Forgetfulness, decreased performance, constant surges in blood pressure, weakness in the arms and legs are only a small part of the symptoms of atherosclerosis that cause discomfort and concern in patients. Unlike atherosclerotic damage to the internal walls of blood vessels, when cholesterol plaques appear on the face and body, a person does not rush to see a doctor: these formations are absolutely painless and tend to grow very slowly, although they indicate gross disturbances in fat metabolism in the body.
Is it possible to treat plaques on the body only as a cosmetic defect? Do they require treatment and how to prevent their reappearance? Let's look at these questions in more detail.
Causes
Why do plaques form? The skin (the treatment of these protrusions will be presented below) is prone to the formation of all kinds of sores. At the same time, experts say that there are quite a few factors that can influence their formation.
From the point of view of traditional medicine, the main cause of plaques is age-related changes in the body. However, a lot depends on the human factor, including your attitude towards your health and skin in general.
Methods used to treat the disease
When choosing what and how best to treat psoriasis on the face, it is important to listen to the opinion of specialists who offer local treatment using effective medications, such as ointments and creams, gels and sprays.
The main problem of treatment is the sensitivity of the affected skin, so it is necessary to carefully and carefully select drugs, taking into account the possibility of individual intolerance to the ingredients of single-component or multi-component, certified and high-quality drugs.
Main types
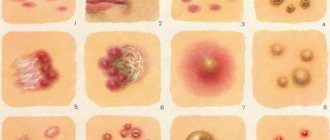
Plaques on the skin, photos of which you can see in this article, can be different. Their main types include the following:
- seborrheic keratosis;
- senile keratoma;
- xanthelasma;
- papillomas;
- white vitiligo.
We will tell you right now what these skin diseases are and how they should be treated correctly.
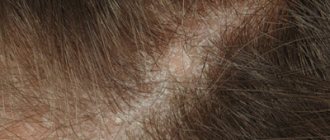
The first signs and general symptoms of psoriasis on the face
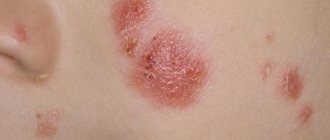
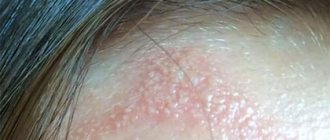
Redness, significant swelling and keratinization of the epidermis on the face indicate the development of the disease and can be observed on such areas of the face as the skin of the forehead and the area between the nose and upper lip, in the area of the eyebrows and hairline.
The difficulty in diagnosing lies in the fact that dead skin flakes from the scalp are mistaken for dandruff, so experts recommend that you definitely contact a dermatologist without self-medicating, because this can lead to the active development of infection and damage to a larger area of the epidermis.
Seborrheic warts
Most often, seborrheic keratosis occurs in older people. The harbinger of this disease is a yellow spot on the skin, on which a formation subsequently forms.
Typically, this growth appears on exposed parts of the body, including the arms, neck and face. The main reason for the development of seborrheic keratosis is excessive sunbathing.
According to experts, such plaques on the skin are benign formations. However, there is no need to worry that they will contribute to the development of skin cancer. Such protrusions are quite harmless.
Seborrheic warts are treated in different ways. Plaques are excised surgically, chemically and other methods. By the way, the removal of these formations is carried out only for aesthetic purposes. By themselves, they do not pose any danger to human life and health.
Medically known stages of psoriasis
The pathological process of hyperactivity of cells of the immune system, according to medical classification, leads to the development of the disease and can be determined at different stages, such as progress, stabilization and regression.
Having identified the causes of psoriasis on the face, you can begin to treat the disease at the first stage of progress, when plaques appear on the skin and the inflammatory process is actively proceeding, when stabilization, new lesions do not appear, and with regression, peeling of the skin and itching practically recede, without creating discomfort for the patient.
Senile keratoma
Just as in the previous case, such formations are characteristic of the body of elderly people who have long crossed the threshold of advanced age. Such plaques on the skin are benign. It should be noted that they are in many ways similar to seborrheic warts. Senile keratoma differs from the latter only in that it poses a threat to the patient’s health.
Doctors say that keratoma is an excellent springboard for the development of a precancerous skin condition. So how to get rid of this disease? Treatment of senile keratoma consists of its surgical removal and further prevention of the appearance of new formations. If any occur, they should also be removed using the method suggested by the specialist.
Xanthomatosis
The xanthomas themselves in this condition can have a different appearance, which largely depends on the reasons that led to the development of xanthomatosis. Thus, eruptive xanthomas are isolated, which are first red, then yellowish in color, but the purple rim remains around them for a long time. They have clear boundaries and a hemispherical shape. Tuberous xanthomas are characterized by a symmetrical formation, have a yellow or brown color and can reach quite large sizes - up to 2-3 centimeters. Flat xanthomas, detected in some types of xanthomatosis, are yellow spots or plaques that often appear on the palmar surfaces of the hand. Also, tendon xanthomas and xanthelasmas - fatty deposits on the eyelids - are sometimes classified into separate types.
The classification of a condition such as xanthomatosis is inextricably linked with types of lipid metabolism disorders. The type of such disorders depends on the nature of lipid formations on the skin and in other tissues, the age of their development, the clinical course and a number of other factors. All causes of hyperlipidemia leading to xanthomatosis are divided into two groups - primary and secondary. Primary ones, in turn, are divided into five varieties, which are characterized by pathologies of different parts of lipid metabolism:
- The first type
– in the blood there is a high level of triglycerides and chylomicrons. Xanthomatosis in this condition is represented by eruptive xanthomas, which can spread throughout the body, but their predominant localization is the buttocks and the flexor surfaces of the elbows and knees. A feature of this form of the disease is the spontaneous disappearance of lipid deposits on the skin with a decrease in triglyceride levels. This type of xanthomatosis most often affects children. - The second type
of hyperlipidemia is diagnosed with a simultaneous increase in the level of very low density lipoproteins and cholesterol. This xanthomatosis is mainly characterized by tendon xanthomas ranging in size from a few millimeters to 3-4 centimeters, but flat or tuberous skin deposits of lipids are also possible. Most often, this type of disease affects people over 20 years of age. - The third type
- with it, abnormal forms of lipoproteins (beta-lipoproteins) and high levels of triglycerides and cholesterol are observed in the blood. Xanthomatosis with this hyperlipoproteinemia is characterized by the development of flat xanthomas on the palms and upper extremities; tendon and eruptive accumulations of lipids are extremely rare. Can be diagnosed in people over 30 years of age. - The fourth type
of hyperlipidemia is characterized by very high levels of triglycerides and very low density lipoproteins against the background of normal cholesterol levels. With it, xanthomatosis develops in the form of eruptive and tuberous xanthomas of various localizations. The age of manifestation of skin manifestations is 30-40 years. - The fifth type
is diagnosed with high levels of chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins, as well as a high concentration of triglycerides. The clinical course of xanthomatosis characteristic of this condition is numerous eruptive xanthomas against the background of hepatosplenomegaly, heart defects and severe atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels.
Thus, if the cause of xanthomatosis is the primary form of hyperlipidemia, then by the nature of the rash, the age of the patient and other symptoms, its type can be approximately determined. With regard to secondary types of lipid metabolism disorders, such a clear relationship is not detected. The course of xanthomatosis depends on the severity of the lipid metabolism disorder and the reactivity of the body - the appearance of both single small xanthoma and multiple deposits of fat-like substances throughout the body with a diameter of up to 3-4 centimeters is possible. In the case of secondary xanthomatosis, the clinical picture of the disease is always supplemented by symptoms of the underlying pathology, which caused the failure of fat metabolism (diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis of the liver, and others).
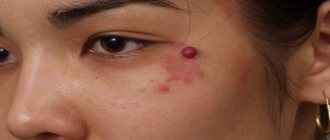
Xanthoma eyelids
Why do some people develop xanthelasma? Unfortunately, modern medicine has never found an answer to this question. It should be especially noted that ignorance of the causes of the development of eyelid xanthoma significantly complicates the implementation of preventive measures. However, experts have gone quite far in developing a treatment regimen for this formation. You can get rid of it in different ways, from surgical excision to exposure to laser beams or critical temperatures.
Speaking about xanthelasma, we cannot help but say that such formations most often appear in the fairer sex. They occur on the skin of the eyelids and quite strongly affect the self-esteem of women. That is why xanthoma removal is the main task for patients.
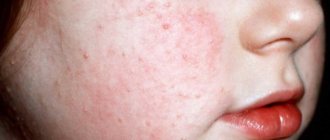
Factors of occurrence and causes of development of psoriasis
There is a complex of primary factors that determine a high probability of developing an unpleasant disease that is difficult to treat, these include genetic predisposition and the presence of a similar diagnosis in blood relatives.
In addition, the cause of the disease may be a previous infection of the epidermis or significant trauma to the skin and complex invasive intervention, an increased environment of stress and emotional distress, endocrine diseases and a certain hormonal imbalance.
Papillomas
What are brown plaques? The skin of many people is characterized by the development of so-called papillomas. Absolutely anyone, at any age, can encounter these formations. They appear especially often after prolonged sunbathing in a solarium or in the sun without the use of special creams that protect the epidermis.
Depending on the external characteristics, experts distinguish four types of papillomas:
- flat;
- on a pronounced “leg”;
- on a small “leg”;
- plaque papillomas.
The favorite places for such formations are exposed parts of the body that are most often exposed to sunlight (for example, arms, neck, face, back, shoulders).
Papilloma can be removed surgically, as well as with laser and other methods. However, doctors do not recommend doing this. If such a plaque does not cause discomfort, then it is better not to touch it. This is due to the fact that if excision is unsuccessful, it can transform into a malignant tumor.
Occupational therapy
Researchers have proposed a method for treating senile warts and age-related keratomas with increased doses of ascorbic acid. The drug is taken orally 0.5–1.5 g 3 times a day after meals. Ascorbic acid has antioxidant properties. The process of spreading and increasing the size of senile warts is stopped, but existing keratomas do not regress.
The doctor prescribes taking ascorbic acid for 1–2 months. Then you need to take a break for a month. In total, several courses of therapy will be required. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the body. If signs of intolerance or side effects appear, treatment with ascorbic acid should be discontinued.
You should definitely consult a doctor in the following cases:
- the keratoma is inflamed and bleeding;
- senile wart increases rapidly;
- signs of malignant degeneration appeared;
- there is a risk of damage in places of constant friction on the neck, waist, and armpits.
Dermatologists suggest lubricating senile warts (age-related keratomas) with hormonal ointments - Flucinar or Fluorocort. The products reduce the intensity of inflammation and improve skin condition. Hormonal drugs cannot be used for a long time - skin atrophy develops.
Ways to remove senile warts:
- cauterization with liquid nitrogen;
- electrocoagulation;
- laser therapy;
- surgical intervention (curettage).
Destruction of age-related keratomas - freezing with liquid nitrogen. It takes several sessions for a bubble to form under the keratoma. At the moment of freezing, only numbness is felt, pain appears during thawing. A senile wart dies and falls off, the skin heals without complications (a small scar remains).
White vitiligo
White patches on human skin are called vitiligo. They can cover almost the entire body. It should be noted that this formation is the only type of plaque that occurs symmetrically. If vitiligo has formed on one side of the body, then very soon it will appear on the other half of the body.
The main reason for the development of plaques of this kind is a failure in the production of melanin, that is, the substance that is responsible for the color of skin cells. Autoimmune diseases may be secondary causes of this disease.
Vitiligo can be treated, but with great difficulty. As a rule, for the treatment of this disease, drugs are used that increase the sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet rays, followed by irradiation with them.
Cure of this disease is completely impossible without eliminating the accompanying pathological conditions.
Clinical picture and diagnostic principles
Typically, tumor-like formations in atherosclerosis have typical manifestations and do not cause difficulties in diagnosis.
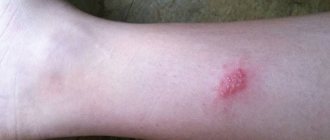
Cholesterol plaques develop most often on the face. Usually they are multiple in nature and appear as yellowish stripes of various sizes located on the eyelids, the skin of the inner and outer corners of the eyes. Such formations are called xanthelasma.
Xanthomas on the skin of the body can have various symptoms: the color of the formations varies from white-yellow to deep brown, the shape from flat to nodular, and the size from 1-2 millimeters to several centimeters. Often the plaque is surrounded by dry areas of healthy skin. Painlessness and a tendency to grow slowly are typical.
Plaques are less common on the legs than on the face and upper body. If the foot becomes the site of formation of cholesterol plaques, they are often injured, causing chronic, low-grade inflammation and discomfort during long walking.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of xanthomatosis is usually not difficult: an experienced doctor can assume the cholesterol nature of the plaque even during examination. In difficult cases, a biopsy is performed followed by morphological examination. Before starting treatment, it is important to determine the cause of the disease. To do this, a comprehensive examination of the body is carried out:
Laboratory tests:
- General clinical blood and urine tests;
- Biochemical blood test with determination of total protein, direct and indirect bilirubin, liver enzymes ACAT and ALAT, urea and creatinine, alpha-amylase;
- Determination of blood sugar;
- Blood lipidogram, including calculation of the concentration of total cholesterol, chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL, HDL, as well as the atherogenic coefficient;
- Genetic tests - according to indications;
- Instrumental examinations: Ultrasound of the liver.
Based on the results of the examination, complex therapy for the disease is carried out: treating only its individual symptom - a cosmetic defect on the skin - is ineffective.
The following factors contribute to an increase in low-density cholesterol:
- Eating fatty and difficult-to-digest foods in large quantities. These include fatty meats, baked goods made with low-grade fats, milk and milk products with a high percentage of fat content. In addition, when purchasing products, you should carefully study its composition indicated on the label. Coconut and palm oil are the main sources of LDL.
- Sedentary lifestyle. Physical activity helps to change the percentage of lipoproteins - the number of “good” lipoproteins increases, and LDL decreases.
- Overweight. Predisposes to an increase in the amount of low-density lipoproteins.
- Heredity and age. After 20 years of age, physiologically, the level of cholesterol in the blood gradually begins to increase, contrary to previous factors. Moreover, if a person is genetically predisposed to such diseases, then it is necessary to constantly monitor the level of cholesterol in the blood.