Many people experience cold sores. Less commonly, the infectious process develops in the intimate area. Herpes on the hands is not common, but its manifestations cause no less discomfort to a person. As soon as differential diagnosis is carried out, treatment measures must be urgently started. If treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, further spread of the virus throughout the body is possible.
The causative agent of herpes on the hands
Herpes is caused by a virus of the Herpesviridae family. Unlike a bacterial infection, it has DNA.
Virology knows 8 types of herpes simplex virus (HSV). The causative agent of infection on the hands is 3 strains of the virus:
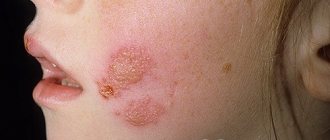
- HSV type 1. Causes herpetic colds on the skin and mucous membrane of the nasolabial area. It rarely appears on the hands and fingers.
- HSV type 2. Affects the genitals. The transition of the disease from the primary focus to the hands is facilitated by the person himself.
- HSV type 3 (Varicella zoster). Causes chickenpox and herpes zoster.
Under favorable conditions, other types of herpesvirus may also appear on the upper extremities.
Ways of infection with herpes:
- Primary. Infection occurs through the skin of the hands through direct contact of a person with a carrier of herpes (handshake).
- Secondary. Typically for HSV types 1 and 2, a person has a lip or genital infection.
- Distribution of viral agents throughout the body. It is observed with a weakened immune system or systemic diseases in the body.
Forecast
If we are talking about herpes on the skin of the hands, which occurs without complications, then the prognosis is favorable. If there are problems with the immune system, the disease can constantly progress. In such cases, the patient must be under constant medical supervision.
Every person who has developed herpes, regardless of the location, must understand that under no circumstances should one pierce the blisters or open the crust. Such activities carry a high risk of developing a secondary bacterial infection. There is also a risk that the virus will spread from your hands to other parts of the body.
Within 15-20 days from the moment the first bubbles appear, they will completely disappear, including the crust. If the recovery process is delayed, this may indicate that complications have begun.
Types of herpetic hand lesions
Different types of herpes can be present in the human body at the same time. Typically, infectious processes do not manifest themselves in any way, but when the opportunity arises, they enter the active phase, appearing in the form of a rash and inflammation on the skin.
Types of herpesvirus on hands:
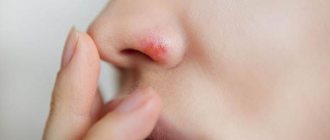
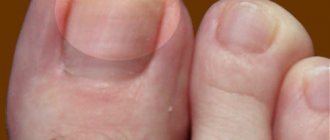
- Herpetic panaritium. Mainly affects the fingers. The painful condition in 60% of cases is provoked by HSV type 1.
- Bubbles with liquid. The symptoms are similar to allergic rashes. Caused by HSV type 2.
- Shingles. Characteristic of the chest and lower back. The appearance of shingles on the arm indicates the rapid spread of the disease.
The herpes virus is able to penetrate blood vessels, affecting blood cells, negatively affecting the peripheral and central nervous systems, and liver tissue.
The following are at increased risk of herpes infection on the hands:
- dentists, gynecologists;
- contact sports athletes (wrestling, rugby, boxing);
- people who are promiscuous;
- children with herpes on the lips, constantly pulling their fingers into their mouths.
Causes of the disease and its causative agent
Herpes on the hand is caused by the same pathogens as the disease on the lips or genitals:
- Herpes simplex virus type 1 (most often causing the labial form of the disease, that is, on the lips);
- Herpes simplex virus type 2 (usually the causative agent of the genital form).
There are no statistics that would show which of these pathogens most often causes herpetic whitlow. However, for practical purposes of treating the disease, this is not so important, since the symptoms, the nature of the course and the specifics of therapy are the same for lesions on the hands caused by both pathogens.
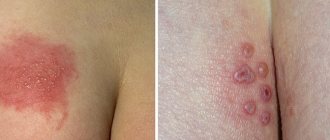
Note: in exceptional cases, herpes zoster may develop on the arm - it is also called herpes zoster, and is caused by the reactivation of the Varicella Zoster virus in the body. This sometimes occurs with significant suppression of the immune system, and the disease is accompanied by extensive lesions of the body (usually one-sided) with the spread of rashes on the face, neck, shoulders, and elbows. It is important to understand that shingles only on the hands, without simultaneous manifestation in other parts of the body, almost never develops.
The photographs show an example of shingles:
In general, herpetic rashes on the hands appear quite rarely due to the fact that in order to be localized here, the virus must initially enter the body through the skin of the hands - usually through the skin on the fingers, less often through the skin on the wrists or palms. For virus particles, this is much more difficult to do than to penetrate the skin on the lips, since the epidermis on the fingers is much rougher and thicker, and its protective abilities are higher.
During relapses, herpes manifests itself precisely in those parts of the body through which the virus initially entered the body. So, for example, if infection occurs through the lips, then the corresponding symptoms of the disease will appear on the lips, and if through the genitals, on the genitals. This is due to the specifics of the virus’s interaction with the body: once it enters tissue, it cannot spread quickly, but only affects relatively small areas under the skin.
By the way, it is also useful to read:
- Details about herpes on the body: from causes and symptoms to treatment methods
- Prevention of herpes from A to Z
But as soon as the virus penetrates one of the nerve cells, along its processes it reaches the nerve nodes in the spinal cord, and here, in the nuclei of neurons, the genetic information of the virus is stored for the rest of a person’s life, and the cell itself constantly produces new virions.
When the disease relapses, the viral particles produced by the neuron are displaced along the same processes into peripheral tissues innervated by the same nerve cell; in other words, into the same tissues through which the body was infected. This is where herpetic rashes appear, although sometimes the disease recurs asymptomatically.
Note: the possibility of migration of the virus between different parts of the nervous system is practically excluded, and therefore, having contracted herpes on the lips, one cannot suffer, for example, from the genital form of the disease. Accordingly, the disease on the hands develops only when the virus enters the body through the skin of the hands.
We conclude: the reason for the appearance of herpes on the hands is infection with a herpes virus infection that occurred through the skin of the hands. Rashes here may appear periodically due to weakened immunity, which leads to a relapse of the infection that persists in the body.
Thus, the next manifestation of the disease can be triggered by any bacterial or viral disease, hypothermia, injury, severe stress, irrational diet - everything that affects the state of the immune system.
The photo below shows another example of herpes on the fingers:
As a rule, infection of the hands with the herpes simplex virus occurs when there are scratches on the fingers (even very small ones), abrasions, cracks under the nails and touching infected surfaces with these hands. In the presence of such scratches, the soft tissues under the skin are exposed, and viral particles that enter here can relatively easily penetrate into the cells.
According to statistics, herpes on the hands most often occurs in the following categories of patients:
- Children with colds on the lips or herpetic stomatitis and the habit of constantly sucking their fingers;
- Women involved in prostitution;
- Athletes involved in contact sports - wrestling, rugby, etc.;
- Dentists who, through negligence, become infected from their own patients who have symptoms of herpes on the lips (however, today this happens much less frequently than it used to be).
It is among athletes that sometimes even such rare forms of the disease as the appearance of a herpetic rash on the shoulder or elbow are registered. In other categories of patients, such localization of rashes is almost never observed.
It is useful to keep in mind that you can become infected with herpes if you have one of the following conditions:
- The recipient is not immune to the HSV-1 and HSV-2 viruses. The obvious consequence is that adults rarely become infected with herpes on their hands, since the majority (for different countries from 70% to 95%) are already carriers of the virus in any form - labial, genital - and have the appropriate antibodies to it;
- The course of relapse of labial herpes. This is more typical for children who are already infected, even if they are immune. Relapse occurs in cases where the immune system weakens, the body cannot control the reproduction of the virus, and when it penetrates into new tissues, they may become infected. In this situation, autoinfection from the patient himself is possible (a typical situation is that a child with a cold on the lips sucks a finger with a scratch, after which he develops a viral infection of his hands).
Likewise, there is a risk of infection of the eyes or genitals if a hand infected with the herpes virus is touched.
If the patient has previously suffered from herpes, but at the moment he has no signs of relapse, then the likelihood of infection is practically excluded even through contact with the patient when the symptoms of the disease manifest themselves.
Reasons for the development of herpes on the hands
The appearance of herpetic lesions on the hands is provoked by various factors:
- injury to hands, fingers;
- weakening of local or general immunity;
- acute cold;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- severe hypothermia of the hands;
- postoperative period;
- physical or mental fatigue;
- exhaustion of the nervous system;
- sudden changes in outside temperature;
- transfer of herpes from the genitals, mouth to hands.
Genital or labial herpes present in a person is not capable of independent migration. The spread of the disease to the hands and fingers is facilitated by the person himself when he touches infected parts of the body.
Pregnancy and the virus
Due to the high probability of damage to internal organs, the virus is very dangerous for women during pregnancy. Herpes on the arm during pregnancy should be a reason to consult a doctor, since there is a risk that the birth will end in the birth of a stillborn child or the woman will not be able to carry the fetus to term. Even if the child is born, there is a high risk if the mother has herpes that the baby will have hyperplasia of the limbs, mental retardation, growth retardation and other problems.
Features of infection in children
Herpes on the hands in childhood is caused by internal or external reasons:
- The immune system of children under 3 years of age copes more easily with an infection attack. The body contains antibodies received from the mother. The appearance of the disease on the upper extremities indicates a weakened immune system.
- Older children become infected with the virus through contaminated toys and unwashed hands upon contact with a carrier of the disease, involuntarily transferring infected biomaterial to healthy areas of the skin.
- Intrauterine infection of a child is observed if a woman was a carrier of herpes before pregnancy. Infection of the fetus occurs through the umbilical cord or at the time of birth.
Children are most often susceptible to herpetic infections on the upper extremities:
- Prone to frequent manifestations of labial herpes. The habit of constantly putting your fingers in your mouth leads to the development of infection on your hands.
- After hypothermia or overheating. Such conditions provoke the activity of the virus. The child should be dressed according to weather conditions.
Other types of herpesvirus are also found on the hands of children:
- Third. Manifests itself in the form of chickenpox.
- Fifth (cytomegalovirus infection). A herpetic disease of a congenital nature, provoked by HSV type 5, in 60-80% of situations is formed in the form of petechiae, which are small hemorrhages.
- Sixth and seventh. They cause fictitious rubella (exanthema, childhood roseola). The disease manifests itself as a pinpoint rash throughout the body and requires differential diagnosis to exclude true rubella.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of herpes on the hands is not fundamentally different from eliminating manifestations on other parts of the body. In general, the course of treatment is usually 20 days. Specific antiviral medications, immunomodulators, itching relievers, and local antiseptics are used. If pain is present, anesthetic creams and ointments can be used.
Throughout the course of treatment, you must carefully monitor personal hygiene and adhere to a healthy lifestyle. And the main thing is that even in the absence of special treatment measures, manifestations of the virus of the HSV-1 and HSV-2 types completely disappear within 14-21 days.
Symptoms of the disease
In adults and children, the disease occurs with extensive symptoms. The nature of the symptoms depends on the phase of the disease.
First stage:
- itching;
- swelling;
- burning;
- elevated temperature;
- skin redness;
- soreness in the area of the rash.
The second stage occurs on days 2-3:
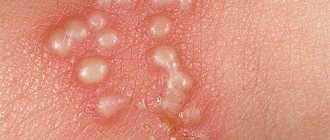
- formation in the interdigital area, on the inside of the hands and the ulnar recess of painful blisters with liquid inclusions;
- the combination of blisters into large vesicles, when damaged, wounds form.
In children, rashes look like roseola (painless flat hyperemic patches with a diameter of 3-5 mm) or small, very itchy blisters (vesicles) up to 5 mm in size with serous fluid inside.
The child becomes restless, involuntarily scratching the blisters. Secondary skin infection occurs. The skin surface swells and becomes saturated with blistering fluid or becomes covered with a dry crust.
Do not puncture the bubbles in an attempt to remove the contents. The liquid can spread the virus to healthy areas of the skin.
The third stage appears after 3-4 days:
- bubbles burst;
- liquid substance flows out.
Fourth stage:
- drying of blisters;
- crust formation;
- skin renewal.
If the disease becomes complicated, felons form on 1-2 fingers or palms - a sign of acute purulent inflammation of the tissues of the fingers.
The severe course of the disease is accompanied by a persistent pain syndrome (myalgia, neuralgia and tingling) and symptoms of intoxication of the body (hyperthermia, headache, deterioration of well-being, increased nervousness).
Herpes zoster
Shingles is a type of disease caused by the activity of the herpes zoster virus. It is characterized by extensive localization of rashes and severe pain. With the development of pathology, damage to the nervous system and disruption of its functioning is possible.
To treat this type of herpesvirus, novocaine blockers, narcotic and non-narcotic analgesics, ointments with capsaicin, and anticonvulsants are used. These agents have antiphlogistic, antiviral and antibacterial effects, relieve pain, itching, and burning. The most effective ointments for the treatment of acute infectious pathology are Lycroderm, Lycrogel, Mataren-Plus, Erythromycin and Tetracycline ointments.
Localization
In an adult, the disease manifests itself in the following areas of the upper limbs:
- Often. On the fingers and between the fingers. Most often the nail area and lateral phalanges are affected.
- Rarely. Palms and back of the hand.
- Very rarely. Skin of elbows, forearms and shoulders.
Depending on the type of infection, the disease can affect not only the hands, but also other parts of the body:
- the rash spreads along the peripheral nerve fibers, causing a skin reaction throughout the body;
- the infection appears on the hands with subsequent systemic damage to other parts of the body and organs.
How to distinguish herpes from similar rashes?
It is not always possible to distinguish herpes on the finger from other skin diseases by external signs. Rashes are formed due to an allergic reaction, insect bites and other reasons. Before treatment at home, herpes should be differentiated from diseases with similar clinical signs:
Bacterial felon. The disease is characterized by tissue suppuration and decreased mobility of the finger joints.
Allergic reaction. Herpetic panaritium affects small areas of the body. In an allergic reaction, the rash covers almost the entire arm.
Insect bite. The latter cause the formation of blisters with clear liquid, characteristic of herpes. However, herpes infection has a longer course and is rare. Blisters after insect bites go away faster.
If it is impossible to identify the disease based on external signs, a differential diagnosis is prescribed, which includes the following procedures:
- linked immunosorbent assay;
- polymerase chain reaction.
Both analyzes make it possible to identify the pathogen and select the optimal methods for treating herpes. Medicines are prescribed by a dermatologist.
Diagnostics
A herpetic infection on the hands requires extensive diagnostics, which makes it possible to accurately determine the type of pathogen and assess the state of the immune system of a sick person.
For this purpose it is prescribed:
- scraping a sample of the affected area of skin;
- testing the internal contents of the bubbles;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- immunogram (venous blood test).
Special blood tests are performed:
- REEF. Rules out the presence of syphilis.
- PCR analysis. Specifies the type of pathogen, establishes the value of its concentration in the body.
- ELISA. Detects antibodies to herpes agents.
Causes
A virus is a non-cellular infectious agent that is the most numerous biological form existing on earth. It can only reproduce inside the cells of living beings. Viruses spread in several ways - airborne, fecal-oral, sexual and household. The herpes strain often enters the human body in early childhood, but may not make itself felt for years, being in a passive form. The main reason for the appearance of herpetic rashes is the presence of one of the viral strains in the body.
In the presence of factors that provoke the transition of the disease to an active form, the virus recurs and begins to actively multiply, which manifests itself in the appearance of a rash on the hands. Reasons contributing to relapse include:
- hypothermia of the hands;
- decreased immunity due to previous infectious diseases;
- severe fatigue;
- unstable emotional background, stress;
- injuries to hands and fingers;
- presence of skin damage, cracks, scratches;
- eczema, dermatitis, neurodermatitis (as secondary factors contributing to the transfer of the herpes virus from the main site of localization);
- long exposure to the sun or solarium.
Treatment methods
If you have signs of herpes on your hands, you should visit a dermatologist. For the disease, a comprehensive treatment approach is practiced in two directions:
- suppression of infection activity;
- increasing the protective functions of the body.
Medications
For herpes on the hands, medications of various forms are prescribed - gels, ointments, injections, tablets of different medication groups:
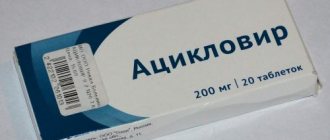
- Antiviral. Prescribed in the first week of treatment. They have a direct effect on the infection, effectively relieving pain, redness and itching (Acyclovir, Valaciclovir, Zovirax, Acigerpin, Medovir, Vivorax).
- Immunostimulants. Improve the quality of immunity (Interferon, Viferon).
- Antihistamines. Relieves the feeling of itching, exhibits a calming effect (Tavegil, Diazolin and Suprastin).
- Painkillers. Relieves painful discomfort. External agents containing lidocaine or benzocaine (Lidocaine, Luan, Heparin ointment) are prescribed.
- Anti-inflammatory. Eliminate the intensity of the inflammatory process (Galavit, Cycloferon).
- Antibiotics. Indicated in cases of bacterial infections (Amoxiclav, Cefuroxime, Zinnat).
- Antiseptics. They have a local antiseptic effect (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Fukortsin, brilliant green, iodine).
The duration of therapeutic measures is at least 20 days. During the treatment period, you need to maintain personal hygiene, take vitamin supplements, and eat right.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine offers many non-standard ways to treat herpetic rashes on the hands.
The following have a particularly high healing effect:
- Honey. Relieves pain, heals and accelerates tissue restoration: Honey in combination with streptocide. Grind 1 tablet of streptocide and combine with 1 tsp. liquid honey. Transfer the resulting mass to a bandage and apply it to the sore spot for 15 minutes 4-5 times a day.
- Honey and fir oil. Mix the components in equal proportions and apply to the affected skin for 10 minutes once a day. Carefully remove any remaining medication with a cotton swab.
Skin treatment
Local treatment of herpes on the arm should be carried out with antiviral creams, ointments and gels. Local treatment is good because the medicine directly affects the causative agents of the disease. Ointments eliminate itching and redness. However, it has been proven that their use is advisable only at the initial stage of the inflammatory process, the first 5-7 days.
Recommended products for use: Zovirax, Acyclovir, Medovir, Acigerpin and others. All of these drugs have acyclovir as their active ingredient. But patients should know that these ointments do not have such a strong effect as when used on the lips, since the skin of the hands is much rougher.
Acyclovir-based ointments are not used in disease prevention.
Possible consequences and complications
With an uncomplicated form of the disease, the prognosis is always favorable. The duration of the disease is 2-3 weeks with the absolute disappearance of crusts.
If the disease drags on, there is a possibility of the following complications:
- Weak immunity. The danger of infection progression and its transition to a more severe form.
- Newborns. In the first week of life, cytomegalovirus infection is dangerous for children. The disease is acute with pronounced symptoms and a high risk of death.
- Pregnancy. The virus in the active phase negatively affects the fetus.
Prevention
To prevent infection with the virus or its recurrence, you should follow the recommended preventive measures. The primary task is to strengthen the immune system, which is achieved by following the rules of a healthy diet, taking a complex of vitamins and hardening. The basic rules that can be followed to significantly reduce the risk of herpes infection are as follows:
- maintaining hygiene;
- use of antibacterial agents;
- rejection of bad habits;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Prevention of the development of herpes on the hands
Compliance with preventive measures will help avoid infection with the herpes virus, and if the disease is present, further spread. This requires:
- strengthen immunity;
- give up alcohol and smoking;
- Healthy food;
- avoid stress;
- avoid prolonged exposure to the sun;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- exercise;
- avoid contact with a carrier of the virus;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- Avoid hypothermia and overheating.
To increase the protective functions of the body, it is useful to take a course of multivitamin complexes 2 times a year.
If a person has glossitis or genital herpes, it is necessary to systematically treat their hands with an antiseptic or laundry soap.
Herpesvirus appears on hands for various reasons. At the first signs of illness, be sure to seek medical help. Timely initiation of complex treatment speeds up recovery and prevents the transition of herpes to more aggressive forms.
Preparations for oral administration
Systemic medications for herpes on the hands are extremely rarely used. After all, a virus that manifests itself on the hands almost never leads to complications that require the use of medications orally.
Antiviral drugs will have to be taken if the patient’s immunity cannot cope. However, such drugs cannot be used without the recommendation of a doctor, since most of them have quite serious side effects. Another part of the drugs cannot be used in pediatrics, and a number of tablets are even contraindicated for treatment under the age of 18 years.
Doctors often prescribe Acyclovir or a more modern analogue, Valacyclovir. These drugs are used every 4 hours throughout the day, but no more than 5 days in a row.
Severe itching with herpes on the hands can be eliminated with antihistamines: Suprastin, Loratadine and others.
To quickly relieve symptoms, doctors recommend using drugs from the interferon series. The most effective include: “Genferon light”, “Viferon” (suspensions) and others. It is recommended to include immunomodulators, preferably of plant origin, in the treatment complex.
Traditional recipes for ointments
As an auxiliary method of therapy, the use of ointments prepared on the basis of healing components of natural origin is allowed. To create medicines for external use that are active against herpes viruses, plants with pronounced antiphlogistic, antiviral, antimicrobial, wound-healing, regenerating, restorative and soothing effects are used. These are aloe, chamomile flowers and leaves, wormwood, garlic, echinacea, willow and many others.