Why do papillomas appear?
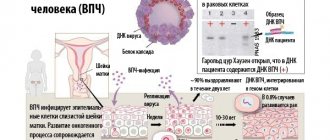
The etiology of papillomas is most often viral. The causative agent is human papillomavirus (HPV) - family Papovaviridae (simian vacuolating virus). More than 130 strains are known, each of which has its own characteristics and manifests itself differently. The virus is not persistent in the external environment; infection occurs through direct contact. Predisposing factors to infection are smoking, vitamin deficiency, endometriosis, and immunodeficiencies.
When HPV enters the body, it first infects the basal (lying on the surface) epithelial cells. The penetration of the virus into the body is facilitated by microtraumas and cracks. The virus can multiply for a long time, but does not manifest itself clinically. If HPV multiplies in the stratum corneum of the skin, cell hyperplasia is observed over time.
Why do papillomas itch?
The location, color, and shape of the neoplasm depend on its causative agent. And the causes of itching mainly depend on the characteristics of papillomas.
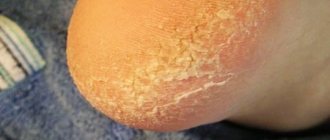
Plantar papillomas, the causative agent of which is HPV 1, 2, 4, are small in size and have a lump shape. They are characterized by severe itching and even pain, especially while walking. New growths are confused with calluses and attempts are made to cauterize, open, or use medications to eliminate them. Pressure injuries and exposure to chemicals contained in medications cause irritation and itching.
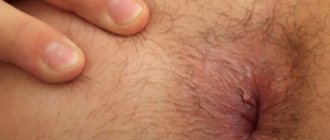
Thread-like papillomas, or acrochords, arise as a result of damage to the body by HPV 3, 5, 8. Neoplasms are localized in the groin area, armpits, neck, and skin around the eyes. Acrochords, located in places where trauma is possible, often become inflamed and cause discomfort. If the papilloma on the eyelid itches, but does not turn red or enlarge, most likely it was carelessly caught, for example, while washing. If the tumor becomes inflamed or larger, you should consult a doctor.
Possible complications
Without timely detection of the causes of itching, there is a possibility of complications and unpleasant conditions developing. If we summarize all the possible consequences of an itchy growth, then there is a threat:
- introduction of pathogens;
- suppuration of the problem area;
- tissue necrosis;
- sepsis;
- papillomatosis.
A person needs to understand that minor changes in the previous state in the presence of HPV may indicate serious disorders of the body. To prevent this, it is necessary to promptly seek help, treat the disease, and notify the doctor about new symptoms.
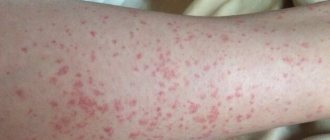
A papilloma that is itchy and red requires increased attention. At the first sign of such a symptom, you should immediately notify your doctor. Otherwise, the patient risks facing dangerous consequences.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Is it possible to scratch papillomas?
Papilloma is a small, dense or soft-to-touch formation on a long or short stalk. Neoplasia consists of connective tissue stroma and epithelium. The stroma is filled with small vessels, and if they are traumatized, bleeding is possible.
If the papillomas itch, then touching them is highly recommended. Any strain of the virus can infect a person. They are divided into three groups according to the degree of oncogenicity:
- Low risk. Single neoplasms, only on the surface of the skin, do not pose a threat to the body. They only cause a cosmetic defect.
- Moderate oncogenicity. Under the influence of certain factors, they can cause changes in the genome of cells.
- High oncogenic risk. Papillomas with this strain of the virus often degenerate into cancerous tumors.
Scratching the latter can lead to accelerated cell division. Papilloma, as a rule, increases in size and changes color (the stratum corneum changes to a new one). The tumor may not only itch, but also hurt, and your overall health may worsen. If you have such symptoms, you should see a dermatologist and oncologist.
Signs of HPV infection
The papillomavirus does not cause any acute symptoms; it often goes away without symptoms. A persistent infection remains, develops in the body, and over time can develop into cancer. This can be prevented by consulting a doctor in time.
When infected with a virus, only external signs appear - neoplasms, which can be seen with your own eyes or during a routine examination by a specialist. Itching or redness of the papilloma also often occurs.
How the disease is transmitted
The disease is transmitted only by contact from person to person:
- through microcracks in the mucous membrane during sexual intercourse or during a kiss;
- when shaking hands;
- from mother to child during pregnancy.
It is possible to reduce the risk of intrauterine infection or transmission of the virus during childbirth. To do this, before pregnancy, it is better for girls to undergo a test for the presence of a viral infection.
Locations of growths
Warts form all over the body. They usually affect:
- hands;
- legs;
- neck;
- back;
- tongue and other mucous membranes;
- genitals.
New growths can appear from the first month of infection. The location of the growths depends on the characteristics of the human immune system and associated pathologies. In medicine, multiple occurrences of viral rashes are called papillomatosis.
What do papillomas look like?
Papillomas are papillary neoplasms on a thin stalk that appear on the skin and mucous membranes. This is an unpleasant looking growth. They spoil the appearance if they appear on the face, neck or hands. Warts can vary in color (light or black), shape (elongated or flat) and size (from 1 mm to 2 cm).
Symptoms of tumor degeneration
Viruses that infect the mucous membranes are dangerous to humans. When they multiply, warts form. During development, neoplasms can change their appearance. They grow, the surface changes from rough to smooth and vice versa, it bleeds and becomes inflamed. When warts begin to itch, patients often do not pay attention to the itching, but it can be a sign of the growths becoming malignant.
There are additional signs that make it possible to recognize degeneration:
- color change to black;
- the tumor hurts when touched;
- drying of the papilloma, after which it may fall off;
- the papilloma turned red;
- inflammation of the skin at the site of the formation;
- the appearance of ulcers with bleeding.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only he will be able to make the correct diagnosis, determine the degeneration of the wart and prescribe effective treatment. Doing anything on your own without a doctor's permission is dangerous!
Factors influencing the occurrence of itching
Why do papillomas itch on the neck, eyelid or elsewhere? A virus is to blame for the appearance of tumors. Its presence is abnormal, the body tries to fight it, the immune system gradually weakens. And since the virus is localized in papillomas, they become more sensitive and react more sharply to various irritants.
The most common irritants that cause itching are:
- Uncomfortable clothing or jewelry. Tight underwear rubs against the papilloma, and the irritated skin begins to itch. Synthetic fabrics or clothing dyes can also be irritating. Papillomas in the neck area may itch from friction with the metal of jewelry.
- Allergy to soap, shower gel. Manifestations of allergies, such as redness, itching, usually occur in pathologically changed areas of the skin (scars, rashes, swelling, neoplasms).
- Poor hygiene. Rare trips to the shower, especially in hot weather or during physical activity, as well as in diseases accompanied by profuse sweating, contribute to the proliferation of pathogenic flora. Failure to comply with hygiene can threaten the introduction of another infection into the body. Reduced immunity contributes to the activation of HPV.
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation. As is known, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays (sun, solarium) on the skin promotes malignancy even in cells not affected by the virus. If the cause of papillomas is a virus of high oncogenic risk, then ultraviolet light will accelerate the development of cancer. Itching may be a consequence of active cell division.
- Hormonal drugs. Incorrectly selected steroid medications or non-compliance with the rules for taking them can cause hormonal imbalances in the body. Against their background, HPV may become more active.
Is itchy papillomas dangerous?
To understand whether danger exists in each specific case, you should understand what factors provoked this sensation.
In the presence of external provoking factors, after they are eliminated, the feeling of discomfort disappears, and the condition of the growth returns to normal.
Papilloma can begin to itch if there are serious problems with the body or cause their formation.
When scratching, there is a risk of damaging the growth, and this can happen accidentally.
Then, in addition to itching, other symptoms will appear:
- the appearance of redness around the tumor.
- painful sensations.
- growth tear.
- discoloration, including black.
- increase in the size of papilloma, intensive growth.
- loss of shape.
- bleeding of the growth.
- the appearance of cracks on the surface of the neoplasm.
If the cause of the itching is not identified in time, the risk of developing negative consequences increases.
There is a risk of the following complications:
- infection by pathogenic microorganisms;
- development of papillomatosis;
- suppuration of the affected area;
- development of sepsis;
- tissue necrosis.
One of the most dangerous complications is the possibility of papilloma degenerating into melanoma.
Melanoma takes about two months to form, after which the person is diagnosed with cancer.
Melanoma is one of the most terrible complications, since the development of this form of cancer cannot be stopped.
She is not amenable to chemotherapy and other procedures.
Therefore, if discomfort appears in the area where skin tumors are localized, you should immediately seek advice from the appropriate medical institution.
Timely measures taken will save health, and in some cases, life.
Papilloma itches, what should I do?
Itching at the site of tumors is always caused by some reason. If papillomas on the body itch, there is no need to panic right away. First you need to evaluate their size and color. It is necessary to exclude as much as possible everything that can cause irritation of papilloma: uncomfortable clothes, low-quality jewelry, any substances that cause allergies, prolonged exposure to the sun.
If you observe visible changes in the tumor (enlargement, redness) and pain, you should visit a doctor. The greatest danger is the excessive activity of the virus. HPV is embedded in human DNA and spreads through the natural process of cell division. Under the influence of certain factors, the virus changes the genome of the cell, and it begins to divide randomly. Of course, not all hyperplasias develop into malignant tumors, but only a doctor can accurately determine the nature of the tumor.
What can be the consequences of itching papilloma?
Remember! It is absolutely forbidden to scratch such areas! Since at this moment the virus begins to actively divide and in case of mechanical damage with fingers or devices, there is a high risk of degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one.
Skin cancer that arises from a wart is called melanoma. This pathology spreads very quickly throughout the body, since the skin covers the entire exogenous surface of the skin. And often it metastasizes within 3 months. Skin cancer causes sores all over the flesh. Melanoma is a quick and painful death.
Medicines that relieve itching and their use
The examination always takes some time. If the papillomas itch, and the itching is difficult to tolerate, you can use medications to alleviate the situation. Before using them, you should consult your doctor. Drugs that help relieve itching:
- Antihistamines. The products reduce hyperemia (redness occurs from scratching the skin with fingers), prevent the development of edema, and reduce capillary permeability. In addition, if the itching occurs due to allergies, then antihistamines will eliminate the cause itself. Medicines should be chosen with fewer side effects and greater and faster therapeutic effectiveness. These include: “Fenistil”, “Zodak”, “Zyrtec”.
- Local anti-inflammatory drugs, calcineurin inhibitors. The drugs act locally without causing skin atrophy or side effects. The most popular ointments are “Elidel”, “Protopic”, “Tacropic”.
- Antiseptics. The drugs have antimicrobial activity and prevent inflammatory processes. Unfortunately, they are not effective against viruses and are not suitable for preventing HPV. Miramistin and Chlorhexidine will help you quickly get rid of itching and inflammation.
How to get rid of itching yourself
Recommendation - before starting any manipulations, coordinate your actions with your doctor.
- Those with sensitive, irritation-prone skin should choose clothes made from natural fabrics that are well ventilated and loose. Synthetic materials do not allow air to pass through well, resulting in sweat accumulation, increased friction of clothing on the skin, resulting in irritation and itching.
- Lotions and compresses made from infusions of medicinal herbs have a soothing and antipruritic effect. As a rule, take 1 tbsp. l. plants, pour 250 ml of boiling water and leave until cool. Chamomile, calendula, mint, and string are well suited for such purposes.
- Alcohol infusion of calendula relieves itching and has a bactericidal effect. You can make it yourself - pour 10 grams of raw materials into a bottle with 70% alcohol. Let it steep for 14 days, then strain. Use several times a day (wipe affected areas).
- Propolis ointment or tincture will also help relieve itching and irritation. Apply a cloth soaked in the product to the affected area, after 10 minutes the unpleasant symptoms will disappear.
- Treat irritated skin with a decoction of bay leaves. Pour 250 ml of boiling water over 3 large bay leaves, simmer over low heat until the amount of water is reduced to a widow. After removing the broth, add boiled water to it (exactly as much as has boiled away) and use three times a day (more often).
Folk remedies to help relieve irritation
You can get rid of the unpleasant feeling of irritation not only with the help of medications; some folk remedies are no less effective:
- You can eliminate itching with a mixture of chopped garlic and butter in a 1:1 ratio. The pulp is placed in gauze and applied to the tumors for 30 minutes, then washed off with water.
- If papillomas on the neck itch, where the use of garlic is not advisable, you can use castor oil. New growths are also lubricated with it twice a day, but unlike garlic mass, oil can be used for no more than five days in a row.
- The feeling of irritation and inflammation is well relieved by cabbage leaves. They must be applied to the tumors for 40 minutes. You can apply it at any free time, the number of times has no restrictions. Some claim that using this method they got rid of papillomas altogether.
Medicines
It is better not to bring the condition to a crisis and remove the tumor in time. But medications can also relieve the symptoms of papillomatosis:
- Third generation antihistamines, Cetrin is the most effective.
- Interferon preparations that activate defenses and allow the body to fight infection on its own.
- Antiviral drugs that block virus replication (Allokin-alpha).
- Immunomodulators strengthen the immune system (Immunomax, Likopid).
- Means for topical use: oxolinic ointment has an antipruritic and analgesic effect.
- The oily liquid Feresol disinfects and cauterizes growths, reducing them in size.
Is it possible to remove papillomas?
This is usually one of the first questions that arises when tumors appear. If the papillomas itch, it would be very logical to simply get rid of them - eliminating the object that causes itching will automatically relieve the discomfort.
It is strictly forbidden to remove them yourself. Many medical organizations offer papillomas removal services. Their cost depends on the method:
- cryodestruction – destruction of pathological epidermal growths by exposing them to liquid nitrogen;
- electrocoagulation – a procedure for removing low-frequency electric current;
- laser destruction – destruction of a tumor using a laser.
Only papillomas of low oncogenic risk can be removed. Before invasive manipulation, an examination is mandatory.
Prevention
Ways to prevent infection:
- Vaccination of girls aged 10-14 years against certain strains of the virus with high oncogenicity.
- Pickiness in intimate relationships, limited number of sexual partners.
- Protected sex (barrier contraceptives).
- Active lifestyle.
- Quitting smoking, alcoholic drinks, drugs.
- Compliance with hygiene rules (do not use other people's things, cosmetics, combs, dishes, towels, etc.).
- Wear rubber slippers in public swimming pools and safety glasses and a cap while in the water.
- Treat acute and chronic diseases in a timely manner.
Important addition: Phosphogliv for psoriasis
Prevention of malignancy:
- Do not scratch the growths under any circumstances, as this can cause bleeding and cause infection.
- After removing the growths, follow all the doctor’s recommendations and ensure proper care of the postoperative wound.
- Avoid contact of papillomas with clothing, especially with its rough parts - seams, zippers, buttons.
- If possible, wear clothes made from natural fabrics to avoid allergic reactions that will negatively affect the condition of the formations.
- Do not wear jewelry on the damaged area.
- Protect papillomas from ultraviolet radiation.
- Have regular check-ups with your doctor, especially if you have genital warts.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Undergo preventive examinations.
- Monitor the appearance of the growth and, in case of changes, immediately consult a doctor.
- If you experience sensations such as pain, itching, or other symptoms in the area of the rash, consult a specialist.
What to do if it itches at the site of papilloma removal
Removing tumors does not guarantee that they will not appear again. It is necessary to eliminate the cause - HPV. If this is not done, the virus can become active at any time and tumors will appear again.
The main reason that the skin itches after papilloma removal is precisely the activation of HPV. The place where the operation to eliminate the tumor was performed is the most vulnerable at first. General therapy, as well as compliance with all medical recommendations, will help reduce the risk of recurrence of papillomas. If itching occurs after removal, you should immediately inform your doctor.
Removal of papillomas
When papillomas appear on the body, it is necessary to remove them, since they contain a large concentration of viruses.
The removal procedure is one of the stages of complex HPV therapy.
If the growths are not removed, the patient will pose a danger to the people around him and be a source of infection.
Due to the inconvenient location of papillomas on the body, they are subject to frequent trauma, so this factor is an indication for their removal.
At the present stage, in order to get rid of growths, hardware technologies are used that can quickly destroy the tumor.
The patient does not require special preparation and the recovery period is reduced.
Methods for removing papillomas
- Using a laser beam. The technique allows you to remove growths in one session. The removal method is painless, since local anesthesia is performed before excision. The risk of relapse is minimal.
- The use of liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction) to remove papilloma. Under the influence of low temperature, the growth freezes and then dies. During the healing process, the place where the growth was located itches. This method is not used in the facial area, since the likelihood of scar formation remains high.
- Diathermocoagulation (electrocoagulation). Electric current is used for removal. There is no risk of bleeding, since coagulation of blood vessels occurs during the burning process.
- Radio wave technique. Refers to gentle methods of removing tumors. The procedure is characterized by the absence of pain, bleeding and precise execution. After removal, no scars are formed.
The advantages of two useful methods are that they make it possible to take biomaterial for histology.
In the presence of large papillomas, removal is carried out using a scalpel.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
After removing the pathological tissue, sutures are applied and a sterile gauze bandage is applied over them.
The rehabilitation period lasts longer than with other methods.
The resulting biomaterial can be subjected to histological analysis.