Condylomas of the vulva – neoplasms of a benign nature, localized on the labia.
Often combined with the same manifestations in adjacent areas (inguinal folds, perianal area).
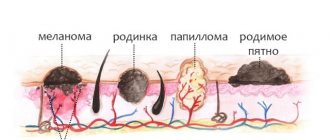
Often condylomas are called warts or papillomas, although there are differences between these concepts.
- A wart is a collective concept for any growths that rise above the surface of the skin.
- Papilloma is a viral neoplasm that appears on any part of the body with the exception of the mucous membranes of the genital organs. The color of the papilloma either does not differ from the area of the skin on which it is located or more often acquires pigmentation from light pink to dark brown. Also, hair can grow on the body of papillomas, and this should not be regarded as a pathology. The shape of papillomas is usually oval or round, the surface is smooth. They rarely become inflamed, but can become injured and bleed due to sudden mechanical damage.
- Condylomas are neoplasms of a viral nature located on the mucous membranes of the urogenital zone, as well as in folds of the skin subject to constant friction with clothing.
Condylomas can be pointed or broad.
Wide ones are more often a manifestation of a syphilitic infection, and genital warts of the vulva and perianal zone are a sign of a viral infection.
Vulvar condylomas in women are formations with irregular outlines on a wide, but most often thin, stalk.
They are flesh-colored and arranged singly or in clusters.
Prone to merging and forming irregularly shaped conglomerates.
The appearance of such formations is often compared to cauliflower.
Treatment and removal of vulvar condylomas
The appearance of condylomas serves as a signal for the development of pathology.
This fact is not ignored.
In addition to surgical removal, it is imperative to undergo a course of antiviral therapy.
Currently, it is impossible to completely get rid of HPV.
But the transfer of HPV into a latent course will prevent the formation of new elements.
Surgical removal occurs using different methods:
- cryodestruction (condyloma is “frozen” with liquid nitrogen and then removed);
- electrocoagulation (condyloma is removed with electric current);
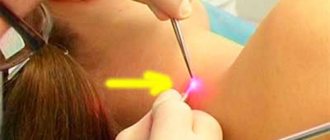
- laser removal (a modern method based on the use of laser technology);
- radio wave removal;
- treatment with special chemicals (condylomas become necrotic and rejected);
- interferon therapy (they are treated with a special drug to increase the human body’s resistance to HPV, and after some time they self-destruct).
These are quite effective methods.
But in order to prevent relapses of condylomas, it is important to adhere to preventive measures and improve your sexual contacts.
Prevention consists of:
- safe sex with a condom;
- the right foods (diet), fruits and vitamin supplements to strengthen the immune system;
- giving up alcoholic beverages and tobacco products;
- regular examinations by a gynecologist;
- annual testing for HIV infection and syphilis (even in the absence of symptoms);
- baths for the vulva with decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, echinacea, calendula, etc.).
Such prevention eliminates the recurrence of condylomas.
Patient reviews
She removed condyloma from the vagina using a special Surgitron device. I had one session and the tumors disappeared. She underwent the procedure without complications and experienced no pain. There is no relapse.
Alena, 27 years old
During the next gynecological examination, they found condylomas in my vagina. The doctor advised to get rid of them with a laser. I was given anesthesia first, so I didn’t feel any pain. There was no relapse after the operation.
Oksana, 32 years old
When registering for pregnancy, I was diagnosed with condylomas in the vagina.
The doctor advised them to be removed after childbirth. Due to changes in hormonal levels, the tumors began to increase in size, so I was scheduled for surgery to remove them immediately after the birth of the baby. With the help of a laser, I quickly got rid of vaginal discomfort. Irina, 36 years old
Comparison of methods for removing vulvar warts
Unfortunately, at the moment, there is no absolutely relapse-free method of removal.
Each method has its own disadvantages and advantages.
Which method will be most effective in a particular case is determined by the type of condylomas, their number, medical experience in this field of activity and the patient’s preferences.
But, first of all, it is necessary to take into account the localization and accessibility of the rash.
It is this parameter that determines the choice of removal technique.
The highest efficiency from the use of electrocoagulation and radio wave methods is ninety-ninety-five percent.
The cryodestructive method has about eighty-five percent.
Laser removal has about seventy percent.
Relapses most often occur after laser removal - from twenty-three to fifty-two percent.
After cryodestruction - from twenty-five to forty.
The radio wave method gives figures from twenty to twenty-five percent of cases.
And the best results for the electrocoagulation method are from nineteen to twenty-four percent.
Surgical removal is only a symptomatic treatment; the reason for their appearance is HPV remains.
Therefore, the possibility of condylomas reappearing always remains.
We must always remember this and strive to transfer HPV into a latent existence.
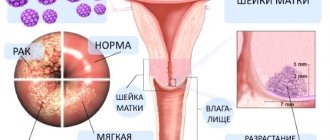
Vulvar condylomas: differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of vulvar condylomas caused by HPV disease is carried out with:
- syphilitic condylomas lata;
- molluscum contagiosum;
- bowenoid papulosis;
- angiokeratoacanthoma;
- lichen planus;
- soft fibroma;
- pilar cyst;
- folliculitis;
- psoriasis;
- malignant neoplasms and the like.
An experienced doctor will always make the correct differential diagnosis.
Based on objective data and laboratory data, he will diagnose condylomas caused by HPV.
Difficulties with diagnosis arise if there is a concomitant pathology with HPV.
Then the symptoms of one disease overlap with another.
The state of a woman’s immunity is always diagnosed, and according to indications, immunocorrective therapy and additional examination are performed.
If there is a suspicion of oncopathology and degeneration of condylomas, then a biopsy is taken and all the necessary cytological studies are carried out.
There is no need to do an HPV test just like that, without the need.
A study involving taking material for a biopsy is important if the condylomas are pigmented and have an atypical appearance.
If they constantly recur after removal, if the treatment is ineffective and the clinical picture worsens.
If difficulties arise in diagnosis, ulceration and necrosis.
Diagnosis of vulvar condylomas is carried out visually, by palpation and using colposcopy and urethroscopy.
Additionally, according to indications, anoscopy is performed.
Types of formations
Externally, condylomas resemble warts; the area of one lesion can reach 3 cm. Growths can occur in any part of the vulva.
Condylomas can be divided into 2 main types :
- Exophytic or pointed - visually look like cone-shaped elevations above the surface of the epithelium. They have a pinkish or flesh color. At first, a single growth appears, then during the development process whole groups are formed, merging with each other. A characteristic feature is that condylomas in the group are almost the same size. The location of genital warts is the vulva, cervix, urethra.
- Endophytic or wide e - clearly differ from pointed neoplasms, since they have a wide flat base. In this case, the lesion itself does not protrude from the outside, but grows inside the tissue. Although when the lesions merge, the picture resembles genital warts. As a rule, condylomas lata are observed in the vaginal area; after some time they can spread inside, provoking the development of malignant processes in the cervix. The main danger is that a routine gynecological examination is not always able to detect such neoplasms. In addition, the appearance and growth of endophytic condylomas is a clear indication of secondary syphilis.
Vulvar condylomas: incubation period and HPV infection
The average incubation period for HPV is about three months.
But sometimes from two to three weeks to several years.
HPV is an STI, so the main route of infection with the virus is sexual contact.
Moreover, not only genital, but anal and anal contacts pose a danger.
Using a condom does not provide any particular advantage in terms of infection.
You can also become infected when using it.
The mother's birth canal can pose a risk of infection to the baby.
But good immune defense can help him avoid getting infected.
You can also become infected through handshakes and kisses.
The risk of intra-family infection is especially high.
And finally, the fourth method is self-infection.
When shaving or hair removal is a way of transferring HPV from one area of the body to another.
Anyone at any age can become infected.
But the better your immune defense, the less likely you are to get HPV.
In terms of frequency of infection, HPV is a more common variant of infection than other viral STIs, such as HIV infection and herpes infection.
The prevalence of HPV is very high.
Almost all sexually active men and women have it.
Epidemiology
Pointed condylomatosis is an infectious viral disease
Pointed condylomatosis is an infectious viral disease found in venereological clinics, 3 times less often than gonorrhea in both sexes, but 9 times more often in men and 25 times more often in women than infectious syphilis. Consequently, genital warts are one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases characterized by ulceration or tumorous manifestations. Statistically in our country, condylomatosis acuminata is not taken into account, and therefore its distribution among the population can only be judged by relative data. The disease is diagnosed most often at the age of 20-25 years (from 52 to 54.8 percent). at the age of 26-30 years (from 9.7 to 12.3 percent). less often at the age of 13-19 years (about 10 percent) and 15-17 years (from 5.3 to 7.9 percent). However, the disease is possible in early childhood and old age. It is more common among prostitutes and women who have had a large number of sexual partners.
The causative agent of genital condylomatosis is a filterable virus from a group of viruses that are morphologically identical to one of them that causes the development of warts on the skin, but differs from it in antigenic composition.
The disease is contagious, and eutoinoculation is often observed. The development of genital warts is promoted by various local irritants, heat, moisture, and skin maceration. A combined disease is often observed, or rather the development of condylomas in patients with sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and others) and accompanied by copious discharge from the urethra, cervix, vagina, rectum. I believe that genital warts develop more often in women, especially during pregnancy, and in case of poor hygiene of the genital organs (accumulation of smegma in men, contact of genital discharge on the surrounding skin in women), and with existing immune disorders.
What tests are taken for vulvar condylomas?
It is important for women to undergo a genetic analysis of condylomas, which allows them to assess the possibility of malignancy.
Often, emerging vulvar condylomas threaten to degenerate into malignant neoplasms.
For any symptoms, when condylomas appear, you need to submit biomaterial and be tested for the presence of HPV.
It is necessary to determine not just the presence of HPV in the body, but the degree of danger of a given HPV strain in relation to the treatment of condylomas in oncopathology.
When pregnancy is planned, there is infertility, pregnancy ends in miscarriages and pathology during pregnancy, HPV tests are also necessary.
It is necessary to screen the woman’s sexual partner for the presence of HPV.
Because they probably have unprotected sex.
And with the high contagiousness of HPV, the sexual partner is most likely also infected.
The biomaterial for the study is cells obtained from condylomas.
In addition to the fact of the presence of HPV in the body and its strain, they evaluate what the virus has already done and the degree of its oncogenicity.
To conduct a cytological examination, epithelial cells of condylomas are examined microscopically.
If the cells have changed, this indicates the presence of HPV in the body.
The survey is simple and cheap, but has a low degree of accuracy.
The result of the study will be ready in about a week.
In the form of a digital code.
If it is one, then there is no HPV.
Two – there are cells characteristic of the inflammatory process.
Three – questionable results, additional analysis is required.
Four or five indicates the presence of cells affected by HPV.
In addition to this method, a histological analysis of the biopsy specimen is performed.
It is used to determine the degree of malignancy of condyloma.
The analysis period is three days.
If everything is done correctly, then the PCR method, with an almost one hundred percent guarantee, can detect the DNA of the human papillomavirus.
The result is ready in one to two days, sometimes within five hours.
Sometimes, if condylomas are present, the virus is no longer in the blood.
This is possible if the immune system has strengthened and suppressed HPV in the body.
But condylomas still need to be removed surgically.
Why are genital warts dangerous?
Genital warts are dangerous because they are easily transmitted to a sexual partner. Moreover, endophytic formations contain the causative agent of syphilis in large quantities, and even protected sex can cause infection.
Pointed formations are not so dangerous in this regard. Infection occurs only when the virus reaches the surface of the skin; during other periods, the risk of transmission is minimal. On the other hand, a man can be the primary source of infection for a woman who has genital warts. Therefore, both partners should undergo diagnostics.
Most often, the development and growth of genital warts of the vulva occurs in combination with inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, for example, inflammation of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, endometrium, urethra, and bladder.
Very often, these diseases have a chronic course and subtle symptoms, so specialists do not prescribe a number of necessary medications. In 9 out of 10 cases, vulvar condylomas are diagnosed along with ureaplasma, mycoplasma, chlamydia, candidiasis, herpes, cytomegalovirus infection, and vaginal dysbiosis.
HIV infection and condylomas
Among people living with HIV, HPV is the most common STI.
HIV-infected women are characterized by the presence of multiple genital warts.
There is also a recurrent course of HPV disease, when the immunoregulatory index and the level of CD4 cells sharply decrease.
When affected by HIV infection, the addition of other infections, including HPV, increases significantly.
If immunodeficiency increases, then there are more condylomas, they are larger, merging, and HPV is difficult to treat.
Intraepithelial neoplasia increases against the background of HIV infection.
In general, the combination of HIV infection and human papillomavirus is very difficult to cure and requires constant monitoring and observation.
Control observation
Patients with genital condylomas are subject to constant dispensary observation during treatment.
Patients with genital condylomas are subject to constant dispensary observation during treatment. Attention is paid to the general well-being of the patient, the response to treatment in the foci of the disease and the dynamics of regression of genital warts. If necessary, the drug, treatment method is changed, or gentle anti-irritation therapy is added, i.e. In each specific case, the approach is individual, in compliance with the principle of “do no harm.” Clinical observation is also necessary in order to prevent relapse of the disease in time and not to miss tumor metaplasia of giant condylomas.
Complications in the presence of condylomas on the vulva
Some people think that condylomas are harmless.
But their presence leads to various complications:
- bleeding from condylomas due to trauma from underwear, which leads to pain, discomfort and secondary infection in the wound surface of condylomas;
- spread of condylomas from the vulva, to the uterus and vagina;
- malignancy of condylomas;
- decreased quality of life and negative impact on the body;
- with sexual intercourse unprotected by a condom, HPV is highly contagious.
Removing condylomas and eliminating the causes that caused them, as well as strengthening the immune system, helps in overcoming such complications.
Diagnostic measures
In normal conditions, in the absence of secondary infection, making an accurate diagnosis is not particularly difficult, but it is important to remember that vegetative papules (extended condylomas) have a wide base and a dense elastic consistency; in secret, many white treponemes are revealed.
It is much more difficult to determine the diagnosis when two types of condylomas form on the vulva and vagina: genital and broad. Diagnostic measures to identify the spirochete and other symptoms of syphilis with the diagnosis of RSC will help to accurately determine the disease.
Daijin test for vulvar condylomas
The Daijin test is used to identify the human papillomavirus and determine its type:
- Whether HPV belongs to high-oncogenic or low-oncogenic.
- Fixation of clinically significant concentrations of the virus in body tissues.
Technologically, the test is related to the hybridization effect.
When an RNA probe binds to human papillomavirus DNA.
Subsequently, monoclonal antibodies bind the resulting hybrid, and these antibodies are enzymatically labeled.
The daijin test ends with chemiluminescence (registration of the intensity of the light flux from the test sample).
To conduct the Daijin test, various biomaterials are used.
Prevention
Personal prevention consists of hygienic maintenance of the skin and mucous membranes of the genitourinary organs, careful treatment of the disease, abstinence from sexual intercourse until complete recovery and termination of dispensary observation. Treatment of diseases that promote or create conditions for its development is of great preventive importance.
Public prevention consists of timely identification, examination, if necessary, and treatment of partners who have had sexual intercourse with the patient after his contact with the source of infection, as well as identification of patients with genital condylomatosis during all types of preventive medical examinations.
Sources:
- https://medportal.ru/enc/venerology/condyloma/
- https://www.womenhealthnet.ru/gynaecological-disorders/7143.html
- https://www.goodoktor.ru/21.html
- https://ilive.com.ua/health/kondilomatoz_107006i15954.html
- https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_venereology/condyloma
Drugs and treatment regimen for vulvar condylomatosis
The goals of treatment are aimed at eliminating the clinical picture of HPV, since HPV remains in the body forever.
Today it is impossible to completely get rid of the presence of HPV in the body.
If treatment is not carried out, the condylomas either do not grow or progress.
If there are other STIs in a woman’s body, then the clinical manifestations of HPV are treated over a three times longer period.
Modern therapy does not have antiviral drugs with a specific effect on HPV.
The drugs that successfully treat herpes simplex (acyclovir and ganciclovir) have no place for the treatment of HPV - they are ineffective.
Vaccination is considered the ideal method for treating and preventing condylomas.
Local treatment is effective with imiquimod ointment or an aqueous solution of solcoderm.
General treatment with the immunomodulator isoprinosine.
It is also treated locally with cytotoxic drugs (podophyllin, podophyllotoxin, 5-fluorouracil).
They are applied in the form of a solution or cream directly to the condylomas.
There is an integrated approach to the treatment of condylomatosis.
Along with the tableted drug for general use, Yodantipirin, destruction of condylomas is used topically (solkovagin or solcoderm is used).
Genferon suppositories are administered intravaginally or into the rectum for about ten days.
According to the experience of use, epithelization at the site of removed condylomas is completed by the fourth day.
No pain.
Follow-up examinations fifteen, thirty, forty-one and seventy-five days later, as well as six and nine months after the treatment measures, showed no relapses.
That is, the condylomas no longer grew.
Thirty and seventy-five days after treatment, PCR showed no active HPV in the body.
Vulvar condylomas: immunological treatment and immunogram
HPV is always present in the cells of epithelial tissue, and the destruction of condylomas does not exclude their recurrence.
Therefore, the immunological agent interferon can be used for monotherapy and for complex treatment.
Interferon is an endogenous cytokine that has antiviral, antiproliferative and immunomodulatory effects.
IF inducers have shown effectiveness in treatment.
In total, three types of interferon are used - leukocyte content (L-IF), fibroblast - F-IF and T-lymphocyte - T-IF.
The most effective action among all interferons (various methods, schemes and doses of application) is L-IF (leukocyte) interferon.
Interferon has a local, intralesional and systemic method of application.
It has been noticed that when interferons are used in treated women, the level of viral DNA decreases.
PCR shows these results.
And this is combined with an improvement in the clinical picture.
Unsystematic use of interferon leads to relapse.
If treatment is carried out according to a specific algorithm that takes into account all important parameters, then relapses are reduced, up to their complete absence.
Since HPV causes a decrease in immunity (immunosuppressive state), it is very important to know what form the immune system is in.
For this purpose an immunogram is done.
Histological examination and biopsy of vulvar condylomas
Histological examination and biopsy for vulvar condylomas are mandatory if the HPV type is oncogenic and there is a high risk of malignancy of condylomas.
The occurrence of vulvar cancer is influenced by:
- the presence of early sexual intercourse, especially if there are many partners, and numerous abortions;
- smoking;
- presence of other STIs;
- presence of occupational hazards;
- presence of immunodeficiency states;
- presence of obesity and diabetes;
- presence of family predisposition;
- presence of chronic vulvitis;
- presence of leukoplakia;
- the presence of condylomas and warty growths in the vulva area;
- presence of high fertility.
Malignant neoplasms are also treated using a combined method (a combination of surgical treatment and radiation therapy).
Symptoms of the disease
Papillomas in women are most often located on the external genitalia. When there is a large accumulation of them, they can resemble the comb of a rooster. If women have genital warts in the groin, they can be distinguished by their long stalk. Due to increased humidity and sweating, papillomas in the groin are injured and can become inflamed.
The most dangerous are flat condylomas in intimate places. They are provoked by genotypes of high oncogenic risk. Such a papilloma on the labia slightly rises above the mucous membranes and rarely merges with the rest into large formations. They are quite difficult to notice when they first appear.
Women with HPV may experience the following symptoms:
- Pain and itching in the genital area.
- Nonspecific vaginal discharge.
- The labia are slightly swollen.
- Irregularities and small compactions in the intimate area.
New growths may appear on the pubic area and other areas. Papillomas of the vulva and vagina are observed quite often. Regardless of their location, mandatory removal is required.
When condylomas form on the cervix, the following symptoms occur:
- Pain of unknown origin in the lower abdomen.
- Bloody issues.
- Weight loss and loss of appetite.
- Discomfort and pain during sex.
With these symptoms, a mandatory colcoscopy is required to rule out a precancerous condition, and if so, begin timely treatment. In this case, it is impossible to diagnose the disease yourself.