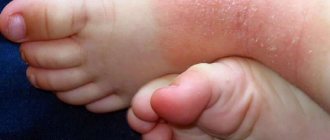
Causes of eczema on hands
The causes of hand eczema are not fully understood. However, experts tend to attribute this dermatological problem to polyetiological diseases, that is, to those that arise as a result of the influence of a number of factors. These are both external and internal reasons, which are most often combined with the existing tendency of the skin to form microbubble epidermitis. This feature of the epidermal layer of the skin can be either congenital or acquired.
Potent trigger factors for eczema on the hands include:
- Lack of microelements necessary for the body;
- Lack of B vitamins, especially vitamin B6;
- Parasitic damage to the human body (pinworms, roundworms, lamblia, etc.);
- Insufficient intake of unsaturated fatty acids from food;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the excretory systems;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the intestine, its dysbiosis;
- Gallbladder diseases, in particular cholecystitis;
- Irregularities in the functioning of the immune system.
In addition, scientists have identified several types of the disease that can affect the skin of the upper extremities.
Each of these forms has its own causes for the development of eczema on the hands and fingers:
- Causes of idiopathic eczema on the hands:
- Excessive nervous tension.
- Stressful situations that traumatize the psyche.
- Disruption of the autonomic nervous system.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland (euthyroidism, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism).
- Diabetes.
- Disturbances in the digestive process.
- Genetic predisposition.
(on topic: atopic dermatitis in adults and children)
- Causes of atopic eczema:
- Atopic eczema is a common companion for people who are predisposed to allergies. The reaction can occur to pet fur, plant pollen, indoor dust, food components and other irritants.
- Hereditary predisposition to atopic diseases influences the appearance of atopic eczema. Often, patients with eczema on the hands and fingers are diagnosed with asthmatic bronchitis, bronchial asthma. Moreover, these diseases can be traced in family history.
- Causes of occupational eczema:
Occupational eczema appears as a result of exposure of the skin of the hands to chemical components that irritate it. Pathogenic substances can be presented in the form of gases, smoke, vapors, in liquid and solid states. Most often, workers in the metallurgical industry, construction, pharmaceutical industries, and people working in the printing industry are exposed to occupational eczema. Substances such as formaldehyde, nickel, chromium, lead, manganese, cobalt, formaldehyde, epoxy resins, nickel, etc. are dangerous.
The longer aggressive substances are exposed to the skin of the hands, the higher the risk of developing eczema. Appearing first on the hands, occupational eczema can spread to other parts of the body.
- Causes of microbial eczema:
- Microbial eczema occurs as a result of sensitization of the skin of the hands to antigens produced by fungi and bacteria.
- The cause may be a long-term non-healing purulent wound, a trophic ulcer, a cut, abrasion, burn or other injury.
- Causes of dyshidrotic eczema:
- Interaction of hand skin with surfactants.
- Occupational factors that have a negative impact on the skin of the hands.
- Irrational ingestion or local application of drugs.
- Incorrect use of cosmetics and detergents.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- Hand skin injuries.
- Exposure to cold or sunlight on the skin of the hands.
- Past infectious diseases.
- Hyperhidrosis of the palms.
Varieties of eczema such as seborrheic eczema or varicose eczema are not typical for the skin of the hands.
Is eczema inherited?
Many parents fear that eczema is contagious and is passed on genetically. There's no need to worry. Eczema itself is not inherited. The disease is not inherited, but only a predisposition to it. If your closest blood relatives have been diagnosed with any dermatosis, then it is likely that the child will develop skin problems. Neurodermatitis, eczema or allergies in both parents doubles the risk of developing a similar pathology in the baby.
Timely cured pathology minimizes the likelihood of transmitting the disease by inheritance. Adults should also lead a healthy lifestyle and remember to monitor their nervous and endocrine systems.
Breastfeeding a child will help reduce the likelihood of a hereditary form. The minimum possible period of breastfeeding a baby should be 6 months. This contributes to the formation of the baby's immunity.
Can a child get eczema from another person? Even in the presence of suppuration and inflammation of the skin, it is impossible to transmit eczema to a child from any other person. Microorganisms that enter healthy skin will be destroyed by immune cells.
Symptoms of eczema on hands
Symptoms of hand eczema will vary depending on what type of condition affects the person.
- Symptoms of idiopathic eczema on the hands:
- The rash may appear as erythema, papules, or blisters. They are localized on open areas of the body, including the legs and arms, and are most often symmetrical.
- The beginning of an exacerbation of the disease is characterized by the appearance of bubbles, which subsequently merge and, after destruction, form erosions.
- The entire process of inflammation is accompanied by severe skin itching, which may precede the onset of the disease.
- When the process becomes chronic, lichenification of the skin occurs.
- Symptoms of atopic eczema on the hands:
- The skin swells and turns red, covered with small blisters.
- The bubbles resolve, leaving behind areas of weeping.
- As the disease progresses, the skin becomes covered with crusts and scales, becomes dry, and begins to peel.
- Itching can plague the patient both during remission and during exacerbation of eczema. However, when the process enters the acute phase, the itching becomes extremely pronounced.
- Symptoms of occupational eczema on the hands:
- Inflammation appears only in those areas of the skin that come into contact with the irritant. It is the hands and fingers that are most susceptible to the appearance of occupational eczema.
- As the disease progresses, eczema spreads to other areas of the body.
- The inflammation process occurs like idiopathic eczema.
- Symptoms of microbial eczema:
- Microbial eczema is located around existing wounds, burns, fistulas with purulent inflammation.
- Eczema initially affects only that part of the skin where there is a pustular disease. The stratum corneum peels off, peeling begins, or exudate separates.
- Subsequently, the exudate dries and forms crusts.
- Eczema is not treated, then it begins to affect symmetrically located skin areas.
- As a rule, itching does not bother the patient much.
- Symptoms of dyshidrotic eczema:
- A rash appears that looks like small blisters filled with liquid.
- The rash initially appears on the sides of the fingers and then spreads to the palms.
- The skin becomes swollen and red.
- After the vesicles open, erosions appear on the inflamed areas and become profusely wet. At the same time, the skin begins to peel off.
- The disease is accompanied by severe itching.
- Often a secondary infection occurs, which provokes the appearance of pain, cracks, and lichenification.
Coin-shaped eczema in children
In children, coin-shaped eczema is much less common than other types. According to the latest data, identification of patients with this disease occurs with a frequency of 1:300. That is, for every 300 children diagnosed with it, one case is coin-shaped. Its successful treatment depends on the timely contact of parents to the doctor, since the course of the disease occurs much faster than in adults. This leads to a transition from an acute form of coin-shaped eczema to a chronic form in a fairly short time.
Adequate therapy can not only eliminate symptoms, but also prevent their occurrence in the future. Weeping or coin-shaped eczema causes great discomfort to the child if measures to diagnose and treat the disease are not taken in time.
Answers to popular questions
- Is it possible to cure eczema on hands permanently? Modern medicine cannot cure eczema on the hands forever, since this disease is chronic in nature with periods of exacerbation. However, it is possible to achieve stable remission if proper treatment is selected.
- Is hand eczema contagious? Eczema on the hands, as well as on other parts of the body, is not a contagious disease.
- Is it possible to get eczema on your hands wet? Do not get eczema on your hands wet. If the skin of your hands needs cleansing, then special oils should be used for this. When washing dishes, if there is any need for contact with water, you must first put on cotton gloves and rubber gloves over them.
Contagious or not?
It’s not just those around you who are wondering: is eczema contagious? The patient himself thinks about this. Doctors give a clear answer: eczema is not transmitted from person to person.
Microbial eczema can be classified as a relatively contagious form. In this case, it is not the eczema itself that is transmitted, but only the infection located on the patient’s skin. This is a bacterium (or fungal microorganism). The likelihood of infection is very low. Harmful bacteria can be transmitted to others only through very close contact. If the patient uses various antiseptics, then the risk of infection is very small.
The disease develops against a background of weakened immunity. It is often passed on by inheritance. You cannot get sick from contact with a sick person. If you use household items of a person with eczema, it is also impossible to become infected.
Eczema is similar in development to asthma, in which the immune system plays a major role. Eczema manifests itself with the same symptoms and is characterized by the release of large amounts of bioactive substances. The skin becomes inflamed with eczema, and with asthma there is a narrowing of the bronchi.
The immune system is often weakened due to some chronic illness. In childhood, this is most often an exudative diathesis. It is impossible to answer the question of whether or not the disease will develop into eczema. To avoid this disease, you must follow a diet. In addition, parents should ensure that household allergens irritate the child’s body as little as possible. It is also important to promptly treat all skin diseases.
It is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own. This can only be done by a dermatologist. He examines the patient and sends him for tests. This is a test for sugar and possible helminths. The gastrointestinal tract is fully examined. In addition, other laboratory tests are prescribed.
How to treat eczema on hands?
Treatment is selected for each patient individually. In this case, the specialist takes into account the type of disease, how pronounced the inflammation process is, as well as the age of the patient, the presence of other diseases, etc. It is possible to bring the disease into a stage of stable remission only with an integrated approach to treatment.
- General therapy:
General therapy should include correction of existing dysfunctions of all organs, normalization of metabolism, and increase of the body's immune defense. It is important to pay attention to reducing the negative impact from the external environment.
Nonspecific therapy aimed at reducing the body's individual sensitivity to existing allergens has been recognized as effective. In this case, the patient is prescribed antihistamines, immunosuppressants, glucocorticoids, and cytostatics. In parallel, autohemotherapy, hirudotherapy, blood transfusion, and lactotherapy are carried out.
If the disease is severe, doctors refer the patient for plasmapheresis, hemo- and enterosorption.
- Therapy for neurotic disorders:
- Taking small doses of tranquilizers (Nozepam, Chlozepid, Phenazepam). The drugs can only be prescribed by a doctor, and the total course of treatment should not exceed 10 days.
- Bromcamphor and Sodium bromide are taken as sedatives for two weeks.
- Sedatives of plant origin are: Valerian extract, Persen, Novopassit, Sedasen, Peony tincture.
- Therapy aimed at eliminating intoxication of the body:
- Enterosorbents can be prescribed as a course for 10 days: Multisorb, Polyphepan, Polysorb, Enterosgel, Filtrum STI, Atoxil.
- Intravenous administration of calcium chloride or sodium thiosulfate is possible.
- If the disease is complicated by a fungal infection, then a solution of Hexamethylenetetramine is prescribed.
- Calcium gluconate is injected intramuscularly. The number of injections should not exceed 10.
- Therapy with hormonal drugs:
If there is an urgent need (if the disease persists), then the disease is treated with hormonal agents. Such treatment can only be prescribed by a doctor. The course cannot be long, since the use of corticosteroids has a number of side effects that can negatively affect a person’s overall health.
Particularly dangerous is the independent long-term use of hormonal drugs. If the eczema has not spread beyond the hands, then, as a rule, doctors limit themselves to local treatment only. For more extensive lesions, it is recommended to take hormones orally for a period of no more than 15 days. For this purpose, drugs such as: Triamcinolone, Prednisolone, Corticotropin, Dexamethasone can be used.
- Therapy with vitamins:
Any type of eczema on the hands is an indication for taking vitamins. However, they must be used with caution and only as prescribed by a doctor. For eczema, the following are prescribed: injection of B vitamins, taking Folic acid, taking Nicotinic and Ascorbic acid, taking vitamin E.
- Therapy using antiallergy drugs:
- During an exacerbation of eczema, Chloropyramine, Diphenhydramine, Promethazine are prescribed. Method of administration: parenteral.
- If the disease is of moderate severity, then oral administration of the same drugs is prescribed.
- As the inflammation process subsides, it is recommended to switch to third and second generation antihistamines. This could be: Cetirizine (Zyrtec, Zodak, Parlazin, Cetrin), Ebastine (Kestin), Loratadine (Dezal, Lordestin, Erius), etc.
- It is possible to take Ketotifen.
- Therapy using immunomodulators:
Immunomodulators are not prescribed to all patients with eczema. They can be taken only after undergoing an examination by an immunologist and performing all the necessary tests. The doctor may prescribe medications such as: Timomimetics (Imunofan, Timalin, Thymogen), phagocytosis stimulants (Lykopid, Polyoxidonium, Prodigiozan), as well as Plazmol, humisol solution, placenta extract, vitreous body.
- Therapy aimed at normalizing the functioning of the digestive organs:
Often eczema on the hands appears in parallel with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. To get rid of them, it is recommended to take drugs such as: Ermital, Pancreatin, Creon, Micrazim, Pangrol, Gastenorm, Biozim, Pepfiz, Pangrol, Enzistal, Festal, Solyzym.
If a violation of the intestinal microflora is detected, then a course of probiotics is indicated, for example, Lactobacterin, Hilak Forte, Rioflora-immuno, Bifiform, Linex, etc.
- Therapy for microbial eczema:
If a patient is diagnosed with microbial eczema, then it is impossible to do without the use of antibacterial drugs. Ointments with an antimicrobial effect are prescribed externally, and antibiotics from the following groups are recommended internally: cephalosporins (1st generation), macrolides, fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides. Antimycotics are prescribed when a secondary infection occurs.
Local therapy for eczema on the hands
If a patient is diagnosed with microbial eczema, then he needs to lubricate the crust on his hands:
- Brilliant green, Methyl violet solution, Gentian violet solution.
- Creams and aerosols: Panthenol, Polcortolon, Levovinisol.
- If the disease is chronic, lotions with a solution of Resorcinol or Ethacridine Lactate are recommended.
Lotion can have an anti-inflammatory effect and reduce itching with the application of the following compositions:
- Goulard;
- Burov's fluid;
- Resorcinol in solution up to 1%;
- Copper sulfate, zinc sulfate in solution 0.1%;
- Silver nitrate in solution 0.15%;
- Phenol in solution up to 5%;
- Citric acid in solution 1%;
- Metol solution up to 1.0%;
- Podophylline ointment;
- Diphenhydramine paste.
Effective means for relieving acute inflammation are powders with white clay, zinc oxide, and wheat starch. When the disease subsides somewhat, you can use zinc oil, as well as neutral ointments that do not contain active ingredients.
A solution of boric acid, a solution of tannin, and a solution of galascorbine helps eliminate swelling of the skin, reduce weeping, and remove redness.
To speed up the healing process at the stage of extinction of inflammation, you can use Lassara paste, zinc ointment with the addition of Naftalan paste, Ichthyol paste, Boron-zinc and Boron-naphthalan paste, Dermatol and Methyluracil paste.
As for corticosteroid ointments, to get rid of eczema on the hands, doctors often prescribe Elokom, Advantan, Skin-cap, Flucinar, Celestoderm. If the patient has microbial eczema, then it is best to use Trimistin, Lorinden S, Celestoderm with Garamycin, Travocort, Kremgen.
Hand eczema responds well to physical therapy. Therefore, such treatment methods as: baths with radon, with mineral water, diphenhydramine inhalations, electrosleep, general galvanization, diadynamic therapy, ultrasound treatment, laser therapy, utraphonophoresis with drugs, ultraviolet treatment, ozone therapy, magnetic therapy, paraffin baths, acupuncture are often used .
It is important to adhere to a therapeutic diet and avoid consuming large amounts of salt, excluding spicy, fatty fried and smoked foods. You should not consume chocolate, coffee, alcohol, eggs, as these products are potential allergens. Preference should be given to a dairy-vegetable diet.
Treatment and prevention of eczema
At the first appearance of symptoms of the disease, you should consult a doctor. Self-diagnosis is impossible, as it requires laboratory tests to rule out helminthiasis, diabetes mellitus, and so on.
For treatment, hormone therapy, taking sedatives, and staying in a sanatorium are recommended. The main condition for recovery is personal hygiene. During the acute period of illness, water procedures are prohibited, except for herbal baths. Take them for no more than 10 minutes, using chamomile, string, calendula and other herbs. This will help relieve itching and inflammation from the affected areas.
Eczema is not curable, but following certain doctor’s recommendations reduces the frequency of its manifestations and softens the course of the disease in case of exacerbation.
Rules to follow
- Balanced diet.
- Use rubber gloves when cleaning wet.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Elimination of salty and spicy foods from the diet.
- Minimizing stressful situations as one of the main causes of illness.
- Timely consultation with a doctor at the first suspicion of eczema.
An integrated approach to the treatment and prevention of skin pathologies will help restore beauty and attractiveness to patients. This will give you self-confidence and keep your body healthy.
Types of eczema, its manifestations
The main symptoms of the disease are rashes that appear on the skin and are accompanied by constant itching and burning. Over time, the skin in problem areas begins to peel off, the vesicles that formed earlier crack and weeping appears in their place. In the event of a bacterial infection, which is quite likely in the absence of treatment, pustules may form in the affected areas.
The pathology is characterized by a recurrent nature and seasonal exacerbations, which once again confirms the negative answer to the question: is microbial eczema contagious or not?
Type of eczema:
- True eczema. The primary location of the pathology is the skin of the face; small bubbles filled with clear liquid appear here. In the absence of timely treatment, the symptoms of the disease become more noticeable, itching appears, the rash grows and spreads to the epidermis of the upper and lower extremities. The vesicles crack and oozes form in their place;
- Varicose eczema. Varicose eczema or so-called stasis dermatitis develops in patients suffering from varicose veins;
- Microbial eczema. Eczema occurs in problem areas of the skin where a fistula or ulcer has previously formed. The affected area is usually covered with a crust, which subsequently cracks and weeping remains in its place. The main cause of the development of microbial eczema is considered to be dysfunction of the immune system and malfunctions of the nervous system. A factor contributing to the manifestation of this type of dermatitis is the body’s predisposition to fungal infections and microbes;
- Eczema of the lips. It appears around the lips; this form is characterized by the appearance of scales, crusts and cracks in the affected areas. Weeping does not form;
- Seborrheic eczema. The localization of the disease is the scalp, axillary area, and shoulder blade area.