Vesicles, papules and pustules: what are they?
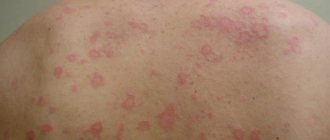
Rashes on the epidermis are characterized by the morphological elements of the rash, which include papules, vesicles, pustules, blisters, spots and tubercles. A papule is a nodular formation with a diameter of 0.1 to 2 cm. Such elements often leave behind pigmentation and peeling.
A vesicle is a small spherical vesicle that rises above the surface of the epidermis. Inside contains a clear, colorless or cloudy liquid. The element is located in the superficial layers of the skin.
Papule (left) and pustule (right)
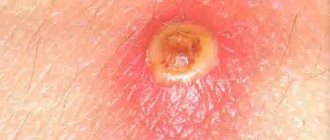
The pustule looks like a small yellow ball with a white spot on top and purulent contents. Over time, the formation bursts. Such elements hurt when touched. The skin around the pustule is hyperemic and swollen. After opening the abscess, a crust forms, which disappears after a while.
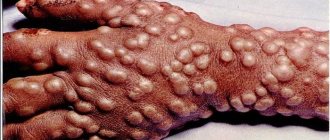
People often turn to dermatologists with the problem of acne and warts on the body. These formations look like papules. A wart is a keratinized solid formation with a diameter of 0.1 to 1 cm. It can be located in the papillary layer, on the surface of the dermis.
Warts
Warts do not form inflammation around themselves, do not hurt or cause itching. At first they do not differ from the color of the skin, but over time they can darken, become brown or black.
Acne papules, unlike warts, are characterized by an inflammatory process and are painful to the touch. There are pimples without inflammation - comedones.
Symptoms
A vesicular rash is difficult to miss. Its elements rise above the surface of the skin and are often accompanied by subjective discomfort, in particular burning or itching. The latter is very characteristic of processes of allergic origin, and can be quite pronounced.
There is often a halo of redness around the blisters, and they are located on a somewhat swollen base. Inside there is a clear or serous-hemorrhagic fluid. If a secondary infection (staphylo-streptococcal) occurs, the contents become cloudy and can become purulent. When the vesicles are opened, erosions form in their place - small defects in the epithelium with a weeping surface. They heal without scars.
Vesicles can be located anywhere on the body. For example, with atopic dermatitis or eczema, this is determined by the place of contact with the pathological factor, and with herpes simplex and herpes zoster, it is determined by the localization of the pathogen. Chicken pox is accompanied by damage to the entire skin, including the mucous membranes.
Objective symptoms will provide a lot of information necessary to understand the pathological process.
Types and classification
Papules and pustules have different locations, sizes, shapes, and colors. This allows them to be classified into certain types. Assigning a formation to a specific type allows the dermatologist to select an effective treatment regimen.
Depending on the depth of occurrence of papules, there are:
- epidermal (superficial);
- dermal (in the papillary layer);
- epidermodermal (mixed).
By size:
- lenticular (0.5x0.5 cm);
- plaques (diameter larger than a large coin)
- miliary (with a pinhead);
- numular (5-kopeck size).
The shape of papules is:
- flat;
- hemispherical;
- polygonal;
- cone-shaped (follicular).
Based on the color of the formation, they are classified into:
- pink;
- brown;
- white;
- red;
- purple.
According to the presence of an inflammatory process:
- inflamed;
- uninflamed.
Other types of papules:
- lichenoid (flaky, characteristic of lichen);
- syphilitic (round red formations on the skin and mucous membrane, capable of merging and ulcerating);
- bowenoid (red spots, related to precancerous conditions of the dermis);
- Gottron's papules (nodules located in the area of the proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints);
- fibrous (formed in single numbers, localized on the nose);
- erythematous (localized on the extensor surfaces of the joints, characteristic of vasculitis and lupus erythematosus);
- piezogenic (slightly protruding round formations the color of the epidermis, formed in the heel area).
Pustules are classified according to the following criteria:
- by localization into follicular, intradermal and subcorneal;
- by pathogenesis into autoimmune, infectious;
- by the number of cameras into single-chamber and multi-chamber.
5.Elements of acne (comedones, papules, pustules, nodes).Severity of acne
Determination of the severity of acne.
It is necessary to determine which elements of the rash are present on your skin.
Elements of acne
There are primary and secondary elements that are formed from the primary ones.
Primary elements include comedones, papules, pustules and nodes.
| Closed comedones | Open comedones |
There are two types of comedones - open and closed. Open comedones look like white dots or nodules and have a white “head”. Closed comedones look like blackheads (“blackheads”). Comedones are most often located on the forehead and chin.
| Papules | Pustules | Nodes |
Papules
These are dense red formations that give the skin a lumpy appearance, with a diameter of no more than 5 mm. They don’t go away long enough and can fester
Pustules
- dense formations that rise above the surrounding tissue and whose cavity contains pus. After opening, scars may remain. Sometimes it is quite difficult to classify a formation as a papule or pustule, so the term papulopustule is used.
Nodes
– larger (more than 5 mm) and deep dense elements, filled with contents of sebum and pus. They are often painful. Purulent decay of the nodes leads to the formation of a cyst. Scars may remain at the site of the nodes.
Secondary elements for acne
1.crust
2.scales
| So, having studied the elements of the rash, you need to count the number of different elements in good lighting; for convenience, you can use a magnifying mirror. |
1st degree – mild course
1.The number of comedones is no more than 12,
2. There are a few papulopustules (hard inflammatory formations with purulent contents), but no more than 11-12.
3. Characteristic is a wave-like course, alternating minor improvements and exacerbations (for example, in women there is a relationship with the menstrual cycle)
2 degree moderate severity
1.Number of comedones 12-30
2.Number of papulopustules 12-22
3. Detection of comedones and papulopusts on the body
4. There are nodes - no more than 4, pigment disorders
5. Characteristic is the absence of spontaneous improvements; there is a constant emergence of new elements.
3 Severe course
1. Number of comedones 30 and above
2. The number of papulopustules is more than 22
3. The number of nodes is more than 4, scars, persistent pigment disorders, keloids.
3. Symptoms such as soreness of the elements are characteristic; acne can merge and form denser lesions. Low effect when using external therapy.
“Geography” of rashes. Some experts are of the opinion that the presence of rashes, mainly located on certain areas of the face, may indirectly indicate problems in the functioning of internal organs.
Acne on the forehead.
Most often, rashes in this area signal a malfunction of the gallbladder, pancreas, or intestines. This may include cholelithiasis, intestinal dysbiosis, dyskinesia, etc.
The skin signals an excess of toxins, this may be due to a disrupted diet (predominance of fatty foods, canned food, confectionery, carbonated drinks).
Also, such rashes are characteristic of an overdose of drugs (large amounts of dietary supplements, hormonal drugs, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs)
Rash on the bridge of the nose.
Most likely, there is liver damage; these can be either mild disorders due to the consumption of heavy food and alcohol, or severe disorders associated with a violation of the cleansing function of the liver. Oriental medicine also associates such rashes with constant nervous tension and the accumulation of negative emotions.
Rash in the area under the eyes.
This area is associated with the kidneys and adrenal glands. These can be inflammatory processes, genitourinary infections, etc. This condition can also provoke mental and physical exhaustion (strict diet, sleep disturbance).
Rashes on the cheeks, chest, shoulder blades.
Rashes in this area may be associated with pulmonary function disorder, smoking. Mental energy of melancholy, hopelessness, loneliness, feeling of lack of air.
Rashes in the nasal area (tip of the nose and wings).
Disturbances in the area of blood circulation and cardiovascular system. State of fear, anxiety, passivity.
Lip area and shoulders
The gastrointestinal tract suffers, the usual symptoms are heartburn, colic, pain after eating, constipation. Often during examination, worms are found. Mental states of painful thoughts, increased vulnerability, sadness.
Chin and jaw line.
Disruptions in the hormonal sphere, this could be an increased amount of male sex hormones, ovarian dysfunction, ovarian cysts, vaginal dysbiosis.
| Now you can proceed directly to the choice of treatment. Remember, all forms of acne require external therapy. If you choose on your own, you can use one of the proposed schemes. |
Treatment.
Pharmaceutical companies offer a large number of drugs for the treatment of acne; then the most effective drugs for the treatment of acne will be discussed and schemes for their use will be presented.
Source: https://dr.kirov-cosmetic.ru/elementy-ugrevoy-sypi.html
Localization on the body
Pustules can be located on the skin of the neck, head and torso.
In men, they can be localized in the penis area. There are pustules on the lips, genitals, arms and legs, back and abdomen, heels, face, tongue. Skin papules occur as a result of hormonal imbalance and a tumor process. The rash on the genitals is called pearlescent papule. It appears in the form of small pimples that do not cause discomfort.
Localized around the head of the penis. Develops due to blockage of the sebaceous glands.
Causes
Papules and pustules occur for various reasons. Most often they are formed as a result of the active activity of microbes, viruses, and fungi.
Also, the reasons for the formation of papules and pustules are:
- disruptions in the functioning of the stomach, liver and intestines. Observed in certain pathologies of internal organs, with improper and irregular nutrition;
- hormonal imbalance. Hormone levels change during puberty, pregnancy, menopause;
- physical, emotional fatigue. Lack of wakefulness and rest, insomnia, and stressful conditions lead to weakened immunity. This reduces the body’s resistance to diseases, including those of an epidermal nature;
- blockage of the sebaceous glands. Occurs with cholesterosis, impaired metabolism, poor hygiene;
- allergies to hygiene products, food, animal hair, insect bites.
Pustule: difference from papule, photo, treatment
Papules and pustules are formations that affect the skin. Diseases and environmental factors can provoke the occurrence of elements. Having determined the nature of the formations and the reason for their appearance, it will be possible to prescribe effective treatment methods.
How to distinguish between types of acne and the causes of their appearance
Human skin protects the body from the external environment, secretes oil and sweat. The smallest holes or pores often become places where sebum, parasitic bacteria and fungi accumulate.
There are types of acne that cause a person to experience physical and aesthetic discomfort. Inflammation of the sebaceous glands, redness, swelling and suppuration of skin tissue most often occurs with acne.
Let's figure out how to treat this disease depending on the origin of the elements of the rash.
Uninflamed
A closed comedon is a small bump without a cavity. Appears under the top layer of skin at the location of the pilosebaceous follicle.
An open comedon is an accumulation of sebum and keratin scales in the pores of the skin. Black dots got their name because they turn dark when the pigment is oxidized by oxygen in the air.
Inflamed pimples
- A papule is a dense red bump measuring 5 mm or slightly larger. Often painful sensations associated with inflammation.
- A pustule is a pimple with pus inside, which is visible from the outside as a white top with a red rim.
- Dermatologists often call these types of acne papulopustules. It appears at the site of an inflamed comedon, and after squeezing and improper healing, traces (spots, scars) remain.
- Bubble (vesicle) - The rash element has a cavity filled with serous or serous-hemorrhagic fluid.
- Knot. Occurs when the affected area of skin grows and covers neighboring tissues. This is a very painful pimple that leaves a scar on the skin.
- Cyst.
The painful element of acne, difficult to treat. Color - red-brown or bluish. Inside there is a cavity with pus that has grown in volume.
Causes of various types of acne
Puberty, pregnancy, the menstrual cycle, taking steroid drugs, stress - this is just the beginning of the list of hormonal changes in the human body. In childhood, adolescence and young adulthood, these problems lead to an inflammatory skin disease - seborrheic acne.
After 1991, the classification of acne by Plevig and Kligman became widespread:
- Acne in children (neonatal and infant).
- Juvenile acne: comedonal, papulopustular, mechanical, etc.
- Acne in adults: tropical; late in women; postmenopausal; doping; fulminant with excess androgens in men.
- Contact acne: cosmetic; fatty and tarry, chloracne.
After 30 years, acne is called “late” because different types of acne appear against the background of diseases of internal organs or chromosomal disorders. Provoked and contact acne occurs due to mechanical damage, the use of medications, and the action of oils and petroleum products.
The following types of acne are not associated with acne:
Gram-negative folliculitis during treatment with antibiotics and inflammation of the hair follicles.
Pyoderma is a purulent-inflammatory manifestation of the activity of skin microflora.
Rosacea (rosacea) is a condition characterized by red pimples with white heads and rosacea (redness of the skin). The exact reasons have not been established; scientists consider the main factors to be vascular and hormonal disorders, reactions of the endocrine system to the secretions of skin mites.
A furuncle is an acute inflammation of the pilosebaceous follicle with adjacent tissue due to the activity of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. A large reddish bump with a bubble of white pus appears in the hair area, and after it heals, a scar remains.
Diseases with papules
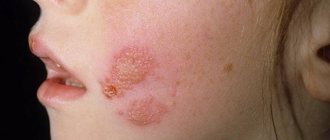
Rashes are characteristic of the following pathologies: psoriasis, measles, scabies, anthrax, syphilis, atopic dermatitis, herpes, typhus, eczema, Kaposi's sarcoma, streptococcal impetigo.
The diseases differ in the appearance of the papules, their location and other associated symptoms:
. It is an autoimmune chronic disease that affects the skin. Manifested by weakness, fatigue, depression. The main symptom is spots that rise slightly above the surface of the skin. Red psoriasis papules vary in size and shape: teardrop-shaped, coin-shaped, and dotted. Initially, the size of the formation is 3-4 mm, but as the disease progresses, the papules increase to 10 or more centimeters. Morphological elements affect the entire body and can merge;
psoriasis- eczema _ This is a neuro-allergic recurrent pathology that manifests itself in the upper layers of the dermis. This disease is characterized by a rash that causes itching and burning. At first the skin turns red. Then small pink-red papules form. As inflammation progresses, they transform into vesicles and pustules. After opening the formation, weeping eczema occurs. When the inflammatory process subsides, the skin turns pale, erosion becomes crusty;
- scabies _ The disease is contagious and is caused by parasitic scabies mites on the skin. Elements of the rash are represented by scabies. They look like dirty gray lines of a straight or curved shape. Elongated papules and pustules can form under them. The formations cause severe itching. When scratching, erosions occur;
- Kaposi's sarcoma . These are multiple malignant neoplasms on the skin. First, papules form, similar to rashes caused by lichen ruber. Places of localization are the arms, legs, and feet. Papules peel, increase in size (can reach 5 cm), and are painful. After resorption, the nodules leave pigmented impressions. Kaposi's sarcomatosis can metastasize to the lungs, bones, and liver. In this case, the person experiences a bloody cough and diarrhea, and a high fever;
- syphilis . This is a sexually transmitted systemic disease of an infectious nature that affects the mucous membranes, skin, nervous system, bones, and internal organs. Papular syphilides appear during the period of exacerbation of the disease. They can be meliar, lenticular, numular, plaque. In primary syphilis, the formation looks like a round ulcer with a smooth bottom and even edges. Erosion is painful. Small ulcers appear on the mucous membranes. Chancres up to 5 cm in diameter are observed in the abdomen, thighs, chin, forearms and hands. Secondary syphilis manifests itself as nodules, spots, papular-pustular rash, and vesicles. Formations can occur on any part of the body; they do not merge. Their color and shape vary. The skin around the syphilides does not swell or become inflamed;
- streptococcal impetigo . This is a contagious pathology of streptococcal nature. Initially, bluish-red papules appear on the skin, which can be eroded. Then they transform into vesicles with an edematous and hyperemic base. Localized in the area of the buttocks, thighs, back and abdomen;
- atopic dermatitis . This is a non-contagious, chronic inflammatory skin disease. It manifests itself as follicular papules and plaques on the extensor surface of the limbs and trunk. In adults, atopic dermatitis is characterized by pigmentation, secondary leukoderma. Whitish spots form in the cheek area.
What does a papule look like?
A skin papule is considered a fairly common form of rash. This formation is also called a nodule; it is most often localized in the upper layers of the epidermis and is essentially a dense ball (protrusion) of a small size. Papules are usually painless, but can be inflamed and cause discomfort. The color of such elements of the rash is reddish; when pressed, the color changes to a paler one. Sometimes they indicate the development of various ailments.
Papules can be:
- Superficial. Such nodules form in the uppermost layer of the dermis and are painless or cause only minor discomfort. The diameter of such pimples ranges from 1 to 5 mm. After eliminating the superficial papule, a temporary pigment mark may remain on the skin.
- Deep. Such nodes extend throughout the entire thickness of the dermis, reaching more than 5 mm in diameter. They are painful to the touch and can be colored red or even bluish-purple. Scar changes may remain in place of such papules.
- Cysts. If there has been a large inflammatory infiltrate under the skin for a long time, a scar capsule filled with purulent contents or a significant amount of sebum may form in its place. Such a formation also takes the form of a papule - a pimple, but is essentially a cyst.
Only a dermatologist can determine the type of skin rashes and select the optimal methods for correcting them.
Diagnostic methods
If papules, pustules, or vesicles appear, it is recommended to visit a dermatologist, consult with an infectious disease specialist, venereologist or allergist. At the appointment, the doctor interviews the patient, examines the skin using a dermatoscope, and prescribes a series of examinations.
The following diagnostic techniques are used:
- liver tests;
- stool analysis for worm eggs;
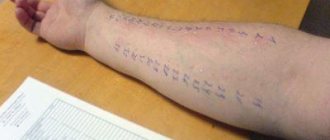
- skin allergy tests;
- bacterial sowing;
- biopsy;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- chest x-ray;
- HIV test;
- plasma analysis for hormone levels;
- skin scraping microscopy;
- urine test.
Most dermatological research techniques are painless. They allow you to identify the disease and select a treatment regimen.
How to treat?
To treat papular and pustular rashes, different methods are used: medications, folk remedies, and herbal medicine.
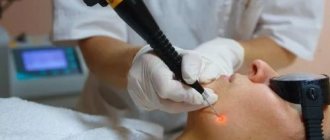
The choice depends on the type of disease diagnosed. For greater effectiveness, complex treatment is indicated. After eliminating the acute condition of a skin disease, spots and scars may remain on the body. To remove them, biorevitalization, mesotherapy, laser therapy, and grinding are used.
Drug therapy
To treat dermatological diseases, medications of different effects and release forms are used. Bacterial, viral, and fungal skin lesions are treated with antimycotics, antibiotics, and antiviral agents.
To relieve swelling and redness, anti-inflammatory and healing gels and creams are prescribed. To increase the body's defenses, doctors prescribe vitamin complexes.
For liver, intestinal and gastric disorders, medications are used aimed at restoring the functioning of the organ (hepatoprotective drugs, probiotics).
Treatment of spotty skin rash with folk remedies
Alternative medicine also provides a good healing effect. Herbal medicine is carried out and the healing properties of various products are used. Traditional healers recommend many recipes to combat spotty rashes on the skin.
The most effective folk remedies:
- one nutmeg, a little galangal and ginger, pour alcohol. Place in a warm place for a couple of days. Wipe the affected areas of the body with the prepared tincture. Additionally, it is recommended to drink a decoction of elderberry and yarrow flowers, one cup per day;
- Pour a tablespoon of oak bark into a glass of boiling water and simmer for a quarter of an hour. After cooling, strain the liquid. Wipe damaged tissues three times a day;
- lubricate the spotty rash with viburnum juice. Additionally, you should take an infusion: grind the berries and pour boiling water over a tablespoon. Leave for five hours and strain. Drink 150 ml 4 times a day;
- mix 100 g of purified sulfur and 300 g of pork fat. Apply to the affected area of skin until the spotty rash disappears.
How to distinguish papules from pustules: features of the rash
Papules and pustules are formations that affect the skin. Diseases and environmental factors can provoke the occurrence of elements. Having determined the nature of the formations and the reason for their appearance, it will be possible to prescribe effective treatment methods.
What are papule and pustule
Papule is an element of the rash, localized in the upper layers of the skin; the attributes do not have a cavity with pus or liquid. They have a mild course, may be accompanied by inflammation, and there is no discomfort when touching the affected area.
After the development of papules and pustules is completed, there are no traces or scars left on the skin. Formations can appear with syphilis, meningitis, an allergic reaction, or occur after a scabies mite bite.
A pustule is a formation with a head, a capsule filled with purulent masses that provoke inflammation, unlike papules. When an element ruptures, a substance leaks out and a dry crust appears on the skin.
If the formations are isolated in nature and are not accompanied by pathological processes, they disappear without a trace.
In case of profuse rashes with pronounced discharge, an examination is carried out for the presence of pathologies.
Difference between papules and pustules
You can recognize the formations yourself by reading the list of their external manifestations. By contacting a specialist, you will be able to correctly identify the nature of the rash and assess your health status. The doctor determines the difference between a papule and a pustule by the location of the formations, signs of development, and appearance.
Do you need advice from an experienced doctor? Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
To prescribe therapy, minimize the likelihood of worsening the situation due to self-medication, and prevent undesirable consequences, become familiar with the characteristic signs of nodules and the symptoms of pustules.
Appearance
The papule resembles a small round, oval or cone-shaped nodule with clear boundaries. The size of the defect, like pustules, varies from a few mm to 3 centimeters in diameter. The formations may rise above the skin or remain flat and inconspicuous. The attributes have a dense, elastic structure.
The color of the papules varies depending on the disease that caused it, and can range from pearly white to pronounced red. The main difference from a pustule is the absence of purulent contents. When you press on the formation, it turns pale, the manipulation does not cause pain. Sometimes swelling of the skin is observed, and when the attributes merge, plaques form.
Pustules are pimples ranging in size from a pin to a pea with a pronounced head with purulent contents, unlike papules. When the shell breaks through, the mass comes out, and the resulting wound becomes covered with a crust.
If the formation is single, there are no associated ailments, the problem area of the skin is quickly restored.
When multiple foci of inflammation are observed, the attributes can merge, leading to an extensive pathological process that provokes scarring on the skin.
Pustules and papules are often confused with vesicles - small bubbles with exudate.
Reasons for education
The appearance of pustules is promoted by unfavorable external and internal factors. They are often the result of blockage of the sebaceous ducts with the contents spreading under the skin. Papules are provoked by infectious diseases affecting the body (molluscum contagiosum, syphilis, herpes, HPV, phthiriasis).
With acne, pustules, vesicles, and comedones are found on the face.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of rashes. The development of skin nodules is influenced by unfavorable environmental factors and internal changes accompanied by infectious invasions. The main causes of damage to the epidermis by pustules and papules:
- The introduction of a bacterial pathogen through microtrauma from the use of contaminated razors, touching the skin with unwashed hands, and the use of other people's hygiene products.
- Excessive sweating, causing microscopic damage to the surface.
- Problems with metabolic processes can cause pustules. Disruption of the systems responsible for metabolism contributes to the development of papules.
- Hormonal imbalances that often affect women. The occurrence of acne is observed during menstruation, puberty in adolescents, pregnancy, when the body undergoes restructuring.
- Taking medications. Drugs that affect the functioning of the endocrine system can trigger the formation of pustules on the skin.
- Immune suppression. Diseases accompanied by a decrease in the body's defense mechanisms lead to the appearance of papules and activation of viral processes.
To determine the cause of the appearance of tumors, diagnostics are carried out at a medical center.
Localization
Papules can appear on any part of the skin, depending on the disease that caused the rash. Pustules appear on the face, trunk, and limbs.
When the body is affected by molluscum contagiosum, nodules cover the scalp, abdomen, limbs, and genitals. Pearlescent pimples are located around the head of the penis.
Formations caused by syphilis affect the torso, anogenital area, and oral cavity.
Wart formations, which are often confused with papules and pustules, appear on the backs of the palms and fingers.
Based on the severity of the damage to the epidermal layer, formations are divided into superficial and deep.
For pustules, the typical location is the skin where the hair is located. The follicles become a cavity for the accumulation of purulent mass; often abscesses form on the chin, forehead, neck, armpits, groin area, in place of the papule.
With pustular psoriasis, there are attributes on the heels and palms. Based on the depth of penetration into the skin, ulcers are divided into dermal and epidermal.
Signs
The occurrence of formations is accompanied by characteristic signs and symptoms that help to recognize the nature of the element and prescribe treatment for pustules or papules.
When nodules occur without an inflammatory process, the skin does not change its original appearance. An element of dense consistency is formed on the surface, hardly noticeable against the general background.
Before a rash occurs, the epidermis acquires a red tint, becomes swollen, hot, causing itching.
The presence of pain in the area affected by the papule depends on the disease that caused the appearance of the elements.
Pustules, like purulent formations, begin to develop with redness, thickening appears on the skin, accompanied by burning, itching, and swelling of the tissues.
When the abscess matures, a white rod appears, tension in the skin in the area of the attribute, and discomfort are felt.
Depending on the size and location, pain and symptoms of general intoxication may be present, in contrast to papular formations.
Features of the treatment of papillary and pustular rashes
The method for removing skin rashes is selected after determining the cause of the papules. Based on a diagnostic study, the dermatologist selects an individual therapeutic regimen. Drug treatment involves the use of antibacterial ointments, iodine solution, antiseptics, the method of application of which is described in the instructions on the packaging.
For severe pustular overgrowth, antibiotics are prescribed. Sometimes papules in a mild form of development act as a cosmetic defect that does not require treatment with pharmaceutical preparations.
Traditional medicine includes home recipes for treating pustules and papules on the face and body using improvised means. Decoctions of oak or calendula bark, lemon juice, chamomile tincture, vinegar, and aloe are used.
The substances will help get rid of external manifestations, but will not eliminate the cause of the rash. Before carrying out therapy, self-medication, go to the hospital.
Papules and pustules can be a sign of a disorder in the body. Having discovered elements of a rash, consult a doctor to get medical help and eliminate the formations without the risk of complications.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Source: https://VashaDerma.ru/dermatologiya/syp/papuly-i-pustuly