The aging of the body, in addition to the appearance of wrinkles on the skin, is sometimes accompanied by a more serious change called cutaneous horn. An animal horn-like appendage can appear on any part of the body. Its formation causes discomfort, but you cannot remove the formation yourself, since this is not just an age-related change in the skin, but a benign tumor.
The development of a cutaneous horn is an age-related, unaesthetic, non-malignant neoplasm that can also cause physical discomfort.
What is cutaneous horn?
The cutaneous horn is a neoplasm rising above the surface of the skin on the human epithelium, characterized by a dense structure and cylindrical shape. Typically, manifestations of the cutaneous horn are single and clearly visible to both the patient and others. Multiple cutaneous horns are extremely rare.
The disease got its name due to visual associations: in appearance, the neoplasm resembles an animal horn. In humans, the cutaneous horn can take a variety of shapes: it can be straight, curved or spirally twisted. But, usually, the cutaneous horn is a cone or cylinder consisting of keratinized skin, similar in composition and tissue density to the nail plate. Its color varies from light yellow to dark brown. The diameter of the formation can range from several millimeters to tens of centimeters. The length of the keratinization in some cases reaches 30 centimeters.
Cutaneous horn is classified as a benign skin formation, but this does not mean that it is harmless. It is possible to accurately determine the nature of the tumor only through histological examination. In addition, the affected area of the skin, even after removing the growth, becomes a “weak spot.” Sometimes a cutaneous horn is a sign of a dangerous cancer - squamous cell carcinoma.
The Frenchwoman has a horn
One of the first recorded cases was associated with a rather long neoplasm. In Paris in the early 19th century, a widow named Madame Dimanche grew a horn from the center of her forehead. It developed over six years. At that time the woman was 76 years old.
She was told that this was not a fatal disease, and therefore she refused surgery to remove the formation. It soon became clear that it did not stop growing on its own, and it began to interfere with the woman’s daily lifestyle. However, the French woman eventually had the tumor removed when it was 10 inches long, hanging so low it almost reached her chin.
Tumor localization
Although cutaneous horn can occur on any part of the skin, the face, neck, scalp, and eyelid skin are more susceptible to the disease. The tumor is much less common in areas of the head adjacent to the mucous membranes: the skin of the lips and nose. Even more rare are cases of cutaneous horn on the fingers, genitals and other parts of the body. Smokers are susceptible to the development of diseases on the mucous membranes of the larynx. Favorite places for the formation of this tumor are wrinkles, skin folds, places of friction and compression of the skin.
Prognosis and prevention
After removal of a horny keratoma, it is recommended to undergo an annual examination and monitor all formations on the body. This allows you to do RTM diagnostics. In more than 90% of cases, removal of the skin horn goes well and without relapses. If there is a suspicion of malignancy of the neoplasm, the patient is taken to the dispensary for further observation and treatment.
Several preventative measures for patients who have undergone keratoma keratoma removal:
- protect the operated area of skin from injury and damage;
- avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight;
- Strengthen your immune system by adding more vitamins and nutrients to your diet.
Causes of cutaneous horn development
Most often, cutaneous horn appears in older people - the development of the disease is facilitated by age-related metabolic disorders, leading to the proliferation of outer cells of the upper ball of the epidermis. But in the presence of unfavorable factors, the disease can even affect the skin of a baby.
German scientists have suggested that cutaneous horn develops as a result of a molecular failure in the differentiation of skin cells, which produces modified collagen. Some scientists believe that there is a hereditary predisposition to cutaneous horn disease.
Today it is generally accepted that the following processes occur during the development of the cutaneous horn:
- accelerated mitotic division of skin cells;
- accelerated migration of skin cells overflowing with keratin to the surface;
- acceleration of genetically programmed physiological cell death;
- accumulation of keratinized skin cells, leading to the growth of the cutaneous horn in length.
Cutaneous horn often affects women , as they have more pronounced hormonal imbalances.
The internal risks of developing a cutaneous horn include the presence of the following abnormalities in a person:
- excess weight;
- hypovitaminosis;
- pathologies of the digestive system;
- seborrhea;
- psoriasis;
- keratoderma;
- frequent stress.
External causes of cutaneous horn include the following:
- poor circulation in places where the skin is excessively compressed by clothing;
- skin contact with aggressive environments (strong acids, alkalis);
- lack of personal hygiene;
- infection with fungal infections;
- mechanical damage to warts or papillomas;
- excessive exposure to open sun.
The above factors stimulate the manifestation of hyperkeratosis - pathological growth of the stratum corneum of the skin. One of the histological manifestations of hyperkeratosis is the cutaneous horn. Often this disease is accompanied by other skin lesions: papillomatosis, acanthosis, keratoacanthoma.
Diagnostics
When any neoplasm appears on the skin, it needs to be examined and histologically analyzed. It will determine the exact nature of the pathology and allow you to make a prognosis of the disease. Due to differential examination, squamous cell carcinoma is excluded. To do this, a biopsy of a piece of tumor tissue is performed.
The most vulnerable place of such a growth is its base. All the basic processes take place in it, due to which tissue growth and the development of the skin horn began. To carry out a detailed analysis, material is taken from its base. Thanks to this, a benign or malignant form of the disease is identified.
Forms of the disease
Primary cutaneous horn
It occurs on previously healthy skin without any visible prerequisites. The course of the disease is accompanied by a slow growth of the horn in length, as well as darkening of its color and coarsening of the structure. The inflammatory process is rarely a companion to the primary form of cutaneous horn. It is also uncharacteristic for the tumor to degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Secondary cutaneous horn
It occurs at the site of skin damage, inflammation, removed warts, papillomas and other epidermal defects. A frequent companion to the secondary form of cutaneous horn is the inflammatory process. In the secondary form, the disease is often aggressive, develops rapidly and can become malignant.
The primary form of the disease can develop into a secondary one. Therefore, if a tumor is detected, you should promptly consult a dermatologist.
Classification
Dermatologists distinguish two main types of the disease:
- Primary or benign. Such a cutaneous horn appears on the skin suddenly, for no apparent reason. It is characterized by a completely benign course and the absence of an inflammatory component. The neoplasm can have very different localizations; it can cause cosmetic or practical inconvenience, which becomes the main reason for targeted treatment. If such a skin horn does not bother the patient, it is recommended to only monitor him.
- Secondary or malignant. Such a growth occurs due to the transformation of the primary formation due to the influence of external or internal provoking factors. For this condition, the presence of an inflammatory process at the base of the growth is typical. Secondary cutaneous horn is considered a rather dangerous pathology, as it can quickly become malignant. Such a tumor cannot be left untreated.
Symptoms of the disease
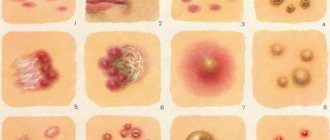
In most cases, cutaneous horn is diagnosed by pronounced external symptoms. At the initial stage, the disease appears as a yellowish bump on the skin. As the tumor grows, it takes on the shape of a horn, which narrows towards the end. The base of the tumor is initially thickened and usually does not grow in diameter; it can be characterized by inflammation of the circumference, as well as itching in the area of the base of the tumor. Over time, grooves encircling the neoplasm begin to spread from the base of the skin horn. The neoplasm has clear boundaries; outside the inflamed rim, the tumor is surrounded by healthy tissue. Under the foot of the skin horn, the rate of metabolic processes is increased, blood continues to flow to the foot of the horn, but does not penetrate inside due to the cessation of blood flow and lymph flow in the tumor. But the patient does not experience pain.
Photo of cutaneous horn
The most common signs
What is cutaneous horn and how does it manifest itself clinically?
Horny epidermal hyperplasia is a formation of a rather dark color, a dense consistency to the touch, with a clear contour, a smooth surface, and there is an inflammatory rim around the very base. Horny keratoma comes in various shapes: from cone-shaped, spiky, to cylindrical, and has a variety of sizes from ten to fifteen centimeters and much larger.
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
Most often the focus is single, but there are exceptions in the form of multiple formations.
The favorite location is the skin, but cases of appearance on the mucous membranes have also been recorded. In particular, on the lips of people who smoke cigarettes - this is associated with leukoplakia.
Squamous cell carcinoma is sometimes hidden under the signs of a cutaneous horn. The information in the table will help you notice a dangerous disease in time and consult a doctor.
| basic information | Cutaneous horn | Squamous cell skin cancer |
| Provoking factors | Wart injuries, autoimmune pathologies, hyperplasia | Sun exposure, addictions, HPV, decreased immunity |
| Patient age | After 45-50 years | After 65 years |
| Size | Up to 1 cm in diameter | From 2 mm to several centimeters, grows quickly |
| Color | Grey, dark brown | White, red, brown |
| Form of education | Cone-shaped, but initially round or oval | Irregular, without clear boundaries |
| Soreness | Absent | There is itching, bleeding, discomfort |
| Treatment method | Surgical followed by histological examination | Surgery, radiation therapy |
Treatment of cutaneous horn
Modern medicine has developed several methods for treating cutaneous horns, but the most effective is its removal, which is carried out both in specialized cosmetology and oncology institutions.
You should not remove the skin horn yourself. Despite the painless course of the disease, the cutaneous horn can become a source of malignant neoplasm. When surgically removing a tumor, your doctor will clean the area of skin at the base of the horn that may contain cancer cells. And also, a histological analysis of the neoplasm will be performed, excluding its malignant properties.
General treatments
- Anti-inflammatory therapy
Although most of the formation is keratinized and devoid of sensitivity, the junction of the cutaneous horn with the epithelium is often characterized by the presence of an inflammatory process. Therefore, in the initial stages of skin horn treatment, anti-inflammatory and skin soothing agents are used.
- Visual observation
Other diseases whose course is similar to the manifestations of cutaneous horn should be excluded.
- Traditional methods
The application of compresses made from onion peels, aloe and propolis tincture is recommended by traditional medicine for the treatment of cutaneous horns.
Unfortunately, there are no medications that can resolve this tumor without surgery.
Removal of cutaneous horn
Methods for removing skin horn include the following:
- electrocoagulation;
- laser method;
- radio wave method;
- surgical method;
- cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen.
All of them allow you to quickly remove skin horn from the surface of the skin. The surgical method is traditional, has virtually no contraindications, but requires local anesthesia and leaves a small scar at the operation site. Electrocoagulation, laser and radio wave methods may be contraindicated for people who have concomitant cancer diseases. Destruction of the skin horn with liquid nitrogen is carried out pointwise, has no contraindications and is the recommended method for removing the skin horn.
Treatment with folk remedies
Using traditional medicine methods, you cannot completely get rid of the disease, but you can reduce the intensity of its growth. The following tools are used for this:
- Aloe. Place 1 leaf of the plant in the freezer for 3 days, then remove the shell from it and apply it to the affected area overnight as a compress and attach it with an adhesive bandage.
- Onion peel. Wash 40 g of husks, dry them, and then pour 1 glass of vinegar. Leave to brew for 15 days in a dark place. Use the infusion for compresses, which should be kept on the skin for 30 minutes to 2 hours every day.
- Propolis. Apply a piece of propolis to the pathology and secure with a bandage for 5 days. In total, you need to conduct 3 such courses, lasting 5 days.