Last Updated on 05/05/2020 by administrator
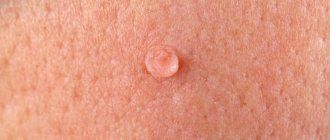
Basal cell papilloma is a specific formation on the skin that develops from the basal layer of the epithelium under the influence of the human papilloma virus. It is currently known that more than 90% of people on the planet are carriers of various strains of the human papillomavirus.
Many of these strains do not cause any growths on the skin, but there are some that lead to the appearance of specific warts. Basal cell papillomas are characterized by extremely slow growth. They are usually benign in nature and extremely rarely transform into malignant tumors. side effects of xarelto in the elderly.
Often, such papillomas develop in people over 50 years of age. Such papillomas are not large in size. As a rule, they reach from 1 mm to 4 cm in diameter. Typically, such neoplasms are localized on the open surface of the skin, near the hair follicle. Considering that such formations never metastasize, they do not have to be removed, because in most cases they do not cause any physical discomfort.
Causes and symptoms of basal cell papilloma
papillomavirus is a group of 27 types of papillomaviruses. Each of which has species-specific antigens. This provokes mutation of human skin cells. Because of this, there is a high probability of degeneration of a benign neoplasm into the cancer stage. There are the following favorable factors that contribute to the rapid development of the virus in the human body:
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Frequent exposure to stress.
- Lack of vitamins and minerals.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Poor nutrition.
- Physical overload.
- Transmission of infectious and inflammatory diseases.
papillomavirus can progress in the body asymptomatically for many months. If a person has a strong immune system, the infection may not go into the growth stage and disappear altogether. With a weak immune system, neoplasms usually occur. Following which, the following unpleasant symptoms appear:
- Burning skin.
- Difficulty in labor.
- Bloody vaginal discharge.
- Bleeding when the growth is damaged.
- Itching.
- Pain syndrome.
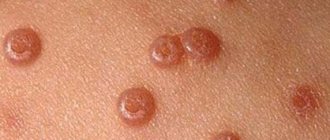
Basal cell papilloma appears as pigmentation, nodule and ulceration.
Benign formations have a convex, nodular appearance with black or light specks. Only a doctor can determine the type of virus and prescribe the correct treatment. This happens only after examination and taking the necessary tests.
Is basal cell papilloma dangerous?
Papilloma is a neoplasm that does not progress to the stage of cancer in children. Adults, if growths are detected on the body, should immediately seek help from a doctor. The fact is that often, seborrheic keratosis is found in the structure of the growth, which occurs due to age-related changes. In many cases, this is the main reason for the degeneration of the growth into a malignant tumor.
It is important to know that keratotic papilloma does not go away on its own! It requires high-quality and long-term treatment!
For women, basal cell keratosis papilloma is dangerous for causing cancer of the rectum, uterus and cervix. There is also a high probability of developing cervical erosion. Women who are addicted to alcohol and addicted to smoking are especially at risk of complications. That is why, if growths or their modifications are detected on the body, you need to immediately give up bad habits.
For men, this disease does not pose any particular threat. Often, male representatives are carriers of the papillomavirus. At the same time, the favorite place to localize the growth is the groin area. Which leads to rapid infection of the partner.
Diagnostics of education
If a growth is detected, you should visit a dermatologist. Diagnosis of papilloma is carried out by visual examination.
To clarify the type of formation, the doctor prescribes a series of studies.
- PCR method - determines the presence and quantitative content of the virus. Clarifies the classification of papilloma, as well as the nature of the disease.
- Biopsy - a piece of growth is removed for examination.
- Cytology – checks the probable malignancy and level of tumorigenicity.
Attention! These procedures are mandatory for any type of growth, since it is important to exclude the appearance of seborrheic keratosis. The disease is similar to basal cell papilloma, but the form is formed due to age-related changes on the surface of the skin, and not due to HPV.
If the diagnosis reveals the degeneration of HPV into basal cell carcinoma, the dermatologist redirects the patient to an oncologist. The doctor will conduct additional research and prescribe more effective treatment.
Drug treatment of growth
Drug treatment is the most common method of eliminating diseases. It includes taking medications and applying them externally. This method must be carried out strictly according to the prescription of a medical specialist. Under strict control of treatment effectiveness. The most effective remedies for eliminating warts are:
- Podophyllin is a cauterizing drug with cytostatic and necrotizing effects. Its use directly depends on the location of the warts. If the oral cavity is damaged, the neoplasm should be removed, and the damaged area should be generously lubricated with podophyllin once a day for 2-10 days. For papillomatosis of the bladder, the solution is injected into the internal cavity once a day for 3 days. The duration of treatment can be increased by the doctor to 3 weeks. This drug is contraindicated for women during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as for children under 12 years of age.
- Feresol is a cauterizing drug that coagulates skin proteins. Using a special spatula located under the lid of the drug, the medicine is applied to the growth 2 times with an interval of 5 minutes. The duration of treatment is 4 days, with constant breaks of 7 days. Contraindications for use are children under 7 years of age and people with pigmented nevi.
- Immunomax is an immunostimulating drug. For adults, this drug must be administered intramuscularly at a dose of 100 units over 6 days, following the following regimen: 3 days of injections, 4 days of rest, 3 days of injections. This drug is contraindicated in children under 12 years of age and in the presence of allergic reactions to the components of the drug.
Important! If drug treatment does not bring positive results after 3-4 days, you should immediately consult a doctor to change medications!
Pathological anatomy
Macroscopically, papilloma is usually delimited, dia. up to 1-2 cm, dense or soft to the touch tumor on a thin long or short stalk, less often - on a wide base. In rare cases, papillomas reach large sizes. With papillomatosis, the surface of the skin or mucous membrane is covered over a significant area with papillary growths. The surface of the papilloma is uneven, fine- or coarse-grained, reminiscent of cauliflower or cockscombs. Skin papilloma can have a different color - from white to dirty brown (depending on the blood supply to the stromal vessels and the pigment content in the basal layer of the epithelium); Papilloma of the mucous membrane is often colorless or pearly white, but sometimes acquires a purple or black color due to hemorrhages into its tissue. Bladder papilloma can be hardened due to deposits of calcium salts.
Rice. 4. Microscopic specimen of papilloma of the oral mucosa: the surface of the papilloma is covered with a layer of stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium (1) with deep acanthotic cords plunging into the connective tissue stroma rich in thin-walled vessels (2); hematoxylin-eosin staining; x 20. Fig. 5. Microscopic specimen of papilloma of the esophageal mucosa: numerous papillary growths of stratified squamous epithelium and connective tissue stroma are visible; hematoxylin-eosin staining; x 20.
Microscopically, papilloma (color Fig. 4) consists of two tissue components - connective tissue stroma and epithelium. Based on the nature of the epithelium, they distinguish between squamous cell (covered with stratified squamous epithelium) and transitional cell (covered with transitional epithelium) papillomas. The connective tissue of the tumor stroma can be loose or dense, often edematous, sometimes with mucus phenomena, a greater or lesser number of vessels and, as a rule, with signs of inflammation. In cases where the papilloma stroma is significantly developed and sclerotic, we speak of fibropapilloma. In the epithelium covering the papilloma, the number of cell layers is usually increased, and the epithelial cells are larger than normal. At the same time, noticeable hyperkeratosis is observed in the skin papilloma; in papillomas that arise on the mucous membranes, keratinization is usually less pronounced (tsvetn. Fig. 5), the cells of the superficial layer of the epithelium are pale colored. Sometimes there are papillomas of the mucous membranes, covered with stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium, which developed as a result of metaplasia (see).
In some papillomas, the phenomena of acanthosis (see), usually accompanied by high mitotic activity of the cells of the basal layer of the epithelium, may be expressed.
Various skin papillomas may differ from each other in their histological structure. Thus, ordinary skin papillomas are characterized by the presence of vacuolated epithelial cells in the basal layer and areas of parakeratosis; with senile keratosis, papillomas with atypia and polymorphism of epithelial cells appear; basal cell papilloma is characterized by the presence of the same type of dark cells and horny cysts.
Surgical treatment of the disease
There are a huge variety of methods and means for removing papillomas. The appointment by a medical specialist of a specifically suitable one is directly based on the location of the formation, the presence of other diseases and complications in a particular patient. Surgical removal of warts is considered more effective than medical removal. This is due to the lower risk of re-growth and the possibility of removing large papillomas.
Surgical methods include:
- Cryodestruction - freezing the tumor with liquid nitrogen.
- Electrocoagulation – burning out the growth with an electric current.
- Laser method.
- Radio wave removal.
Each of the presented methods reduces the risk of bleeding and the formation of postoperative scars. It is possible to eliminate several warts in one session. All procedures are considered painless, although they cause discomfort. Postoperative periods do not last long and in most cases pass without negative consequences.
External characteristics of the disease
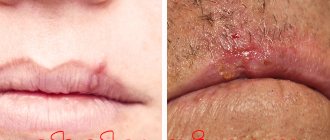
According to their appearance, papillomas are divided into: pointed, simple and flat. In this case, the first is characterized by the presence of a pink, pointed tip. When several pointed papillomas merge, the formation of a “cockscomb” is observed. It is worth noting that this type of papillomavirus is transmitted exclusively through sexual contact.
Simple warts are characterized by a dark color and similarity to shiny bumps. The most common locations for them are the face, legs and arms. They are easily confused with a callus due to the stratum corneum of the skin. They rarely degenerate into a malignant formation, but there are still recorded cases.
Flat growths appear in the form of small nodules. Their surface is slightly flattened, and their size does not exceed 8 cm. Most often, flat warts are found in children and adolescents. This is due to a sharp surge in hormones and their social activity.
What formations are mistakenly considered papillomas?
Doctors consider the development of growths to be a serious reason to make an appointment; some may be dangerous. Papillomas are often confused with other pathologies, which often develop into cancer.
Pearly papules
Small whitish nodules can be observed around the head of the male penis in representatives of the stronger sex, which are mistakenly taken for rashes of venereal origin. Such nodes are called pearlescent papules. They are confused with genital warts. But pearl ones do not harm.
Preauricular formations
Prealicular fistula - if in the parotid zone (usually behind the ear) a pink-grayish round formation measuring 0.5-50 mm has developed and become inflamed, then this is not one of the types of papillomas, but an inflammatory process of the lymphatic system.
Other
There are other formations that are similar to various types of papillomas:
- Keratoma is a formation on the skin, similar to a freckle, dark brown. Over the years, the spot becomes keratinized and begins to peel off, looking like seborrheic plaques of an almost black hue. Dimensions approximately 10-20 mm. Looks like raisins pressed into the skin. They can be individual or form a group. There are no symptoms of the disease. Keratomas usually self-amputate (fall off).
- Epulis is a productive formation, similar to a tumor. Formed as a result of local irritants. With epulis, you can notice a non-painful soft or dense protrusion on the gum, over which redness develops.
- Xanthoma is a disease that forms when fat metabolism is disrupted. Focal growths on the skin with altered cells, which consist of lipid inclusions. Xanthomas form in people with an excess of cholesterol in the blood.
- Gingivitis. Pathology of the gums, which is characterized by an inflammatory process - redness, swelling, bleeding.
- Adenoma is a benign tumor that forms from glandular epithelium. The course of the disease depends on the characteristics of the site of formation and the rate of growth.
In order not to confuse the manifestation of HPV with other types of diseases, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the first changes.
Mechanism of infection and prevention
Infection with the virus occurs through sexual, domestic and hematogenous routes. A newborn can intercept the disease from the mother as it passes through the birth canal. It is worth noting that women, more often than men, become infected through sexual contact. While among men, the household method of infection is common.
You can become infected with papilloma through minor abrasions and cuts. That is why it is necessary to treat fresh wounds with antiseptic solutions and secure them with adhesive tape!
Papilloma is a benign growth, the occurrence of which can be avoided. To do this, you need to take vitamin and mineral complexes in a timely manner, get rid of bad habits and adhere to a healthy diet. For girls who have not become sexually active, advanced vaccines are recommended: Gardasil and Cervarix. This will help avoid both sexual and domestic infections with papilloma.
How does the disease occur?
Basically, all this happens due to the entry of the papilloma virus into the mucosa. How does this happen:
- a possible infection through domestic means, through any injury or damage to the human body;
- most often, infection occurs through sexual contact with an infected partner;
- no matter how well the blood is checked during transfusion, the possibility of such infection is also considered;
- During childbirth, a mother infected with HPV can transmit it to her child when passing through the birth canal.
Blood transfusion is one of the ways of transmitting the virus