About the disease
Scabies has been known to mankind since the Old Testament, where it was first described.
For quite a long time, people considered the unbearable itching that “attacked” at night as a heavenly punishment. But already in the Middle Ages, doctors began to guess that the cause of the terrible scratching was a parasite. The scabies mite was only discovered when the microscope was opened. In the 17th century, doctors were able to not only examine in detail the small “culprit” of the unpleasant disease, but also describe scabies, and also propose the first official measures to combat it. Scabies itch (this is the name of the mite that causes the disease) makes the disease extremely contagious, since it takes only 15-20 minutes for it to penetrate a person’s skin and begin to parasitize under it. Outbreaks of scabies are most often recorded in Russia in autumn and winter. And to a greater extent, it is not children who suffer from this skin disease, as it might seem, but teenagers. In newborns, scabies is rarely detected only if the parents or those who care for the baby have it.
On average, medical statistics say that 5-6% of the world's population have had scabies at least once in their lives. Older schoolchildren and teenagers account for about a quarter of all cases. The official name of the disease is scabies. The more common name “scabies” fully reflects the main and most painful symptom of the disease - the skin under which the itch settles is unbearably itchy.
Teenagers are in first place in terms of the number of diseases. On the second floor are primary and secondary schoolchildren. Children of preschool age are only in third grade.
About the pathogen
The scabies mite is small in size. The largest females reach a length of half a millimeter, and males are half that size. The sexual activity of scabies increases when it becomes cool around, which is why outbreaks of scabies occur in winter and autumn.
The zeds mate on the surface of human skin, the males then die as unnecessary, and the females begin to make “tunnels” in the epidermis for laying eggs. These burrows are called scabies burrows. Females prefer to lay eggs at night, and the process of making tunnels is perceived by humans as an unbearable itch. The eggs usually take up to 4 days to hatch. Then the new individuals themselves begin to make new passages inside the skin, and after two weeks, mature females and males emerge from the surface of the skin to repeat everything all over again.
During the day, itches do not show much activity, which is why a person practically does not feel their presence during daylight hours. At night, when the females are in full swing working to develop new territories (they move along the surface of the skin at a speed of 2.5-3 centimeters per minute), and also “dig” passages into the skin, the itching is at its peak of activity. At this time, their ability to become infected increases.
At first glance, it is not entirely clear what scabies mites can feed on. However, it is easy to find an answer to this question, knowing that itching is capable of dissolving the keratin layer of the skin with the help of its own saliva. The parasites feed on the substance obtained during the dissolution process.
The incubation period from the moment a scabies mite comes into contact with the skin of a healthy child until the onset of pathological processes does not exceed half an hour . And it can take up to 4 weeks before the first symptoms appear, since the body does not yet have time to react allergically to the vital substances of the parasites.
With repeated infection, when the body is already “familiar” with itching, only 24 hours may pass from the moment of infection to the first symptoms.
Clinical manifestations and symptoms
To avoid accidental contact infection, it is necessary to know the signs of different types of scabies.
What visual signs can be used to identify:
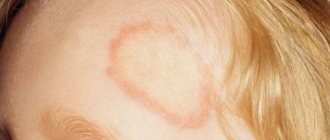
- On the surface of the skin there are barely visible grayish-white, slightly tortuous short strips of internal tunnels gnawed by mites.
- Elements of a rash (red blisters), usually in pairs, appear along them.
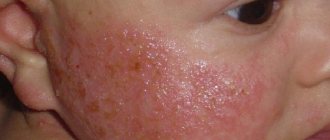
- Pimples and blisters are localized on the interdigital spaces, wrists, intimate areas, abdomen, under the breasts (in women, children), and armpits.
- Papules and blisters itch constantly, and the intensity of the itching increases at night.
After scratching the vesicles, crusts form on them, under which not only mites live, but also numerous pathogenic bacteria are concentrated.
Appears in people who carefully monitor body hygiene: frequently wash their hands, take baths and showers daily.
Due to the fact that there is a constant mechanical removal of mites from the skin with water and soap, the signs of scabies are usually erased:
- The vesicles of the rash are located rarely and are hardly noticeable, or instead there are only red spots.
- There may not be any convolutions from the moves, but if there are, they are isolated.
- There are few short spots and scratches from scratching.
- Localization - in the navel area, between the fingers, on the chest.
- Itching during the day is mild, but worsens at night.
On the surface of the skin are formed:
- The nodular rash is small with gray exudate, becoming covered with dense dark scabs after scratching.
- Red-bluish large papules and spots, blisters, on top of which passages of itching are visually noticeable.
- All tumors itch terribly at night.
If patients ignore normal treatment, they risk scabious purulent pyoderma.
The danger of Norwegian scabies (crusted) is the increase in general intoxication of the body due to the vital activity of an incredibly large number of itches.
Signs:
- Numerous elements of the rash merge together.
- Their surface is a dense, dry brown shell or a purulent continuous mess.
- Inside this mass of growth on the skin, there is a multi-row (deeper into the epidermis) layering of scabies containing itch eggs.
- A person's lymph nodes become enlarged.
- Itching may be minor (due to a decrease in the sensitivity of neuroreceptors due to their extensive damage).
- The number of mites sometimes reaches more than 150 mites per 1 cm of skin.
Fortunately, this form develops very rarely in modern society, since doctors today have many methods for detecting scabies.
Causes
The causative agent of scabies in children is the scabies mite Sarcoptes scabiei - an anthroponotic parasite; spends most of the time in the skin of the human host, feeding on the scales of the stratum corneum of the epidermis; In the external environment, the tick quickly dies. The scabies mite is small in size (up to 0.5 mm), round in shape and whitish-yellow in color, and is most active at night.
Infection with scabies in children occurs predominantly directly, through close, prolonged contact with the skin of the patient (most often, when sleeping together in the same bed), sometimes indirectly - through infected household items (toys, clothes and bedding). In the epidemiology of scabies in children, the leading source is the family unit. It is also possible to transmit the causative agent of scabies to children in crowded groups - orphanages, hospitals, camps, as well as in sports sections, swimming pools, baths, trains and hotels. In the youth group, scabies infection often occurs through sexual contact.
Preventive measures
A person can become ill from contact with an infected person. But there are cases when people become infected after close contact with things. Compliance with hygiene standards will partially protect against infections. Things need to be thoroughly boiled, soaked and washed (temperature 60 degrees). You should not wear clothes after you are infected. Carry out wet cleaning of the house daily. In parallel with the treatment of adults, the premises are thoroughly cleaned and disinfected. In case of contact with a patient, a one-time treatment with anti-scabies mites on the areas that came into contact with the infected person will be sufficient. After all, you can avoid getting infected with scabies. But this is a difficult process. By observing primary (personal hygiene rules) and secondary prevention measures (isolation of the patient, treatment after contact, disinfection), you can protect yourself. The sooner prevention begins, the better. After all, anyone can get sick.
Transmission routes
You can only get infected with scabies from a sick person, and if there is close and sufficiently long-term skin-to-skin contact . Children can become infected from their parents if they sleep in the same bed with them or if they are picked up at night. Children's groups where there is skin contact, for example, sections of contact sports (wrestling, karate, sambo, hand-to-hand combat, artistic gymnastics, pair and team dancing) can also pose a danger from the point of view of infection.
For quite a long time it was believed that children could become infected through shared toys, bedding and household items. However, recent studies show that this probability is negligible. Close skin contact is required. An interesting experiment in support of this statement was conducted in Great Britain, where about 300 volunteers took turns going to bed in which people with scabies had been lying before them. Only four were able to become infected through bedding.
The reasons that contribute to infection are quite obvious:
- poor sanitary condition of the home;
- social disadvantage;
- violation of hygiene standards;
- cold season (the less sweat on the skin, which has a certain antimicrobial activity and activity against itching, the higher the risk of infection).
Risk factors
The main risk factors are unsanitary conditions, high density of people, non-compliance with hygiene standards. The following factors predispose to infection:
- skin damage;
- diseases of the cardiovascular and circulatory system;
- weak immunity;
- eating disorders;
- night and evening time of day;
- infectious diseases.
The social status of the family plays an important role in the development of the disease. Children living in unsanitary conditions have an additional risk of being exposed to this unpleasant parasite.
Types of scabies
To reliably diagnose scabies in a child, it is not enough to know its general symptoms: rashes, redness and itching. It is important to have information about the types of disease, methods of infection and important signs characteristic of scabies in childhood.
The symptoms of scabies infection known to science divide it into the following types:
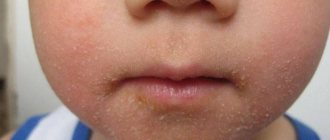
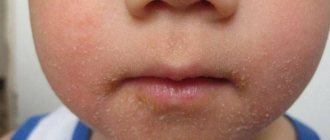
- Typical scabies is the most common. It is characterized by the appearance of scabious stripes (tracts) on areas of the child’s skin (elbows, interdigital area of the hands, wrists, neck, scalp); itching, with an increased effect in the evening; rashes on the skin; crust formation.
- Scabies without mite tunneling - develops as a result of undeveloped larvae of a female mite coming into contact with a child's skin (usually through bedding). As a result of their vital activity, allergic rashes, vesicles or skin papules appear. The larvae do not make passages, but parasitize on the surface of the epidermis. The duration of the disease is up to three weeks. It may develop into typical scabies.
- Norwegian scabies is a rare species that occurs in children, but there are documented cases. Scabies burrows are large, the lesions are significant. Inflammation and the formation of papules are observed throughout the body. It usually affects people (also children) with weak immunity (HIV-infected, cancer patients). Signs: scab-like hardening of the skin, dry, dull hair, enlarged lymph nodes, unpleasant odor.
- Nodular scabies is a secondary type, possible after treatment of the main type of disease. It affects the surface of the genitals and past lesions in the child. Symptoms: itching, small nodules, lumpiness on the surface.
- Discrete scabies is an erased, “intelligent” form of scabies. It can even affect clean people who carefully monitor the cleanliness of their bodies. There are no visible signs of scabies, but the child complains of constant itching. A careful examination reveals microscopic rashes in the form of vesicles and vesicular nodules.
- Pseudoscabies - can develop as a result of contact with an infected animal, when the mite parasitizing on its body passes onto the child’s skin. This type is characterized by allergic rashes and severe itching, but does not require treatment and goes away without complications within three weeks. The main thing is not to let your child scratch the skin, so as not to cause an infection.
What is the essence of diagnosing scabies in children?
Parents who notice unusual elements on the child's skin, as well as if there is itching, should immediately contact their pediatrician. After the examination, the latter will refer you to a dermatologist for consultation. He, in turn, must carefully collect anamnesis and complaints. Information about contact with patients is important, and it is also necessary to find out the situation in the family and in the institution that the child visits.
Initially, the doctor should pay attention to the external manifestations of the disease. Clinically suspicious elements will be: scabies, rashes, scratching. Favorite localization will also suggest the disease: interdigital spaces, hands, wrists, lower abdomen, flexor part of the elbow joint.
Additional research methods do not always provide an accurate answer. Therefore, the diagnosis can be established without laboratory diagnostics. But you shouldn’t neglect it. For better visualization, scabies are stained with iodine solution or brilliant green . After the dye is absorbed, clearly colored, sinuous lines remain on the skin.
The mechanical method of removing a mite involves the doctor inserting a sterile needle into the scabies tract. There, the tick attaches to the needle and it is removed from the affected area of the skin. The resulting pathogen is placed on a glass slide and examined under a microscope.
also used for microscopic examination . A special solution is dripped onto the suspicious area of skin. After a few minutes, scraping is performed with a scalpel. The contents are placed on a glass slide and microscopy is performed.
Through a microscope you can see the female mite, eggs, and larvae. If only waste products are found, then scraping must be carried out on other areas of the skin.
First signs
Depending on the form of entry of the pathogen, the first signs begin to appear within the first two weeks. If a scabies larva is transferred to the human body, then it needs to develop into an adult. On average, ripening takes 10-14 days. If a sexually mature female gets on the skin, then at night she begins to actively make subcutaneous passages and lay eggs in them - this causes itching. The implementation process takes about a quarter of an hour. In 30 days, one individual can produce up to 50 million larvae.
It is important to know! The life cycle of a tick is 1.5-2 months from the moment of appearance. First, an egg appears, then a larva, and after maturation a sexually mature individual. READ ALSO: tick bite in a child: symptoms with photos and methods of treatment
The most important sign of scabies is the presence of scabies. Favorite places for itching, where the rash first begins to appear:
- folds between the fingers;
- elbow bends;
- umbilical region;
- neck;
- breast.
The photo shows that the passages are a grayish line up to 1 cm long and have an entrance and exit. The first one is usually wider than the second one. At the end of the passage, a bubble is formed in which the female is located.
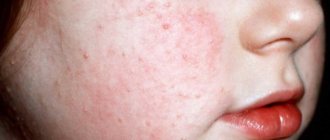
General symptoms of the disease
The initial stage of the disease is characterized by vesicular rashes on the skin and night itching. As the disease develops, it intensifies, and a person, scratching the affected areas, spreads the infection throughout the body, carrying larvae under the nails. After taking a hot shower or bath, the itching increases.
Subsequently, the forms of rashes become more diverse; these can be erosions, hyperemic areas, scabs, papules, vesicles. Localization is not limited to secluded places. In newborns, the tick gnaws passages on the scalp. Children become restless and irritable; sleep disturbances and insomnia appear. Due to secondary infection, an increase in body temperature is possible. Symptoms can be either isolated or appear in aggregate, which makes diagnosis difficult.
How to treat scabies?
Children react acutely to contact with scabies mites. The main signs of the disease are redness of the skin and severe itching, concentrated in the wrists, palms, elbows, torso, face, and head. At the first signs of scabies, you need to immediately begin treatment using effective pharmaceutical drugs and folk remedies. An infected person should limit contact with others and exclude the use of common household items.
Scabies has a short incubation period, and the disease quickly causes serious complications without proper treatment.
Therapeutic measures include the use of drugs based on antiparasitic components. In combination with disinfection, they can eliminate the causative agent of the disease in a few days. In this case, the itching remains for several weeks.
There are products that can destroy ticks after the first use, but they have many side effects and contraindications, including use by pregnant women and children.
How to cure scabies on the face without leaving scars
Typically, in adults, ticks do not live on the face and do not dig burrows, since the structure of the skin is quite dense. In exceptional cases (with complications of scabies), the following remedies will help.
Fast acaricidal preparations that prevent the formation of deep and long tick burrows under the skin:
- Spregal (aerosol).
- Lindane (lotion).
- Crotamion (lotion).
- Malathion (lotion).
The use of these products instantly destroys adult itches and prevents their penetration into the thickness of the epidermis. Prevents acne infection by pathogenic microbes.
In order for the ruts in the mite tunnels to smooth out more quickly, after treating scabies, you need to lubricate your facial skin with one of the medicinal gels (creams):
All of them have excellent regenerative and dermatoprotective properties. Accelerate epithelization of the skin, nourish and smooth it.
Pharmacy drugs
The most popular medications that help get rid of scabies are ointments, creams, lotions, emulsions, and sprays. Do not wash for 12-24 hours after using them. The medicine is applied to any part of the body except the scalp, face and neck. The list of effective medications with an antiparasitic effect includes:
- Zinc and Sulfur ointment;
- Permethrin ointment;
- Benzyl benzoate;
- Balsamic liniment according to Vishnevsky;
- Crotamiton;
- Medifox;
- Ivermectin;
- Spregal.
Ointment formulations are not expensive, but are highly effective. After their use at an early stage, the risk of relapse is minimized. Aerosols are gentler. They are recommended to be used as prophylaxis.
In children, scabies is often accompanied by a bacterial infection as they scratch the skin rash.
To alleviate the immunoallergic reaction, antipruritic, antihistamine and corticosteroid drugs are additionally prescribed: Claritin, Zodak, Erius, Cetrin, Aleron, Hydrocortisone ointment. Any moisturizer will help reduce itching. If your child constantly scratches his wounds, he may become infected. Antimicrobial ointments suppress the proliferation of pathogenic flora: Levomekol, Penicillin, Lamisil, Tetracycline ointment.
Application of Sulfur Ointment
Sulfur ointment is considered the most common means of combating scabies mites. Its use is possible for both adults and children. The drug has virtually no contraindications or side effects. It quickly stops the inflammatory process, providing an antibacterial and antiseptic effect.
The paste-like composition contains sulfur, which, penetrating deep into the subcutaneous tissue, causes the production of sulfides and propionic acid. These substances inhibit respiration and cause paralysis in ticks, which leads to their death. Sulfur ointment is an inexpensive drug that can be used to start therapy even in children. It has both advantages and disadvantages:
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Improves blood clotting | Poor absorption into the skin and rough texture |
| Prevents further infection | Sweating disorder |
| Relieves puffiness | Repulsive smell |
| Protects skin from the negative effects of external factors | Change in skin color after application, which lasts for another 3-4 days |
| Suitable for pregnant women and small children | Possible allergies |
With a content of 33% of the active component, the drug has a rapid therapeutic effect, however, it is extremely toxic. Children use 10% ointment. It acts more slowly, but is considered absolutely safe. The sulfur composition is rubbed into the infected tissues and healthy areas around them. The maximum period of use is 1 week.
Permethrin and Zinc ointment
The main ingredient of Permethrin ointment is permethrin, which has anti-inflammatory, insecticidal, bactericidal, anti-scabies, acaricidal, and anti-pediculosis properties. Once on the integument, the compound is introduced into the body of parasites and their larvae, disrupting the functioning of the nervous system, causing paralysis and death. The product is used externally, applied with a cotton swab to the problem area, and then intensively rubbed into the skin. After 12-24 hours, the composition should be washed off with water and soap, and also change clothes.
The medicine is approved for use in children over three years of age. Exposure time in childhood is 12 hours. The interval between re-application is 1-2 days. The ointment can be reused no more than five times.
Zinc ointment 10% is not the main treatment. It is used as an additional remedy that relieves inflammation and eliminates itching. This is a mildly acting, gentle medicine that can protect the skin from infection, heal wounds, scratches, and scratches. It has no contraindications, except for individual intolerance to the components included in the formulation.
Benzyl benzoate and Vishnevsky ointment
This is a synthetic drug based on benzyl benzoate that can cope with any parasites that affect the dermis. It not only causes rapid death of ticks, but also eliminates their waste products. Not prescribed for children under 3 years of age, women during lactation and pregnancy. The 10% composition is designed specifically for the children's age category, since the high concentration of active components is extremely toxic.
The ointment is applied to the skin after hygiene procedures. One treatment of problem areas requires at least half of the bottle. The manipulation is carried out on the 1st, 3rd, 5th day in the evening. The duration of therapy is 7-10 days.
Vishnevsky ointment contains birch tar, which perfectly fights dermatological diseases. Xeroform and castor oil enhance its effect. The ointment composition has no contraindications and:
- reduces the inflammatory process;
- relieves itching;
- heals damaged tissues.
The disadvantages of the product include a specific odor, which with prolonged use takes a very long time to disappear. Like all ointment compositions, the medicine is applied in a thin layer to the skin, rubbing into problem areas. It is not prescribed for children under 3 years of age, as side effects can cause serious health problems, including impairment of mental development and memory.
Using Crotamiton and Medifox
Crotamiton lotion and cream is one of the most effective drugs for treating scabies. Consists of a 10% solution of crotamiton, an anti-itch compound. It simultaneously destroys the pathogen and relieves itching. After application to the skin, it accumulates in the body of parasites, which allows them to be destroyed. Additionally, the active component of the drug blocks the receptors of the epidermis, due to which the itching stops for 6 hours.
The lotion is applied externally to a clean body. It is applied to the skin from the neck to the toes and hands and rubbed until completely absorbed. After which they put on clean clothes and go to bed in a clean bed. The next morning, the skin treatment is repeated, and a bath is taken only 48 hours after the first application of the medicine. The duration of therapy is three days. This drug is not prescribed to children under 12 years of age.
Medifox is less toxic. It quickly suppresses itching, eliminates rashes and other signs of scabies in children and adults. The main active ingredient permethrin has powerful:
- anti-pediculosis;
- insecticidal;
- acaricidal property.
The medicine is available in the form of a gel and a concentrated emulsion. The concentrate is diluted in water, then take a shower, wipe dry and treat all affected areas of the skin, avoiding the neck, face, and hair. Treatment should be carried out at night. The duration of therapy is 3 days.
Aerosol Spregal
The product in the form of an aerosol Spregal contains esbiol and piperonyl butoxide - neurotoxic poisons for parasites. After spraying, the active components penetrate the nervous system of insects, causing their death. A day after treatment, no traces of the drug are found in the bloodstream. The insecticidal medicine is approved for use by people of any age. However, therapy cannot be carried out in case of obstructive bronchitis, bronchial asthma, lactation, or individual intolerance to the active ingredients.
When treating the body with an aerosol or ointment, you need to pay attention to hard-to-reach places: the perianal area, soles, interdigital areas, subungual beds, genitals.
Another effective insecticidal agent is a 0.5% malathion solution. It has powerful antiparasitic properties and is used for hypersensitivity to permethrin-based medications. The drug is recommended for use by children over 2 years of age.
Drugs Ivermectin and Lindane
Ivermectin is a universal antiparasitic agent. It is suitable for treating both humans and animals. Available in solutions, tablets, paste, cream-gel. During the treatment process, the main active component ivermectin disrupts the functions of the nervous system of parasites and destroys them. The dosage of the drug is calculated individually, depending on the age category of the patient and the severity of the disease. For children over 5 years of age, the dose is 5 mg per 1 kg of body weight. The drug in tablet form is taken orally once a day with plenty of liquid.
Lindane is used in the form of a lotion to treat scabies. The product is applied to the entire body, excluding the head area. Wash off with warm water three hours after application (children under 10 years old). Adults leave the drug overnight. The course of therapy is three days. Due to its strong toxicity, this product is not used often. It has many contraindications and is not used in children under 3 years of age. Contraindications include epilepsy, pregnancy and lactation, old age, suppressed immunity, skin damage, and individual intolerance.
Demyanovich method
This method of treatment is used extremely rarely. It is quite labor-intensive and ineffective. In addition, complex forms of scabies cannot be treated if its pattern has been disrupted. However, an important advantage is the absence of contraindications, which makes it possible to use the Demyanovich method even in children. The treatment regimen is as follows:
- sodium hyposulfate 60% is applied to all affected areas, rubbing the body for 2 minutes;
- allow the covers to dry and rub in a 6% hydrogen chloride solution;
- each area is treated three times for one minute;
- Be sure to allow the skin to dry after each treatment with the solution;
- put on clean clothes, change bed linen;
- do not take a bath for three days.
This method helps cure unspread scabies. It is based on the acaricidal properties of sulfur, which develop during the reaction with sodium hyposulfite and hydrochloric acid. The only side effect that may occur is allergic dermatitis.
Scabies or allergies? All about obsessive itching
Itching is one of the common symptoms with which patients consult a dermatovenerologist. Often the cause of this is allergies. But do not forget about such a disease as scabies. It is important to immediately determine the cause of the itching. How to find out this at the initial stage? What questions should you ask the patient?
What is scabies?
Scabies is a skin disease caused by mites of the genus Sarcoptes scabiei. Infection with this parasitic skin disease occurs through contact. That is, with close bodily contact.
Infection often occurs when people are in the same bed. The stages of tick development that can infect humans are females and larvae. A group of people where there is a person with scabies is called a focus of infection.
When identifying such a lesion, the doctor must immediately report it to the SES.
There are direct and indirect routes of tick transmission. Direct is carried out at night in bed, when the tick is most active. The indirect route is through common objects and bedding. There is also a transient invasion, which can occur in saunas, trains, bathhouses, where streams of people use objects that were used by a patient with scabies.
The pathogenesis of the disease completely reflects the life cycle of the tick, which is divided into 2 periods - a short-term cutaneous phase and a long-term intradermal phase.
The location of the passages in scabies depends on the density of the sweat glands, the type of hair growth, the temperature of the outer skin, the rate of regeneration of the stratum corneum and the structure of the skin. Thus, the passages are often localized on the hands, elbows, wrists and feet, where the thickness of the stratum corneum is greatest.
There are also many passages in those areas of the skin where the density of sweat glands is increased (male genitals, wrists, hands, feet). That is why, when a patient has scabies combined with atopic dermatitis or ichthyosis vulgaris, there are very few scabies. Also, due to dry skin, there are few of them in older people.
But there will be many moves for hyperhidrosis, athlete's foot and dyshidrotic eczema.
But, given the fact that modern people wash their hands with soapy chemicals several times a day, a person with scabies may not have these moves at all. Then diagnosis becomes difficult, because there is no main symptom, but the disease is there.
The only symptom that can help make a preliminary diagnosis is the time of itching. This is the question that should be asked of the patient in order to make a differential diagnosis with allergies. This is due to the daily activity of ticks.
Daily activity of scabies mites.
The female is in a calm state during the day. In the evening and at night, she gnaws through the egg knees, laying an egg in each. At the same time, the female deepens the very bottom of this passage, making the subsequent emergence of the larvae possible.
This is done by every female and every night. One female leaves up to 2 eggs per night.
As a result of this process, the scabies tract on the skin of a person with scabies has a convoluted shape and consists of parts of tracts, which are called the daily element of the tract.
Thus, the nocturnal activity of mites explains the predominance of the direct route of infection through the bed at night and in the evening, as well as the effectiveness of anti-scabies at night.
Clinical picture of scabies
If the infection occurs with larvae, the incubation period lasts 2 weeks. And if the infection occurred from a female, then the clinic is immediately visible. Itching is the main characteristic symptom of scabies.
It occurs as a result of sensitization of the body to the end products of mite activity (excrement, secretions of the oviduct glands, oral secretions).
Itching appears within 1-2 weeks during primary infection, and up to 3 weeks during re-infection.
The second characteristic sign of scabies is the presence of scabies. The skin reacts to the appearance of these same moves. Non-inflammatory vesicles and follicular pustules also appear.
An allergic reaction to the end products of mite metabolism also occurs, which manifests itself on the skin as bloody crusts, scratching and miliary papules. But we have found that each person’s skin reacts differently to tick activity.
Some have no tracts at all (intact tracts), others have vesicles, blisters, pustules and lenticular papules, which are caused by reactive tracts. Now the similarity between allergies and scabies becomes clear.
Diagnostic symptoms for scabies:
- Ardi's symptom is pustular crusts and pustules on and near the elbows.
- Gorchakov's symptom - bloody crusts there.
- Michaelis's symptom is impetigious rashes and bloody crusts in the intergluteal fold with transition to the sacrum.
- Sezari's symptom - upon palpation, an elevation is determined, which indicates the presence of scabies.
Scabies can be complicated by dermatitis and pyoderma. Sometimes - urticaria and microbial eczema.
When a person is infected with ticks from animals (dogs, pigs, horses, wolves, foxes, rabbits), pseudosarcoptosis develops.
With this disease, the incubation period lasts several hours, and typical scabies burrows are absent, because mites do not reproduce in conditions unusual for it.
They only penetrate the skin, causing severe itching. Pseudosarcoptosis is not transmitted from person to person.
Scabies in children occurs with possible damage to the skin of the face and scalp. In infants, even the nail plates can be affected.
Methods for detecting scabies
In our country, the diagnosis of scabies must be confirmed by laboratory tests. For this use:
- Oil vitropression method - the skin is lubricated with mineral oil, after which granulomas are visualized by pressing on the eruptive element.
- A method of staining a suspicious element with a 5% alcohol solution of iodine, ink, ink or aniline dyes.
- Scraping method - detection of contents in the scabies tract, vesicles and papules;
- The method of removing a tick with a needle is after opening the blind end of the stroke. In this case, the sharp needles move in the direction of the stroke and the female is attached with suction cups to the manipulation needle.
- Dermoscopy must be performed on a patient with scabies.
Treatment and prevention of scabies
Treatment of scabies is carried out on an outpatient basis. The most effective and frequently used ointments for scabies are benzyl benzoate, medifox, spregal and sulfur ointment. But, regardless of the treatment chosen, there are general principles for treating patients with scabies:
– treatment of all patients in one focus is carried out simultaneously;
– rubbing ointments should be carried out exclusively in the evening;
– for children under 3 years of age, all areas of the skin should be rubbed; for others, with the exception of the scalp.
– scarbicides are rubbed in only with your hands, after which you need to wash your hands thoroughly;
– the drug must be on the skin for at least 12 hours;
– treatment of complications should be carried out in parallel with the treatment of scabies;
– change of underwear and bed linen is carried out after completion of the treatment process.
Treatment of scabies in children
Children under 1 year old can only use Spregal ointment; from 1 to 3 years old - Spregal and Medifox. From 3 years - no restrictions.
The doctor must remember that when treating scabies, relapses cannot occur, since the mite does not have long, latent periods.
And such “relapses” are the result of non-compliance with treatment regimens, an independent decrease in the concentration of the drug, failure to comply with the period and frequency of ointment application, as well as the use of the drug in the inactive phases of the tick cycle (during the day) and the use of stitched drugs. Reinvasion is possible - re-infection from the primary source of scabies if the latter has not received adequate treatment.
Prevention of scabies involves actively identifying patients during medical examinations and whenever seeking medical help.
It is important to know preventive measures that will reduce the chances of contracting scabies:
– use of personal hygiene products and bed linen;
– adhere to hygiene standards in saunas, swimming pools, baths;
– observe basic hygiene procedures.
It is not always possible to prevent a disease such as scabies, but by remembering the basic rules, you can significantly reduce the risk of infection. And most importantly, after reading this article, you will have no doubt at the initial stage of diagnosis whether it is an allergy or scabies.
Health to you and your patients!
Share:
Source: https://estet-portal.com/doctor/statyi/chesotka-ili-allergiya-vse-o-navyazchivom-zude
Folk remedies
As has been repeated many times above, self-medication is not the best way. Nevertheless, there are situations in which knowledge of traditional methods of getting rid of an illness is required. There are a great many recipes for scabies. Below are just a few of them:
- Mix 0.5 liters of mustard oil with 100 g of mashed garlic, cook this mixture for 15 minutes. Thoroughly wipe the affected areas with the resulting lotion.
- Vinegar diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio.
- Birch tar - applied to the rash for three hours.
- Infusion for external use from juniper branches. For 1 liter of boiling water 10 g of raw materials.
- Ointment: mix 15 g of melted pork lard with 15 g of grated laundry soap, then add 5 grams of tar and sulfur ointment to the resulting mixture.
- For 1 liter of boiling water, add 80 grams of buckthorn, simmer over low heat for ten minutes and let steep for half an hour.
- Another ointment is made by mixing butter and turpentine in a 2:1 ratio.
- Celandine juice and Vaseline, in a ratio of 1:4.
To relieve itching, you can use freshly squeezed tomato and lingonberry juice. They are used topically by rubbing.
Possible complications of scabies
The child’s body is still quite weak and susceptible to various pathologies, so at the first suspicious symptoms you need to act immediately. Ignoring the disease can lead to serious complications:
Possible complications of scabies
- development of a secondary infectious process;
- the appearance of abscesses of a progressive nature;
- lymphangitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes);
- rheumatic heart disease (rheumatic heart disease);
- lymphadenitis (damage to the lymph nodes due to a viral infection);
- furunculosis (purulent-necrotic inflammation of the skin);
- acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (APSGN).
Gorchakov's symptom is one of the complications of scabies
Note! Regardless of the form, under certain conditions scabies can be accompanied by a bacterial infection. Most often, this complication occurs in young children who, despite their parents’ prohibition from scratching skin rashes, continue to do so. As a result, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the resulting wounds on the body.
The horrors of modern scabies - erased symptoms
Typical scabies is becoming less and less common today, the symptoms of which immediately make it possible to identify a parasitic disease from allergic urticaria.
Therefore, people who are sincerely confident that they are not contagious unwittingly expose their children, colleagues, and neighbors to the danger of infection with itch mites.
Meanwhile, untimely detection and treatment of atypical types of scabies often leads to bad consequences: purulent pyoderma, neurodermatitis, microbial eczema. How to recognize the disease and quickly get rid of it?
Which doctor should I contact?
When the first suspicious symptoms appear, the child should be taken to the pediatrician immediately. Often, skin rashes and itching accompany other diseases, not scabies, so you should not self-medicate. This can harm the child's body.
Examination by a pediatric dermatologist
As soon as the pediatrician conducts an initial examination and identifies traces of parasitic skin lesions, he will refer you for examination by a dermatologist. Only a dermatologist should prescribe a course of treatment. He also makes decisions to eliminate possible complications of the disease.
Treatment of scabies
The initial stage of the disease is highly treatable. The choice of treatment method and medications is made by the doctor. Self-medication, especially when it comes to a child, is unacceptable. Treatment of scabies in children is usually carried out with specialized medications, although traditional medicine also has many effective remedies in its arsenal.
Medications
As the main therapy for the treatment of scabies, various topical agents are used - ointments, sprays, creams, emulsions. The most common ones are:
- Benzyl benzoate. Available in the form of ointment and 20% emulsion. If the affected areas are small, it is more convenient to apply ointment to them. When it is necessary to treat a large part of the body, it is more convenient to use an emulsion. The drug is used before bedtime. Before this, the child must be thoroughly washed with soap and then wiped dry. The medicine is rubbed in with massaging movements and allowed to dry. After this, you need to put on clean clothes for the baby and put him to bed. The duration of treatment is 4 days. This is due to the fact that Benzyl benzoate destroys only hatched individuals and does not pose a danger to the eggs. For children under three years of age, the drug is diluted with Vaseline to reduce the concentration. However, for infants it is better to choose another remedy.
- Sulfur ointment 5%. The method of application is the same as for Benzyl benzoate. It has a distinct specific odor. Not prescribed to patients under three years of age.
- Permethrin. Presented in several dosage forms: ointment, spray, cream and lotion. Age limit – up to 1 year.
- Spregal. Available in spray form. Approved for use by pregnant women and infants. Very effective against scabies mites - in more than 80% of cases, treatment requires a single treatment.
In addition to local remedies, antihistamines (Zyrtec, Zodak, Suprastin, Tavegil) are additionally used individually, which reduce itching. For complicated forms of the disease, antibacterial agents are indicated. They are prescribed by a doctor depending on the type of bacteria.
Features of medicines for scabies mites
All drugs for the treatment of scabies perform two tasks at once:
- destroy parasites;
- alleviate the patient's condition, relieving symptoms and promoting skin healing.
To do this, the products must have antiseptic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic properties, and in addition, contain substances that cause the death of ticks. All modern medications used to treat scabies mites can be divided into 3 categories:
- high sulfur content;
- synthetic derivatives of balsamic products;
- drugs with a pronounced acaricidal effect.
Remedy for scabies
A separate line can be taken of traditional medicine, which acts as an auxiliary therapy, making treatment more effective.
Prevention of childhood demodicosis
There are no specific preventive measures that will protect a child from tick infection. It is transmitted through contact, so no one is protected from infection. But there are recommendations that will help protect yourself and your child from the development of pathology:
- daily proper facial care;
- ticks multiply in warm conditions, so it is better not to allow children to walk in the sun for a long time;
- regular visits to the pediatrician;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- healthy lifestyle;
- proper nutrition;
- strengthening the immune system;
- timely treatment of chronic and acquired diseases;
- protection from stress, anxiety, physical and mental fatigue;
- proper rest and sleep.
If the child is already infected, then additional preventive measures need to be taken:
- Daily change of underwear and clothes.
- Refusal to visit the swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna.
- Don't get too cold.
- Don't overstrain your eyes.
- Exclusion from the diet of sweet, spicy, fatty and unhealthy foods.
- Daily change of towels and bed linen.
If you follow the rules and recommendations of your doctor, you will be able to prevent ticks from multiplying on your body, because it is very easy to become infected with ticks. A person may not suspect this for a long time, since the parasite is almost invisible on the body.
To completely get rid of demodicosis, proper long-term treatment will be required. Signs of the disease will disappear in the first days, but the disease itself will only disappear after a month of conservative therapy. It is better not to delay your visit to the doctor and get rid of the problem in a timely manner.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis and distinguish scabies from other skin diseases, it is necessary to conduct several laboratory tests:
Methods for diagnosing scabies
- microscopic examination of the mite after removing it from the scabies tract using a special needle;
- cutting the top layer of skin in the area of scabies to identify mite eggs;
- scraping the skin next to the scabies until traces of blood appear. Then a microscopic examination of the material is carried out. Experts recommend scraping the epidermis in the area between the fingers;
- aspiration of the affected skin by alkaline preparation and further microscopy of the material;
- use of sodium hydrochloride. This procedure helps to identify parasites, but their metabolic products dissolve under the influence of the substance;
- applying ink or iodine tincture to the affected skin. This allows you to identify traces of scabies mites.
Differential diagnosis of scabies
Examining a child for scabies is a complex procedure, so in the diagnostic process, doctors can use special devices, for example, a video dermatoscope. It is capable of magnifying the image more than 500 times, which makes it possible to accurately identify scabies on the body. The dermatologist will also be able to determine the place where the child could become infected.
Diagnosis of scabies in children
If necessary, all family members are tested for parasites. This helps prevent the spread of the disease. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then the doctor draws up an appropriate course of therapy.
Is it contagious?
Allergies have never been a contagious disease. This is an individual reaction of the body that cannot affect anyone else. If an allergy occurs to the same product or substance in two people in contact with each other, then this is more likely a coincidence than an exception to the rule.
The same cannot be said about scabies, since scabies mites are highly contagious parasites that pose a danger to others. If one family member catches scabies, others will inevitably become infected with it in the very near future. Children are the most susceptible to infection, since it is with them that adults tend to come into contact most often.
In any case, it is not recommended to independently diagnose yourself and select treatment, since it is not always easy to distinguish allergies from scabies, and incorrectly selected medications can aggravate the problem. Contacting a specialist and carrying out competently prescribed treatment in a short time will help get rid of the clinical signs of diseases, regardless of what was detected - allergies or scabies.