin A, its derivatives and benzoyl peroxide, which have an oxidizing effect, help get rid of anaerobic bacteria living in acne.
Depending on the severity of the symptoms of follicular acne and pimples, local or systemic antibiotics are included in the treatment. The most commonly used are erythromycin, clindamycin, tetracycline and doxycycline. For adult women struggling with follicular acne, hormonal therapy, such as oral contraceptive pills, may be used.
Papular and maculopapular lesions should not be squeezed out. This will cause the lesions to spread, become infected, and cause unsightly, difficult-to-remove scars.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Prevention
The main method of preventing the disease is maintaining personal cleanliness and sanitation rules when visiting public places, contacting animals and other people. It is necessary that personal hygiene items, shoes and underwear are not used by other people and never take someone else’s.
It is necessary to keep the body, personal belongings and housing clean. This is enough for better prevention of various rashes and skin damage.
Understanding the full danger of diseases, the manifestation of which is a papular rash, and awareness of the need to immediately contact a medical facility is the key to a correct diagnosis and quick recovery. Treatment at home can lead to very serious consequences.
Diagnostic methods
If papules, pustules, or vesicles appear, it is recommended to visit a dermatologist, consult with an infectious disease specialist, venereologist or allergist. At the appointment, the doctor interviews the patient, examines the skin using a dermatoscope, and prescribes a series of examinations.
The following diagnostic techniques are used:
- liver tests;
- stool analysis for worm eggs;
- skin allergy tests;
- bacterial sowing;
- biopsy;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- chest x-ray;
- HIV test;
- plasma analysis for hormone levels;
- skin scraping microscopy;
- urine test.
Most dermatological research techniques are painless. They allow you to identify the disease and select a treatment regimen.
Adequate treatment of any type of rash is possible only after identifying its root cause, in determining which an important place is occupied by differential diagnosis, which is impossible without knowledge of the sequence and differences in the manifestations of diseases that are reflected on the skin. In addition to laboratory tests, to make a correct diagnosis, the doctor must perform a thorough history taking and examination of the patient.
By following the rules of hygiene and sanitary standards when in direct contact with other people, visiting public places, using only personal items (clothing, towels, shoes, underwear) and not interacting with street animals, you can minimize the risk of skin infectious diseases. And personal hygiene with the help of individually selected cosmetics will help keep your skin healthy.