Causes of fungal dermatitis
Fungal dermatitis develops due to increased fungal activity on the skin. The disease mainly affects the top layer of skin. Causes of occurrence include:
- Microtraumas. This is affected by tissue damage, sudden changes in temperature, interaction of the skin with chemical products, and excessive dryness due to frequent washing.
- Increased skin moisture. This can be caused by severe sweating, which is caused by disruption of the endocrine system and excess weight. The appearance of this condition of the epidermis is facilitated by long-term wearing of clothes and shoes made of synthetic materials that do not allow air to pass through well.
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system. The most common cause is diabetes mellitus, in which the acidity of the skin changes, which leads to the proliferation of bacteria.
- Influence of chemical factors. Prolonged contact of the baby's groin area with discharge from diapers. It is the pathological process of wet loosening, impregnation and swelling of the upper layer of skin under the influence of urine and feces that leads to dermatitis.
- Decreased immunity. It can be caused by a previous infection, the use of radiation therapy, frequent stress, nervous overstrain, and intestinal dysfunction.
- Long-term use of antibacterial agents.
- Hereditary factor.
- The use of hormonal drugs for a long time, which leads to a decrease in the activity of defense mechanisms.
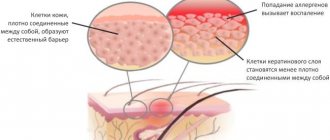
In the presence of one of these factors, fungi overcome the natural skin barrier and begin to actively multiply.
Factors contributing to infection
Anyone can get fungal dermatitis, but there are factors that increase the risk of developing the disease. These factors include:
- Age. Children are most susceptible to fungal skin diseases; skin mycoses often develop even in infants. Elderly people are also at risk. The reason is the imperfect functioning of the immune system. The child’s immune system is not yet developed enough to resist infection. In older people, the immune system often malfunctions.
- Decreased immunity. In adults, mycoses of the skin often develop against the background of other diseases that contribute to the deterioration of the immune system.
- Stress. Severe stress and prolonged nervous tension weaken the body and can cause the development of fungal dermatitis.
- Chronic infections. If there is a focus of chronic infection in the body, then the risk of developing fungal diseases increases.
Advice! The source of infection can be chronic sinusitis, pyelonephritis, or even an untreated tooth with caries.
- High humidity. People who sweat a lot are more likely to suffer from fungal infections. In infants, the development of mycosis is facilitated by non-compliance with hygiene rules and infrequent diaper changes.
Advice! So, the main reasons for the development of fungal dermatitis are decreased immunity and failure to comply with hygiene rules.
Routes of infection
Different types of fungi spread in different ways. You can become infected directly, that is, through contact with a sick person, a sick animal, or soil that has fungal pores. In addition, there is an indirect route of infection through objects that the patient had previously used.
Advice! Following basic hygiene rules will help reduce the risk of disease. You need to have individual hygiene items, not wear someone else’s shoes, not share towels, etc.
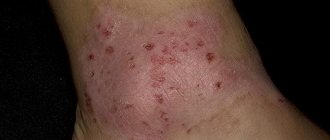
What does fungal dermatitis look like?
With fungal dermatitis, allergic rashes, papules and crusts appear on the skin. The epidermis becomes moist due to excessive sweat production. The rash is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- itching and burning,
- redness of the skin in the affected areas,
- dry or moist skin,
- the upper layer of the epidermis is covered with small pimples, sores and ulcers may appear,
- when touching painful areas, the patient experiences pain,
- if a child has rashes in the perineum, he cries during and after urination,
- If left untreated, blisters and abrasions appear.
If the disease becomes chronic, the patient's hair begins to fall out, nails become brittle and thin, and the skin becomes deformed. After recovery, scars may remain.
Diagnostics
An experienced dermatologist will draw up a preliminary conclusion based on the initial examination.
- However, to reliably confirm the diagnosis and select the appropriate treatment, biomaterial is collected by scraping or imprinting.
- Then a microbiological examination is carried out to check for fungal colonies.
- If it is necessary to determine what type of fungus it belongs to, a culture is sown to obtain a sufficient amount of material.
In case of severe fungal infections and frequent relapses, additional examinations are prescribed to identify provoking factors. It is necessary to be examined for:
- HIV infection:
- blood sugar;
- Hormone tests are required (sometimes).
Features of the disease in newborns
Most often, fungal dermatitis is observed in children of the first year of life. This is due to the fact that the child’s digestive organs are not yet formed. With insufficient care and improper nutrition of the mother or an inappropriate formula, interaction with animals, the child may develop diaper dermatitis. This causes the development of fungal infections on the baby’s mucous membranes and skin.
There are 3 stages of development of candidiasis diaper dermatitis:
- Initial – inflammatory processes occur on the skin, reminiscent of abrasions, which quickly disappear with proper care.
- Marginal dermatitis - appears due to constant friction of the skin against a diaper or diaper. A rash appears, accompanied by constant itching.
- Perianal dermatitis is characterized by rashes in the area of the anus, genitals and inguinal folds. Mostly occurs in children who are bottle-fed.
When the oral mucosa is affected (thrush), whitish rashes with a cheesy consistency appear. The child’s health deteriorates, the child sleeps and eats poorly. Typically, this form of dermatitis occurs in infants.
With complications, purulent discharge appears, body temperature rises sharply, which is accompanied by profuse rashes.
The most common infection is Candida fungi. The mucous membrane of infants has a slightly acidic environment, which is a favorable factor for the development of candidiasis.
Varieties and symptoms
Fungal dermatitis is classified depending on the source of infection and the type of pathogen. If we talk about the localization of the inflammatory focus, then mycosis is divided into:
- superficial – mycosis of the foot, fingers, head;
- deep - mycosis of the mucous membranes, esophagus, lungs, intestines, genitals, epidermis (in advanced situations - mycosis of the skeletal system and brain).
Fungal superficial dermatitis is divided depending on the type of pathogen into:
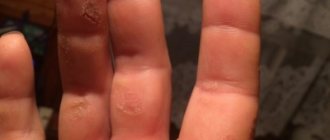
- Dermatomycoses. They are caused by mold fungi. A person scratches the skin vigorously and feels a burning sensation. There is also a change in color and small scales appear. The feet and toenails are most affected. Because of this, the lower extremities begin to smell unpleasant, and the nail plate turns yellow and may collapse.
- Candidiasis. Caused by yeast. Favorite places are the genitals, mucous membranes, nails, and skin. Externally, the fungus looks like diaper rash; a whitish coating covers it on top, which can be easily wiped off with a cotton swab. Often this type of dermatitis affects young children, overweight people and excessive sweating.
- Keratomycosis. They develop due to an imbalance of microflora. With this type, depigmentation of the skin is observed.
Deep fungal infections include:
- cryptococcosis (affects mucous membranes, central nervous system, skin, lungs);
- histoplasmosis (develops mainly in the pulmonary system);
- verrucous dermatitis (favorite places are subcutaneous tissue).
Lack of treatment can lead to the spread of infection to all systems of the body.
The symptoms of mycosis are as follows:
- skin changes color and structure;
- a rash appears (pustules, diaper rash, round red spots, weeping), small scales on the head, smooth skin;
- a lumpy ring forms around the spot protruding above the surface;
- the affected areas of the skin are very itchy, which leads to the formation of crusts;
- if a bacterial infection is attached, a purulent process is observed.
Simultaneously with these signs, there is a deterioration in general health, weakness, fatigue, loss of strength, and fever.
The symptoms of fungal dermatitis are very similar to other skin ailments, which makes it difficult to diagnose.
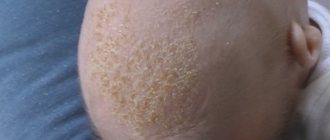
Fungal skin infections in children are most often presented in the form of diaper dermatitis, seborrheic and candidiasis. The latter is characterized by a white coating in the mouth. Seborrheic dermatitis is:
- yellowish-white scales on the face and scalp;
- burning sensation, itching, pain in the affected skin area.
Diaper dermatitis is characterized by blisters, their subsequent drying, and crusting. The skin burns, hurts and itches.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis method makes it possible to exclude diseases with similar symptoms and accurately make a diagnosis. Fungal dermatitis should be distinguished from such pathological conditions as:
- psoriasis,
- scabies,
- streptoderma,
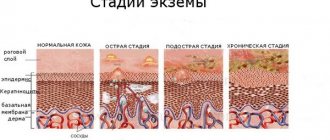
- various types of eczema (including nummular),
- seborrheic dermatitis,
- toxicoderma,
- deprive Vidal.
All these diseases are characterized by skin rashes, but they differ in color, size and course of action. It is possible to differentiate mycotic dermatitis at home, but a visit to the doctor is mandatory.
Causes
Fungi and yeast are normally part of the skin microflora. The immune system of a healthy person regulates the number of their colonies, preventing them from spreading and causing pathological processes.
Under the influence of various factors, and most often when they are combined, the skin partially ceases to cope with its protective function.
This leads to the development of diseases such as:
- fungal dermatitis;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- diaper dermatitis in infants.
Treatment of fungal dermatitis
You cannot treat fungal dermatitis on your own, since the chosen remedy without medical advice can do more harm than good. It is for this reason that the patient needs to adhere to certain rules in order to get rid of fungal pathology:
- consult a doctor promptly,
- get tested,
- get doctor's recommendations,
- observe and fulfill all instructions of the treating specialist throughout the entire course of treatment.
Basically, the course of treatment for fungal dermatitis is about 4-5 weeks, but it all depends on the type and characteristics of the course.
After the diagnosis is established, treatment for the child begins with the use of antifungal ointments. In case of purulent course of the disease, it is necessary to treat the affected areas with antibacterial drugs. For diaper dermatitis, the affected areas are treated with powders, ointments with zinc oxide, and talcum powder. For therapy to be successful and effective, you need to adhere to some rules:
- change diapers promptly,
- avoid phlegm, friction, do not put tight clothes on the child,
- Wipe sweating areas of the skin with antiseptic decoctions,
- observe the temperature regime, avoid overheating,
- maintain hygiene and ventilation.
Most fungal dermatitis is slow in development and difficult to treat. Therefore, you must follow all doctor’s prescriptions to avoid relapses.
Drug therapy
The main treatment for fungal dermatitis is 30 days. Drug therapy includes taking systemic medications and external agents. First of all, the doctor prescribes antifungal drugs.
Itching and inflammation can contribute to mental disorders and sleep disturbances. In this case, sedative sedatives are prescribed.
The use of immunomodulators is mandatory in the treatment of fungal pathology. These include vitamins C, B, E, which increase the body’s protective function. In severe stages, hormonal drugs are prescribed.
Systemic drugs
Fungal dermatitis must be treated comprehensively. This therapy includes medications:
Antimycotic
Antimycotics are the mainstay of treatment for fungal dermatitis. The patient is prescribed systemic medications:
- Diflucan,
- Nizoral,
- Lamisil,
- Fluconazole.
These medications are taken after meals 2-3 times a day for 10 days.
Antihistamines
These medications eliminate swelling, inflammation and the development of allergies. The group of such drugs includes:
- Suprastin,
- Loratadine,
- Diazolin,
- Zyrtec.
The use and dosage of these drugs is prescribed by the attending physician.
Sedatives
Often, fungal dermatitis develops against the background of chronic stress, and constant itching can lead to sleep disturbances. In such cases, the doctor prescribes sedatives. The most commonly used drugs are:
- tinctures of motherwort and peony,
- valerian extract,
- Diphenhydramine,
- Zyrtec,
- Novo-passit.
It is important to remember that such drugs should not be taken by people driving vehicles, as they reduce the reaction rate.
Glucocorticosteroids
They have an anti-inflammatory effect and quickly reduce swelling and itching. They are prescribed for severe cases of the disease in patients who require resuscitation. The group of drugs includes:
- Dexamethasone,
- Prednisolone,
- Methylprednisolone.
Thanks to the use of these drugs, you can quickly get rid of fungal dermatitis.
External means
For mild forms of the disease, external agents are used in the form of antifungal ointments and creams. These preparations are applied 2 times a day to clean and dry skin. Antifungal ointments are recommended to be applied after the rash has completely disappeared within a week.
Types of ointments:
- Clotrimazole,
- Miconazole,
- Nizoral,
- Amyclone,
- Antifungol,
- Pimafucin,
- Nystatin,
- Travogen.
Pimafucin and Nystatin can be used in children from the first days of life.
To avoid relapses and speed up the skin cleansing process, use the non-hormonal product Skin-cap. The drug is antibacterial, wound healing and anti-inflammatory.
Traditional methods
To achieve maximum treatment effect, you can use traditional methods. Some of them:
Honey and aloe. Mix the plant juice with honey in equal proportions until smooth. Let it brew in a dark place. The resulting ointment is rubbed into the affected areas 3 times a day.
Oak bark. Brew raw materials. The resulting infusion is used to wipe the affected areas of the skin several times a day.
Dandelion infusion. 1 tbsp. l. Pour two cups of boiling water over dandelion flowers. Let it brew for 2 days, then strain and take 50 ml orally 2 times a day.
A decoction of birch buds. Take 5 tbsp. l. kidneys and pour a glass of boiling water. Steam for 20 minutes in a sealed container. The finished mixture is applied in the form of compresses to the skin. This compress relieves itching, irritation and softens the skin.
Treatment methods
The usual tactics for fungal dermatoses are conservative treatment . It can be performed at home, on an outpatient basis or in a hospital setting. It all depends on the severity of the condition, the degree of development of the lesion and the pathogen detected.
The main method of therapy is medications . But traditional medicine allows concomitant treatment with folk remedies, diet and enhanced personal hygiene measures.
Medications
The appointment is symptomatic (to eliminate negative feelings and improve the quality of life), but in some cases, treatment of the underlying disease that causes the activation of the fungus and decreased immunity is optimal. Main groups:
- antimycotic (against the causative fungus);
- antihistamines - to relieve inflammatory symptoms;
- immunomodulators (when there are no contraindications) and vitamin complexes (to restore immunity);
- antibacterial agents or antibiotics for coinfection;
- restoratives, sedatives, prebiotics, hormones - if necessary, in severe cases of the disease;
- ointments, creams, sprays, powders, lotions and gels - for local treatment of the lesion.
Self-prescribed treatment and the use of drugs on the advice of strangers (even a pharmacist at a pharmacy) are unacceptable. Some species require targeted administration, but there are also broad-spectrum drugs to which fungi have not yet developed resistance. The dosage and dosage regimen are important, so treatment should be carried out by a dermatologist.
Special diet
A prerequisite for recovery. Based on the general principles of healthy eating. Alcohol, fast food, dairy and sweets, smoked and store-bought products, honey and seafood, as potential allergens, are excluded from the daily diet.
Marinades, hot sauces and spices are not allowed. Food is prepared boiled, stewed or baked. It is good to eat vegetables, water-based cereals, sea fish, vegetable oils, and dietary meat.
Folk remedies
Use without a doctor's permission is prohibited. Natural plant components are used in the form of infusions and decoctions, for baths and compresses (for external use, oral administration. The most famous are oak bark, string, dandelion, birch buds, celandine, chamomile and calendula.
Prevention
Prevention of fungal dermatitis involves the following measures:
- maintaining personal hygiene,
- refusal of self-treatment with systemic drugs, especially glucocorticosteroids and antibiotics,
- proper nutrition,
- increasing the body's protective functions,
- avoidance of stressful situations.
The child’s body does not develop immunity to skin diseases, so it is also necessary to adhere to some preventive measures:
- keep your baby's skin clean,
- For washing, use only baby soap,
- after bathing, do not rub the baby’s delicate skin, but only gently pat dry with a towel,
- carry out air baths regularly.
Another important measure to prevent mycosis is maintaining hygiene in saunas, swimming pools, gyms and showers. In public places, do not walk barefoot, do not use other people's personal items, and do not sit on uncovered benches.
Fighting fungal dermatitis is a long and difficult journey. Only strict adherence to the doctor’s prescriptions and a serious attitude towards treatment will help you forget about this disease forever.
Prevention measures and treatment prognosis
Preventive measures to prevent dermatitis of fungal origin include:
- Using antiseptics after each visit to public places.
- High quality, comfortable and true to size shoes.
- Prohibition on carrying and using personal belongings of an infected person.
- Timely treatment of chronic diseases.
- Following the rules of personal hygiene.
- Exclusion from the diet of sweet, fatty, spicy, salty foods.
- Strengthening the immune system (vitamin therapy, avoiding stress, proper nutrition).
- Timely treatment of wounds and scratches with antiseptic agents.
- Wearing replaceable shoes when in public places.
If you follow all medical recommendations, personal hygiene, and lifestyle adjustments, the likelihood of a recurrence of a fungal infection is reduced to zero.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treating diaper dermatitis with the addition of Candida fungi involve rubbing the reddened skin with medicinal plants. Traditional healers also recommend using the following recipes:
- Pamper your baby's skin by bathing in oats. Oats soothe and soften the dermis.
- You can make lotions from oats. Add 2 teaspoons of oats to 1 liter of boiling water. Stir the solution in the container and let it sit for half an hour. Before use, the broth is filtered through a bandage or a piece of gauze folded in half.
- Mix dry St. John's wort herb with a small amount of olive oil. Simmer the product in a water bath for at least 1 hour. Leave until completely cool. If the solution is not allowed to steep, the oil composition can cause severe burns on the baby’s skin. When the infusion has cooled, moisten a cotton swab and gently blot the areas that are bothered by fungal diaper dermatitis. It is advisable to carry out the manipulation a couple of times a day.
- Potatoes, raw ones, help with inflammation. One root vegetable is ground and the resulting mass is applied to the skin for 20 minutes. Afterwards, the area is washed with warm water, this will soothe the pain and itching.
- A tincture for rubbing against fungus can be made by mixing chamomile, string and celandine, 1 teaspoon each. If each medicinal plant is used to make a separate decoction, take 2 teaspoons of the herb.
Types of dermatitis
Today, there are many different types of dermatitis, but the most common are the following:
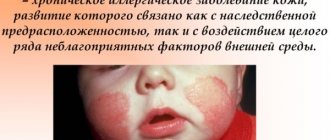
- Allergic dermatitis is a disease that occurs as a result of the penetration of allergen molecules into the body along with food and inhaled air.
- Atopic dermatitis - manifests itself in connection with a genetic predisposition.
- Allergic contact dermatitis is a pathology caused by direct contact of the skin surface with an irritant. The lesion site has clear outlines.
What is diaper dermatitis
Diaper dermatitis is popularly called diaper rash or diaper rash. Although, according to Dr. Komarovsky, it is the use of diapers that reduces the likelihood of this pathology. Diaper dermatitis is an inflammation of the baby's skin caused by environmental influences. Impacts may be:
- mechanical: friction of the body against clothing;
- physical: high air temperature, humidity under the diaper;
- chemical: effects on skin tissue of urine and feces;
- biological: fungal or bacterial process.
Diaper dermatitis is an inflammatory skin irritation that occurs in children under diapers.
Unfortunately, skin lesions of this kind in babies are not so rare.
According to statistics, 35–50% of children under the age of 1 year are susceptible to the disease. Girls are more often affected.
General principles of treatment
Complex therapy will provide quick and effective relief from fungal dermatitis. It includes the use of local drugs, systemic drugs and traditional recipes. General principles of treatment include:
- the use of antihistamines intended to reduce itching: Zyrtec, Diazolin, Suprastin;
- treatment with systemic antimycotic drugs (administered orally). Medicines of this type include Lamisil, Diflucan, Ketoconazole, Fluconazole. The course and regimen of treatment depends on the drug, but usually lasts no more than 3 weeks;
- It is recommended to use sulfur-tar ointment as an anti-inflammatory agent;
- systemic treatment must be combined with local medications. These include various ointments and creams: Bifosin, Mycozoral, Kanizol, Terbinafine. The latter drug is suitable for treating an advanced fungal infection;
- observing basic rules of personal hygiene. Use only your own clothing, hygiene items and household items. When visiting a bathhouse or other public place, you should always wear your own shoes;
- During treatment, you need to limit the consumption of salty, fried and sweet foods; give up alcohol and tobacco products; You should eat only light foods rich in beneficial microelements.
During treatment, it is recommended to combine all of the above methods and carefully monitor the general condition of your body. Strengthening your immune system through a balanced diet, daily routine, and a stable emotional state will help you increase your body's defenses. This, in turn, will protect you from new infections.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of diaper dermatitis are:
- redness;
- rashes;
- itching
Inflammation can manifest itself in varying degrees:
- mild - slight redness, rash, skin peeling on the child’s buttocks and genitals;
Diaper rash on the butt with slight redness is a mild stage of diaper dermatitis, the development of which can be stopped by using a medicinal product - moderate degree is a complication of mild due to prolonged exposure to the causes of irritation and lack of timely treatment.
Characterized by infection with candida bacteria or fungi. The skin reaction is associated with tissue damage; With moderate diaper dermatitis, widespread irritation and peeling of the skin is noticeable - severe (acute) degree is characterized by the presence of a rash, severe redness, erosions, ulcers, swelling and ulcers.
Bright red skin color is associated with the presence of long-term inflammation of a fungal nature
Why fungi don't always cause mycosis
Mycosis is a general term meaning that the skin or other organ is affected by fungi. The fungus is caused by pathogenic microorganisms that are aggressive towards the human body. Mycosis does not have favorite places, so its symptoms appear in different areas of the body.
To date, scientists have studied about 2 million fungi. Each of them has its own structure, shape and size. They live in the surrounding world and can affect the human body, in particular, the genitals, gastrointestinal tract, and oral cavity. But the priority place for these organisms is the skin.
Fungi do not always cause mycosis. Sometimes they are friendly with the bacteria in our body. This “cooperation” creates a favorable microflora and does not harm human health at all. However, most fungi are pathogenic and opportunistic. They are the cause of dangerous dermatological diseases. There are about 500 of them.
The main pathogens of fungal pathology in adults and children:
Physical contact with an infected person most often becomes a source of infection with the fungus. The conductor is damaged skin, sweat glands. Fungal dermatitis in children is most often observed in dermatological practice. Their immunity and digestive tract organs are only at the development stage, so babies are very vulnerable to infectious agents.