Squamous cell papilloma as a symptom of HPV
Squamous cell papilloma is a benign neoplasm on the skin and mucous membranes with a high level of cell malignancy at the DNA level.
Papilloma takes its name from the pathogenic activity in the squamous epithelium. In appearance, the neoplasm resembles a small nipple on a stalk or a tumor-like lump on a wide base. The shade of the growth coincides with the base of the epithelial layer, however, with inflammation and other pathological processes, the color may change.
Depending on the stage of growth, the structure of squamous cell papilloma also changes. At first it is soft, and after a certain time it becomes elastic, almost hard. Simultaneously with the natural aging of the skin in patients over 45-50 years of age, the neoplasm undergoes hyperkeratosis-type changes and becomes brown or black.
Typical localization of growths is determined by the following location:
- skin and mucous membranes;
- respiratory organs, most often the nasal passages, larynx;
- digestive system (pharynx, for example, squamous cell papilloma of the tongue, esophagus, stomach, intestinal tract);
- genitourinary tract (urethra, cervix).
Despite the frequency of occurrence in older people, neoplasms are increasingly being reported in people under 30 years of age.
Squamous cell papilloma on the skin
Squamous cell papillomas are localized on the eyelids, décolleté and chest, neck, in other words, where the skin is thin (more about the causes and treatment of papillomas on the neck and armpits here). Appearance on the upper eyelid leads to serious vision problems and inflammation of the conjunctiva.
The growth of the neoplasm on the skin epithelium occurs slowly, and the growth itself barely reaches 1.2 mm. With intensive growth, the papillomatous lesion becomes similar to an ordinary wart, similar to a small raspberry or blackberry. The shade of the growth coincides with the physiological shade of the base.
Laryngeal papilloma
Squamous cell papillomas in the larynx require adequate treatment, especially in young children (for example, after infection during childbirth). Such neoplasms in children, against the background of absolute health, can disappear on their own.
Pathological neoplasms on the mucous membranes tend to spread rapidly, which is favored by the environment of activity of viral strains.
With prolonged existence, the process of swallowing and breathing is disrupted. Self-amputation of a tumor as a result of trauma can block the airway.
Without adequate treatment, growths almost always turn into malignant tumors.
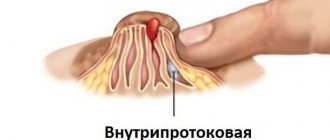
Squamous cell papillomas of the esophagus and stomach
When papillomatous lesions are localized inside the stomach cavity, gastric papillitis develops. The internal structure of the growth is abundantly supplied with capillaries and blood vessels, the base of the papilloma is lined with connective tissue.
Squamous cell papilloma of the stomach consists of multilayered epithelial tissue, resembling small bumps of a pinkish tint. Papillitis is always a multiple process. Even when one growth is diagnosed, a new pathological focus usually begins nearby.
The average size of a neoplasm on the walls of the stomach can reach 2.5-3 mm. The papilloma itself is covered with squamous and transitional cell epithelium, and is lined on top with a transitional epithelial layer.
External manifestations
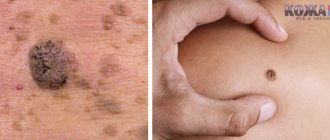
Squamous papillomas rise slightly above the surface of the skin. They look like papillary growths on a thin stalk with a wide base. The diameter of the tumors varies from 1 mm to 2.5 cm.
They are soft to the touch, the color is identical to the color of the adjacent tissues. However, if the disease occurs with hyperkeratosis - keratinization of the epithelium - the PP acquires a whitish, brown, pearl or dark brown tint and becomes hard and flaky.
PPs are submersible - grown deep into the tissue. In this case, the epithelial papillae are located under a layer of squamous epithelium. Typically, neoplasms are painful on palpation, but asymptomatic tumors also occur.
Photos of squamous cell papillomas are presented on the website and medical forums.
Folk remedies
Carry out the procedure three times a day until the warts completely disappear. If the wart has just started to grow, try removing it with the white of a chicken egg. Pour the egg, for example, into a frying pan, and apply the white that remains on the walls of the shell to the wart or papilloma.
To boost immunity and get rid of papilloma, traditional healers advise drinking a special healing infusion for papilloma. Mix equal parts of nettle and plantain leaves, horsetail herb, lemon balm and dandelion root, after thoroughly chopping all the plants. Take 3 tablespoons of the mixture and pour 4 glasses of cold water, put on the stove and boil for 7-10 minutes.
Then leave for 2-3 hours, letting it brew. Drink 3 tablespoons of the infusion 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 7 days. You need to take 1 teaspoon of chopped garlic and mix with 2 teaspoons of any base cream. Apply this product to gauze and apply to the papilloma. You can secure the bandage with a bandage.
This compress should be left for 3-5 hours, then wash the area with warm water and soap. Literally within a month the papillomas disappear. Infusion of herbs and ointment with garlic will help reduce papillomas. Infusion. Chop nettle and plantain leaves, horsetail herb, lemon balm and dandelion root and mix in equal parts.
Ointment 1 tsp. mix chopped garlic with 2 tsp. any base cream, apply to gauze and bandage it to the formation on the skin or fix it with an adhesive plaster. Leave for 3-5 hours, then wash off with warm water and soap. And within a month the papillomas will disappear. Take green walnuts of milky ripeness, cut them into slices and grind in a meat grinder.
Fill a liter jar about 2/3 full with this slurry. Add the rest of the volume with purified kerosene. Now you should close the composition with a tight polyethylene lid and leave for 21 days (always in a dark place!). After three weeks, the resulting product should be filtered through 4 layers of gauze, and the remainder should be squeezed out thoroughly.
Pour the resulting liquid into a dark glass bottle, close tightly and place in a dark, cool place. Actually, you need to lubricate papillomas with this product 1-2 times a day until they go away. The healing process can be accelerated by taking freshly squeezed potato juice orally. You need to drink it twice a day, half an hour before meals. The course of treatment is 2 months.
And one more thing: the removal of papillomas is facilitated by increased immunity. For this, you can drink rosehip infusion or the well-known “Immunal”, which, in fact, is an alcohol tincture of Echinacea. A glass jar is loosely filled 1/3 with green sprouts from potato tubers.
Young spring celandine grass (possibly with roots) is washed, slightly air-dried and placed in the same jar up to 2/3 of the volume, about another 1/3 is filled with young shoots of thuja. Fill the contents with pure alcohol so that the alcohol level is higher than the collection, and leave for 10-15 days under a lid in a dark place. It is not necessary to strain the finished product.
The color of the tincture is dark green, almost black. The wart or papilloma is lubricated with the composition three times a day, three times each time. That is, having smeared the wart once, let it dry for one minute, then smear it again, and so on - three times in the morning, at lunch and in the evening. The course of treatment for one papilloma is 5-12 days.
But be careful not to let the tincture get into your eyes or mucous membranes. It is better to start treatment on the waning moon. All components are highly poisonous plants, so keep them out of the reach of children. Mix 100 ml of alcohol, 2.5 g of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), 2 g of boric acid and 2.5 ml of 5% iodine.
After this, the papilloma will fall off. If you apply an ice cube made from an infusion of string, chaga and celandine to the papilloma for 3-5 minutes three times a day, it will gradually fall off by itself. Papillomas - even numerous ones - can be removed with an egg. Take the shells of two eggs, place them on a baking sheet and place them in an oven preheated to 250°C for 30 minutes.
Then, once the eggshells had cooled, she ground them in a coffee grinder until they were powdered. Pour the powder into a glass container and close the lid tightly. Tear the cotton wool into small pieces.
Sprinkle each papilloma generously with egg powder, cover with cotton wool on top and secure with adhesive tape. Wear this bandage for about 2-3 weeks, changing it once every three days. Papillomas will disappear after the first course of treatment.
Diagnostic measures
Primary diagnosis of HPV even before the onset of papillomatous rashes is complicated by the absence of any obvious symptoms. More often, detection of viral antibodies in a timely manner is possible only if the patient is disciplined in relation to his own health, and during regular examinations by treating specialists.
Even after self-discovery of papillomas on visible parts of the body, people do not rush to see a doctor and, as a result, pay attention to the instability of neoplasms already at the stage of cancer progression.
Squamous cell papillomas are an area of research for dermatovenerologists and oncologists. For several decades now, the relationship between cancer and human papillomavirus infection has been given a special place.
Common diagnostic measures are:
- laboratory tests for viral antibodies;
- polymerase chain reaction for DNA of viral strains;
- histological analysis for cancer cells during biopsy.
For internal localization of papillomas,:
- instrumental studies using ultrasound,
- radiocontrast methods,
- endoscopic examination of mucous organs.
Additionally, examinations and consultations with a proctologist, urologist/gynecologist, oncologist, gastroenterologist, and hepatologist can be performed.
Timely and adequate diagnosis can significantly reduce the risk of cancer of internal organs.
Prevention of cancer is regular mandatory medical examination of patients over 30 years of age.
Features of papillomas
Places where squamous cell papillomas can occur:
- skin: face, collar part of the neck, lower back, arm area;
- mucous membranes: oral cavity, larynx, esophagus, rectum.
Such formations grow slowly, do not cause any inconvenience and do not pose any particular danger to health. But if you are not careful, they can be injured, which can lead to the risk of papilloma transforming into a malignant tumor.
The main cause of papillomas is papillomavirus (lat. Papillomavirus). You can become infected with the virus in several ways:
- sexual intercourse;
- during childbirth;
- everyday life: touching, shaking hands;
- public places and establishments: swimming pools, saunas, baths, gyms;
- neglect of hygiene rules;
- self-infection: shaving or hair removal.
From the histological side, papilloma is an overgrown squamous epithelium and stroma, with uneven tissue atypia. It has a developed circulatory system in its structure. Papillomas do not appear immediately. The virus can remain in the human body for a long time, and manifests itself only in the presence of certain factors:
- weakening of the immune system;
- elderly age;
- dermatoses;
- allergies;
- infectious diseases;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- harmful environment;
- stressful situations;
- genetic predisposition.
Squamous cell papillomas are classified according to their location on the body:
- Squamous cell papilloma of the skin. Such warts appear in places of increased trauma: the skin of the face, neck, hands. Often it does not cause health problems. The question is more about aesthetic appearance.
- Papilloma of the mucous membranes. The problem here is more significant. The mucous membranes of the mouth, larynx, esophagus, and rectum are often irritated. This can lead to their traumatization and subsequent malignancy. In addition, they cause inconvenience, causing sensations of a foreign object, the inability to perform certain functions, and simply cause discomfort.
Stages of development
In the process of development of basal cell papilloma, several stages are distinguished. The relationships between the stages and the corresponding signs of growth change are summarized in the table:
| Stage | Signs |
| First | Small flat spots with a smooth or rough surface begin to form on the body. As the spots develop, they become crusty. Colored areas of the skin appear, covered with a crust of keratinized epidermal cells. |
| Second | The spots take on a convex shape and small papules form. The growths do not peel off and become similar to ordinary warts. |
| Third | Papillomas thicken, darken, and become covered with scales. This stage is characterized by a keratotic type of inflammation. When an injury occurs, bleeding wounds appear on the surface of the keratoma. |
| Fourth | Significant keratinization of growths begins. They harden quickly and are easily injured. Treatment of the disease at this stage of development is mandatory, since the risk of scabs coming off and infection on the wound increases significantly. |
Therapeutic techniques
Flat papillomas of the cervix, mouth and skin bring a lot of discomfort to a person. That is why most patients have a question: how to get rid of unattractive growths? The most commonly prescribed surgical treatment, the main types of which are:
- low temperature exposure;
- laser destruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- removal of papilloma with a scalpel.
It is often possible to remove large papillomas on the body only with the help of classical surgery. For these purposes, medical scissors or a loop-shaped instrument are used. Treatment of laryngeal papilloma can be carried out in two ways: open surgery and endoscopic intervention. The use of the second method shortens the recovery period and reduces the risk of complications. Growths present on the mucous membranes of the esophagus can be removed in the same way. The material removed during the operation is sent for histological analysis.
If there are papillomas in the area of the eyelids and lips, the attending physician may recommend radio wave destruction. The main advantage of this therapeutic technique is the low risk of injury to the skin and mucous membranes, as well as the penetration of pathogenic microflora. Tissue healing occurs without scar formation. To get rid of papillomas on the neck, various chemicals are used:
- trichloroacetic acid;
- potassium permanganate;
- silver or lead salts;
- hydrogen peroxide solution.
After surgery, treatment of papillomatosis continues. The doctor prescribes antiviral drugs, vitamins and immunostimulants. It is recommended to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, harden the body, and eat right. Is it possible to remove flat papillomas at home, what means are used for this?
The main ways to get rid of tumors
Laser removal of papillomas is justified when they are located on the skin. A narrow beam has a targeted effect. Adjacent tissues remain safe. This is suitable for removing PP in hard to reach areas, such as the eyelid.
Another technique involves the targeted use of cold to burn out the site of inflammation - cryotherapy.
The situation is more complicated when the tumors are located on mucous surfaces. In this case, surgery cannot be avoided. A patient diagnosed with squamous cell papilloma of the larynx will be offered 2 treatment options.
- intralarynx - surgery is performed under endoscope control. The technique is popular among doctors. Firstly, it does not provoke complications, and, secondly, there is no need to violate the integrity of nearby tissues;
- extralaryngeal – the doctor performs targeted manipulations under computer control. The operation takes about 35-40 minutes. In order to prescribe it, the doctor must make sure that the tumor is small. For example, if it is determined that the squamous cell papilloma of the tongue has clear boundaries and can be easily removed, surgery is prescribed.
Regardless of the chosen technique, the surgeon conducts a second examination. The purpose of the procedure is to relieve the patient of possible complications. If even a small part of the neoplasm remains inside the epidermis, this will lead to re-infection.
Treatment
Therapy, which is aimed at combating papillomavirus and its manifestations, must perform several tasks simultaneously. Correctly selected treatment stops the spread of the disease, removes rashes and increases the body's protective properties.
For squamous cell papillomas, the following medications are recommended:
- "Panavir";
- "Dremevit";
- "Aldar";
- "Viferon".
Radical treatment may be required. To remove papillomas the following are used:
- Cryotherapy;
- Radiosurgery;
- Electrocoagulation;
- Laser therapy;
- Surgery.
Radical therapy methods are more successful, as they help to minimize the likelihood of disease relapse.
In addition to removing tumors, antiviral therapy will be needed
Is it possible to use traditional methods?
With the permission of a doctor, it is permissible to use traditional methods in the treatment of squamous cell neoplasms on the skin and mucous membranes of organs. For this diagnosis, it is recommended to use:
- Garlic. It is cut into thin slices and attached to problem areas, after which they are fixed with adhesive tape. This compress is made 2 times a day and kept for no more than 3 hours;
- Potato. Drink 100 ml of fresh vegetable juice twice a day, about half an hour before meals. This treatment should be followed for 2 months;
- Celandine. The leaves of the plant are crushed, the juice is squeezed out and evaporated. The finished extract is applied to the problem area three times a day. The results of treatment will be assessed after a month.
Traditional methods should be used in combination with drug therapy to achieve a faster and stronger effect.
Possible complications and precautions
An important precaution to avoid infection and consequences is the exclusion of promiscuous sexual contact. For prevention, girls and young women are vaccinated with Gardasil (vaccination against oncogenic strains). It is recommended to use personal hygiene items, linen, and manicure accessories.
Papillomas do not provoke cancer; the presence of HPV in the body contributes to the development of dysplasia and carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Formations in the bladder are characterized by hematuria and urinary dysfunction. In a child with damage to the larynx with severe papillomatosis, hoarseness with transition to aphonia and stenosis of the organ are recorded.
If there are manifestations of HPV in pregnant women, a special role is given to preventing the risk of infection of the fetus during natural delivery.
It is impossible to completely overcome HPV and its manifestations - flat papilloma (ICD code D23). Treatment of flat papillomas should be comprehensive; it is necessary to start getting rid of them in the initial stages. The risk of relapse remains high. The patient is advised to undergo constant medical supervision with periodic examinations and removal of newly emerging formations.
A rash such as squamous cell papilloma implies a benign neoplasm that is created from squamous epithelial cells. It can occur on different parts of the body. Squamous cell tumors affect not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes.
Symptoms of occurrence
The main symptoms of papillomas:
- manifestation of rashes;
- keratinization of the skin in the affected areas;
- swelling/swelling and redness of nearby skin;
- the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the form of itching or burning in the area where the rash appears.
Symptoms of the presence of squamous cell papilloma depend on the type and location of its location.
Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus
The appearance of squamous cell papillomas in the esophagus is very common, which can trigger the development of esophageal cancer. From the medical side, there is no definite answer why papillomas appear on the walls of the esophagus. However, first of all, papillomas are the most common type of diagnosed tumors.
If you have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, heartburn or pain in the epigastric region, contact a gastroenterologist. The main danger is that over time this pathology can turn into a cancerous form.
The main reasons for the appearance of papillomas on the esophageal mucosa:
- advanced form of gastritis;
- constant heartburn;
- eating spicy food;
- alcohol abuse.
Papillomas on other parts of the body
When a rash occurs in the larynx, difficulty swallowing occurs, difficulty breathing and impaired diction are observed, and there is a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the throat.
With a tumor in the stomach, nausea, increased salivation, belching, and pain in the abdominal area are observed.
On the tongue
Squamous cell papilloma on the tongue can cause a swollen appearance of the tongue. In this case, there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, pain when chewing food, and restrictions in the movement of the tongue.
On the lips
The appearance of papilloma on the lips reflects not very pleasant symptoms. As a rule, the tumor formation in the lip area gradually increases in size, and swelling or swelling of the lips is often observed. There are frequent cases of bleeding of the neoplasm, and pain when touching the papilloma.
In intimate places
Papillomavirus in women in the intimate area can cause the development of serious diseases. Many who have been diagnosed with papillomas subsequently encounter hyperkeratosis, or in another way, the disease is called cervical leukoplakia.
As a rule, a person does not suspect the presence of papilloma in his body, and especially in the esophagus, and symptoms appear already in advanced forms. Or they are diagnosed together with other diseases during diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Detection of the rash is carried out by the patient himself or the doctor during a medical examination. Depending on the location of the rash, the presence of pathology is detected by a dermatologist, gynecologist or gastroenterologist.
To identify papilloma, determine its type and distinguish it from other types of tumor neoplasms, diagnostic procedures will be needed. It is necessary to take blood tests, do a biopsy and undergo histological and cystological examination.
Diagnosis of the disease
Most neoplasms are diagnosed visually by a dermatologist, ENT doctor or gastroenterologist. If necessary, tests (smears, scrapings) and various studies of the stomach (endoscopy) are prescribed.
Diagnosis of this disease depends on the location of the growth. Initially, the patient should be examined by a general practitioner and then referred to a specialist: a dermatologist, gynecologist or gastroenterologist.
It depends on the location of the lesion. If the formation is located on a visible part of the body, then the dermatologist diagnoses it by appearance.
If the source of the disease is hidden from view, then, for example, a gastroenterologist determines the disease using fluoroscopy or other methods. In the rectum, the neoplasm is palpated by palpation, and on the cervix it can be seen on a chair through a glass or on colposcopy.
This is done by a gynecologist. It is important to diagnose this disease in time to avoid complications and irreparable consequences.
A competent specialist will also prescribe the following procedures:
- general blood analysis;
- biopsy;
- PCR method, which will identify the virus, confirming the nature of the formation;
- others depending on location.
What is squamous cell papilloma?
squamous cell papilloma
The stroma can be dense or loose, and signs of inflammation often develop in the connective tissue. The histological structure of tumors is diverse, which complicates not only diagnosis, but also treatment. Fibropapilloma is characterized by significant development of the stroma; skin growths are affected by hyperkeratosis.
Condylomas on the mucous membranes usually accumulate less keratin, but such papillomas can also be affected by severe keratinization. Typically, benign tumors consisting of transitional and squamous epithelium are called “papillomas,” although each type of warty thickening has its own distinctive features.
Here are several types of formations to which clinic patients are happy to say goodbye: Keratopapillomas often affect people after 30 years of age; areas of the body that experience friction from underwear, clothing, and glasses are especially susceptible to it. This type of tumor has a stalk, so when rubbed, it easily breaks off and becomes inflamed.
A seborrheic wart is a basal cell papilloma, its origin associated not with HPV, but with age-related changes in the skin after 45 years. Fibropapilloma is another type of benign skin tumor. The stroma inside grows and affects the dermal tissues and blood vessels. There is a noticeable connection between the clinical picture of HPV infection and the localization of papillomas.
There are about 40 different products and methods for removing skin papillomas. With the cosmetic liquid Superchistotel you can dissolve small keratopapillomas and fibropapillomas at home in 3–10 days. Ointments and gels help restore the normal course of the keratinization process, which is disrupted by the papilloma virus.
Radical methods - laser, radiosurgery, electrothermal, low-temperature - can eliminate papillomas in a matter of minutes. Modern surgical methods are based on the targeted impact on the leg or base of the papilloma with laser, radio waves or liquid nitrogen.
Coagulation of blood vessels in the dermis occurs, which avoids bleeding. Non-contact removal is an almost painless procedure, with a low risk of skin infection at the site of damage. Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus is a rare benign tumor. Such formations grow slowly and do not bother a person for many years.
An unfavorable combination of circumstances - stress, dietary errors, weakened immunity - can provoke the development of esophageal cancer caused by squamous cell papilloma. If the examination confirms the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes comprehensive treatment. These are antiviral drugs, and, at the same time, an operation to remove papillomas.
More difficulties arise if the tumor is localized in the lower third of the esophagus. Although modern video-laparoscopic and endoscopic equipment is used, chipped and broken teeth are rarely avoided. The role of HPV in the development of cancer of the female genital area has been proven.
Dysplasias and carcinomas are associated with squamous cell papilloma of the cervix, but papillomatosis of this organ does not necessarily lead to the formation of a cancerous tumor. Genital warts also affect the male body. The object of virus attack is the anogenital area. The antiviral properties of plants, propolis, and vegetable oils are widely used in the folk fight against papillomas on the skin.
There are methods and means of alternative medicine that can limit the growth of tumors by reducing the activity of HPV. The safest way to achieve this goal is to stimulate the sick person’s own immunity. Alternative medicine for papillomas and warts on the skin: Essential oils (fir, thuja, juniper, basil).
Milky juice of celandine, oil and tincture from its herbs. Tincture of green walnut peel and leaves. Garlic paste with skin cream. Castor oil. At home, squamous cell skin papilloma can be removed with cosmetic liquids, solutions, and gels.
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of squamous cell growths, limited exposure to the sun, good personal hygiene, a healthy lifestyle and a healthy diet will help. It is also necessary to promptly treat dermatological diseases and avoid the influence of stressful situations in every possible way.
External manifestations of HPV are expressed in the formation of condylomas, papillomatous lesions, and warts. The variety of types, shapes and sizes is due to the variety of viral strains. To date, more than a hundred strains of varying levels of oncogenicity are known. Strains with a high risk of malignancy also form squamous cell papillomas, which have extensive localization and are difficult to treat.
Causes of growth
The main reason for the formation of squamous cell papilloma is the entry into the body of an infected papilloma virus, which is possible in the following situations:
- Sexual contact with an infected person, which can be vaginal, anal or oral.
- Household communications. This is a handshake or touching inanimate objects that the carrier of the disease has handled. In this case, the virus penetrates exclusively through open wounds or scratches.
- Ignoring personal hygiene rules. That is, when a person uses other people’s hygiene products (washcloths, towels, etc.).
- Visiting the pool, sauna or gym. This virus develops well in a humid environment, and therefore such places with large crowds of people create an optimal habitat for it.
On this topic
Skin covering
Treatment methods for atheroma without surgery
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 9, 2021
Also, people in the following categories are most susceptible to this disease:
- over the age of 50;
- those under frequent exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- those suffering from other skin diseases;
- working in hazardous industries;
- having disorders of the central nervous system, including depression and other psycho-emotional disorders;
- whose blood relatives had squamous cell papillomas.
Methods of infection
The main cause of papillomatous foci of any nature and character is damage to the body by HPV. The routes of transmission are sexual contact or household infection. Rarely, HPV is transmitted from mother to child during childbirth, by shaking hands.
Up to 95% of the entire population of the planet suffers from viral infection, but most of them are only carriers of HPV. This phenomenon is explained by the strength of human immunity - the stronger it is, the lower the risk of the virus appearing.
Promiscuous sexual intercourse, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, and bad habits can contribute to HPV infection. The mechanism of development of squamous cell papilloma is triggered as a result of the activation of pathogenic viral strains.
Provoking factors are:
- Allergic reactions;
- Chronic pathologies of organs and systems;
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Skin diseases;
- Infectious processes;
- Psycho-emotional instability;
- Age-related changes.
The following can contribute to a decrease in immunity:
- long courses of drug therapy,
- stress and overwork,
- inadequate treatment of frequently recurring colds.
Consequences
Human papillomavirus infection itself does not pose a threat to the life and health of the patient, however, neoplasms as a result of the pathogenic activity of viral strains disrupt the natural processes in the epithelial layers. Squamous cell papillomas grow and form new foci of dysplasia. The consequences depend on the severity and complexity of the pathological process.
This is what squamous cell papilloma looks like on the eyelid:
The prognosis for squamous cell papillomas is mostly favorable, subject to timely diagnosis and adequate treatment. Lack of therapy when localized on the mucous membranes of internal organs in many cases leads to cancer.
How to remove papilloma on the neck at home, read our article.
Treatment process
Modern treatment methods are not able to completely expel human papillomavirus infection from the body, but therapy can significantly slow down the process of tumor malignancy and suppress the viral activity of strains.
Hardware techniques help get rid of pathological growths on the skin and mucous membranes. Complex therapy, along with surgical cosmetology, completely solves the problem of HPV for many years.
Drug therapy
Conservative treatment for human papillomavirus infection is a promising and effective direction. Adequate treatment allows not only to suppress the activity of viral strains, but to significantly increase immunity and restore the regeneration of cellular structures of the epidermal layers.
For HPV and squamous cell papillomas, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Interferon-based immunomodulators : Viferon, Ergoferon, Cycloferon, Anaferon;
- Antiviral drugs with local and systemic effects : Valaciclovir, Acyclovir, Ingavirin;
- Vitamin complexes : Alphabet, Aevit, Complivit;
- Local drugs with symptomatic effects: Feresol, Cryopharma, lapis pencil, oxolinic liniment 60%.
Local preparations in the form of liniments, rinsing solutions, and suppositories are of great importance in eliminating the external manifestations of HPV on visible areas of the skin and mucous membranes.
It is important to use any medications only as prescribed by a doctor in order to avoid toxic reactions and burns of the mucous membranes. Incomplete removal of squamous cell papilloma also provokes cell malignancy and the formation of a malignant tumor.
Removal
Hardware or surgical removal is prescribed not only to eliminate aesthetic defects, but also to eliminate the risk of metastases at the onset of the malignant process.
There are two main tactics:
- Observation (single small and stable papilloma);
- Planned removal.
The main indication for excision of tumors is:
- constant traumatization or high risks of negative impact of external factors;
- secondary infection;
- risk of malignant degeneration of growth cells;
- deterioration of organ function due to papillomatosis;
- the appearance of more and more new foci in the papilloma zone.
Removal is carried out in specialized rooms only after a qualified medical examination.
It is unacceptable to remove the growth yourself to prevent dangerous consequences.
The removal method is selected taking into account the localization of the papillomatous lesion:
- cryodestruction (treatment of the lesion with liquid nitrogen);
- scalpel excision of the growth (cutting out tumors with a scalpel);
- removal of papillomas by electrocoagulation;
- radio wave method;
- laser removal of papillomas;
- chemical method.
When papillomas are localized in the larynx, two main methods of removing the growth are prescribed:
- Extraglottic (open);
- Intralaryngeal (endoscopic).
The second method is most preferable due to the low level of complications and short rehabilitation.
If after removal it is possible to keep the papillomatous lesion intact, then it must be sent for histological examination.
Modern methods of removing growths leave virtually no scar tissue or scars, but not a single method guarantees the absence of relapses. Only a combined approach to the treatment of HPV can provide the necessary therapeutic results.