What is atopic eczema
This is a type of dermatitis with its own distinctive characteristics. Until recently, atopic eczema was classified as neurodermatitis. Then they separated it into a separate pathology. Even children under three years old suffer from it. It is formed mainly due to allergic reactions. Sometimes this disease accompanies asthma. Often worsens after nervous overstrain.
Patients experience excessive production of prostaglandin, which forms biologically active substances. A sick person has too many of these substances. The presence of prostaglandin in the body can lead to skin inflammation because it triggers this process.
Microbial eczema, symptoms
Microbial eczema is distinguished by the fact that the lesions are located asymmetrically, the center of the lesion is covered with purulent crusts, upon opening of which an erosive zone similar to a well is observed, with weeping inside.
The border of the affected area is a curvilinear outline formed by the detaching epidermis. The affected area is colored blue-red, this is due to skin infiltration.
Microbial eczema is accompanied by:
- Edema of the dermis
- Spongiosis
- Sclerosis of the dermis
- Massive acanthosis
- Lymphoid infiltration with the formation of plasma cells
- Exocytosis with the appearance of blisters in the epidermis
Often, manifestations of microbial eczema are localized in places of trophic ulcers, on the stump due to amputation, around fistulas. Also on the limbs and between the folds of the patient’s skin. Quite often, older people suffer from microbial eczema .
Back to contents
How does pathology manifest itself?
The disease manifests itself after prolonged contact with an allergen irritant. It usually affects a large area of skin at once. It turns red, swells slightly, itches a lot and becomes dry. After some time, rashes that look like small bubbles form on the affected area. The latter are filled with serous fluid.
The patient scratches these rashes because they itch very much, causing great discomfort. This leads to the appearance of so-called “serous wells”, as well as cracks and scratches. During this period, the disease is characterized by the presence of weeping wounds, which contribute to the appearance of pathogenic microflora. Bacteria and fungi greatly interfere with the healing of these wounds. After the weeping stage, eczema develops further. The affected skin dries and peels. At this time, the patient experiences an increase in temperature.
Eczema on the hands, initial stage
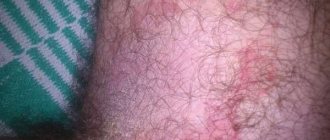
Eczema on the hands in the initial stage can be diagnosed quite easily if you look very carefully at the affected areas. The initial stage of eczema is characterized by local hyperemia, in other words, this is a strong filling of blood vessels in any area of the body. It looks like a rash of scarlet nodules of capillaries.
We can also observe the formation of reddish spots that do not have pronounced, clearly visible outlines of boundaries. Subsequently, the spots or nodular rashes begin to merge in such a way that we begin to observe distinct single plaques, all of which is accompanied by quite noticeable itching. These are the primary characterizing signs of the initial stage of eczema on the hands.
There are a number of stages in the course of the disease:
- Erythematous (characterized by the formation of scarlet inflammatory spots that unite with each other)
- Papular (characterized by the appearance of reddish nodules up to 3 millimeters in size, with defined borders)
- Vesicular (vesicles approximately 2-3 millimeters in size, with serous contents, form on the nodules)
- Weeping stage (characterized by the opening of vesicles and the formation of wells at the opening sites, with serous discharge)
- Cortical (formation of a yellow-grayish crust as a result of drying of the serous fluid)
- Peeling stage (formation of scales and crusts in large quantities, which begin to fall off)
These stages of eczema may vary in duration and appear at different times, which explains the presence of different signs of different stages in one lesion. It is not uncommon that in the central part of the lesion we see a worsening of the inflammatory formation, and towards the edges signs characteristic of the early stages appear.
Video: Treatment of eczema
Back to contents
Characteristic differences between atopic dermatitis and eczema
How is atopic dermatitis different from eczema? These are two different pathologies, however, they are often confused. Only a dermatologist can distinguish them at first glance. The doctor must make the correct diagnosis, because therapy is selected depending on the pathology that affects the skin.
Main differences:
- Eczema forms on open and closed areas of the skin. In addition, the lesion is often observed in a completely different place where the skin comes into contact with the allergen. For example, if your hands are frequently exposed to household chemicals, the lesion may appear not on the hands, but in the area of the elbow joints. Eczema is usually localized in closed areas of the skin.
- Eczema has relapses that do not occur with dermatitis.
- Eczema occurs due to prolonged contact with any allergen. And dermatitis is caused immediately after contact with such an irritant.
- Atopic eczema goes through a wet stage during its development. In dermatitis the latter is absent.
Knowing these characteristic features of the two pathologies, it is not difficult to correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe the necessary therapy.
Eczema on the hands, causes
Many doctors in the field of allergology classify a disease such as eczema on the hands into a separate group of idiopathic diseases, which means that the causes of the disease have not been established. And for now, the true causes of the development of eczema are still constantly being studied, and have not yet been fully identified.
But modern science is steadily evolving; there are already evidence-based factors that have a major influence on determining the occurrence of one or another type of eczema.
Experts have developed a clear understanding that various external and internal signs play a significant role in the onset of eczema. First of all, a violation of the central nervous system (overexcitation of the central nervous system, as a rule, leads to eczemotosis). This alone is undoubtedly not enough:
- Thyroid diseases
- Diabetes mellitus
- Digestive system diseases
- Heredity
- Psycho-emotional stress
All this contributes to the appearance of eczema on the hands.
Other provocateurs for the occurrence of eczema can be problems of the autonomic nervous system, disorders of various types of metabolism (protein, vitamin, fat, carbohydrate).
Autoimmune long-term processes also contribute, which are expressed in skin lesions and a long course of the disease, which is difficult to definitively treat. In addition to all the listed components, you also need an antigen or irritant that will be applied externally to the skin.
Back to contents
What causes the disease
Modern medicine cannot determine the exact cause that causes the symptoms and manifestation of this disease. If atopic eczema becomes chronic, it will accompany a person throughout his life, periodically relapsing and fading. It has been noted that it often appears in those who are predisposed to allergies.
Heredity also plays a role here. For example, the first signs of the disease sometimes appear in babies already in the first months of life. These infants have a history of relatives with allergies or asthma. Eczema and atopic dermatitis also affect adults. The reason for the formation of pathology here is considered to be a whole range of health problems:
- improper functioning of the immune system;
- systemic pathologies;
- stress and depression;
- improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous and endocrine systems;
- incorrectly selected diet.
If eczema appears on the hands, this means that the skin is in contact with an irritant (allergen). The latter could be:
- latex gloves;
- household chemicals;
- cosmetics;
- running water;
- various decorations.
Features of the disease in children
Despite the age factor, wet eczema occurs quite often in children, starting from infancy to 5 years; in this case, the “trigger mechanism” of the disease most often becomes:
- Genetic predisposition;
- An allergic reaction to components of infant formula or allergenic products consumed by a nursing mother, and sometimes to improperly selected personal hygiene products;
- Severe stress due to fear or quarrels between parents;
- Serious gastrointestinal diseases.
Manifestation in children
In the most severe cases, the disease covers larger areas than in adults, including the neck, chest, groin area and between the buttocks. It is almost impossible to keep young children from scratching their itchy skin, which further complicates the course of the disease with an associated bacterial and/or fungal infection.
The disease is very difficult for young children to endure due to painful sensations and requires immediate treatment, and only as prescribed by a doctor, since the treatment of children has its own specific characteristics and requires the use only of drugs specifically designed for a specific childhood.
Symptoms of the disease
Atopic disease mainly appears on the skin of the face, neck, knee, and elbow joints. Initially, the skin turns red and swollen, then dries out and begins to peel. All this time, the affected areas are very itchy.
After a few days, the inflamed areas become covered with a rash in the form of small nodules, blisters filled with serous fluid, and erosions. The skin is very itchy, the patient scratches it, which provokes the release of serous exudate. This leads to the formation of wet surfaces and erosion. If the patient does not scratch the rash, then the inflammatory process can pass without the stage of wetting the surface. The rash will dry out and turn into a thick crust.
After the skin dries, scaly layers appear in the place where there were erosions; after a while they disappear. Often the inflammation does not go away for a long time, during which time the symptoms periodically disappear and reappear. With such a protracted pathology, rough areas and compactions appear on the skin.
Kinds
There are several types of eczema, which differ from each other in location, origin and course of the pathological process.
True
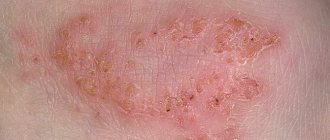
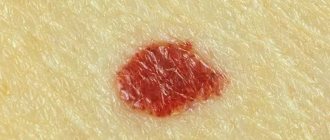
This eczema is characterized by the appearance of papules and vesicles, which open quite quickly. At the same time, a large amount of serous exudate flows to the surface. The skin begins to become wet, at which time a secondary infection often develops. The process may begin for unknown reasons, but there are theories confirming the polyvalence of the etiology. When the acute phase passes, crusts form at the site of the lesion.
The true form is characterized by the absence of smooth contours, multiple and symmetrical arrangement.
The following photographs demonstrate such signs.
With a long chronic course, the manifestation of true eczema is the formation of pigmentation, areas of peeling and hyperkeratosis.
The photo below allows you to consider this stage of the development of the disease. In this case, it strongly resembles psoriasis, so differential diagnosis is required, since the means of treating pathologies will be different.
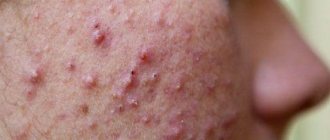
Microbial
A photo of microbial eczema clearly shows that lesions on the skin are located in the area of damage - wounds, burn surfaces and abrasions.
If you look at the atlas of diseases, you can see that microbial eczema is divided into four types - numular (coin-shaped), varicose, sycosiform and nipple areola eczema. The first two species, shown in the following photographs, are more common.
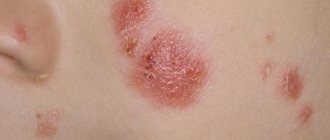
Seborrheic
Below is a photo of seborrheic eczema. It develops as a result of excess production of sebum .
The head (the hairy part), the face in the area of the nasolabial folds, the back of the ear and the neck suffer. With seborrheic eczema, the lesions merge, and as the process becomes chronic, hair loss begins.
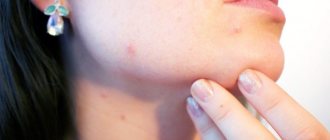
Professional
It occurs on the hands and other parts of the body that are constantly in contact with substances that cause allergic inflammation. This type of disease can be seen in the photo below.
Redness, swelling, and nodular rashes appear. Subsequently, serous crusts and peeling form at the site of the violation.
Often the first symptom of occupational dermatitis is itching and burning in the area where the irritant comes into contact with the body. Treatment of this form should begin by eliminating the influence of the etiological factor.
Dyshidrotic
Dyshidrotic eczema on the body, a photo of which is attached below, usually appears on the palms of the hands, fingers and soles of the feet.
Against the background of mild swelling and redness, multiple pinpoint rashes are visualized. Over time, they become covered with serous or purulent crusts. The appearance of lesions on the thighs and further spread of the rash is considered the transition of the dyshidrotic form to the true one.
Children's
The symptoms of childhood eczema are somewhat different from the manifestations of the disease in adults.
In a child, the exudative component comes first. This phenomenon may look like a cluster of various rashes with a large amount of effusion.
The prerequisites for the development of the disease are often allergic or atopic dermatitis in the baby, a tendency to hypersensitization of the body.
In children, seborrheic, idiopathic and microbial types of eczema are more common. Manifestations of the latter form are visible in the attached photo.
The child becomes nervous, eats poorly and lags behind in development. The addition of a secondary infection and untimely consultation with a doctor can lead to serious consequences. Dr. Komarovsky believes that to eliminate the problem, it is necessary to reconsider the diet, and if the child is breastfed, then the mother’s diet should be adjusted.
Diagnostic measures
The diagnosis is made during the first examination of the patient. Atopic eczema is characterized by:
- redness on the skin;
- peeling;
- rashes;
- itching
The doctor collects anamnesis, interviewing the patient to clarify all the factors that preceded the damage to the dermis. He also studies the symptoms and is interested in the course of the pathology. The diagnosis is clarified after immunological tests are carried out; for this you need to donate blood from a vein to the laboratory.
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe a study of the patient’s immune system, involving specialists such as an allergist, immunologist, nutritionist, etc. Sometimes a microscopic examination is indicated to identify fungi.
UAC and TAM tests detect infection in the body. Eosinophilia is often found in the patient's blood. Disturbances in the digestive tract, which sometimes provoke the disease, are shown by the coprogram. Serological studies differentiate atopic eczema and other pathologies.
If eczema is acute, then the process of keratinization is disrupted. The spinous and papillary layers of the skin swell. In the chronic form of the pathology, keratinization intensifies, the spinous layer thickens. Lymphocytes and histiocytes accumulate near the vessels.
Causes
The main provoking factor is a malfunction or weakening of the immune system, which is unable to withstand the onslaught of a bacterial infection from the outside. An exhausted immune system begins to react inadequately to any irritants. Such reactions on the skin can lead to:
- hormonal imbalance;
- metabolic disease;
- endocrine system failure;
- hereditary factor in case of gene mutation;
- stagnant processes in skin vessels;
- phlebeurysm;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- presence of internal chronic diseases;
- bad ecology;
- use of low-quality cosmetics;
- cosmetic procedures leading to abrasions, cuts (tattoos, peeling);
- diseases of the neuroendocrine system;
- lymphostasis;
- mycosis.
The disease manifests itself as a sign of kidney dysfunction, gastrointestinal tract, due to an increased number of T-lymphocytes and gamma globulins. Frequent causative agents of microbial eczema are candida fungi and staphylococcal (streptococcal) infections.
The pathology is often detected in children with an unformed immune system, when an infectious agent enters the blood through scratches and cracks in the skin. Even a mosquito bite can cause bacteria to multiply. After scratching the affected area, an inflammatory reaction occurs, tissue swelling, itching, and irritation.
Differential diagnosis
To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor needs to thoroughly study the history of the pathology, become familiar with the symptoms and nature of the disease. To differentiate true eczema, atopic and purulent inflammation of the dermis, a biopsy is performed.
To distinguish atopic eczema from scabies and fungal pathologies, a microscopic examination is performed. Their results reveal the cause of the disease. Also, differential diagnosis is carried out with various dermatitis, psoriasis and other pathologies.
Manifestations in cats and dogs
Not only people, but also pets can suffer from wet eczema. The disease in this case is not contagious, but also requires complex treatment.
The causes of the disease (in animals it is often called weeping lichen) are allergic and microbial factors, as well as improper diet and care.
In dogs and cats with long hair, owners do not always detect the affected areas of the skin in time - hyperemic, inflamed, with blisters and weeping, which the animals constantly scratch and introduce infection into them.
Manifestation of dermatitis in cats and dogs
Wet eczema can also appear in short-haired breeds, especially if they are characterized by folded skin, such as on the face of pugs, where the disease is localized.
At the first signs of wet eczema (redness and inflammation of the skin, the appearance of blistering rashes and weeping), you must urgently contact a veterinary hospital for advice and carefully follow the veterinarian’s instructions to avoid chronicity of the disease.
Rules of conduct during therapy
The first thing doctors pay attention to during therapy is the course of the disease and its symptoms. It is important to determine the allergen that provokes the development of the disease. For this reason, the patient is asked to get his opinion on this matter. If the exact irritant cannot be identified, the doctor will refer the patient for allergy testing.
This analysis allows you to determine the patient’s body’s disposition to a specific allergen. After which it must be excluded from a person’s life. Then the therapy will be effective.
For atopic eczema, therapy includes diet. Marinades, pickles, smoked foods and semi-finished products are excluded from the daily diet. Food should be hypoallergenic and preferably protein-vegetable. It is recommended to give preference to plant foods and also exclude allergenic foods from the diet: fruits, berries and red vegetables, citrus fruits, radishes, mushrooms. You should eat lean meats, such as turkey and rabbit. And also reduce the consumption of sweets and starchy foods.
Nutritionists advise fasting during the period of acute atopic eczema (maximum two days). This helps cleanse the body of accumulated toxins. However, you must first consult with a nutritionist and other doctors, because fasting often provokes an exacerbation of other chronic pathologies.
If eczema appears on the upper extremities, the patient should refrain from contact with household chemicals and try to wet their hands as little as possible. You can clean them with cotton swabs. It should be remembered that caring for the affected parts of the skin is of great importance!
This type of eczema has a wide range of different methods and means for therapy. If the treatment is chosen correctly and all its key principles are followed, then it is possible to achieve the transition of the pathology to a stage with rare relapses.
Diet for weeping eczema
- One of the main aspects of prevention is following a diet and not eating foods that can provoke allergies. The most harmful effects can be caused by the consumption of oranges, tangerines, lemons, grapefruits, strawberries, honey, chocolates, and other allergens. A diet is necessary for all sick people, and not just those whose illness is caused by an allergic reaction.
- It is necessary to make your diet varied so that you can get all the necessary vitamin complex. Reducing calorie intake is only necessary if you are obese, since even this can cause the onset of the disease.
- During the development of an exacerbation, try to eat cereals, soups, and fermented milk products. The consumption of strong broths, as well as salt, sweets and baked goods during illness is completely prohibited. By getting rid of this food completely, the cure for the disease will be easy and short-lived, and relapses will not occur.
- An integrated approach will help quickly eliminate the acute stage, and the individual approach of the patient himself plays a huge role in this. If all the doctor’s instructions are followed and there is a desire for recovery, then you can expect quick relief from weeping eczema.