Severe itching, peeling and inflammation of infected tissues are accompanied by scalp fungus. The disease can also cause other pathological conditions that are a serious reason to visit the doctor's office. It is quite problematic to independently determine the development of a fungal infection based on the clinical picture of the disease. This requires a number of diagnostic procedures that help identify the causative agent of the disease and select the optimal drug for its treatment.
Causes of scalp fungus
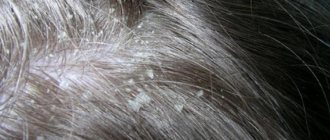
Seborrhea is a sign of scalp fungus
Any fungus, including scalp fungus, is an extremely contagious disease. The carrier is usually a sick person. Spores and the fungus itself actively multiply on the surface of the dermis, and skin flakes become sources of infection. Once on the skin of a healthy person, the fungus begins to multiply rapidly, forming more and more new foci of mycosis.
But infection does not always occur when a healthy person comes into contact with a sick person. To catch a fungus, you need to comply with several favorable factors, including the following:
- Warm.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
- High humidity.
- Microcracks and other damage to the dermis.
- Decreased immunity.
The fungus can be infected both through items of clothing, for example, when trying on a hat in a store or market, and in hairdressers and beauty salons through unsterile scissors. Infestations often occur in gyms, gyms, and other public outdoor activities.
To avoid becoming infected with scalp fungus, you must follow these rules:
This is what scalp fungus looks like in the photo
- Wear a rubber cap in public swimming pools.
- Wash a new hat with laundry soap before use.
- Do not wear a hat indoors to avoid excessive sweating.
- Avoid getting your hair dirty - wash as often as needed.
- Minimize contact with stray animals.
The presence of scalp can be determined by a number of signs and by analyzing the scales.
Prevention
To prevent infection with fungal diseases of the scalp, you need to follow preventive measures, which you should also tell children about:
- do not wear other people’s hats, use only your own combs, hair clips and hair ties;
- when visiting a hairdresser, make sure that all instruments are completely disinfected;
- try not to lean on headrests in public transport;
- do not have contact with stray animals;
- take care of strengthening the immune system: spend more time in the fresh air, eat a balanced diet, take vitamin complexes;
- timely cure all chronic diseases;
- maintain peace of mind.
If you have any incomprehensible symptoms, do not self-medicate, but immediately undergo a full examination by a qualified trichologist or dermatologist.
Symptoms of the disease
Hair is an indicator of the health of the entire body, so monitoring its condition is extremely important. Head fungus has several specific symptoms, as well as several general ones, which can be caused by various diseases. If your hair has become dull, thin, or brittle, you should pay attention to other symptoms.
- Hair has become excessively dry.
- More than 100 hairs fall out per day, some of which are due to thinning.
- Bald patches form.
- You can see black dots on the scalp - stumps from broken hairs.
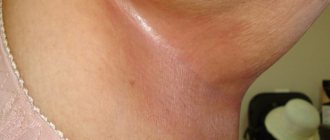
- Pink or red spots appear on the head, which may have a shine.
- Peeling of the skin.
- The appearance of yellowish scales.
- The surface of the skin may become red and slightly raised.
If you notice these symptoms, you should immediately contact a dermatologist or trichologist. This disease is not dangerous, but it has three unpleasant consequences:
- People around you are wary of people with fungus.
- The head does not look aesthetically pleasing; you have to hide bald spots under hats, which is why your head sweats under them and the fungus spreads even more actively.
- With mycosis, parasitic microorganisms release toxic substances that spread through the lymph and bloodstream to all organs and tissues, causing intoxication. It may be accompanied by general weakness, headaches, nausea, and decreased immunity.
General symptoms
Infection of the scalp with a fungus can be recognized by a number of signs characteristic of this pathological condition. Symptoms also allow a specialist to distinguish one form of the disease from another, since they all have their own clinical picture.
A fungus that affects the scalp manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- Deterioration of the general condition of the hair, its dullness and loss of shine;
- Peeling of the epidermis at the site of the lesion;
- Severe hair loss;
- The appearance of bald patches on the head;
- The formation of plaques on the skin that are colored pink;
- Covering plaques and small blisters on their surface with gray or yellow crusts;
- Hair fragility at the base;
- The appearance of purulent lesions on the head.
Any of these symptoms indicate a skin or hair problem. Therefore, when they appear, you need to immediately make an appointment with a specialist.
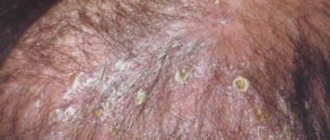
What does scalp fungus look like in the photo?
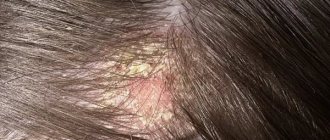
Scalp fungus, ringworm and microsporia look very similar. They look like small, most often oval, bald spots with red plaques. The hair breaks off mainly at the follicle level, leaving the lower part of the hair in the skin - they look like black dots. To the touch, the site of mycosis development may be hot and protruding on the surface.
You can notice bubbles with liquid on the surface of the epidermis, as well as yellow purulent rashes.
If the symptoms you experience are similar to the photos presented in the article, this is a reason to contact specialists who will identify the pathogen and prescribe the correct treatment.
Consequences of fungal scalp infection
Skin diseases do not immediately cause discomfort. But when they become noticeable to others, the disease is clearly already advanced. This is especially true for the head and face. And for women this is even more unpleasant, because hair is one of her main decorations.
With every day of delay, the fungus on the head complicates life more and more, significantly worsening its quality. Itching and irritation of the skin interfere with sleep, irritability appears.
But even in advanced cases, fungal infections of the scalp can be easily treated. After starting treatment, the symptoms quickly disappear, hair begins to grow, and the skin returns to normal. And here the main thing is not to interrupt the treatment of mycosis, but to carry it out in full, as prescribed by the doctor.
If you allow the fungus to develop further, ignoring the increasingly obvious manifestations of fungal infection of the scalp, then a transition to an infiltrative-suppurative form is possible, which will lead to the emergence of foci of purulent inflammation. In such a situation, antibiotics will be required.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of scalp fungus is performed either visually or using tests. For analysis, an element of the epidermis is taken, for example, a small flake of skin, which is examined under a microscope. Within a few minutes after taking a scraping, the doctor can tell what caused the disease.
Hair microscopy
Multiple foci of mycosis
The success of diagnosis is often determined by the correct collection of pathological material for microscopic examination. The outpatient clinic does not always have all the compounds and other conditions for diagnosis. Therefore, suspicious material is often sent for examination by mail. In order for the material for examination to be taken correctly, it is necessary to act very carefully, following the rules for taking biological material. Mycelium threads or fungal spores are most often found along the periphery of the mycotic focus, so scrapings are taken along the edges.
Before microscopy, you should visually determine the most likely type of fungal infection, and based on this, take material for research. In case of a purulent form, material from the lesion should not be taken for analysis, since due to the pus it is impossible to identify and identify the fungus. In addition, in order for the analysis to show a high degree of reliability, several materials should be examined - both healthy and diseased hair can grow in the area where the scalp is damaged by a fungal infection.
Hair, scales, crusts and other material are placed on a glass slide. Large elements are crushed, and the hair is cut into several parts. 3-4 hairs of suspicious structure are placed in the center under a microscope, where 1-2 drops of alkali are applied. Some material needs to be heated. The hair is initially viewed at low resolution, and then at high resolution.
If mycelium threads of different lengths and thicknesses are detected, the doctor makes a diagnosis. Fungal spores can also be identified, which lie either individually or in chains.
Diagnostics using a Wood's fluorescent lamp
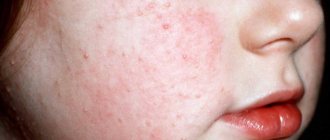
Scalp fungus in a child
This method was first proposed by Robert Wood, a physicist who noticed that some toxic substances, fungi and other microorganisms glow different colors under so-called “black light”. An ultraviolet lamp with long-wave radiation is a source of such radiation. Despite the fact that the device has undergone significant changes, the principle of its operation remains the same. A phosphor is used to obtain a special range of emission peaks.
To accurately diagnose scalp fungus, you must follow these rules:
- The surface of the skin must be clean - without applied creams, ointments and other medications.
- Do not wipe or wash your skin before using the lamp.
- Diagnostics are carried out in complete darkness.
- The patient's eyes should be carefully covered with a scarf or bandage.
- It is necessary to shine the lamp for at least 1 minute.
- The device is located at a distance of 20 cm from the skin surface being diagnosed.
If a blue or blue glow is observed, then the skin is healthy. Yellow, green, orange and brown colors indicate the presence of pathology.
Cultural examination
In patients with mycoses of the scalp, affected hair is taken for examination and removed with epilation tweezers. It is better to choose short, twisted, arched or comma-shaped hair, as well as long hair, but covered with a white or gray sheath at the base. If choosing a hair is difficult, you can use a magnifying glass or magnifying glass. Also, a cultural study is carried out on skin flakes, which are convenient to take with a needle or the sharp end of a scalpel.
Cultural research allows not only to determine the disease, but also to identify its causative agent. It consists in the following. The material is placed in a special bowl, a nutrient medium is added and kept at a certain temperature for up to 30 days. During this time, either there will be increased growth of a particular strain of fungus, or there will be no growth, in which case the culture will be considered negative.
Principles of treatment
Red spot from fungus
In order to get rid of scalp fungus, you should start treatment as early as possible. There are at least two treatment methods - traditional medicine and traditional medicine. The first option suggests the use of compresses, masks and lotions made from soda, salt, iodine, aloe juice, infusions and herbal decoctions. The second option suggests using special pharmacological preparations and medications in the form of ointments, creams, sprays and even specially designed shampoos.
Drug treatment today is considered the most effective way to get rid of unpleasant symptoms. Based on the examination, the doctor prescribes ointments, creams, tablets, shampoos, sprays and other medications to the patient. The most commonly used are nizoral cream and shampoo.
Antimycotics also have their contraindications, so before using them you should read the instructions for the treatment of mycoses of the head. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have the following conditions or diseases:
- renal failure;
- liver diseases;
- hormonal imbalance;
- cancer diseases, oncology;
- problems of the circulatory system.
Anti-fungal creams not only destroy microbial cells, but also relieve symptoms such as itching, inflammation, redness, and dry skin. The tablets should be taken according to a specific schedule prescribed by the doctor. Shampoos are used several times a week, applying them to damp hair and massaging for 7-10 minutes.
Treatment with folk remedies
Alternative medicine methods are no less effective in practice, but they must be used in conjunction with antifungal drugs internally and externally. In the absence of individual intolerance to plant components, here are reliable recipes if a pathogenic fungus suddenly appears on the head:
- If you are not allergic to the oil, you need to apply a burdock or castor oil base to the surface of your head and do not wash off the composition for 15 - 20 minutes. Rinse your hair with diluted vinegar (1:1 ratio).
- Grind the garlic and onion in equal proportions, mix the antiseptic composition, and bring until smooth. Rub into the scalp, carefully treating the areas of pathology, do not rinse for 15 - 20 minutes.
Stages of the disease: what they look like
Scalp fungus develops quite slowly. There are three stages:
- initial;
- average;
- last stage.
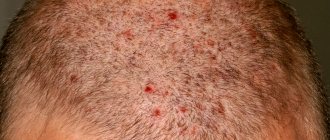
At the first stage, as a rule, the skin begins to peel, turn red, and may become painful when scratched. But in the second stage, some of the hair begins to fall out, break off, and become thinner. At the third stage, bald spots appear, inside of which are pink plaques protruding above the skin level. A yellow pustular infection may appear. At this stage, comprehensive treatment and quarantine are already indicated - the patient is extremely contagious.
Microsporia
Microsporia
Microsporia is a fungal disease that primarily affects the skin and hair, but sometimes the nail plates are also affected. The name of the disease comes from the name of its causative agent - a fungus of the genus Microsporum. In common parlance it is called “ringworm” - the peculiarities of its manifestation are such that the sick person looks as if individual sections of his hair were cut off.
A fungus from a sick person or animal enters the dermis, penetrates into it and begins to actively multiply. If the outbreak appears on the scalp, the fungal spores grow through the hair follicles. As a result, the cuticle is destroyed, spores become clogged between the hair scales, and the hair breaks off. The grub surrounds the hair on all sides, forms a kind of cover and completely fills the bulb. Such hair is a carrier of the disease.
Microsporia is considered the most common fungal infection; both adults and children suffer from it. Microsporia is highly contagious, so it is important to observe quarantine. Most often children and young women get sick, adults get sick less often. This is due to the fact that the hair of adults contains organic acids that can defeat the disease. They slow down the growth of fungi and self-healing occurs.
The main source of the disease are cats, less often dogs. To become infected, you must have direct contact with a sick animal or objects infected with fungal spores. Children are also sometimes infected in sandboxes - once in the soil, the fungus can survive for up to 3 months.
Causes of fungal infection
Fungal infections on the scalp usually occur in people with weakened immune systems. Most often it is diagnosed in children from 3 to 12 years old, as they are actively in contact with the outside world. Sick people and animals become the source of infection. Depending on the pathogen, symptoms appear after several days or months.
In adults, fungal diseases are caused by pathologies of internal organs or hormonal fluctuations. Disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system and blood diseases can provoke excessive sebum production. Changes also occur due to poor hair hygiene, lack of vitamins and nutrients.
Only a specialist can accurately determine the cause of discomfort. Attempts to cope with the problem on your own lead to the rapid spread of the disease.
Many drugs against dandruff and fungus are characterized by a huge number of side effects, which dermatologists are very familiar with. The specialist will select a remedy taking into account the symptoms, type of fungus and individual characteristics of the body.
Trichophytosis
Trichophytosis is a fungal disease that most often affects the skin and hair, and less often the nails.
Trichophytosis of the scalp
The causative agent is the fungus Trichophyton, from which the name of the disease comes. Infection occurs through direct contact with a sick person, as well as with his personal belongings. A special source of the disease are personal hygiene items, as well as hats, combs, scarves, scissors, and bedding. Rarely, transmission of the disease occurs in hairdressing salons, kindergartens, sanatoriums, boarding schools, and schools. Animals can also be carriers of the fungus - especially rodents (mice, rats) and cattle (most often calves).
Infection of a person from an animal occurs through contact with hay, dust, contaminated hair affected by the fungus, and much less often through direct contact between a person and an animal. This disease is most often diagnosed in the fall.
Favus
Favus of the scalp
This disease used to be called scab, but today its official name is favus. It is a fungal infection known since ancient times. Previously, it was a very common disease. The number of patients has decreased due to the growth of hygienic skills, the material well-being of the country's population, the elimination of the mass population of cities with rats and mice, medical examination and sanitary educational work.
The incubation period of favus lasts 2-3 weeks. The disease often progresses to a chronic stage. You can become infected through direct contact with sick people, or through contaminated items such as underwear, shoes, toys, and clothing. Children are most often infected, but it can also be detected for the first time in adults. Self-healing of this disease is not typical. The disease can be provoked by poor nutrition, lack of vitamins, weakened immunity, and poor care.
How to treat scalp fungus
There are a huge number of medications to treat scalp fungus. A particular drug is prescribed by a doctor who determines the exact dosage. The treatment algorithm is influenced by many factors, such as immunity, concomitant diseases - HIV or diabetes, age, pregnancy and more. Most often, a dermatologist or trichologist prescribes a complex treatment consisting of several drugs.
Local treatment
Topical treatment refers to the fact that the medicine is applied topically. Most often, special antimycotic creams, pastes, gels, sprays, and ointments are used. There are a huge number of them, and in each individual case a different drug is prescribed. More often than others, doctors prescribe Clotrimazole ointment or nizoral gel. These medications should be applied to the affected areas 1-3 times daily as directed by your doctor.
Local treatment also includes the use of special shampoos, which can be purchased at any pharmacy.
Complex treatment
Complex treatment consists of taking pills and local medications. Griseofulvin or nizoral tablets are most often prescribed internally.
Preparations for the treatment of scalp fungus
Nizoral is a tablet with the active substance ketoconazole - 200 mg. Ketoconazole is a synthetic imidazole dioxolane derivative that has fungicidal and mycostatic properties against dermatophytes, yeasts (Candida, Malassezia, Torulopsis, Cryptococcus), dimorphic fungi and higher fungi (eumycetes). Excipients of nizoral in tablets: corn starch 80 mg, lactose monohydrate 19 mg, polyvidone-K90 6.6 mg, microcrystalline cellulose 3 mg, colloidal silicon dioxide 0.7 mg, magnesium stearate 0.7 mg, purified water.
Griseofulvin has an active substance with the same name, as well as additional substances: potato starch, lactose (milk sugar), calcium stearate, low molecular weight polyvinylpyrrolidone (povidone). Refers to antifungal agents. Actively fights scalp fungus: Trichophyton, Microsporum, Epydermophyton Achorionum.
Traditional medicine methods
When treating scalp fungus, you should not rely on traditional medicine methods. The disease is very resistant to external factors, so it is imperative to consult a doctor, especially when it comes to children. A child should not be taken to school or kindergarten during illness; his personal hygiene items must be sterilized.
To clean the scalp, you can use folk remedies such as laundry soap, soda compresses, and hydrogen peroxide compresses for purulent lesions. It will also be useful to rinse your hair with a strong solution of chamomile, tea or coffee.
Principles of therapy
It is not easy to cure mycosis on the head. Complete relief from the disease and restoration of hair growth will occur no earlier than in 5-7 months. Therefore, you should be patient and strictly follow all the doctor’s prescriptions and recommendations.
To most effectively get rid of fungal infections and avoid relapses, an integrated approach is required, combining external medications, oral medications and traditional methods that can be successfully used at home.
Keratolytic agents
This group includes drugs whose task is to soften, dissolve and painlessly reject affected hair residues or skin areas. Before use, you need to read the explanations given in the annotation to avoid side effects. Keratolytics used for fungal diseases on the head include:
- Thermikon;
- Terbizil;
- Mycosporus;
- Biphospor.
These medications are contraindicated for use during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and in children under 6 years of age..
Antifungal drugs
The basis of treatment for all types of dermatomycosis on the head is antifungal antibiotics. They are available in several dosage forms: creams, ointments or tablets.
In the early stages of the disease, you can limit yourself only to external application of medications to the affected areas. The following ointments have worked well:
- Ketoconazole;
- Isoconazole;
- Bifonazole.
In severe cases, oral medications are used to quickly stop the spread of infection:
- Griseofulvin;
- Clotrimazole;
- Miconazole;
- Itraconazole;
- Nystatin;
- Orungal.
These medications inhibit fungal colonies of any etiology, both yeast and trichophytosis. They tend to accumulate in the skin and hair, preventing the spread of infection and providing the body with resistance to pathogenic microorganisms.
Antifungal shampoos
Until you completely get rid of the symptoms of the disease, you need to wash your hair not with ordinary, but with medicated shampoos, specially designed for use with mycotic lesions. The most popular are:
- Nizoral;
- Sebozol;
- Mycozoral;
- Dermazol.
They contain ketoconazole, which has fungicidal and antimicrobial effects. Penetrating into the structure of the fungus, this drug disrupts its functioning at the cellular level and leads to death.
Immunomodulators
People with weakened immune systems who do not have enough strength to resist infection are susceptible to dermatomycosis of various etiologies. Immunomodulator drugs help increase the body’s protective resource:
- Anaferon;
- Lymphomyosot;
- Viferon;
- Imudon;
- Remantadine.
Immunomodulators should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor, without exceeding the dosage, since each of the drugs has many contraindications and adverse reactions.
Traditional methods
In the treatment of fungus on the scalp, traditional medicine recipes play a significant role. They can cope with the symptoms of the disease on their own only at a very early stage, but in combination with pharmaceutical products they contribute to a speedy recovery .
The use of decoctions of medicinal herbs and ointments based on bee products, apple cider vinegar, and hydrogen peroxide increases the nutrition of hair follicles, helps restore hair structure, and improves its appearance.
The most popular folk remedies are:
- Grind the herb, calamus, mint and lovage, mix in equal parts and pour boiling water at the rate of 3 liters per 1 glass of raw materials. Leave in a water bath for 1 hour, then strain. Add 3 tablespoons of apple cider vinegar or juice squeezed from a lemon. Use as a hair rinse after washing your hair 2 times a week.
- Tar ointment. Mix birch tar in equal proportions with rendered pork or goose fat. Apply to skin and hair, put on a plastic cap, and then tie a woolen scarf around your head. After 2 hours, wash your hair with antifungal shampoo. Carry out the procedure once every 3 days until the fungus is completely eliminated.
- Onion mask. Pass two medium-sized onions through a meat grinder, add 2 tablespoons of honey and 10 drops of 5% iodine. Apply the mixture to the scalp and leave for 1.5 hours, then wash your hair with laundry soap and rinse with a decoction of herbs. It is recommended to do it 2 times a week.
It is important to know that not all folk remedies are compatible with taking medications, and some of them cannot be applied to the scalp if there are open wounds or abrasions. Therefore, the use of home remedies must be agreed with your doctor.
Shampoos for fungus
There are a huge variety of anti-fungal shampoos. Let's look at the best of them.
- Keto plus. It is based on two active ingredients – zinc pyrithione and ketoconazole. Both substances actively fight peeling, rash, swelling and itching of the skin. Zinc has a drying effect and normalizes the functioning of the sebaceous glands. Ketoconazole directly fights fungal infections at the cellular level - making the fungal membrane thin and permeable. This anti-fungal shampoo should be used twice a week for a month.
- Mycozoral. It also fights all the symptoms of scalp fungus and destroys the fungus. It contains Ketoconazole, which inhibits the biosynthesis of ergosterol in fungi, which leads to a change in the composition of lipid components in membranes and the death of the fungus. It is used 2 times a week until complete recovery.
- Nizoral also works by killing fungus. It is applied to damp hair, foamed and left on the head for 5-7 minutes. In advanced stages, nizoral can be applied daily.
- Sebozole helps get rid of the symptoms of fungus, and it acts very gently, so it can be prescribed to pregnant women and children from 1 year of age.
Symptoms
Symptoms directly depend on the severity of the disease. In the initial stages of the fungus, redness, itching, and dryness appear in the affected area. The skin becomes sensitive, small cracks appear.
Remember: if you do not resort to treatment in time, the fungus can lead to partial or complete baldness. It is important to promptly consult a doctor who treats the fungus.
In more severe forms of the disease, swelling of the affected area and the appearance of pustules may be observed. Then peeling appears. The painful area begins to become covered with yellow or brown crusts.
A fungal infection on the head affects not only the skin, but also the hair. They begin to fade, thin out, break, fall out.
Do I need to take antibiotics?
Brittle hair due to fungus
There is an opinion that the fungus cannot be cured without the use of antibiotics. In fact, this is not the case, but it is worth understanding why doctors sometimes prescribe a course of these drugs.
The most common complication of a fungal disease is the addition of a bacterial infection. The fungus causes damage to the dermis, local immunity decreases, itching causes scratching and injury to the skin, which becomes an excellent breeding ground for harmful bacteria. The main sign that mycosis has developed into a bacterially complicated disease is the presence of pus. In this case, the dermatologist prescribes either a local antimicrobial ointment or a broad-spectrum antibiotic taken orally.
Immunity and scalp fungus
Children most often suffer from scalp fungus, and this is due to several factors. Firstly, the structure of children's hair is soft and permeable, as a result of which fungi easily “take root” and damage many hair follicles at once. Secondly, children's hair does not contain some organic acids. As you know, an acidic environment is not suitable for the life of these parasites, so the hair of an adult person or animal is affected much less frequently.
Thirdly, children have lower immunity to all kinds of diseases, so the disease spreads very quickly. An adult infected person can be a carrier for a long time, but his disease does not manifest itself outwardly.
To speed up recovery, the doctor may prescribe immunostimulating drugs and vitamins.
Traditional methods
Home treatment is mainly local and relieves unpleasant symptoms. In the early stages of diseases, they cope with dandruff, itching, remove flaking, and restore hair.
As a complement to traditional medicine, it strengthens hair and skin defenses. Eucalyptus essential oil is a very good antimicrobial agent; you need to apply it to a comb and go through the entire length of your hair.
Photo: j.chizhe/Shutterstock.com
Burdock oil strengthens hair; it is an inexpensive and effective product. The positive effect is enhanced if mixed with castor oil. Rub into the head once a day.
New stains can be treated with table vinegar. This is an acidic, aggressive environment for fungi. Vinegar is diluted with water 1:1 to avoid burns. Use until symptoms disappear and for another week.
Reviews
- Elizaveta: “We were in the village with our children in the summer, and our daughters were constantly playing with the kittens. And after 2 weeks, hair began to fall out on the scalp, and a red spot appeared on the neck. The doctor diagnosed her with lichen. Children became infected from kittens. We applied Nizoral cream and washed our hair with the same shampoo. The children did not go to school for almost 2 months due to quarantine. The disease was cured the first time, and the hair began to grow back very quickly. I won’t let my children near stray cats anymore.”
- Marina: “My nephew suffered from ringworm. They treated me with ointments and tablets, but I don’t know which ones. I also know that we bought shampoos for scalp fungus at the pharmacy, and all family members washed their hair with this shampoo. This should protect everyone else in the household from becoming infected. By the way, no one became infected, although there are 2 more children at home. The most important thing is to notice the disease in time and prevent the patient from visiting public places. We don’t know where my nephew got infected; there are no sick children around him.”
Forms of the disease and their signs
There are several forms of scalp fungus, each with its own symptoms.
Trichophytosis
This type of fungus, trichophytosis, is very contagious.
Trichophytosis is also commonly called ringworm. The pathology is one of the most complex and severe mycoses. It is characterized by severe hair loss and the appearance of fairly large bald spots on the head.
Trichophytosis is very contagious, so you should minimize your contact with an infected person. The disease itself has several forms:
- Superficial. The first signs of the disease appear 5-7 days after infection. Small spots form on the patient's head, which are very flaky. The hairs in the affected areas quickly break off and become covered with a grayish coating. Patients experience severe itching. Due to scratching, which is difficult to resist, the skin on the head becomes red and swollen;
- Deep. The incubation period of the pathogen of this form of mycosis is limited to 2 months. At first, the disease occurs without obvious symptoms. After about 60 days, a person begins to complain of weakness and general malaise. These conditions are caused by intoxication of the body. An increase in body temperature cannot be ruled out. Red tumor-like spots appear in the infected area. They are very itchy and quickly grow over the entire surface of the scalp.
Deep trichophytosis is more dangerous to human health than superficial trichophytosis.
Microsporosis
Scalp fungus can take the form of microsporosis. Symptoms of this pathology are more often observed in children than in adults. One person can infect all family members with whom he lives in the house. Infection occurs due to the use of household items and other things.
The symptoms of this form of pathology are similar to those of other types of mycosis of the scalp. Therefore, diagnosis and treatment of the disease should be carried out with the participation of a competent specialist.
With the development of microsporosis, peeling of the affected areas of the skin occurs. In these same places, hair begins to break and fall out. On the remaining hairs you can see a gray coating.
Favus
Severe itching and flaking are accompanied by scalp fungus - favus.
As with other fungal diseases of the scalp, favus causes rashes characteristic of the pathology. In this case, they look like crusts, in the center of which hair often grows.
The crust covering the lesions is yellow in color. They grow in the absence of adequate therapy.