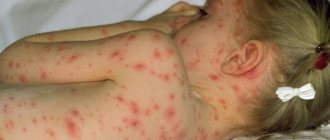
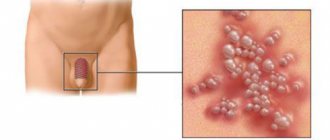
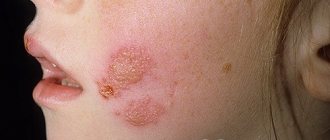
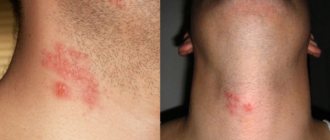
Herpes is a viral disease and occurs quite often in children of all ages. It appears as a rash on the skin or mucous membranes of the body. The vesicles contain a serous substance containing a large number of viral cells. The activity of the second type of virus can cause the development of genital herpes in a child. The rashes are localized in the child’s intimate area: in boys – the scrotum and penis, and in girls – the vagina and labia. The danger of this disease lies in the fact that if treatment is untimely or absent, it spreads to internal organs and nerve tissue.
Ways of infection of children with the HSV-2 virus
Infection with genital herpes is possible:
- In utero. This option of infection entering the fetus’s body is likely if the concentration of the virus in the mother’s body is very high.
- Ascending way. This is one of the variants of intrauterine infection, when the virus from the mother’s body migrates into the amniotic fluid through the placenta. This is possible with a defect in the placental membrane or its detachment.
- Antenatally. Contact with the virus occurs during the process of delivery, when the fetus passes through the birth canal, on the mucous membrane of which the pathogen is present. Infection in this way is possible even if the mother has a sluggish or latent form of the disease.
- Direct and indirect household infection. Colonization of the virus occurs at the moment of contact of a newborn with a source of inflammation (for example, when the carrier of the infection has pronounced herpetic rashes on open areas of the body) or through hygiene items, underwear, etc.
Household infection is rare and is typical for children aged 1 to 5 years, since it is at this age that susceptibility to viruses is maximum. In the baby's blood, the mother's antibodies received through the placenta no longer function, and his own immune system is not yet strong enough.
Classifications of herpes virus types
Herpes belongs to the group of widespread pathologies. The disease manifests itself as lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. The possibility of damage to internal organs cannot be ruled out.
In most cases, herpes is a dormant infection that occurs in a latent form.
| Type of herpes virus | Description | |
| 1 simple type, HSV - 1 | labial (lip) herpes | |
| 2 simple types, HSV - 2 | genital, anogenital | |
| Type 3 (varicella zoster virus or herpes zoster), VZO-OG | rashes are localized in the projections of nerve trunks on the skin | |
| Epstein-Barr type 4 (mononucleosis), EBV | mucous membranes and skin are affected | |
| Type 5 cytomegalovirus, CMV | no obvious symptoms | |
| Type 6, VCH | manifestation of sudden exanthema | |
| 7 type, VCHG-7 | may cause the development of cancer | |
| 8 type, VChG-8 | leads to damage to lymphocytes | |
All of the listed types of herpesvirus infection pose a particular danger to the child, therefore careful attention must be paid to the treatment of the disease in children.
It is necessary to understand the causes and main symptoms of herpes in children of different ages. This is necessary to identify pathology and timely contact a specialist.
What is the danger of herpes infection for children?
When the Herpes simplex 2 virus infects a cell, it invades the cells of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary tract, penetrates into their nucleus and multiplies there, causing destruction of the cell structure. Genital herpes in children rarely occurs in a mild form, expressed only by skin rashes; most often it takes a generalized form, spreading to the internal organs.
The consequences of intrauterine infection can be fetal malformations, as well as premature birth. In children, herpes type HSV-2 can cause:
- Damage to the mucous membrane of the urethra and genitals.
- Disorders of the cardiovascular system.
- Pathologies of the liver, spleen or pancreas.
- Diseases of the central nervous system, including such dangerous ones as meningitis or meningoencephalitis.
- Damage to the organs of vision and hearing.
Due to the increased danger of genital herpes, infants born to a mother who is a carrier of the Herpes simplex 2 virus are placed on special register. They are under medical supervision and undergo periodic examinations for several months in order to early diagnose possible diseases caused by the virus.
Complications and consequences
A baby born from an infected mother may have various pathologies of internal organs. More severe consequences of herpes in newborns and older children include:
- acute urinary retention.
- decreased immunity.
- adhesion of the labia in girls.
- tumors of the prostate and cervix.
With herpes, damage to internal organs often occurs.
Constant physical discomfort leads to psychological problems. The child becomes withdrawn and refuses to communicate with close relatives and peers. In the absence of psychological help, depression develops.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Even with a localized form, genital herpes in childhood is severe. A week after infection, single vesicles - bubbles with liquid contents - appear on the skin and mucous membranes. Then the affected areas become swollen, the rashes increase, forming infiltrates. The most dangerous localization of the rash is on the mucous membrane of the eyes, as it can cause the formation of ulcerative elements and lead to loss of vision.
A typical clinical picture of genital herpes in infants looks like this:
- swelling and redness of the genitals, the presence of a blistering rash on them;
- regurgitation, even vomiting, which occurs after eating;
- diarrhea, in feces - elements of undigested food;
- restless behavior, poor sleep caused by constant itching.
Older children who are able to voice their complaints report pain in the lower abdomen, heaviness in the groin, chills, and headache. Herpetic urethritis often develops, which manifests itself as pain when urinating. General weakness and fatigue are possible. After about a week, the vesicles open, forming painful itchy ulcers covered with dry crusts. During this period, due to the body’s increased immune response, the lymph nodes may enlarge and the temperature may rise.
After two weeks, signs of general intoxication and organ dysfunction join the skin manifestations. Body temperature rises to 39-40°, due to damage to the central nervous system, convulsions and vomiting occur. In such cases, the baby requires urgent medical attention, since in the future he may lose consciousness and fall into a coma.
Features of the disease in newborns
The listed mechanisms of infection do not work with 100% probability, but the risk of infecting children with genital herpes still exists.
The severity of the disease depends on several factors:
- The period of spread of infection in a woman carrying a child. If herpes appears during the first trimester of pregnancy, the full development and even the life of the baby are at great risk.
- The state of the protective functions of the body of the expectant mother.
- Level of treatment effectiveness.
Diagnosis of herpes in babies is possible in the first month of life. Specific rashes appear on the skin of the inner thighs, genital mucosa, as well as on the internal organs of the genitourinary system. The newborn’s immunity has not yet been formed, so it cannot normally fight pathogenic bacteria. For this reason, the disease almost always takes a severe form.
Herpes in the intimate area in children poses a serious danger to their fragile health. The disease threatens:
- Impaired functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- Damage to the eyes, ears, nasopharynx, larynx;
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the spleen, liver, and pancreas;
- Disorder of the functioning of the nervous system;
- Changes in blood composition;
- Various developmental disorders.
Rashes on the genitals are accompanied by diarrhea, profuse and quite frequent regurgitation after eating. These signs serve as a signal to parents that the baby is unwell. If measures are not taken in time, the child’s body will suffer from dehydration, intoxication of the genitourinary system, and inflammatory processes in the brain. If your baby experiences intense regurgitation and diarrhea, you should immediately call an ambulance.
With a viral infection of the central nervous system, the risk of developing meningitis, an inflammation of the membranes of the brain, increases. Its main symptoms are fever, vomiting, severe chills, and convulsions. The disease often ends in death.
Children whose mothers were infected with herpes must be provided with full medical supervision, which helps to detect the disease in a timely manner and quickly stop its destructive effect.
Methods for diagnosing genital herpes
The doctor determines the need to check for the presence of the HSV-2 virus in the child’s body based on a study of the medical history. To carry out differential diagnosis of anogenital herpes, laboratory and instrumental examination methods can be used.
Laboratory methods
The standard list of laboratory tests includes:
- General and biochemical blood tests, which provide information about the development of the inflammatory process, the level of organic acids (uric and sialic) and specialized proteins that are indicators of the immune response (fibrinogen, haptoglobin and CP protein) in the blood serum.
- Bacteriological analysis of smears from mucous membranes.
- General urine analysis - to determine the physico-chemical characteristics of urine, which serve as an indicator of the development of an infectious disease.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent test (ELISA) is a test that detects the presence in the body of antibodies produced to the herpes virus.
- Blood test using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method - determination of the antigen-antibody complex using the immunofluorescence effect. This technique allows you to determine the genotype of the virus and its amount in the body.
Hardware (instrumental) methods
If there is suspicion of viral damage to certain organs, the following may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound (sonography) - examination of tissue using sound waves with a frequency above 20 thousand hertz.
- CT – obtaining a layer-by-layer image of organ tissue using X-ray waves.
- MRI is a research method based on the use of the phenomenon of absorption or reflection of electromagnetic rays by cells containing nuclei.
What is worth knowing about the causes of the disease?
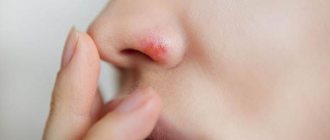
If you see a cold on your lip and find a photo of a similar disease on the Internet, then it’s worth finding out more about it. Typically, doctors divide the manifestation of herpes on the lips into 2 forms:
- Primary herpes. This means that the disease manifests itself in this person for the first time.
- Herpes is recurrent. A disease that has already made itself felt and is now reappearing.
In order to become more familiar with the disease, it is necessary to understand which of them will manifest itself when.
We recommend reading: Rf lifting: reviews
Treatment
Trying to treat herpes in children on your own is prohibited; this can lead to life-threatening consequences for the child. Qualified doctors - pediatricians and infectious disease specialists - should select medications and calculate their dosage depending on the degree of manifestation of the disease and the weight of the child; infants are treated in a hospital setting.
The complex of therapeutic measures usually includes the use of general and local drugs aimed at:
- elimination of external herpetic manifestations;
- suppression of HSV-2 virus activity;
- correction of complications caused by the virus;
- restoration and strengthening of immunity.
Antihistamines
To eliminate the manifestations of allergies - skin itching, irritation, inflammation, the following are used:
- Zyrtec - drops are used from 6 months of age, tablets from 6 years of age.
- Claritin - syrup from 2 years of age, tablets from 12 years of age.
- Erius - from 1 year, tablets from 12 years.
- Astemizole - approved for children over 2 years of age.
- Terfenadine - suspension is used from 3 years, tablets from 6 years.
During an exacerbation, it is also practiced to treat areas affected by herpes with antiseptic solutions and apply ointments containing antiviral drugs. After the vesicles mature and crusts form, the use of ointments with a proteolytic (regenerative) effect gives a good effect.
Antiviral therapy
The antiviral drugs most often used for herpes are acyclovir-based drugs. These are Zovirax, Acyclovir, Ganciclovir, Valaciclovir. They block the processes of virus reproduction, reduce the likelihood of the formation of new rashes and complications on internal organs, accelerate the healing of ulcers, and have an immunostimulating effect. The drugs are produced in the form of injection solutions, tablets, ointments and creams.
It is important to know! Complete removal of the herpes virus from the body cannot be achieved, since it has its own DNA and can remain in the cellular structures of the human body in an inactive, “dormant” form, which is not affected by antibiotics. When we talk about the treatment of herpes, we mean methods that inhibit the reproduction of the infectious agent and eliminate the manifestations of the disease.
Strengthening the immune system
To ensure that the child’s body effectively fights the virus and does not allow it to multiply uncontrollably, drugs with immunostimulating and immunostimulating effects are prescribed. They are used in tablet form, and for infants - in the form of anal suppositories. The most popular means for strengthening the immune system: immunoglobulin, immunal, interferon, arpetol, groprinosin, echinacea tincture.
Therapeutic tactics for herpes in children
If any suspicious symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor. He will prescribe the necessary medications and a certain dosage in accordance with the severity of the disease.
Treatment includes, first of all, antiviral, analgesic therapy and drugs that enhance immunity.
Main stages of general therapy:
- Antiviral drugs - suppress the activity of viruses, preventing its spread, but do not completely eliminate it from the body.
- Painkillers and antihistamines – eliminates itching and burning.
- Sufficient drinking regimen.
- High-calorie diet - includes nuts, fruits, vegetables, meat, greens, dairy products.
- Vitamin therapy is necessary to strengthen the immune system.
- Antipyretic - used when the temperature rises.
Local treatment consists of treating the affected mucosa with antiseptic solutions and antiviral ointments. When crusts form, drugs with a proteolytic effect are indicated.
Thanks to this treatment complex, you can get rid of the symptoms of the disease and reduce the risk of exacerbation.
Prevention
Among the measures to prevent genital herpes in children is the development of clear personal hygiene skills. The herpes virus can remain viable for up to several days, being on dishes, linen, towels, toys, so it is very easy to become infected in public institutions.
If someone in the family has herpes and there are rashes on his skin or mucous membranes, he should wear gloves and a gauze mask when in contact with the child. A carrier of the anogenital herpes virus should also not share utensils, bedding and personal hygiene items. A method of specific prevention is antiherpetic vaccination during the period of asymptomatic virus carriage.
The main preventive measure for intrauterine infection is screening pregnant women for HSV. If the test result is positive in the early stages of pregnancy, the woman is given a one-time injection of immunoglobulin at the rate of 0.2 ml per 1 kg of body weight. If signs of infection are detected at the end of pregnancy, and it is no longer possible to suppress it, delivery by cesarean section is recommended. Although this measure does not completely exclude the possibility of infection of a newborn.
In this video, Dr. Evgeniy Komarovsky talks about herpes, including genital herpes, in children.
What Doctor Komarovsky says
Everyone encounters the herpes virus sooner or later, because there are about 8 types of them. This includes the appearance of sores on the lips, chicken pox, mononucleosis and others. But some people have a predominant genetic predisposition to the absence of external manifestations of the virus. It depends on the state of the immune system. The virus is activated due to stress, illness, and overload. The trend of frequent manifestations of herpes suggests that you need to pay attention to your immunity.
In order to encounter the manifestations of the virus as little as possible, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, give up alcohol and take vitamin complexes that increase the body's resistance.
If there is no exacerbation, but antibodies to the herpes virus are detected during pregnancy or during planning, there is no need to engage in treatment; the body itself is ready to fight the infection and protect the child from it.
All about primary herpes
If you have a cold on your lips, or you found a photo of a similar disease on the Internet, then you need to understand where the disease came from. If we are talking about the appearance of primary herpes, we must go back in our memories to childhood, because that is where the infection occurred.
When a baby is born, his body already has antibodies to this virus, which he receives from the mother during development. A child does not get herpes until the amount of such antibodies in the body is large. Note that at this time the child may already be infected, but outwardly the virus does not make itself felt. As the baby develops, the amount of antibodies in his body begins to decrease. Therefore, usually between the ages of six months and two years, the first outbreak of such a disease occurs.
The above is not just about rashes that appear on the lips. Herpes can appear on the cornea of the eye, and then on the lip. Infection most often occurs when the child is really small. The baby comes into contact with other people; things from people who have been infected may fall into his hands. You can very quickly become infected from a person whose herpes is in the development stage and blisters that have burst or not burst have appeared on their lips. When the wounds on the lips begin to dry out, crusts appear, and only at this moment the risk of infection will decrease.
Few people know, but transmission of the herpes virus is possible even from an infected person to an uninfected person, by touching skin to skin or by shaking hands if the virus does not appear on either the hands or the skin. As a result, it is necessary to highlight the options through which infection occurs:
- Using other people's personal belongings, especially hygiene products.
- Touching things or objects that have been touched by an infected person who has an active manifestation of the virus.
- During a kiss, that is, when the mucous membranes of the mouth touch.
- In the event that an infected person and a non-infected person eat from the same dish with a spoon or fork.
- In case a person who is infected with the virus and one who is not infected are dried with the same towel.
Reappearance of herpes
The difficulty of treating the disease is that after its manifestation, the virus cells will reside not only in the tissues, but also in the nerve fibers. As a result, the virus spreads throughout the body, and then remains in an inactive state in the body for the rest of its life. However, as soon as a favorable moment for the development of the disease appears, the virus immediately makes itself felt. That is why more and more often photos of herpes on the lips on the Internet are a search query that interests many people. Usually, below such photographs you can find out what causes the manifestation of the disease.
The likelihood of manifestation can be minimized by eliminating factors that provoke relapse. These include:
- Contact with a person who has clinical manifestations of the disease.
- Severe hypothermia of the body.
- A noticeable weakening of the immune system, which will often be accompanied by a cold.
- Carrying out chemotherapy, hepatitis, taking steroids.
- Severe dehydration or prolonged exposure to the sun.
- Damage, abrasions and scratches appearing on the lips.
- Stress, noticeable physical fatigue of a person.
- Carrying out cosmetic and dental procedures.
- Critical days for women.
There are many actual prerequisites for the appearance of the disease, and it is impossible to completely eliminate its manifestations in the body.