Causes of the disease
Skin plaques occur due to metabolic disorders and fat deposition on the surface.
The formation of xanthomas is caused by the following pathologies and conditions of the body:
- endocrine diseases;
- hereditary disorder of fat metabolism;
- atherosclerotic heart disease;
- chronic arterial hypertension;
- metabolic syndrome;
- oncological diseases;
- last months of pregnancy;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- pathologies of the kidneys and bile ducts.
The formation of xanthomas on the body is caused by a number of negative factors, including a sedentary lifestyle and obesity.
Factors contributing to the appearance of xanthoma on the skin:
- binge eating;
- age-related changes and aging of the body;
- obesity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- insufficient supply of nutrients;
- long-term use or side effects of medications;
- psychological stress;
- smoking, drinking alcohol;
- consequences of surgery.
Xanthoma causes
Xanthomas are not an independent disease; they are a symptom or result of an acquired or congenital disorder of fat metabolism. Large nodular xanthomas often appear with kidney disease and diabetes. Crater-shaped xanthomas often occur with alcohol abuse, as well as with inflammatory damage to the pancreas.
Tendon xanthoma develops due to blockage of the bile ducts. In addition, these formations can develop after severe operations and as a consequence of various liver diseases. They are also a symptom of diseases such as Lawrence syndrome, Teutschländer syndrome and Brooke syndrome.
Classification of pathology
Cholesterol plaques on the skin vary in appearance, location and reasons for their appearance. The main types of xanthomas are presented in the table:
| Name | Options | |||
| Color | What do they look like? | Size, cm | Location | |
| Flat | Yellow | Flat, shapeless plaques | From 0.1 to 2.5 | Palms, fingers, feet |
| Tuberose | Red-yellow, brown | Nodules, plaques | 1—5 | Elbows, buttocks, knees, fingers |
| Eruptive | Yellow, reddish | Multiple confluent nodules | 0,1—0,4 | Buttocks, shoulders, thighs |
| Tendon | Flesh, yellow | Subcutaneous tumors | 2—7 | Elbows, ankles, knees, tendons of the upper and lower extremities |
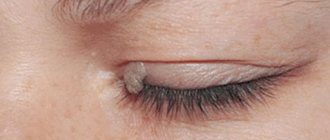
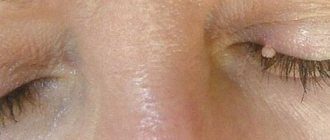
| Xanthelasma of the eyelids | Yellow | Small plaques | From 0.2 to 4 | Eye area |
| Xanthogranulomas | Minor rashes | From 0.1 to 2 | Face, head, upper body | |
Symptoms of the disease
Yellowish formations can occur in different parts of the body and are prone to proliferation.
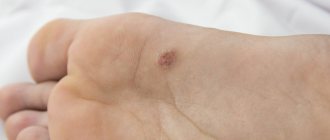
Xanthomas on the skin appear in the form of growths and plaques without pain. Main manifestations of skin defects:
- location on the face, buttocks, fingers, joints or eyelids;
- no pain;
- slow growth;
- yellow or flesh-colored, eruptive xanthomas may have a red rim around them;
- soft or dense consistency;
- thinning and dry skin at the sites of formations;
- tendency to gradually grow and merge with each other (eruptive xanthomatosis).
Conservative treatment of xanthoma: effective methods
Effective conservative techniques, as well as surgical treatment, can be used to treat xanthomas. Conservative therapy involves, first of all, normalizing the level of cholesterol, lipoproteins and triglycerides in the blood. For these purposes, the patient is prescribed a special diet, as well as lipid-lowering drugs, which include:
- statins;
- fibrates;
- bile acids;
- resins;
- probucol;
- a nicotinic acid.
After the start of drug therapy for xanthomas, their different types begin to disappear at different times: eruptive xanthomas - after a week, tuberous xanthomas - after a few months, tendinous xanthomas - within several years.
Features of the disease in a child
Plaques on the skin at an early age occur due to congenital disorders of lipid metabolism. As a child grows up, xanthoma develops under the influence of the following reasons:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- poor nutrition.
Treatment of xanthoma in childhood is as follows:
- dairy-vegetable diet;
- drug therapy;
- surgical removal.
Getting rid of unwanted manifestations is carried out using low temperatures - cryodestruction.
Xanthomas in children, after curing the underlying disease and eliminating negative factors, resolve and disappear on their own. If xanthomas remain on the face, removal is carried out using one of the following methods:
- Cryodestruction - freezing at low temperatures.
- Electrocoagulation - removal by electric current.
- Radio wave surgery is the destruction of pathological tissues by high-frequency directed waves.
Treatment (surgical and therapeutic)
The lack of spontaneous healing and the tendency towards steady growth make people want to get rid of cholesterol nodules. Since xanthomas of the eyelids are companions of various diseases, indicating a violation of lipid metabolism, the underlying pathology should be treated. Relief of the main underlying disease (fatty hepatosis, diabetes mellitus) makes it possible to stop the progression of the increase in the size and number of plaques on the eyelids for a long time.
Recommended:
- Following a diet with limited consumption of animal fats.
- Taking medications that normalize liver function.
- Reducing blood cholesterol levels.
According to indications, the doctor prescribes choleretic drugs and statins. It is impossible to cure xanthoma of the eyelids with medications. If the patient wishes, the formation is removed using a laser, electrocoagulation or surgery.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is a treatment method in which pathological tissue is destroyed using an electric current. Elimination of xanthoma on the eyelid is performed with a one-step operation. Before the procedure, they are separated with scissors, and their base is cauterized with an electrode. Local anesthesia is administered in advance. A crust forms in place of the plaques on the eyelids. It disappears 7-10 days after electrocoagulation.
Contraindications:
- Herpetic infection.
- High blood pressure.
- Epilepsy.
- State of fever.
- ARVI.
- Allergy to anesthetic drugs.
There are no scars left at the site of the defect after the procedure. The treatment method is quite popular due to its safety, ease of use and effectiveness.
Radio wave destruction
The essence of the method is to expose the affected area to high-frequency radio waves. Cells lying in the path of radio waves coming from the electrode undergo evaporation due to the heat generated. The water inside the cells seems to “boil.” Their volume increases, the shells burst, and destruction occurs.
The treatment method is non-contact and practically bloodless, and is not accompanied by mechanical destruction of tissue. The procedure lasts 10-15 minutes depending on the size of the xanthoma. Postoperative pain is minimal since the nerve endings are not affected. Healing occurs in the absence of swelling and scars. Contraindications:
- Any disease in the acute stage.
- Inflammatory processes on the skin.
- Pregnancy.
- Menstruation.
Radio wave treatment is an alternative to surgical excision, as there is no risk of bleeding or infection.
Laser treatment
One of the most modern and effective ways to eliminate eyelid xanthomas is laser treatment. Using the technique reduces the risk of scarring and the duration of the rehabilitation period. It involves the layer-by-layer action of a laser beam on the defective area within healthy tissues, followed by treatment of the wound surface with an antiseptic solution. The laser allows for high precision with minimal trauma to surrounding healthy cells.
The procedure lasts 20-30 minutes, sometimes 1 to 3 sessions are required. The recovery period is up to 7 days. To protect the eyes from the laser beam, special devices (nameplates) made of medical steel are used. After manipulation, the wound remains open or a sterile bandage is applied and does not require complex care.
Contraindications:
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Chronic diseases in the stage of decompensation.
- Acute infectious diseases.
- Increased individual skin sensitivity.
Large cholesterol plaques are removed traditionally. It is recommended to get rid of them using a surgical scalpel followed by cosmetic sutures. The method is effective, but traumatic. Elimination of the defect does not require a hospital stay; it can be treated on an outpatient basis.
In the long-term postoperative period, dense scars may appear, impeding the mobility of the eyelid and causing a cosmetic defect. To prevent the development of deformity, corticosteroid ointment is prescribed as a local treatment for three weeks.
All types of surgical interventions are a category of minimally invasive operations; they do not require much time and do not require a person to be put under general anesthesia.
Diagnostics
To determine the causes of defects, you must consult a dermatologist. Initially, a history of the disease is collected and a visual examination of the patient’s skin is performed. The following examinations are prescribed:
- Diascopy is an assessment of the nature of a neoplasm using a glass slide.
- General tests (blood, urine) to determine the condition of the urinary system and the functioning of the body.
- Biochemical blood test - study of disorders in internal organs.
- Lipidogram - detection of high cholesterol in the blood.
- Body mass index - determination of the patient’s weight.
An additional procedure in diagnosing pathology is magnetic resonance imaging.
Additionally, the following studies are carried out:
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
- Biopsy with histological examination - examination of a fragment of the affected tissue to determine the nature of the pathological process.
- Blood test for thyroid hormones. An assessment of hormonal levels and diabetic predisposition are determined.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Layer-by-layer scanning of the selected area.
- Positron emission tomography (PET). It is the identification of initial metabolic disorders in the body.
Treatment of defects
Methods of influencing cholesterol plaque on the body depend on the causes of formation and the severity of the pathological process. Therapy includes:
- changing your diet to reduce fat;
- maintaining body weight;
- performing light physical exercise.
If there is a disease that causes xanthomas, the attending physician selects drug treatment individually for each patient. The main drugs are presented in the table:
| Group of drugs | Impact | Name |
| Statins | Reduce cholesterol | "Zokor" |
| Prevents cardiovascular complications | "Rosucard" | |
| Fibrates | Increases the amount of healthy cholesterol | "Traykor" |
| Bile acid sequestrants | Stimulates the production and elimination of fats | "Questran" |
| Antioxidants | Restores and heals skin cells | "Lycopene" |
| Vitamins | Saturate the body with nutrients | "Polivit Geriatric" |
| Cholesterol absorption inhibitors | Prevents fat absorption | "Ezetrol" |
| Nicotinic acid preparations | Regulate lipid levels | "Niacin" |
| Hormonal | Normalizes the production of thyroid hormones | "Euthirox" |
Cholesterol plaque can be removed by surgical intervention, one type of which is the use of a laser.
The following types of surgery help get rid of cholesterol plaque:
- Chemotherapy is the use of trichloroacetic acid to break down abnormal cells.
- Electrocoagulation is the cauterization of defects with a directed electric current.
- Laser removal - heating and destruction of xanthomas with a laser beam.
- Cryodestruction - freezing and further cauterization of growths (not used for plaques on the face).
- Radio wave excision - heating and evaporation of tumors.
- Surgical intervention - cutting out xanthomas with a scalpel.
Prevention of xanthoma of the eyelid
After removing xanthelasma, conscious adherence to your diet will help prevent its reappearance. A dairy-vegetable diet with a sharp restriction of carbohydrates is indicated. Eating fermented milk products helps break down and remove cholesterol from the body. Fatty meats and fish are excluded, as are alcoholic drinks. It is important to monitor your weight to avoid obesity.
Usually, the recommendation is clinical observation by a therapist to exclude the early development of coronary heart disease and atherosclerosis. Significant physical activity is contraindicated.
People sometimes do not immediately pay attention to changed eyelids or believe that there is nothing wrong with it. But if you have such problems, you shouldn’t put off visiting a doctor. After all, xanthomas on the eyelids indicate possible diseases of the cardiovascular system. They warn of the threat of a heart attack or stroke. Therefore, at the first “eye” manifestations, it is necessary to begin the prevention of these diseases.