Yellow spots on the head, what are they?
A disease such as seborrheic dermatitis most often affects men, but this does not mean that it cannot affect women. The disease begins to develop gradually, and in winter the symptoms may intensify.
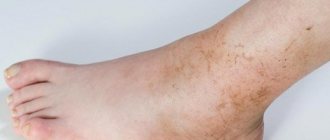
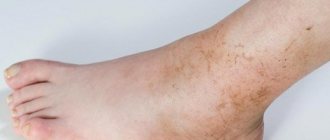
Yellow spots on the head of an adult can peel off, the size does not exceed twenty millimeters. You may feel wet and small cracks or crusts may appear. In order to make an accurate diagnosis, a visual examination of the patient is often sufficient.
The disease is quite common; it is believed that every fifth person on our planet suffers from it. When the scalp is affected, alopecia may occur. In the summer, relief usually occurs; many patients benefit from exposure to the sun.
In severe cases, erythroderma may develop. If you notice the first symptoms of the disease on your head, you must definitely visit a medical facility, in particular a trichologist or dermatologist.
Tips and tricks to resolve the problem
To get rid of crust on the scalp, it is important:
- find out from the doctor why the flaky areas appeared;
- strengthen the immune system. This will help: a course of vitamins, exercise, sufficient consumption of vegetables and fruits, giving up alcohol and tobacco;
- eliminate stressful conditions;
- drink about 2 liters of pure water per day;
- stick to a healthy diet (avoiding fatty, spicy, etc.). Normal activity of the gastrointestinal tract will reduce the formation of affected areas;
- choose shampoos and other caring cosmetics without aggressive ingredients. It is better to take plant-based products;
- get rid of the allergen, if we are talking about allergic manifestations of dandruff;
- use medicinal cosmetics prescribed by the doctor.
Folk remedies also give good results as a complete treatment, or complementing drug treatment.
After successful therapy, dandruff in the form of a crust on the epidermis may return, especially if you do not adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
Treatment
If yellow spots appear on your head, they must be examined. Since the disease is chronic, treatment takes a very long time. As mentioned above, the sun helps many people for treatment.
Shampoos containing selenium sulfide help a lot. Ketoconazole can be used only at the first stage of the disease, and subsequently it can be used as prophylaxis to avoid re-development of the disease.
When you wake up in the morning, you can remove the crusts that have formed on the stains. To do this, you need to dilute the shampoo in water and soak a cotton swab in it. After the scales are removed, you need to treat the skin with special products prescribed by the doctor.
On the shelves of pharmacies today there are a large number of different drugs that can be used to get rid of yellow spots on the head and cure such an unpleasant disease as seborrheic dermatitis. However, before using them, you must consult a doctor. In general, the treatment is successful, but only if it is correct and starts on time.
Yellow dandruff
One of the symptoms of the oily variety of seborrheic dermatitis is dandruff, which appears due to the fact that the sebaceous glands produce too much secretion, creating a favorable environment for the growth of the Malassezia fungus. With seborrheic dermatitis, the content of the fungus Malassezia Furfur increases. (1) Yellow dandruff is a sign of the oily variety of seborrheic dermatitis. We will now talk about the causes of its occurrence and methods of treatment.
Why does yellow dandruff appear on the head?
Increased activity of the sebaceous glands and the proliferation of Malassezia, leading to the appearance of oily seborrhea, is only a consequence. Here are the main factors that directly affect the functioning of the sebaceous glands of the scalp:
- Hereditary factor. There is a genetic predisposition to various forms of seborrheic dermatitis, and this is one of the main reasons for its occurrence. Although predisposition does not mean that the disease will definitely develop
- Problems of the endocrine system and disorders of the body's secretions.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which also affect secretion.
- Stress. Constant experiences lead to malfunctions of various organs, and the internal and external secretion organs are no exception.
- Hormonal changes. With an increase in the amount of male hormones in the body, active production of sebum begins, which is typical during puberty. This may also be a consequence of taking hormonal drugs (2) (3).
Symptoms
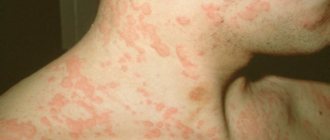
The presence of spots on the head, the appearance of which is accompanied by inflammatory processes, peeling of the skin, hair loss, severe itching or other symptoms, can be the cause of a variety of dermatological diseases or fungal formations.
It is recommended to consult a specialist, since only he can make an accurate diagnosis.
In most cases, such symptoms are evidence of one of the following ailments:
Ringworm
This is one of the most common and at the same time severe fungal diseases. A characteristic symptom is pathological hair loss, leading to partial baldness or the formation of large bald spots that are visible even to the naked eye.
The disease is highly contagious and can be transmitted to another person through direct contact with the patient or his personal belongings and hygiene equipment.
Infection through contact with sick animals is much less common, but there is still a risk. The difficulty of timely detection of the disease lies in the long incubation period, when there is no manifestation of the main symptoms; such a process can last from one week to several months.
Microsporosis
You can get infected both from sick people and from animals. In most cases, children under 12 years of age are infected and transmit the disease to their family members. A distinctive feature is the high rate of spread of spores, so isolated cases of infection can often be the first sign of an impending epidemic. Inflammatory processes rarely occur, but the affected areas usually become slightly swollen and covered with a purulent crust.
The main symptoms are very similar to the symptoms of other types of fungal infections, so an accurate diagnosis can only be made by a specialist.
Scab
It is transmitted in exactly the same way as the other described diseases. The main manifestation is the appearance of characteristic yellow crusts, in the center of which hair usually grows. Lack of therapy can lead to severe spread of lesions, skin atrophy and complete baldness.
Psoriasis
Spots are already a secondary symptom that manifests itself in the presence of inflammation. First of all, excessive peeling of the skin, mild irritation and itching occurs, leading to scratching of the affected areas of the skin. As psoriasis develops, plaques with a gray crust or plaque form, so this disease is often confused with seborrheic dermatitis.
Seborrheic dermatitis
And other diseases of this type, which are caused by the activity of fungi, and provoke the occurrence of inflammatory processes. With timely detection and proper treatment in the initial stages, usually all symptoms go away fairly quickly.
Two forms of oily seborrhea
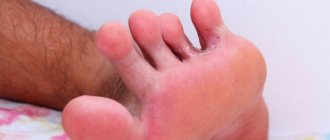
Oily seborrheic dermatitis can appear in liquid and thick forms. In the liquid form, the hair begins to become shiny, as if it had been generously lubricated with oil. Due to the increased activity of the sebaceous glands, pores expand and a large amount of sebum is released onto the surface of the skin. The active activity of the Malassezia fungus, which quickly multiplies in sebum, leads to keratinization of the epidermis (the upper cover of the scalp), resulting in the formation of yellow particles, that is, yellow dandruff, which is not shaken off as easily as dry white dandruff. In addition, the process of dandruff formation is accompanied by frequent itching, which is caused by chemically active waste products of Malassezia. If no measures are taken for a long time, a person’s hair may begin to fall out, acne, boils and other purulent formations may appear. This is due to the fact that in some places it is difficult for the secretion to escape.
The thick form of the oily variety of seborrheic dermatitis is more dangerous because the skin pores become clogged due to the fact that sebum mixes with keratinized particles of the epidermis and the surface of the head becomes covered with a yellow crust. As a result, plugs form in the sebaceous ducts and the secretion cannot come out, which leads to the appearance of large purulent formations, for example, atheroma. The thick form, like the liquid one, is accompanied by severe itching.
Brown marks
Sometimes completely unexpected brown spots appear on the skin under the hair. They can be either completely natural or signal some kind of malfunction in the body.
Dark spots
Even under the hair, quite large pigment spots may well be hidden. Most often, such accumulations of melanin are visible from childhood, but they can also occur throughout life, for example, after injuries, burns, illnesses, hormonal changes and taking certain medications.
Most often, age spots do not pose any threat to health. You just need to remember their presence and periodically monitor them for changes in shape, increase or damage
If such situations develop, it is important to consult a dermatologist
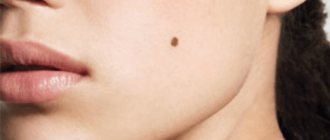
Nevi
Nevi are the same accumulations of melanin, small moles that may well be present on the scalp. Most often they are harmless, but with a protruding round shape they can be potentially dangerous due to the high risk of injury. Owners of moles under their hair should consult a doctor before coloring their hair, as nevi may not react to the chemicals in the best way.
Moles can be dangerous in terms of malignancy.
Melanoma
This is a type of cancer that most often arises from pathologically changed moles. Fortunately, with timely diagnosis, melanoma is highly treatable, so you should definitely consult a doctor if the nevus:
- It grows, changes shape, color and outline.
- Itches, hurts or itches.
- It bleeds, becomes crusty, etc.
How to treat yellow dandruff?
If you have yellow dandruff and an itchy head, the first thing you should do is see a trichologist - a doctor specializing in skin diseases. After examination and diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment, which usually includes taking antifungal medications, since the first task is to destroy the colonies of the Malassezia fungus, returning its content in sebum to normal levels (50% - (1). This will help cleanse the epidermis and hair from dandruff, and then you need to understand the cause of seborrheic dermatitis.
Since seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic disease, preventive therapy is necessary after a course of treatment. To eliminate the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis, ketoconazole, zinc-containing products, and tar are used at least twice a week for a month. Further, these same medications should be used for preventive purposes at least once every two weeks. This will keep the number of Malassezia fungus colonies in sebum within physiological limits and ensure an adequate level of secretion production (4).
Among the medicines, we will highlight medicated shampoos with ketoconazole. This substance has proven effective in controlling Malassezia colonies. (5) Ketoconazole suppresses excess fungal activity, thereby preventing the development of seborrheic dermatitis with yellow dandruff and other skin diseases that are often combined with various types of seborrhea. The medicinal shampoo "Perhotal", which contains ketoconazole, was tested by specialists from the Krasnoyarsk Regional Gerontological Center. https://perhotal.ru/wp-content/uploads/research-124.pdf. Among the subjects, 48 people suffered from various forms of seborrheic dermatitis, and after the second application of shampoo, the patients lost itching, flaking of the scalp decreased, and the amount of dandruff significantly decreased.
Perhotal shampoo is available in two forms: for treatment, shampoo with a 2% ketoconazole content is used, and for the prevention of seborrhea, a 1% form is used. Treatment is carried out with 2% ketoconazole 2-3 times a week (the shampoo is applied for 5 minutes) for 1 month, depending on the type of lesion and the severity of the disease. Preventive procedures using 1% ketoconazole are carried out once a week for a month.
Diagnostics
If you suspect a particular disease of the scalp and hair, then you need to contact a specialist on these issues, i.e. trichologist. After listening to complaints, collecting information about lifestyle and conducting an external examination, the doctor will prescribe tests. Specialists in the laboratory will examine hair, blood, and in some cases even perform a biopsy to accurately determine the nature of the disease.
At home, you can treat your scalp and hair by following a diet that excludes harmful foods. This is necessary to prevent allergic reactions. The second step would be to use medicated shampoos and limit coloring compounds. To rinse your hair, you can use not just water, but make decoctions or infusions of medicinal herbs, for example, chamomile or nettle. Medicines will help get rid of problems: antifungals, multivitamin complexes, biogenic preparations.
If you ask your doctor how to get rid of crusts, he may recommend ointment (applied with a cotton swab), shampoo (frequent washing) or a combination of these products. In particularly advanced cases, antibiotic therapy and other alternative methods are prescribed.
An important way to diagnose the disorder is to visit a dermatologist, who can determine the type of disease and the reasons that caused the appearance of crusts on the head. The patient is prescribed a skin scraping, a Wood's lamp examination, a blood test, and allergy tests.
Additionally, an examination is carried out by other specialists - a gynecologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, gastroenterologist, etc.
What other types of dandruff are there?
(6)
- Yellow dandruff, caused by the related fungus Malassezia globosa, is characterized by flaking yellow scales. Some symptoms are similar to all types of dandruff: yellow particles peel off from the surface of the scalp, the functioning of the sebaceous glands is disrupted, hair loss and the development of other, more serious forms of dermatitis are possible.
- White or gray-white dandruff is characteristic of dry seborrhea. At the same time, the sebaceous glands do not work enough, not producing the required amount of secretion, as a result of which the skin begins to dry and peel, which leads to the appearance of white dandruff.
- Red, or rather, reddish dandruff is called so conventionally. Occurs when there is inflammation of the epidermis, which is affected by fungal infections or suffers from dermatitis. A person combs the diseased areas until they bleed, causing dead white-pink particles to fall off.
- Black dandruff is not actually dandruff, but acne peeling and remnants of acne and other formations protruding on the skin, as well as coagulated blood that was picked off while combing the head.
Brown dandruff may not be dandruff at all, since this color often develops with lice. (7)
References
Yellow spots on a child's headRate this post
Yellow spots on a baby's head are a completely normal phenomenon that almost all parents encounter. They mainly occur in children in the first months of their life. In medicine they have their own name - seborrheic dermatitis.
Scalp diseases: names, descriptions and photos
Next, you can read the description of various skin diseases in humans and their treatment, and also see what diseases of the scalp look like in the photo.
Dermatological
Eczema
- Reasons for appearance. Despite the fact that this disease has been known to mankind for several centuries, specific reasons for its occurrence have not yet been found. But there are a number of factors that can contribute to the appearance and progression of seborrheic eczema. Let's list them: prolonged contact with irritating or aggressive substances (this can be any detergent or hair dye);
- intolerance to any food products;
- long-term skin infection.
Seborrhea
- Causes . The main cause of this disease is the improper functioning of the sebaceous glands. However, they do not produce enough elements that can protect the skin from drying out.
- Localization . Seborrhea can appear on the scalp, face, chin, and chest.
- Manifestations and symptoms . The epithelium becomes rougher at the site of inflammation. The skin begins to turn red, inflamed, and itch. When the sebaceous glands are overly active, yellow scales appear in this place. And in those places where the sebaceous glands do not work enough, the epidermis begins to peel off.
- Treatment . Normalize your diet. Stop drinking alcohol and nicotine. Maintain skin hygiene. Under no circumstances should you try to get rid of acne and pimples on your own. If all of the above does not help, go to see a doctor, or read this article, in which we will talk about seborrheic dermatitis and methods of its treatment.
You can learn more about the diagnosis and treatment of seborrhea from the video:
Acne
In simple words, it is a skin rash in the form of pimples or acne, which occurs in 80% of cases in young people aged 12 to 25 years.
- Causes . There can be a lot of them:
- excessive use of cosmetics (powder, eye shadow, foundation, even suntan oil);
- skin contact with substances containing oils, greases or tar;
- prolonged friction of the epidermis on the tissue;
- increased sweating;
- taking steroids;
- self-removal of acne;
- excessive cleanliness, in which even the slightest microbes will cause inflammation;
- hormonal changes;
- abnormalities in the functioning of the ovaries;
- chronic diseases.
- Localization . Acne can appear on any skin area of the body, but most often they are noticed on the face, lower back, neck and chest.
- Symptoms and manifestations . Pustules appear on the surface of the dermis in the form of bright red tubercles with a purulent tip. Most often, after acne disappears, it leaves scars in the form of dimples on the skin, which are impossible to get rid of.
- Treatment . There may be several options: the use of ointments and creams against acne;
- taking antibiotics that will fight the infection from the inside;
- contacting a doctor who will prescribe comprehensive treatment.
Cancer
Skin cancer is a malignant tumor disease of the skin that occurs as a result of atypical transformation of its cells and is characterized by significant polymorphism.
- Reasons : frequent exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- the result of prolonged exposure to chemicals;
- permanent injuries involving the area of scars or moles;
- heredity;
- transformation of other skin diseases.
- The appearance of a dark area of skin that increases over time.
Infectious diseases of the scalp
Trichophytosis
The causes of trichophytosis are often contact with infected people, less often with animals. Lichen can be localized on any open areas of the skin. The symptoms of trichophytosis are as follows:
- formation of areas of peeling on the skin;
- hair breaking (while a gray coating remains on the broken curl);
- the affected area begins to itch and turn red;
- the patient feels general malaise, weakness;
- a rash appears;
- nail color changes;
- In reddened areas, you can often observe the appearance of a crust and blisters.
REFERENCE! For the treatment of trichophytosis, ointments based on miconazole, clotrimazole, terbinafine, as well as tincture of iodine 2 - 5%, sulfuric ointment 10 - 20%, sulfur-salicylic ointment, sulfur-tar ointment are well suited.
A detailed description of the symptoms of trichophytosis in this video:
Microsporia
The causes of the infection are the same as for the previous infection: contact with an infected person or animal.
Moreover, the symptoms of the skin disease are also very similar to trichophotia. But with microscopy, the color of the nails does not change, and the person does not feel any discomfort. It is better not to start treatment without consulting a doctor. Ideally, laboratory tests should be carried out. Video with a detailed description of the symptoms of the disease and diagnostic methods:
Trichophoria
Inflammation of the scalp, accompanied by severe itching and redness. In this case, the hair begins to fall out excessively, and a black dot appears in the place of hair growth. The fungus is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person. Treatment is prescribed by the doctor depending on the degree of inflammation and the course of the disease.
Pediculosis
Damage to the scalp by small parasites - lice. Because of this, the carrier of the infection constantly feels itching of the epidermis of the head .
Identifying pediculosis is not particularly difficult - lice larvae and eggs are visible on the hair, as well as tiny blood residues that usually settle on the comb. The doctor immediately diagnoses this disease and prescribes treatment with drugs available for purchase at any pharmacy.
Video about pediculosis:
Folliculitis
In the early stages of this disease, small red bumps, called follicles, appear on the scalp. If measures are not taken to treat this infection in time, these follicles can turn into huge wounds that will be extremely difficult to cure , in addition, this disease can develop into mycosis. Treatment is carried out with antiseptic agents, local and systemic use of antibiotics, antimycotics, acyclovir, and antiviral drugs.
Impetigo
A disease caused by staphylococci or streptococci. Bacteria enter the body through wounds, making them even larger. Then crusty, yellow blisters appear that ooze constantly. If they are peeled off, the blisters will spread further throughout the body. In 99% of cases, antibiotics and antiseptics help fight ampetigo.
Furunculosis
Acute purulent inflammation caused by the appearance of a boil. It occurs when bacteria enters the hair follicle. The epidermis “swells,” turns red, fills with pus, and swells. The resulting boil is painful to touch. Treatment of furunculosis is prescribed by a doctor, based on the nature and stage of the disease.
Autoimmune
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic scalp and hair disease. Therefore, it is impossible to cure it; you can only reduce its manifestations by using special ointments, creams, shampoos and soaps. Sometimes patients resort to physiotherapeutic procedures. Psoriasis is characterized by a rash consisting of papules covered with loose, easily removable silvery scales. There are many reasons for the appearance of this disease, but experts cannot come to a single solution.
Scleroderma
At the beginning of the disease, the epidermis swells, but soon becomes denser.
And after a short time it cannot be separated from other fabrics or pulled into folds. Appearing on the scalp, scleroderma often causes baldness. Doctors name many reasons:
- hypothermia;
- injury;
- infection;
- vaccination;
- heredity.
IMPORTANT! Treatment in this case requires long-term treatment and under the constant supervision of a doctor.
lupus erythematosus
The reasons for the appearance are unknown, but usually specialists blame it on malfunctions of the immune system. It appears as pink spots on the skin, which thicken over time and begin to peel off. And after healing they leave scars. Lupus may cause hair loss. The disease should be treated only after a doctor’s prescription.
Other
- Ingrown hair – with this disease, the hair does not come out, but bends and grows into the skin under the stratum corneum. In such areas, small nodules form, which cause itching, often unbearable.
- Hypertrichosis (or hairiness) is excessive hair growth that is unusual for a given area of the dermis and does not correspond to gender and age.
- Hirsutism is excessive hair growth in women. Typically, signs of hirsutism are the appearance of a mustache and beard in women.
- Hypotrichosis is a whole complex of diseases that lead to one final outcome - partial or complete baldness.
Causes of spots
Why do yellow spots appear on a child’s head? Children have fairly delicate skin; the epidermis is not yet developed as well as in adults. The sweat glands work very weakly, while the sebaceous glands, on the contrary, actively work, which is why such an imbalance occurs in the work of the glands. The skin becomes very vulnerable to environmental factors and it’s easy to catch some infections.
Most often, yellow flaky spots on a child’s head appear when the head sweats frequently. It is possible that mothers dress their children very warmly.
A sweaty head simply cannot cope with such an imbalance on its own, so the development of dermatitis cannot be avoided.
Yellow spots on a baby's head photo
Even a mother’s poor diet can lead to illness. The thing is that an allergic reaction may develop to the introduction of new complementary foods, and this is a provoking factor for the development of dermatitis.
Take a close look at the spots and crusts on your head; they should come off easily. If, after you have removed them, abrasions or wet areas remain, you must consult a doctor. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate.
Children with these diseases do not need treatment. To wash your hair, you must use hypoallergenic shampoos, they should be for children. The crusts need to be removed, but this procedure must be carried out correctly.
A few hours before bathing, you need to treat your baby's head with baby oil. Almond or olive oil works well for this. If you don’t have it on hand, you can use Vaseline.
Wash your hair well and then dry it with a towel. In order to remove the crust, you need to use a special brush, the teeth of which should be round. By combing your hair, the crusts will be removed.
Do not under any circumstances try to remove them, otherwise you may injure the head. It's not always possible to delete everything in one session, so there's no need to get upset. Maybe they just haven't softened enough. Next time, hold the oil longer and repeat the procedure again.
When birth pressures disappear
If red spots on the back of a newborn’s head appeared after a natural birth and the doctor said that these were birth clamps, then there is no need to treat them. They go away on their own in a few weeks or months. But there are also cases when pigmentation goes away only in adolescence.
If a child is embarrassed by this cosmetic defect, it can be removed using laser resurfacing by contacting a cosmetologist.
Forms of the disease
Seborrheic crusts (gneiss) are a common phenomenon among infants. As the baby grows, this problem disappears on its own. But it happens that gneiss bothers older children, and such situations require special attention.
Let's look at how seborrhea manifests itself. There are three forms of the disease:
- Mild - when only the top of the head is affected, sometimes the ears. The children's general health is normal.
- The moderate form is when the entire face and neck become red and peel, and the body and limbs are partially affected by dermatitis. The scales on the head are large, children become capricious, diarrhea appears, and regurgitation becomes more frequent.
- The severe stage is accompanied by the appearance of a continuous plaque on the head or “baby cap.” An infection occurs, causing suppuration. The baby loses his appetite, is lethargic and does not gain weight well.
Reasons for appearance
There is no definite answer to the question of why children have a crust on their heads. Doctors identify only possible provoking factors, which include:
- Development of the endocrine system. In the newborn period, endocrine functions malfunction - the sebaceous glands begin to secrete intensely. This leads to the formation of gneiss.
- Poor hygiene. Scales on the head appear after prolonged wearing of hats. Sweaty skin, too frequent washing, inappropriate washing gels and shampoos - all this provokes the formation of the disease.
- Inappropriate diet. Seborrhea occurs due to poorly tolerated formula or early introduction of complementary foods. Improper nutrition of the mother during breastfeeding can also lead to a malfunction of the baby’s endocrine system.
- Fungal infection. The fungus is constantly present in human skin, but hormonal imbalances contribute to its proliferation. This provokes the appearance of yellow scales.
- Weakened immunity. When the immune functions of the body are weakened, children experience disruption of the sebaceous glands and proliferation of fungus.
Dermatitis in children and adolescents
“Crusts appeared on the head of a 2-year-old child. What to do?" - parents panic on the forums. First of all, you need to remember that before the age of three, this phenomenon is very common. This affects the increased work of the sebaceous glands.
Perhaps the problem is a lack of vitamin B (biotin), which is responsible for metabolism in the body. The very appearance of the crust does not cause discomfort, and with appropriate treatment and compliance with hygiene rules, they disappear without a trace.
When a crust forms on the head of a 3-year-old child, this fact should alert parents. There may be several reasons for this:
- improper hair care;
- overheating in the headdress, when the head begins to sweat;
- use of unnatural cosmetics that cause irritation;
- dry scalp from frequent bathing;
- allergies to new foods.
If all these factors are excluded, and seborrhea in 3-year-old children does not go away, then the reasons may be much more serious, for example, disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland or the central nervous system. In this case, you should immediately contact your pediatrician.
There are situations when, at a young age, the child’s parents do not face such a problem, but first learn about dermatitis when their child is 5-6 years old. A crust on the head of a 5-year-old child is quite rare, just like in teenagers. But it still happens. This phenomenon is often associated with a bacterial infection. It is treated with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy.
If the onset of the disease is accompanied by increased weight gain, doctors suspect Leiner's disease in a young patient. In addition, scales on the skin in children 5-6 years of age and older may be symptoms of diathesis, psoriasis or atopic dermatitis.
What you need to know
Seborrheic crusts on the head are an inflammatory disease. The cause of its occurrence is a fungus that promotes natural exfoliation of the upper layers of the skin.
It is this that provokes the appearance of dandruff, and later a crust appears in the scalp. The fungus is most active on oily skin, but those with dry and normal hair can also become victims of seborrheic dermatitis.
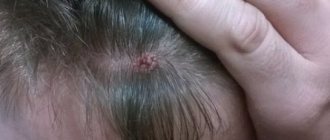
At the first symptoms of the disease, the skin itches. After this, small reddish spots appear on the head, which peel off. A crust forms on the scalp from dead epidermal cells.
It can be easily separated and adhere firmly to the skin. In the latter case, its separation is associated with pain, and can also cause the formation of wounds and even ulcers. If no measures are taken, the itching intensifies, and the person notices that the head is covered with clearly visible dandruff.
At first, seborrheic dermatitis is not particularly dangerous. There is physical and aesthetic discomfort. It also creates a certain obstacle to hair growth in the area of crust formation. But if the problem is not dealt with, a bacterial infection is added to the disease. This means that in addition to a crust on the head, other diseases may appear. When the condition is severely neglected, hair begins to fall out, forming bald spots.
Signs of seborrhea most often appear in the autumn-winter period, when a person’s immunity is weakened.
Important! Dandruff is a fungal disease, and it can be transmitted through personal hygiene products: comb, towels, etc.
A crust of dandruff appearing on the scalp in children can be considered normal, but in adults it is a signal of alarming symptoms. If a flaky and itchy layer forms on the scalp, this is a reason to consult a doctor (trichologist or dermatologist) for a thorough examination. After all, it is not always the case that the scalp is covered with a white crust – this is a manifestation of fungal activity. White flaky formations can be a signal of more serious problems: psoriasis, scabies (the activity of the scabies mite), favus (the appearance of the achorion fungus, another name for the disease is scab, favus lichen), ringworm, etc.
The earlier the visit to a specialist, the easier the diagnosis is made and the faster the treatment.
How to get rid of crusts
Parents are wondering how to remove crusts on their child’s head, and whether this can be done. It is necessary to remove them, because careless movement can accidentally tear off the crust. This will lead to infection of the resulting wound on the skin.
To get rid of crusts on a child’s head, you should:
- wash your hair with baby shampoo;
- blot with a towel;
- moisten a cotton pad with sunflower or olive oil and gently rub the crusts;
- put the baby to sleep in a cotton bonnet or hat;
- In the morning, comb out the crusts with a soft comb or brush;
- wash your hair, comb it.
These actions should not be carried out more than twice a week. The procedure is also repeated for seborrhea behind the ears and on the eyebrows.
There is also another method in which an hour (or at least 20 minutes) before taking a bath, slightly heated oil (burdock, baby, olive) is rubbed onto the baby’s head. Then they put on a hat.
While bathing, wash your hair with shampoo and remove flakes. Then comb out the remaining scabs.
Let's look at how to comb out the crust in more detail. Take a blunt-tooth comb and comb your hair from front to back. After this, use a soft brush. The fontanel area requires special attention; crusts must be removed from it, only with caution. When combing, the scales may become separated from the hair.
If seborrheic dermatitis appears regularly, the presence of diathesis or other allergies is suspected. In this situation, you should contact a dermatologist and allergist.
Medicines
In general, gneiss does not require drug treatment, with the exception of the severe stage. In this case, children are prescribed antibiotics (for skin infection) and antihistamines to reduce itching.
Since the reasons for the appearance of scales differ in each case, treatment is selected individually.
To eliminate various forms of the disease, use:
- antifungal ointments (Lamisil, Mycospor and others);
- anti-fungal shampoo (Nizorex, Sebazol, Dermazol);
- corticosteroid ointments (“Ecolom”);
- zinc ointment to relieve inflammation;
- preparations for diseased skin (“Topicrem”, “Bioderma Sensibio”);
- vitamin complexes;
- antihistamines (Citrine, Diazolin).
Mustela shampoo or foam helps get rid of yellow crusts. Its composition is hypoallergenic, the shampoo softens scales and also has an antibacterial effect.
Folk remedies
If the disease is not advanced, you can get rid of it with the help of alternative medicine, or combine such methods with medical prescriptions.
It is one of the most popular remedies in the fight against dandruff.
How to use: pour 60 g of powder with boiling water (you need enough water to get the consistency of sour cream), then cool. You can also dilute the ointment with rosemary and/or tea tree essential oils. Apply to affected areas for half an hour and rinse with warm water.
To prevent your curls from becoming colored, it is better to use colorless henna. The recipe can be supplemented with a decoction of St. John's wort, apple cider vinegar, orange juice, burdock oil, and blue clay.
Unripe (green) walnut
Option #1. 100 g of crushed nut shells are poured with vodka (0.5 l) and infused for 2 weeks. Afterwards the infusion is filtered. Used by massaging into the skin every other day for 20 days.
Option #2. 300 g of crushed leaves, peel and shell are poured into a liter of water and brought to a boil in a water bath. Then the broth is removed from the heat and infused for 2 hours.
How to use: As a rinse after washing your hair. Afterwards, wrap your head in a towel and leave for at least 10 minutes. Repeat the procedure 3-5 times. The effect is noticeable from the first use.
Important. Walnut can dye strands a dark color, so it is better not to use it on light-colored hair.
Kefir
Apply with rubbing movements to the entire surface of the scalp and leave for half an hour. Wash off with rinse aid (1 tbsp dry mustard diluted in 1 liter of warm water). Do it daily for a week. Then repeat the procedure for preventive purposes once a month.
Burdock root
The young root of the plant is crushed (in a meat grinder or grater) and mixed with vegetable oil (1:3). Next, the mixture must be infused for an hour in a glass jar. Then strain and rub into the skin 2-3 times a week. Warm up before use. There should be a total of 10 such rubbings. The next course is repeated after 20 days.
Burr oil
When heated, apply to the scalp. Then the head must be covered with polyethylene, wrapped in a towel and left for 2 hours. Rinse off.
nettle leaves
A tablespoon of crushed leaves is poured into a glass of boiling water. The resulting infusion must be covered, wrapped and kept for 1.5 hours. Strain. Apply to skin after washing, cover head with a bag and leave for 40 minutes. There is no need to wash your curls after the procedure. Use the product twice a week.
Chamomile flowers
Boil table 2. spoons of flowers with 1 liter of water. Cool and strain. Dilute with plain water in a ratio of 1:10 and rinse your hair after washing three times a week. Do 15 procedures, then pause for 3 weeks and repeat the course again.
Chamomile gives light strands a golden hue.
Sage
Infuse for 1 table. spoon of dry sage herb with 1 glass of boiling water for 24 hours. Rub in every other day for a month. This remedy is good for dry seborrhea. For oily dandruff, replace the water in the recipe with a glass of vodka.
Tea tree oil
Powerful antiseptic. For treatment, it is better to add it to shampoo. In its pure form it can cause burns.
Oak bark
For medicinal purposes, you need to prepare an infusion of a tablespoon of bark, poured with 400 ml of boiling water. All this is infused in a water bath for 5 minutes, then filtered. Rub the infusion into the scalp 3-4 times a day, adding a tablespoon of flower honey to the liquid.