In most cases, boils in children appear due to weakened immunity. It appears to be a purulent abscess that occurs as a result of inflammation of the hair follicles, sebaceous glands and connective tissue. The occurrence of such a disease brings a lot of inconvenience to the child.
A boil in a child occurs due to a decrease in immunity
A single inflammation can be easily removed at home, but if a large area of skin is affected, full treatment will be required. The appearance of a large number of ulcers indicates the development of a disease such as furunculosis. Let's look at the causes and treatment of this disease.
Causes
Furunculosis in children can occur due to a variety of factors:
- regular contamination of the skin;
- small wounds caused by an abrasion, splinter, scrape or scratching;
- constant consumption of unhealthy food or lack of vitamins;
- decreased immune system;
- frequent sweating;
- metabolic disease;
- air pollution;
- strong change in body temperature;
- infectious diseases;
- stressful situations.
A boil can also appear in an infant when proper skin care and personal hygiene are not observed. People with diabetes and problems with the endocrine system are also prone to this disease.
A long course of taking glucocorticosteroid medications and severe diseases can also trigger the appearance of a boil.
Children often develop boils in their noses because they pick at them with dirty hands and often have a runny nose.
When you find a boil on a child’s body, you should think about what could have caused it. This will allow you to quickly recover from the disease and prevent its recurrence.
Ulcers can appear in different forms, and it is not always clear whether it is furunculosis or not. If the inflammation becomes larger, you should consult a doctor immediately. Home treatment is possible only if there is only a single abscess on the child’s body. If there is a large accumulation of them, you cannot self-medicate.
Stress in a child can cause boils
A boil is very similar to a regular pimple. Therefore, parents do not always attach special importance to it and do not provide any treatment. It seems to them that such an abscess will soon go away on its own. But as a result, complications arise that can lead to sepsis.
Therefore, it is very important to know what characteristic symptoms a boil has:
- a single pustule appears on the skin (it is elevated above the skin and has a bright red halo around the abscess, which is a dense rod);
- after 3-4 days a white spot appears on the top (this indicates the formation of pus);
- the maturation of the abscess is quite painful;
- itching and tingling appear at the site of the pimple;
- temperature rise to 39°C;
- lethargy and moodiness appear, the baby begins to sleep and eat poorly;
- the lymph nodes located near the abscess gradually increase in size.
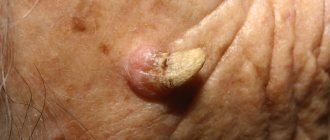
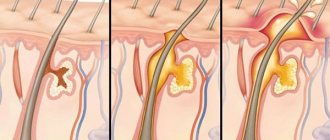
A boil can appear in any part of the skin where hair is present. It takes about 10 days for it to fully mature and disappear. From a medical point of view, the entire process from onset to healing is divided into several stages:
- Infiltration. The process of swelling and compaction.
- Necrosis. Increased intoxication, a rod begins to form.
- Healing. After ripening, the pus comes out and a scar with granulation tissue remains. The inflamed tissue begins to turn pale and slightly blue.
A furuncle differs from acne in its long and painful gestation period. Not every inflammatory process can go away on its own. In order not to cause discomfort to the child and prevent furunculosis from developing, he must be shown to a specialist and, if necessary, all treatment must be performed. The treatment course should be prescribed based on the results of appropriate diagnostics.
A boil can cause a fever
Signs and stages
Without knowing how a boil develops, it can easily be confused with an ordinary pimple. In this case, parents do not carry out treatment, exposing the baby to the risk of all sorts of complications.
You can recognize a boil in children by the following signs:
- a future boil always forms around the hair follicle;
- the localization site is red and painful;
- upon palpation, a rather dense node (infiltrate) is felt;
- possible increase in temperature (up to 38-39 degrees);
- the affected area itches and a tingling sensation is felt.
These are common symptoms of the initial stage of the disease (infiltrative), which cannot be ignored. Next comes the second stage of development of the boil - purulent-necrotic masses are formed:
- inflammation spreads to surrounding tissues, sebaceous glands;
- the size of the abscess increases and can reach 5 cm;
- yellow-green masses are visible in the center of the pustule;
- melting of the boil tissue is observed - fistula openings appear.
Such symptoms indicate that the boil is ready for self-cleaning - this is the third stage - opening of the abscess and its healing:
- the thin skin on the surface of the boil bursts;
- purulent exudate comes out;
- Inside the opened ulcer, necrotic masses (the core of the abscess) are visible - do not try to squeeze it out, it will come off on its own.
After cleansing, the cavity is filled with granulations - the wound healing process begins. At first, the affected tissues acquire a purplish-blue tint, but over time they lighten, leaving an inconspicuous scar.
From the appearance of the first symptoms to the opening of a boil in a child (as well as in an adult), 7-10 days pass, sometimes longer.
A boil must necessarily go through all three stages of development - infiltrative, purulent and restorative. Never open an abscess yourself, especially prematurely, the consequences can be disastrous.
Treatment of boils
It is very easy and simple to cure a single boil in a child at home. But if the source of inflammation is very deep or it is in a hard-to-reach place or is located on the face, then you should definitely consult an experienced surgeon.
And also, you should not put off going to the doctor if the boil has formed on a moving part of the body. Indeed, in this case it will be constantly exposed to external influences. For example, a boil on the leg, namely on the knee, will cause a serious problem for a baby under one year old. After all, it is at this age that they actively begin to crawl, and there is a high probability of contamination of the source of inflammation.
When treating a boil yourself, you should first of all use means that will provoke a breakthrough in the release of pus. Compresses are used for this. They perform an anti-inflammatory function and draw out pus.
Ichthyol ointment, Vishnevsky balm, aloe pulp and crushed leaves of golden mustache help a lot. Any of these products are applied to a cotton pad, applied to the inflamed area and secured with a bandage or plaster. When using a bandage, do not bandage it too tightly. Such a bandage will not allow the pus to come out and will only worsen the situation.
This compress lasts about 4–6 hours and then is removed. The next procedure is possible only after 4 hours, because the skin needs to rest. You can constantly apply one product or alternate several. Vishnevsky balm with aloe juice helps very well.
As soon as the boil has fully matured and a tear appears, it should be carefully squeezed out. Squeezing should be done slowly and thoroughly until all the pus is removed. After this, hydrogen peroxide is poured into the wound and everything is washed thoroughly. Next, the cavity is filled with Levomekolev ointment and closed with a bandage. Dressing must be done every 4-5 hours until the wound is completely healed.
Golden mustache is used for compresses
Risk areas
Since staphylococcus enters the body through small wounds on the skin, the arms, legs and face of the little man are at risk. It is especially dangerous when a boil forms on a child’s face, under the arms, between the buttocks or in the eye. When a boil occurs in a child’s nose, there is a risk of contracting a purulent infection of the brain - the blood supply arteries to the face and brain are closely connected and, if treated incorrectly, the pus and blood will quickly spread throughout the body. This causes:
- blindness;
- meningitis;
- sepsis.
Treatment of furunculosis using folk remedies
Treatment of furunculosis in children should begin from the inside. First you need to plan a balanced diet. Be sure to remove sweets, baked goods, fatty foods, smoked foods and milk from the menu. And also, there is no need to stuff your child with immunomodulators and other vitamin and mineral complexes.
Folk remedies will help you cope with furunculosis. Brewer's yeast is very popular. They are sold in pharmacies and are available to everyone . This product normalizes intestinal microflora and improves skin condition. It can cope not only with furunculosis, but also with acne. Birch tar also helps get rid of the disease. It has antibacterial functions. It is able to cleanse the blood of harmful bacteria and stop the development of the disease.
But still, you should not self-medicate for furunculosis; it is better to consult a specialist. The hospital will conduct a full comprehensive examination, identify the cause of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. In some cases, a blood purification procedure is required.
Brewer's yeast perfectly restores the body
Which doctor should I contact?
If a boil appears in a child, it is best to consult a dermatologist. After examination, a small patient may be referred for treatment to a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, hematologist, infectious disease specialist, or immunologist. A cosmetologist will help eliminate the consequences of furunculosis. A nutritionist will tell you about the nutritional characteristics of this disease. In some cases, the help of a surgeon is required.
Furuncle on the face
The most common and most dangerous is the appearance of a boil on the eye. This inflammatory process is often called barley. It is a hard-type elevation that looks like a pimple.
Boils on the eye ripen very quickly, so there is a high probability of an increase in temperature. In the initial stages, an unpleasant burning or itching may occur. After this, a slight swelling appears, accompanied by pain.
It is necessary to treat such a disease as soon as swelling appears. In this case, the treatment will be less painful and will not provoke negative consequences.
There are simple recommendations that should be followed when treating a boil on the eye:
- complete cessation of the use of cosmetics and contact lenses;
- A bag of brewed tea can help relieve swelling, but it will only help if the cause of its occurrence is not an infection;
- Along with the prescribed course of treatment, you can make compresses from calendula decoction.
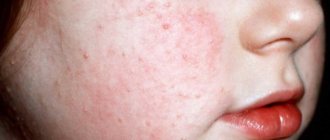
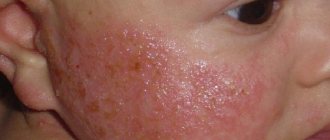
Very often a boil can be found on the cheek. In this case, it is very often confused with a simple pimple. As a result, they squeeze out and introduce an infection, which provokes a severe inflammatory process.
To reduce inflammation on the cheek and speed up the maturation of the boil, you can wipe it daily with medical alcohol or calendula tincture. But do not put too much pressure on the inflamed area.
There is no need to start a boil on your cheek, otherwise it may leave an ugly scar.
Calendula in the form of a tincture is used to wipe an abscess
Prevention
To prevent your child from developing a boil, you should follow some preventive measures:
- The diet should not contain a lot of sweets and fatty foods. It is desirable that the menu include more dark green vegetables.
- A child needs a daily dose of vitamin C and the entire group of B vitamins. A sufficient amount of these substances is contained in rose hips and citrus fruits. If a child is sick, it is advisable to give him rosehip tincture 3-4 times a day. After all, in a weakened body there is a high probability of a boil appearing.
- Constant personal hygiene. Your child's skin should always be clean. It is worth explaining to him that you cannot touch your skin with dirty hands.
- Any wounds, scratches, or bites should be immediately treated with an alcohol solution, iodine or brilliant green.
If a course of treatment has already been prescribed by a doctor, then it is advisable to include iron intake in it. This microelement will block the further spread of the inflammatory process.
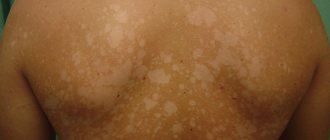
A furuncle or boil is an acute inflammatory process of the hair follicle and surrounding tissues, usually occupying a wide area. In appearance, a boil differs from a regular pimple in that the area of skin 1-4 cm above it first turns red, after which it becomes dark burgundy or even bluish in color. The so-called purulent plug rises above the inflamed tissue, and a rod may also be visible.
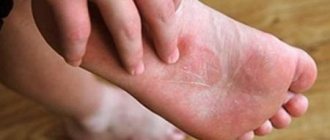
A boil in a child can appear on absolutely any part of the body, except for parts devoid of hair (palms and feet).
It is impossible to single out one specific reason for the appearance of boils in children. Furunculosis is usually accompanied by many different factors, such as:
- weakened immune system;
- improper skin care or non-compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- constantly contaminated skin;
- increased sweating;
- seborrhea;
- disruption of the body's metabolic processes;
- Staphylococcus aureus or white;
- scratches, abrasions or any other microtraumas on the skin;
- avitaminosis;
- diabetes;
- hair ingrown into the skin;
- suffered serious illnesses (pneumonia, tonsillitis, bronchitis, etc.)
- stress, etc.
If a boil appears in a seemingly healthy child, then it is worth considering what the cause of its occurrence was, in order to quickly treat it and minimize the risk of recurrence. Usually, if there is a microtrauma on the body, then an infection (usually staphylococcus) penetrates through it and then multiplies there. After which purulent inflammation appears, affecting the hair follicle and the tissues adjacent to it.
Staphylococcus causes furunculosis in children with weak immunity and skin injuries. Typically, staphylococcus does not cause serious problems, since the body’s defenses fight it, but if the factors listed above are observed, the infection causes a boil.
It is necessary to carefully care for the child’s skin so as not to injure it.
The question of how to treat a boil worries many mothers. First of all, treatment of a boil can be divided into conservative treatment and treatment of the abscess itself, which should be selected by a highly qualified doctor. Because it will determine the general condition of the child, at what stage of maturation the boil is located and what type of treatment is suitable.
If several boils appear at once, the child’s temperature may even rise to 39°C, then it is necessary to give an antipyretic.
It is worth remembering that under no circumstances should you squeeze the boil, as this can cause quite serious complications. At first, the reddened area around the boil is quite hard, sometimes even hot, after which it becomes softer.
If a boil appears on the face, then it should be treated in a hospital. Because boils on the face are very dangerous and often require surgery to treat them.
In the initial stages, before pus forms, the resulting formation can be cured using ultraviolet light, without prescribing antibiotics.
In cases where the boil has already begun to ripen, bandages with ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky ointment are applied to it. These ointments draw out pus and relieve inflammation, after which they promote wound healing. If the abscess is quite deep, the surrounding tissues are injected with antibiotics. All this is done until the boil opens. You cannot open it yourself because of the risk of introducing another infection; the consequences can be very dire, including blood poisoning. Also, the skin around the abscess is treated with antiseptic drugs.
If the abscess does not open on its own, then the doctor does this, allowing the accumulated pus to come out.
After the abscess has been opened, the resulting wound is treated with hydrogen peroxide. After which a bandage soaked in a sodium chloride solution is applied. In some cases, drainage is installed. You should not try to remove the core of the boil, because if it is not ripe, it may tear during the removal process, which will cause an even greater aggravation.
After all the pus has come out, bandages with a healing ointment, such as Levomekol, are applied to the wound.
If boils appear again after treatment, this may indicate chronic furunculosis. In this case, hospital treatment is necessary.
In addition, other methods of treating this disease are used.
To treat the skin around the boil, in addition to hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green, salicylic or boric acid are also used.
UHF therapy is used to promote the maturation of the abscess and its further healing. In this case, the boil is exposed to a high-quality electromagnetic field. Typically, the oscillation frequency is 27.12 MHz or 40.68 MHz.
In addition to ichthyol and Vishnevsky ointments, tetracycline, heparin, Baneocin and Bactroban are used.
Antibiotics that are active against staphylococcus are often used: Oxallin, Mecillin, Cephalexin, etc.
If boils appear again and again, then autohemotherapy is performed. This is a procedure in which the child is injected intramuscularly or under the skin, depending on the boils, with his own blood from a vein. It strengthens weakened immunity. Transfusion helps not only in the treatment of furunculosis, but also keeps the body in good shape.
In extreme cases, surgery is necessary. In this case, the skin over the abscess is cut, after which the affected tissue is removed and everything is thoroughly cleaned of pus. Often the wound heals on its own, but if it is very large, stitches may be required. Next, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, and vitamins are prescribed.
An alternative to surgery is laser therapy. Today it is successfully used in the treatment of furunculosis. This method has a number of advantages over others. This:
- Lead time. Clearing pus from one boil in a child with a laser takes no more than half an hour.
- The boil is completely removed in just one session.
- This method is non-contact and sterile, so the risk of any infection is reduced to zero.
- After laser removal of the abscess, there are no scars or scars left.
- Laser. Can be used at any stage of maturation.
- No side effects or complications, and no contraindications.
- Can be used at any age.
After treating a boil, you need to take a course of vitamins prescribed by your doctor to strengthen your immune system. Spend more time in the fresh air and observe personal hygiene rules.
Traditional therapy
The doctor will determine how to treat the boil based on the severity of the disease. In an uncomplicated form of the disease (a single boil), no specific therapy is required - the main thing is to wait for the abscess to spontaneously open, and then treat the wound with an antiseptic solution (furacilin, hydrogen peroxide, iodine).
You can speed up the process of maturation of the abscess by applying Vishnevsky or Ichthyol ointment, Shostakovsky balm and other drugs that draw out pus to the site of the lesion. Such manipulations will shorten the period of illness by several days.
If an already mature boil cannot break through on its own, the doctor pierces a thin layer of skin on its surface and releases the pathogenic exudate out. If the neoplasm is large, silicone drainage is introduced into its cavity, which improves the outflow of contents. After 2-3 days, the wound is disinfected and a bandage is applied with antibacterial ointment (Levomekol, Fucidin, Bactroban, others). To avoid complications, follow all recommendations of your doctor.
Treatment of chronic furunculosis is carried out with systemic antibiotics. Immunomodulatory medications and vitamins are also prescribed.
In addition, it is necessary to treat concomitant pathologies.
- Antibiotics. If the abscess is deeply localized, the affected area is injected with antibacterial drugs - this will prevent further spread of the infection and reverse the pathological process. In case of multiple contamination, medications are taken orally or administered intramuscularly (Azithromycin, Sumamed, Ceftriaxone).
- Vitamin therapy. Most often, children are prescribed oral intake of vitamins A, B1, B2, C, PP, but intramuscular administration may also be recommended.
- Immunomodulators. Drugs that stimulate the immune system are taken strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor (Interferon, Myelopid, Seramil).
In addition, physiotherapy (Ural irradiation, UHF, laser treatment) can be used for therapeutic purposes. In case of deep abscesses, surgical opening of the abscess can be performed, since the risk of an abscess breaking into the anatomical cavities in this case increases.
Furuncle in a baby
Inflammation often occurs due to poor personal hygiene and weakened immunity. But it happens that a boil appears in a healthy baby and he is properly and well cared for. This happens because the immunity of young children is still imperfect and not fully formed, and the body cannot protect the baby from bacteria.
Treatment of boils in infants does not differ from the treatment of older children, but it must take place in a hospital, since a small child is not able to take a pill and is prescribed injections.
The baby is also given compresses with antibacterial ointments. Boils must be handled carefully as the abscess may rupture and blood poisoning may occur.
Boils appear much more often in children of different ages than in adults.
The reasons for the appearance of these formations include:
severe sweating - this especially often leads to boils in newborns. They have not sufficiently adapted to extrauterine conditions; the slightest overheating causes profuse sweating. When rubbing against clothing, irritation appears, and opportunistic microorganisms easily penetrate deep into the skin;- disruption of the endocrine or digestive systems;
- insufficient hygienic skin care.
Furunculosis can appear against the background of infectious diseases with a general decrease in immunity. Treatment of the purulent-inflammatory process in children is carried out according to the same therapeutic regimen as in adults, but for newborns this disease is very dangerous and can cause death.
Diagnostic procedures
At the first stage of the appearance of a boil in a child, when it is still maturing, doctors perform a dermatoscopy of the formation - the inflammation is examined using a special device for an accurate diagnosis. Afterwards, a smear is taken and the discharge from the wound is submitted for bacterial culture. This is done to determine the cause of the infectious disease, as well as to establish bacterial resistance to antibiotics. Both before enucleation of chiria and after the procedure, the patient undergoes a blood test in order to find out the state of the little person’s immunity, as well as to identify other diseases and possible complications.
Boils in a small child
Boil is a purulent-inflammatory process, the cause of which is the penetration of opportunistic microorganisms, streptococci and staphylococci - most often Staphylococcus aureus - into the upper layer of the dermis. Pus appears in the hair follicle itself, the surrounding soft tissues are involved in the inflammatory process, and pronounced swelling appears. Until the abscess is completely ripe, touching the inflamed area is extremely painful.
For children under one year old, the penetration of this type of infection into the body poses a real threat to health and even life.
Symptoms indicating that Staphylococcus aureus has entered the body of infants are:
- febrile state - severe moodiness and increased temperature;
- swelling of soft tissues - the upper layer of the epithelium and joints;
- cough, sometimes with bloody mucus;
- breathing disorder.
That is why treatment of furunculosis in children under one year of age should begin at the stage of infiltration, after mandatory consultation with a pediatrician. Home remedies - heating - are dangerous for babies. If this seal overheats, the capsule may open and pathogenic bacteria will spread throughout the body.
For older children, boils that appear on the face, in the area of the nasolabial triangle or on the head - in the occipital part - are especially dangerous. This area contains a large number of blood vessels through which infection can enter the brain.
After the appearance of purulent neoplasms on the body of children, one cannot expect them to disappear on their own.
If left untreated, serious complications may occur:
- furunculosis – frequent appearance of multiple boils;
- lymphangitis and lymphadenitis - an inflammatory process of lymph ducts and lymph nodes;
- phlegmon is an acute inflammatory process of the subcutaneous fat layer;
- thrombophlebitis – inflammation of blood vessels, accompanied by the formation of blood clots;
- abscess - the formation of a purulent cavity in the surrounding tissues;
- sepsis is blood poisoning.
The appearance of a boil - even a single one - is a serious reason to consult a pediatrician.
Treatment of boils in newborns
Medical measures for the treatment of children in the first year of life are prescribed on the basis of the clinical picture, taking into account the general state of health and physiological development of the individual infant:
Children are isolated from sources of infection. Before contacting a baby, adults must wash their hands thoroughly, preferably wear a gauze bandage, and be sure to wear home clothes and clean shoes. Many adults, without knowing it, are carriers of a staphylococcal infection, which does not pose any danger to them. If pathogenic microorganisms get to sick children, their general condition will become even more serious.- Antibiotic injections are required. Antibacterial drugs of different types can be used to completely destroy infectious agents.
- Medicines are used to thin the blood. They break up clots that quickly form in children of the first year of life and prevent the development of thrombophlebitis.
Quite often it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention to open boils. The wound is drained and surrounding tissues that have already melted during the inflammatory process are removed.
In severe cases, a blood transfusion may be required.