The causes of various human diseases can be not only bacteria and viruses, but also parasites. Some of them affect internal organs, others – skin and hair. Some parasites, such as the demodex mite, live in symbiosis with humans and only under the influence of various factors begin to cause harm to the host.
Most people don't know what a subcutaneous mite looks like because it is so small. But despite its microscopic size, the parasite is capable of causing enormous harm, so it is a good idea to know about the symptoms and treatment of the disease it causes.
What is a subcutaneous mite?
The subcutaneous demodex mite is a parasite that lives in the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. According to statistics, 97% of the world's population is the habitat of these individuals. Scientists claim that parasitic insects in a latent form (less than 3 living individuals per sebaceous gland) are beneficial to the body. After all, they destroy most pathogenic bacteria, preventing the body from becoming infected with viruses and infections.
A permanent inhabitant of the skin is the subcutaneous acne mite (Demodex folliculorum and D. brevis) - an opportunistic microorganism
Ticks that parasitize human skin reach a length of no more than 0.48 mm. Individuals with a translucent body can only be seen under a microscope. To the naked eye, these arthropods look like white pimples, devoid of vital signs.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
Monday, January 09, 2012 02:00 + to quote book
You can often see faces spoiled
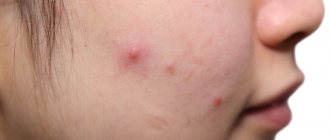
by a lot of acne , the fight against which takes considerable effort and nerves. One of the causes of acne may be demodicosis, or, more simply, subcutaneous mite, which usually affects oily skin.
It lives in the pilosebaceous follicles, or bulbs, from which hairs grow, in the secretion of the sebaceous glands of the facial skin. Until a person reaches puberty, these glands do not work, and there is usually no problem. But during puberty, sex hormones begin to be produced, which “turn on” the sebaceous glands. During this transitional period, many girls, and even more boys (15% of them are forced to seek medical help), have acne on their faces, which, of course, greatly interferes with practical life and makes it difficult to communicate with people of the opposite sex. Subcutaneous mites can also infect healthy facial skin if it contains a lot of subcutaneous fat. Sometimes the mite settles in the area of eyebrows and eyelashes. If the fat of the sebaceous glands disappears, the tick has nothing to eat, and it disappears without any treatment. But if the skin remains oily, the mite will multiply, and special efforts are required to defeat it.
Demodicosis is detected by determining the hormonal factor in the blood and using a special analysis. The subcutaneous fat is squeezed out and examined in saline (then the mite present in this fat is mobile) or in alkali (then it loses mobility). The presence of a tick confirms the correctness of the diagnosis.
It appears in diseases such as oral dermatitis - inflammation of the perioral border of the lips and chronic inflammation of the sebaceous glands, popularly called rosacea. They most often occur in women near the nose and in the nasolabial folds during menopause, as well as due to disorders of the endocrine, autonomic, reproductive systems and digestive tract. And the chronic course of diseases of these systems, in turn, is supported by the subcutaneous mite living in the sebaceous glands. If there are a lot of mites, granulomas form on the face - bulges that are accumulations of these same mites. One of the reasons for the formation of subcutaneous mites is the presence of male sex hormones - both natural, associated with puberty, and introduced into the body by the use of anabolic steroids (muscle pumping agents), as well as contraceptives and cosmetic products based on hormonal ointments. The development of subcutaneous mites is facilitated by a hot, humid climate and irritation of the same areas of the skin, for example, by tightly fitting clothing.
If a person genetically has dry skin and the pores are not enlarged, he is unlikely to be susceptible to demodicosis.
Thus, the root cause of demodicosis is acne, which, in turn, develops due to the existence of a subcutaneous mite. That is, a vicious circle arises in which cause and effect are closed, and breaking this circle is not at all easy.
When patients with rosacea come to me, they are characterized by increased nervousness due to vascular disorders in the digestive tract. Because of their nervousness, these patients often experience blood rushing to the face, and their rosacea begins to literally glow red. Such patients are immediately prescribed a diet common to all allergic diseases: do not eat spicy, salty, sweet foods, that is, those that intensely nourish and excite the subcutaneous mite. They cannot eat hot food - only warm food. Under no circumstances should you stand over steam when cooking, do not visit a steam room, avoid prolonged exposure to the sun and work in hot rooms. High temperature stimulates the mite.
All preparations containing sulfur have a depressing effect on ticks. Now, unfortunately, it is increasingly rare to find simple sulfur ointment in pharmacies - it is still preserved in small settlements where old, not very “fashionable” pharmacies remain. Also good are sulfur salicylic ointment, Wilkinson ointment (it has a characteristic black color), veterinary ointment “Yam” (used for parasitic and tick-borne diseases in animals), benzyl benzoate 10%.
However, the problem is that all these sulfur-based ointments act differently on different people and in some cases can increase redness in the inflamed areas of the face and itching. Therefore, these ointments should be used with caution: first try how this particular ointment will affect a small area of skin. There is no irritation, redness, inflammation - that means it’s possible.
Any of the mentioned ointments is applied to acne-affected areas of the skin and left for 4-6 hours. This is far from the most pleasant treatment: the “mask” of sulfur ointments is not aesthetically pleasing and does not have the most pleasant smell (perhaps the exception in this regard is benzyl benzoate). After this period, the ointment should be removed using boiled and cooled refined sunflower oil and apply any steroid ointment: sinaflan or flucinar, or lorinden C, lorinden A. More modern ointments are afloderm and elokom. You can use any of these ointments.
In recent years, more pleasant sensations, but, accordingly, more expensive products have appeared - Skinoren, the entire anti-acne cosmetic line Klerasil: gel, lotions for the morning and evening, cream, cleansing antibacterial wipes that remove sebum from the face, moisturizing emulsion. Now you can buy exactly the same ointment at the pharmacy - metrogil-gel. There are modern domestic products in pharmacies - “Black Pearl”, “Clean Line”, “New Cosmetic Line”. They are in many ways similar to klerasil, but much cheaper.
If a patient with demadecosis is on the road and does not have the opportunity to regularly care for his facial skin, he can simply soak a napkin with a lotion of salicylic acid and aloe extract and wipe his face at least three times a day.
For many years I have been using the method of my teacher and mentor, professor-dermatologist Anatoly Petrovich Rakcheev, who, unfortunately, has already left this world. The basis of the method is Vidal's milk. It consists of camphor, sulfur, salicylic acid, boric acid, glycerin and alcohol. Vidal's milk is prepared in prescription departments according to a prescription prescribed by a dermatologist. Shake Vidal's milk before use. In fact, this is the same as newfangled and expensive cosmetics, only without decorative aromatic additives.
In the evening, patients use Vidal's milk, and in the morning they wipe their face with chloramphenicol. And also my personal development: I mix in several types of alcohol - salicylic 1%, boric 3% and camphor 3%. All these alcohols are bought at the pharmacy in bottles of equal volume, mixed in equal proportions and poured into one bottle.
An important role in the treatment of subcutaneous mites is played by a course of antibiotics and Trichopolum, an antiparasitic drug that perfectly kills mites, 0.25 grams twice a day for 10-14 days. Among the antibacterial drugs, tetracyclines are good, cheap and effective (however, they are contraindicated for pregnant women and children under 8 years of age).
Previously, doctors themselves made metronidazole, trichopolum ointment according to Professor Rakcheev’s method: they took shaving cream with vitamin F, for 100 grams of cream - 10 grams of trichopolum (they bought 10 tablets, crushed them in a mortar and mixed with the cream).
Among antibiotics, macropen is also very good. It is taken one tablet three times a day before meals for 10 days. In general, all antibiotics are best taken 15-20 minutes after meals, but macrofoams are an exception. A good modern drug is Unidox Solutab, one tablet three times a day, 10 days.
Now there are many modern, very effective antibiotics, they can be used, but only the attending physician prescribes them.
Because of antibiotics, motility and innervation of the gastrointestinal tract suffer, so enzymatic preparations are definitely needed - such as festap, digestal, mezim-forte, penzital, any of them to choose from, one tablet three times a day with meals.
After antibacterial therapy, I always prescribe drugs that improve the microflora - Lactobacterin, Bifidumbacterin, Bifiform, Linnex, Floradefilus. To increase immunity, I prescribe echinacea herb tincture or preparations containing echinacea and cat's claw. But the immune, antifungal drug po d'arco is especially good (this is the bark of a tree from Brazil, the Indians noticed: the only tree on which mushrooms do not grow, one capsule is taken three times a day with meals, one jar is enough for a month.
In especially severe cases, when acne inflammation is severe, I prescribe retinoids - preparations containing vitamin A. But retinoids are still expensive, so instead of them you can use any vitamin complex with a high content of vitamin A.
Prevention is no less important than therapeutic measures for patients with demodicosis, especially for people genetically prone to this disease. They should not overheat, smoked meats and spices, any irritating food are prohibited, they should not drink cocoa and coffee, eat canned meat and fish, chocolate, alcohol is absolutely excluded, and oil-based cosmetics are unacceptable. In other words, it is necessary to exclude everything that feeds or stimulates the reproduction of subcutaneous mites.
The diet should be selected so that the food is rich in vitamins A, B and C: liver, carrots, spinach, pumpkin, apricots, peaches, asparagus, broccoli, green peas, cabbage, seeds, buckwheat, coarse bread, sprouted cereals.
Foci of chronic infections that suppress the immune system have a great impact on demodicosis, so timely treatment of caries, tonsillitis, cholecystitis, and diseases of the female genital area should be carried out. In this case, it is necessary to use immunostimulating drugs.
Be healthy!
| Categories: | home remedies, traditional medicine diseases, problems and their treatment |
Tags:
Demodectic mange How to deal with subcutaneous mites
Cited 49 times Liked by: 6 users
Like share
0
Like
- 6
I liked the post - Quoted
- 0
Saved
- Add to quote book
- 0
Save to links
Liked6
0
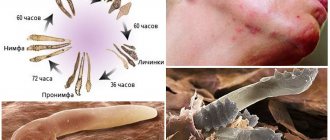
Structure and characteristics of the parasite
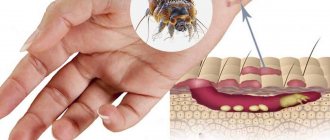
Demodex in humans is an individual with a thin translucent body and four pairs of limbs. Females are larger than males. Scientists distinguish only two types of subcutaneous mites:
- Demodex brevis. These parasites live in the sebaceous glands of the skin. Their body is small - the length does not exceed 0.4 mm in females.
- Demodex folliculorum lives in hair follicles. This arthropod parasitizes not only on the body of women. In men, the parasite lives in the hair follicles of the beard, eyebrows, and eyelashes.
Infection with subcutaneous mites occurs without a reaction from the immune system. Individuals live in the upper layers of the dermis, so they do not cause resistance from the body. Representatives of these species of arthropods love a warm environment when the air temperature exceeds +30 0C. Therefore, an exacerbation of the dermatological manifestations of demodex occurs in the summer, during the intensive reproduction of mites.
Mites can leave hair follicles and move slowly across the skin at a speed of 8–16 cm per hour
The female lays eggs in the deep layers of the epidermis during hormonal imbalance, metabolic disorders and other changes in the body. The immune system begins to react to the appearance of foreign particles in the sebaceous glands (follicles), resulting in dermatitis characteristic of the pathology.
What does a tick look like, and what types of ticks are there?
There are two forms of mites that live under human skin. This is a long tick, which is characterized by an elongated body of an oblong shape. This tick has a well differentiated head, thorax and abdomen. The body is covered with a dense chitinous shell. Females and males do not differ in size.
The second form of the tick is short. They are characterized by a shortened body with a pointed rear end and a short and flattened head end. Males are smaller in size than females. The thoracic region of the tick is wide and lacks a chitinous shell, that is, it is vulnerable.
Causes and symptoms of parasite infection
There are many reasons for Demodex skin infection. The subcutaneous mite is quickly transmitted by touching, kissing, or using someone else's towel or clothing. There are several factors that provoke intensive reproduction of the parasite:
- Weakened immune system.
- Hormonal disbalance.
- Pathological changes in the functioning of the endocrine system.
- Stressful situations.
- Use of hormonal food additives and decorative cosmetics with hormonal components.
- Gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Constant stressful situations, nervous overstrain.
The mite penetrates into the deep layers of the skin and sebaceous glands, while absorbing useful substances from the roots, hair and glands
People who frequently visit the sauna and solarium are at risk of ticks appearing on the face and other parts of the body. The risk of exacerbation increases with long-term use of medications and foods that disrupt the normal microflora of the skin.
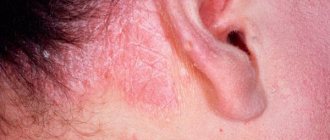
Symptoms of exacerbation of the action of subcutaneous mites on the face are typical for dermatoses. An experienced doctor can easily identify an advanced form of disease progression based on visual manifestations:
- An oily sheen appears on the skin, accompanied by local formations of acne and comedones. Photos of the dermatological manifestation of demodex are easy to find on the Internet;
- sometimes on the face the subcutaneous mite appears in the form of painful microscopic ulcers;
- dermatitis is accompanied by itching and redness, intensifying in the evening;
- as the disease worsens, areas of the rash lose sensitivity, the color of the skin changes, and its elasticity decreases;
- with an advanced form of infection with a subcutaneous mite, hair loss (eyelashes) or the appearance of white plaque in their root area is observed.
Visual manifestations of Demodex infection are very similar to the manifestations of pathologies that provoke increased production of subcutaneous sebum and blockage of pores.
The parasite causes significant harm as it carries harmful microbes into the body.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of parasite activity is redness of the skin of the face, and not necessarily the presence of acne. Since the subcutaneous mite is so small, it is not so easy to see. It is necessary to pay attention to the presence of the following signs:
- The appearance of itching , the sensation of “crawling goosebumps” - a similar phenomenon occurs as a result of an allergic reaction to the decay products and vital activity of the parasite. The symptom worsens after washing.
- Dilation of blood capillaries on the surface of the skin.
- Peeling of the skin.
- The appearance of small bubbles .
- The appearance of pimples, pustules , acne - occurs as a secondary infection due to the constant presence of an irritant. In advanced stages, acne can develop into purulent abscesses. Squeezing out formations leads to the spread of the pathogen.
- loss in affected areas.
- Unhealthy shine of the skin - appears due to the increased work of the sebaceous glands.
- Redness of the skin is observed due to the development of inflammation. If at this stage the patient does not receive the necessary therapy, then the skin in these places becomes uneven and bumpy.
- Deformation of the nose is observed against the background of the degeneration of healthy tissue into connective tissue.
- Swelling of the eyelids.
- Loss of eyelashes, in advanced stages they stick together in the morning.
- Increased lacrimation , discharge from the eyes, inflammation of the conjunctiva.
On this topic
- Pimples
How to quickly get rid of acne on the chin
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 27, 2021
If such signs appear, it is necessary to consult a doctor; prescribing the correct treatment will make it possible to avoid the development of serious pathologies and will not lead to a noticeable deterioration in the condition of the skin.
However, you need to remember that stopping the activity of the subcutaneous mite is not so easy and it will take a lot of time and effort.
Stages of disease development
Dermatologists identify only four stages in the progression of subcutaneous mite infection. Each of them has its own clinical picture:
- At the initial stage, when the subcutaneous mite has just appeared on the face, infection with the parasite is expressed in the form of small redness, which quickly passes.
- If arthropods have settled in the follicles of the eyelashes, the patient has a feeling of the presence of sand in the eyes. Spider veins may also appear. This is the second stage of pathology development.
- In the absence of timely treatment measures, the disease progresses rapidly. Persistent red spots appear, pimples appear on the face, the localized areas of the spider veins increase, and the eyes look inflamed.
- The fourth stage in the development of pathology is the appearance of a progressive inflammatory process, accompanied by swelling. The nose turns red and becomes swollen. If the location of the parasites is the eyelids, rapid deterioration of vision is observed.
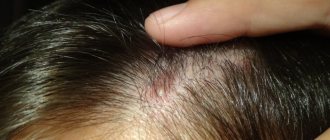
The sooner the patient contacts a dermatologist, the more effective the course of treatment will be. If demodicosis affects the follicles of the main scalp, an unpleasant odor appears, which is accompanied by hair loss.
It is quite easy to notice the lesion; the skin becomes dark gray, thickened, and pimples and blackheads often appear.
How to determine whether a person is infected with a tick or not?
Diagnosis of demodicosis is carried out in two ways:
- Visual examination - a rash, acne appears on the nose, cheeks or lips, and the face turns red. The skin becomes greasy, moist, and painful. Later, the face begins to itch, eyelashes fall out, and the patient feels as if someone is crawling under his skin.
- Laboratory tests - a scraping from the skin or the secretion of the sebaceous glands is taken. For the test results to be reliable, the patient must stop using cosmetics and not wash his face 24 hours before the test.
If treatment for demodicosis is not started in time, the disease will become chronic and will regularly remind the person of itself.
Stages and symptoms (rash, itching) of demodicosis
Diagnosis of pathology
If a dermatologist suspects a patient is parasitized by a subcutaneous mite, he prescribes laboratory tests of biological material. Before taking samples for analysis, you should not use decorative cosmetics or alkaline personal hygiene products for 5–7 days.
Depending on the area affected by parasites, the type of biological material required for diagnosis is determined:
- for the ocular form of demodex, the doctor uses tweezers to take 1–2 eyelashes from each eyelid of the patient;
- if the appearance of a parasite that causes dermatoses of skin areas (Demodex brevis) is suspected, biological material squeezed out from an eel located in the suspected area where the mites are located is taken for analysis.
During the study of the obtained samples, the number of adult individuals is calculated, as well as the type of parasitic arthropods. Based on the results of laboratory tests, an individual course of therapy is determined. The patient is treated by a dermatologist when the spread of Demodex brevis is diagnosed. Or an ophthalmologist for the ocular form of infection.
Laboratory testing is very simple and allows for quick diagnosis
Pimples and redness: is it demodicosis?
Purulent pimples, redness, itching and soreness do not always mean an attack of demodicosis.
In dermatology, it is customary to conduct a comprehensive examination of patients with suspected parasites in order to distinguish the activation of demodex from other diseases similar in their manifestations:
- pyoderma,
- seborrheic dermatitis,
- rosacea,
- juvenile acne.
What makes demodicosis so unpleasant is that without special treatment any regimen will be ineffective : acne is acne, but parasites require a special approach. This is why a good dermatologist will always prescribe a separate test for demodicosis.
If the assumption is confirmed and eggs or adults are found in the scraping, the therapeutic course will have to include acaricidal drugs in order to reduce the population of parasites and block the intensity of their reproduction.
Basic treatment methods
The easiest way to treat demodexes is at the initial stage of development with pathologists. Therapy for the disease is long-term – at least 1.5 months. The doctor selects medications depending on the area where the parasites are located. Hormonal tablets and ointments are recommended for use in patients with metabolic and endocrine system disorders. If the patient does not have an imbalance, taking hormonal drugs leads to suppression of the immune system, which is why the subcutaneous mite on the face begins to multiply even more actively.
Dermatoses caused by parasites are treated comprehensively. Medicines are selected whose action is aimed at normalizing the functioning of the skin glands and reducing their production of sebum. Local medications must be prescribed. At the same time, it is recommended to take immunostimulating agents that help strengthen the body's protective functions. And to treat advanced forms of demodex, antibiotics are prescribed.
For local (local) use the following are most often prescribed:
- "Ichthyol ointment" with zinc. This product dries the skin perfectly and has a powerful antiseptic effect.
- Metrogyl and Metronidazole are broad-spectrum antibiotics. They affect the source of pathology as an antioxidant, accelerating the healing process.
- If the parasites infect the hair, use Permethrin cream shampoo to treat the mite on the head. The active components of the products kill arthropods, disinfect the skin, and promote rapid recovery.
The most common drug for treating demodex mites on the face is sulfur-containing ointments.
For the most effective therapy, during the course of treatment, patients must stop using decorative cosmetics and not visit the sauna and solarium. You should also try to reduce your exposure to direct sunlight.
Preparations for oral administration
In the treatment of demodicosis, it is important to kill the parasite inside the body. Therefore, doctors prescribe tablets that have antiparasitic, immunomodulatory, and antihistamine effects.
Tavegil tablets . To eliminate signs of allergy, 1 pill is prescribed 2 times a day.
Detox tablets . This is an immunomodulatory drug, you need to take it 1 pill 2 times a day. Duration of use – 3 months.
Rekitsen remedy . This is a sorbent, you need to take it 1 tablespoon 3 times a day, the duration of treatment is 1 month.
Tablets Trichopolum . They have an antibacterial effect, the pills destroy pathogenic microorganisms and destroy them.
The drug is prescribed to adults and children over 10 years of age, 1-2 tablets 3 times a day during or after meals. The duration of treatment with Trichopolum is 1 week, no more.
This drug contains metronidazole, a substance that kills subcutaneous mites. Therefore, very often patients make chatterboxes with metronidazole, mixing it with other ingredients.
Recipe for an effective chatterbox against demodicosis:
- tablets Trichopolum, Streptocide, mumiyo - 6 tablets of each drug;
- vodka – 100 ml.
Mix all ingredients with vodka, apply the prepared medicinal mass with a cotton pad to problem areas. It is best to make a mask at night, wash your face in the morning and wipe your face with lotion with an antibacterial effect.
Streptocide and Trichopolum tablets dissolve very poorly in vodka, so before applying the mask against demodicosis, the bottle of medicine must be shaken each time.
Supportive treatment measures
Therapy for Demodex always includes auxiliary measures. They speed up recovery and prevent the possibility of relapses. Typically this is:
- use of personal hygiene products for daily skin care. The attending physician himself selects cosmetic products for the patient. Creams and lotions should moisturize the skin, not nourish it. Do not use ointments with a heavy, greasy texture;
- taking vitamin complexes that improve skin metabolic processes. Such drugs include “Ascorbic acid”, B vitamins;
- The patient must follow a strict diet during the treatment period. Fatty, spicy and salty foods are excluded from the diet. The amount of carbon is limited. The menu includes dishes from fresh vegetables, wholemeal bread, low-fat dairy products;
- physiotherapy is used as an auxiliary method of treatment for subcutaneous mites. The most popular procedures are cryomassage, cryopilling, and mesotherapy.
To increase the protective functions of the body, a balanced diet is necessary.
If the proliferation of parasites is caused by the presence of concomitant pathologies of the endocrine system or gastrointestinal tract, auxiliary treatment measures are aimed at eliminating these problems.
Sebum regulators
To remove favorable conditions for mites to live on the skin, you need to use sebum-regulating drugs, for example, soap with salicylic acid, ichthyol soap.
You can also use tar soap to dry the skin and remove grease. This remedy with a specific odor has antiparasitic, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects.
It is enough to lather your entire face with tar soap every evening, and after 2 minutes, rinse your skin thoroughly. This product tightens pores, relieves itching, irritation, and relieves inflammation.
Traditional medicine recipes
The secrets of healers will help neutralize the effect of subcutaneous mites only at the initial stage of infection. The most popular remedies in the fight against rapidly progressive dermatitis caused by the proliferation of parasites in the pores are:
- daily mask of tar soap. The soap mixture is applied to problem areas and washed off with warm water after 20–30 minutes. The skin is then treated with moisturizer. The course of treatment is 14 days;
- sour natural juices (cherry, black currant, lemon, etc.) have a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin with demodex. Freshly squeezed juice (1 tbsp) is mixed with egg white and applied to the affected areas. The mask is left for 15 minutes, then washed off with warm water. Oily skin shine noticeably decreases after 3–5 procedures;
- If Demodex folliculorum affects the eyes, compresses from aloe juice will help relieve swelling. A cotton swab soaked in the concentrate is applied to the eyes 3-4 times a day.
In advanced forms of the disease, traditional methods of treatment are ineffective. In order not to aggravate the situation, if the inflammation of the skin rashes noticeably progresses, you should consult a doctor.
Demodex facial mite: treatment
Demodicosis is a chronic disease that is difficult to completely get rid of. The main difficulty in treating pathology is the poor effectiveness of classical antiparasitic drugs. To eliminate demodicosis, complex treatment followed by specific care is necessary.
Ointments for the treatment of demodex
Since Demodex is an ectoparasite, it is advisable to use topical products to eliminate it:
- Demalan cream is a natural remedy with dermatotropic and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Sulfur ointment has an antimicrobial and antiparasitic effect.
- Nittifor is an insecticidal agent that promotes stable remissions in demodicosis.
- Benzyl benzoate medical ointment.
- Zinc ointment.
The regimen and course of treatment are determined individually.
Traditional methods
In addition to traditional methods of treatment, you can use folk ones. But it is strongly recommended to consult your doctor first.
Be sure to read:
Demodicosis of the scalp: treatment at home, the best remedies and shampoos
The following remedies are considered the most effective:
- Herbal ointment. Grind 2 tbsp. l. wormwood and tansy flowers, mixed with tbsp. l. animal fat or petroleum jelly. The composition is heated in a water bath until a homogeneous mass is formed. The ointment is applied twice a day.
- Juniper decoction. A glass of dried juniper fruits is poured with hot water, boiled for a quarter of an hour, and left for 30 minutes. The affected area is treated with a filtered decoction.
- Mask. Apples and horseradish are passed through a meat grinder. Mix 2 tbsp. l. applesauce and tsp. horseradish. The mask is applied to the skin for half an hour and washed off with warm water.
Folk remedies, like traditional ones, require course application.
Methods for preventing the spread of demodex
Prevention of recurrence of subcutaneous mites is simple. It is based on compliance with generally accepted rules of personal hygiene:
- Cosmetics, towels, bed linen and clothing must be individual - each family member has his own personal set.
- If a daughter and mother (sisters, father and son) have common clothes in their wardrobe, they should be washed and ironed before each change of owner.
- Bed linen is washed at high temperatures and ironed. If there is no automatic washing machine, pillowcases, sheets and other components of the set are boiled down.
- After each workout in the gym, you take a shower. You cannot go home wearing the clothes you wore during training. At home, the tracksuit, cap, socks, and wristbands are washed.
- After contact with animals, be sure to wash your hands with soap. The risk of becoming infected with subcutaneous mites from a pet is minimal. Ticks that parasitize animals have a different nature and habitat. However, there is a risk of contracting infections and worms.
- For facial skin care, it is recommended to use fresh infusions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort), which have a powerful antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect.
Following these simple rules will reduce the risk of infection with subcutaneous mites to a minimum.