Causes of dermatitis in pregnant women
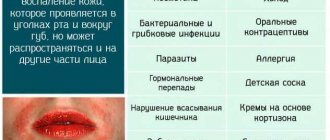
Dermatitis is usually called an inflammatory skin lesion that is formed under the influence of irritating factors of various nature. During pregnancy, hormonal, endocrinological, immunological, vascular and metabolic changes occur in the body. They are the ones that can influence the condition of the skin and be factors that provoke dermatitis.
The reasons for the awakening of symptoms of dermatitis during pregnancy are also considered:
- exposure to household, seasonal and other allergens;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- climatic conditions;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- toxicosis;
- “mother-fetus” conflict, or “Rh-conflict”.
Women with skin problems at the planning stage of pregnancy must undergo a consultation with a dermatologist.
Causes
Normally, human skin has protective functions, however, the period of bearing a child is almost always accompanied by a weakening of both local and general immunity. The female body becomes more susceptible to infections and external factors. The consequence of this condition can be inflammation of the skin. Most often, inflammatory processes are localized in the forehead and temples, on the neck, elbows and under the knees, in skin folds.
In addition to the weakening of general immunity, hormonal changes occur in a woman’s body. Increased production of estrogen, progesterone and cortisol suppresses the local immunity of the skin, resulting in the activation of opportunistic bacteria that are present on the skin of any person.
The main factors that provoke skin inflammation are:
- physical impact (excessive friction and pressure on the skin, clothing made of synthetic fabrics, solar radiation, high or low temperature);
- chemicals (household chemicals and personal care products, cosmetics);
- medications for topical use (for example, hormonal ointments and creams).
- The risk of developing pathology increases with constant nervous tension, frequent stress, physical fatigue, chronic bacterial or viral pathologies, and skin mycoses.
During pregnancy, dermatitis is often diagnosed in women who have a hereditary tendency to allergic reactions.
Physiological changes in the skin in pregnant women
A woman carrying a baby should be aware that there are physiological changes in the skin that do not require specific treatment. These include:
- erythema nodosum (inflammatory damage to blood vessels with the formation of nodes in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, localized on the extensor surfaces of the lower extremities);
- vascular network;
- melasma (dark brown spots on the face and neck);
- hyperpigmentation, which you can read about here;
- stretch marks (stretch marks);
- marble skin on legs.
Many women are bothered by itching, especially in the second trimester of pregnancy. More often it is localized in the abdomen and inner thighs. To exclude the presence of skin diseases, you should consult a dermatologist.
External description of dermatosis
One of the common signs of dermatosis is the appearance of dark pigment spots on the skin, which can be found in almost every pregnant woman. They can appear on any part of the body. Usually, the longer the period, the more visible these spots become. This manifestation is considered a normal condition of the body that is not subject to treatment.
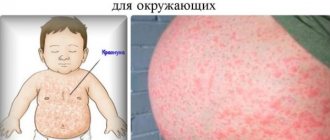
Manifestations of dermatosis can be in the form of:
- bubbles;
- ulcers;
- rash;
- crusts;
- warts;
- acne;
- eczema;
- itching.
Treatment of dermatitis in pregnant women
Dermatitis during pregnancy should be treated using gentle methods. A course of medication therapy is prescribed depending on the form and type of pathological condition, the severity of its course and the risk of developing negative consequences for the mother and fetus.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, dermatologists do not recommend the use of systemic (hormonal) drugs that can penetrate the placental barrier into the fetal blood. Complex treatment in this case looks like this:
- hypoallergenic diet (strict for 5-7 days, then expanding the list of products);
- antipruritic talkers;
- antihistamine creams and ointments;
- sorbents (activated carbon);
- moisturizing cosmetics;
- phototherapy.
IMPORTANT: it is strictly prohibited to use methotrexate, NSAIDs, systemic retinoids and corticosteroids during pregnancy.
Starting from the second trimester of pregnancy, in severe cases of dermatitis, the doctor may prescribe a course of oral medications. The most commonly used are antiallergic tablets "Cetirizine" - as prescribed by a doctor, sedative tinctures of valerian or motherwort, probiotics that restore the balance of microorganisms in the intestines, antibiotics (according to strict indications).
Most sensitive dermatitis is treated only with special creams and ointments. It is desirable that they be plant-based. Wundehil ointment for pregnant women, which contains several types of herbal tinctures, has a good therapeutic effect. Gistan and La-Cri creams help relieve inflammation and itching in dermatitis. You can learn about ointments for the treatment of hand dermatitis here.
IMPORTANT: hormonal ointments are used in exceptional cases under the strict supervision of a doctor. Self-medication with such means is not acceptable!
Possible complications
Allergic dermatitis causes severe, unbearable itching. A woman constantly scratches her skin, which leads to injury. Violation of the integrity of the skin leads to a decrease in its protective properties.
Pathogenic microorganisms enter abrasions and cause a fungal or microbial infection. Particularly dangerous is the bacterial infection that causes pyoderma. Purulent rashes appear on the skin, which form crusts after drying. This condition can cause general malaise and fever.
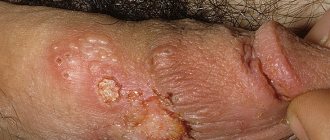
Viral lesions can trigger the appearance of herpes and conjunctivitis of the eyes. Vesicles appear on the skin, inside of which there is a clear liquid. Most often the face and mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, and eyes are affected.
Actions in case of exacerbation during pregnancy
From the moment of pregnancy, a woman should closely monitor her health and, when the first symptoms of dermatitis occur, seek professional help.
As soon as an exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease occurs, the following rules must be followed:
- create the correct hypoallergenic menu;
- give up decorative cosmetics;
- minimize the use of household chemicals;
- ensure a comfortable climate in the living space with mandatory daily wet cleaning;
- be less nervous.
During an exacerbation, you can use traditional medicine, for example, decoctions of oak bark, sea buckthorn or yarrow. Damaged skin can be lubricated with homemade ointments based on goose or rabbit fat with the addition of aloe juice, eucalyptus oil and sea buckthorn.
Additional treatments
The main rules are high-quality body care and hygiene using moisturizing creams.
To reduce itching, avoiding spicy foods and smoked foods, spices, as well as citrus fruits and chocolate can help.
Additional medications may be required to remove harmful substances and generally cleanse the body. One drug that is safe for the health and development of the fetus is Polysorb, which consists of silicon. It removes harmful substances naturally. It cannot be taken constantly, as it removes useful substances and vitamins from the body of a pregnant woman.
A decoction of chamomile and oak bark will help relieve itching. You should wipe the affected areas of the skin several times a day.
You should also avoid using cosmetics and deodorants. You can only use baby creams, moisturizers, or special ointments for pregnant women.
Komarovsky's opinion
Dr. Komarovsky advises first of all to understand the causes of dermatitis during pregnancy. If you find and exclude the allergen that causes unpleasant symptoms, then drug treatment will consist only of cleansing the body of toxic substances, nothing more. For this purpose, enterosorbents, probiotics and water (up to 2 liters per day) are used. When itching and flaking of the skin is severe, you can choose a special cream with a moisturizing effect. Domestic cream “D-Panthenol” or German “Bepanten” will do.
In severe situations, you cannot do without the use of medications. Dr. Komarovsky notes: all tablets must be safe for mother and baby. If the instructions contain the line “there is no data on possible embryotoxic, teratogenic and mutagenic effects on the fetus,” then it is better not to take such a drug.
Classification and characteristic symptoms
The manifestations of dermatitis during pregnancy are varied, but generally doctors adhere to the following classification:
Atopic dermatitis
The disease is hereditary and can appear in different trimesters of pregnancy.
If the mother had this type of allergy during pregnancy, there is almost a 100% chance that the child will inherit it.
Symptoms of the disease:
- peeling;
- rash;
- redness;
- swelling of the affected area;
- darkening of the skin around the eyes.
The disease manifests itself in mild, moderate and severe forms. In the mild stage, cure occurs after avoiding contact with the allergen. The average form requires cleansing the body with sorbents. Severe forms require drug therapy.
At each stage of development of the disease, manifestations have characteristics:
- First stage : symptoms are mild: mild itching, slight redness.
- Second stage : the rash spreads to large areas, starting from the abdomen. The itching intensifies, irritability and insomnia appear.
- Third stage : general intoxication of the body, nausea, and skin flushing are observed. At this stage, hospitalization of the pregnant woman, intensive care and monitoring of the condition of the fetus are necessary.
Polymorphic dermatitis
This form often develops in the third trimester. The reason is the rapid growth of the fetus. The stretched skin of the abdomen begins to become covered with red plaques of irregular shape.
Polymorphic dermatosis does not affect the condition of the fetus . After childbirth, the symptoms disappear on their own.
Perioral dermatitis
This type of allergy is characterized by watery growths on the skin, which a woman has to put up with. The use of antihistamines in the 1st and 2nd trimester is not permissible, so treatment is postponed until the end.
The causes of perioral dermatitis can be:
- fluoride toothpastes;
- intestinal diseases;
- hormonal ointments;
- fungus in hair follicles;
- cosmetics.
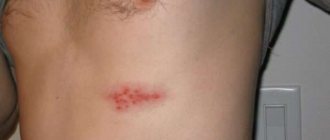
Contact
The provoking factor for inflammation in this form is contact with the skin of various materials.
The symptom of the disease is a rash of varying intensity and color. Sometimes real blisters form on the skin.
The following materials may cause a skin reaction:
- cosmetics;
- jewelry made of metal or plastic;
- household chemicals;
- paints, varnishes;
- synthetic fabrics.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Manifestations of allergies are localized in places where sebaceous glands accumulate . Early manifestations are itchy spots on the scalp, neck, behind the ears, and on the back. Then the inflammation moves to the face, the redness becomes covered with scales. The rash is covered with greasy scales. The hair in the plaque area is dull, brittle, and then begins to fall out.
Toxic erythrema
Dermatitis developing in the last trimester. Large, bright plaques appear in the abdominal area. The form does not affect the fetus and goes away on its own after birth.
Additional symptoms
Many forms of allergic dermatitis are associated with attempts to adapt the skin to new conditions.
At the same time, she reacts with the formation of the following symptoms:
- Stretch marks (striae or stripes).
- Papillomas are flesh-colored neoplasms that form in whole groups on the neck and under the armpits.
- Herpes - rashes on the lips and genitals.
- Prurigo (prurigo) is a neuroallergomatosis in the form of small nodules.
- Psoriasis is scaly rashes all over the body.
- Eczema - blisters that burst at the slightest touch.
- Hives are widespread redness and blisters throughout the body, starting in the lower abdomen.
Prevention
An important place is occupied by preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of allergic dermatitis.
Pregnant women need:
- Avoid eating fried, spicy and smoked foods.
- Avoid sauces, seafood, citrus fruits, and sweets.
- Avoid contact with allergens.
- Use only hypoallergenic cosmetics.
- Ventilate the room daily and regularly carry out wet cleaning.
- Do not stay under the scorching rays of the sun for a long time.
Diagnostics
Despite the pronounced clinical symptoms, making a correct diagnosis for dermatosis of pregnancy is often difficult due to the nonspecificity of the rashes, which can be observed in many skin diseases. The gestational origin of the pathology is supported by its occurrence during pregnancy, the absence of signs of microbial damage, the staged development of the elements of the rash, and their spread over the skin. In diagnostic terms, the most informative are:
- Determination of antibody content
. Atopic dermatitis is characterized by an increase in the content of IgE, a specific marker of allergic reactions. With herpes in pregnant women, the content of IgG4 antibodies increases in the blood of patients; in all patients, direct immunofluorescence determines the deposition of complement 3 along the basement membrane, which is sometimes combined with the deposition of IgG. Using ELISA, anti-collagen antibodies characteristic of pemphigoid are detected. - Skin biopsy examination
. The results of histological studies are more indicative of pemphigoid and polymorphic dermatoses. In both cases, swelling of the dermis and perivascular inflammation with tissue infiltration by lymphocytes, eosinophils, and histiocytes are observed. For herpes of pregnant women, subepidermal blisters are pathognomonic, for polymorphic dermatosis - epidermal spongiosis. Pathohistological changes in atopic dermatitis and itching of pregnancy are less specific. - Blood chemistry
. The standard method for diagnosing obstetric cholestasis is the study of pigment metabolism. Due to the impaired outflow of bile, a high level of bile acids is determined in the blood. In 10-20% of pregnant women with severe dermatosis, the bilirubin content increases. In 70% of cases, the activity of liver enzymes increases, especially ALT and AST. In other gestational dermatoses, biochemical blood parameters are usually not affected.
To exclude bacterial and fungal infections, it is recommended to culture the scraping or discharge of the rash for microflora and fluorescent diagnostics. Differential diagnosis is carried out between different types of gestational dermatoses, excluding scabies, drug toxicoderma, diffuse neurodermatitis, Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis, seborrhea, acne, microbial folliculitis, eczema, hepatitis and other liver diseases. A dermatologist is involved in examining the patient; if indicated, an infectious disease specialist, a neurologist, a gastroenterologist, a hepatologist, and a toxicologist.
Urgent help
Self-medication is contraindicated for allergic dermatitis. But before visiting a doctor, a woman can give herself first aid.
The following rules must be adhered to:
- avoid contact with the allergen;
- take Activated carbon;
- rinse the rash areas with running water;
- apply alcohol wipes to areas of inflammation;
- take an antihistamine.