2860
0
One of the most aggressive types of skin cancer is called melanoma. It is largely dangerous not so much in itself as in its ability to rapidly spread infected cells to other systems and parts of the human body. Therefore, melanoma can cause metastases in the lungs, liver, lymph nodes and other organs.
What are metastases
Melanoma metastases are a secondary focus of malignancy. The spread of atypical cells occurs in two ways - hematogenous and lymphogenous. In the first way, the spread of metastases occurs through the bloodstream. This type of transmission causes secondary infection of the bones, brain, liver, and lungs. The lymphogenous transmission route spreads metastases with the lymph flow. Spread occurs first to regional lymph nodes, then to distant ones.
Atypical cells settle in lymph nodes, various organs and tissues. Metastasis occurs very quickly in organs that are abundantly supplied with blood - the brain, liver, kidney and lungs.
Metastases in the brain
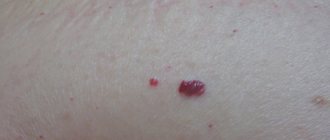
A characteristic feature of metastasis of pigmented melanoma is the spread of growth islands of malignant tumors on the skin. There are germinations into deeper layers of the skin.
The aggressiveness of the disease is expressed in the fact that spontaneous regressive melanoma occurs - self-destruction of the primary focus, in which the process of metastasis of the lymph nodes is started. This type occurs in 2%.
Characteristics
This pathology is characterized by:
- adverse consequences;
- fast growth;
- itching and bleeding;
- development on any part of the body;
- shiny and knotty surface;
- shaped like a dome, large and symmetrical;
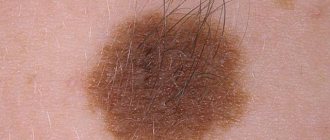
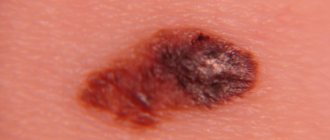
- color varies from pigmentless to black. A non-pigmented neoplasm is especially dangerous, since it is not always possible to detect it in time;
- uneven pigmentation, more intense in the center. Sometimes a black rim appears around the base.
Benign nevi often become the substrate for growth, but melanoma can also occur on unchanged skin.
Symptoms of metastasis
Atypical cells can appear in any organ of the human body. First of all, damage occurs to the lymph nodes, skin, liver, kidneys and lungs.
Skin manifestations
Found in 18% of all other forms. The following is observed: the appearance of satellites (the primary tumor creates islands around itself that resemble a scattering of ink spots); spots that look like erysipelas (red-blue spots); hyperemic subcutaneous formations of dense texture.
Brain
Metastasis affects the central nervous system. Expressed in headaches, nausea, dizziness, ataxia. With a strong focus of metastasis, epileptic seizures may occur.
Lungs
The patient may notice that the lymph node is inflamed in the axillary or supraclavicular area. Then a dry, irritating cough begins to bother you. Affecting the pleural cavity, metastases provoke shortness of breath and the development of respiratory failure. When the tumor focus decomposes, purulent or sputum mixed with blood occurs.
Metastases in the lungs
Liver
There is an increase in the size of the organ beyond the boundaries of the costal arch, and accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. It is possible to develop swelling of the legs - metastatic tumors compress the vena cava, inhibiting reverse blood flow.
Bones
It manifests itself in areas of osteoporosis due to an increase in alkaline phosphatase and calcium in the blood. With a small load, fractures form. Confirmed by x-ray.
Scientifically proven fact: the smaller the thickness of the disease and the degree of germination into the deep layers, the lower the likelihood of metastases spreading. With a thickness of up to 0.76 mm - the probability is low, with a thickness of 0.76-4.0 mm - average prevalence, and thickness above 4.0 mm - high probability of tumor spread.
Causes of nodular melanoma
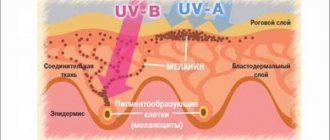
One of the main triggers that underlie the development of nodular melanoma is the recent increase in the total time of exposure to the ultraviolet part of the spectrum of natural sunlight on human skin, which is not always genetically prepared for this. As a result of excessive insolation, not only keratinocytes and melanocytes are damaged, but also suppression of antitumor immunity occurs, associated with impaired function of natural killer cells. This increases the risk of developing melanoma.
Doctors identify other risk factors for melanoma:
- Skin phototype I–II (proneness to sunburn of the skin, blue eyes, red hair, fair skin);
- The total number of benign melanocytic nevi on human skin;
- The presence of freckles and lentigines (flat formations on the skin of a brown color with clear boundaries and slow growth);
- 3 or more episodes of severe sunburn of the skin during life;
- The presence of three or more atypical melanocytic nevi;
- Familial accumulation of melanoma cases in close relatives.
If you are at high risk of developing melanoma, you should be constantly monitored by a dermatologist-oncologist.
Diagnosis of metastases
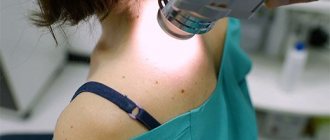
Diagnosis of metastases in melanoma is carried out by a dermatologist or oncologist. Histology of the excreted biopsy is required to confirm that it is malignant.
Metastases are diagnosed by scintigraphy (injection of a radioactive component), magnetic resonance imaging (detecting how widely the cancer has begun to spread in the body), and computed tomography.
It is important to conduct an ultrasound of the organs (liver, kidneys, lungs, brain), bones and lymphatic system. Diagnosis is difficult when determining whether the metastatic activity is primary (the formation of melanoma on the skin) or whether it is a secondary element of the tumor process.
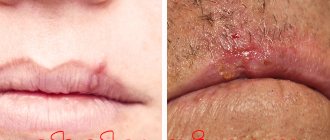
Differences between moles and melanomas
The spread of melanoma to the heart occurs in isolated cases.
Distribution of metastases:
| Localization | Symptoms | Diagnostics |
| Superficial and deep layers | Islands of pigment formations: in women in the lower extremities, in men on the back. | Visual examination, biopsy. |
| Lungs | Cough, shortness of breath, fluid in the pleural cavity. | Fluorography, CT. |
| Liver | Nausea, weakness, weight loss, organ increases in size. | CBC, ultrasound examination. |
| Brain | Headache, cramps. | MRI. |
| Bones | Joint pain, anemia, frequent fractures. | X-ray, MRI. |
| Gastrointestinal tract | Perforation of the intestinal wall, bloating, nausea, loss of appetite. | MRI. |
Causes
There are a number of reasons that cause a tumor or contribute to its development. They are called risk factors and are divided into groups of exogenous factors, that is, those found in the environment, and endogenous, that is, generated by the human body itself. This division can be considered conditional, because a person cannot refuse to interact with the outside world. Therefore, there is often a combined effect of causes.
Endogenous risk factors
All endogenous factors can be divided into two groups. The first includes the biological characteristics of the human body, the presence of which can increase the likelihood of developing melanoma. These include the following possible reasons:
- racial or ethnic predisposition. For example, people with dark skin suffer from melanoma four times less often than people with light skin;
- anthropometric indicators;
- heredity;
- the level of pigmentation of the body - the lower this level, the more often the disease occurs;
- immune system disorders;
- endocrine and reproductive factors in women.
The second group includes tumor precursors, that is, pathological changes in the skin that can degenerate into a malignant neoplasm. For example, such factors are nevi, Dubreuil melanosis and skin xeroderma pigmentosum.
Exogenous risk factors
This group includes physical, chemical and biological agents from the environment that can directly affect the skin. Physical factors include:
- ultraviolet radiation;
- electromagnetic radiation;
- fluorescent lighting;
- ionizing radiation;
- chronic skin trauma.
Chemical risk factors are important only for people who, due to their occupation, are in constant contact with harmful chemicals that can contribute to the development of melanoma. For example, the occurrence of neoplasms is common among miners working with coal, workers in rubber manufacturing, petrochemical, and pharmaceutical enterprises. Biological risk factors are dietary habits (high content of animal fats and proteins, lack of fresh vegetables and fruits), viral infections, as well as certain medications (estrogen-containing hormonal drugs).
Rules for the treatment of melanoma and metastases
At the appointment, the doctor examines the mole (or spot) that is bothering the patient. Small moles are not biopsied; a decision is made to remove the entire nevus. What does treatment include:
Laser removal of melanoma
- Surgical intervention - removal is performed for a single lesion. Melanoma that has metastasized to the lymph nodes must also be removed.
- Chemotherapy – treatment is carried out with antitumor pharmaceutical drugs (Dacarbazine, Temozolomide). An innovative method - treatment with electrical impulses - interacts positively with chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapy is a new method of combating metastases. Effective even in recurrent forms of the disease. The pharmaceutical drugs Interleukin-2 and Imiquimod help the immune system find and attack tumor cells throughout the body. A vaccine against melanoma is being developed.
- TIL immunotherapy (translation - tumor lymphocyte infiltration) - stimulation of natural human immunity. After removing a small number of metastases, atypical cells and TIL cells (lymphocytes embedded in the tumor to destroy it) are removed. After extraction, the cell undergoes reproduction in artificial conditions for several weeks, after which it is injected into the patient along with blood plasma.
- Targeted therapy allows you to quickly and effectively cope with the manifestation of metastases. Drugs such as Sorafenib, Dabrafenib, Nivolumab act directly on the oncological process without affecting healthy tissues and organs (unlike radiation and chemotherapy).
- Radiation therapy (gamma radiation) - allows you to regress and remove foci of metastatic activity in places difficult for surgical access.
Metastases in lymph nodes, liver, lungs, brain
Treatment of lymph nodes is carried out through surgery. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are preliminarily performed to obtain a favorable prognosis for the outcome of the operation.
Melanoma metastases enter the liver through the hematogenous route. Standard treatment protocols become difficult due to the susceptibility of hepatocytes to different types of radiation. The artery supplying the liver is embolized with chemotherapy drugs. This method allows you to influence liver metastases without putting healthy organs at risk.
To target lung metastases, therapy is primarily used to reduce the ability of atypical cells to metastasize. At the same time, a decreasing size of the tumor process appears.
Special stereotactic therapy has been developed for the treatment of brain metastases. A special mask is made, wearing which the patient can be sure that healthy brain tissue will not be exposed to radiation. Tumor regression occurs due to irradiation from three dimensions using an accelerator rotating around the head at different levels.
Characteristics of metastatic melanoma
Characteristics of advanced metastatic melanoma include:
- location of distant metastases;
- number and size of tumors;
- an increase in the level of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the blood serum, which usually indicates the spread of the tumor to internal organs.
There are three subclasses of metastatic melanoma. This division is based on the location of metastases and LDH levels:
- M1a:
the tumor metastasizes to a distant area of the skin, subcutaneous tissue or distant lymph nodes; LDH is normal. - M1b:
tumor metastasizes to the lungs; LDH is normal. - M1c:
tumor has metastasized to organs other than the lungs, LDH is normal, or there are any distant metastases with elevated LDH levels.
Prevention and relapse
If it is possible to defeat the cancer process, the patient should be more careful about his health. In 50% of cases, relapse occurs. The success of treatment depends on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed. The first stage is curable. At the second stage, the five-year survival rate is 25-40%.
The patient should consult a dermatologist for an explanation of which moles are dangerous. The skin is regularly examined for new moles, and the lymph nodes are checked. You should avoid uncontrolled exposure to the sun and visiting a solarium. Find out the prognosis and how tumor symptoms change after metastases. The disease is easier to prevent than to cure.
Symptoms
In the first stage, symptoms may be completely absent. This fact is the main reason for poor prognosis: people seek help only when the lesions become irreversible. The first symptoms that the patient feels include burning, itching and bleeding. But these signs indicate the development of melanoma and belong to later stages. General symptoms of tumors are:
- weakness;
- elevated temperature;
- weight loss;
- causeless fatigue;
- loss of appetite.
When metastases appear, the patient feels pain in the affected internal organs. There are also disturbances in their functioning.
Forecast
The fatal outcome from skin disease is 90%. The five-year survival rate is almost 100% when diagnosed at stages zero and first. When the tumor grows into the deeper layers of the skin, this figure is halved. The third and fourth stages can be considered favorable if there is no spread to vital organs. It is important to take into account the patient’s condition, the presence of aggravating chronic diseases and age to determine the life expectancy of cancer.
Recently, clinics in Israel and Germany have been using modern diagnostic methods that make it possible to determine oncological pathology at an early stage. Detection of the disease at the very beginning provides a 100% guarantee that the disease will not spread and a positive prognosis.
Prognosis for nodular melanoma
This is a malignant and extremely dangerous cancer process. The prognosis depends on the stage at which the disease is diagnosed. The initial stage of the disease is predicted according to Clark. According to this scale, there are 5 levels of processes spreading to the skin. There is no metastasis. A complete cure is possible.
The late stage may be characterized by the thickness of the lesion according to Breslow. This is a signal that the disease has entered the body. The prognosis for these signs is unfavorable. The fatality rate can be more than half of the cases.
Treatment of melanomas of the gastrointestinal tract
Treatment tactics for nodular melanomas of the gastrointestinal tract depend on the degree of tumor progression. Often the disease is detected at advanced stages, and removal of the primary tumor is not always possible.
In cases where the tumor spreads to neighboring organs or has distant metastases, targeted and immunotherapy may be most effective. This approach makes it possible to reduce the rate of tumor growth, improve survival and quality of life of the patient.
In some medical institutions in Europe, the USA, as well as oncology clinics in Israel, methods of immunotherapy for common melanomas are highlighted in a special section. Special clinical protocols have been developed for this purpose.
The additional use of stereotactic surgery techniques makes it possible to reduce the volume of inoperable tumors and reduce pathological symptoms.