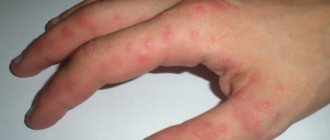
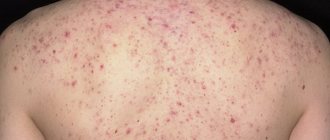
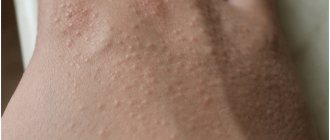
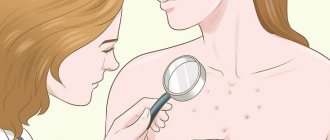
Maculopapular rash causes flat and raised skin lesions. Maculopapular rashes usually indicate an infection or an allergic reaction to something.
This type of rash is a symptom of another illness, rather than the condition itself. People with maculopapular rash should see their doctor, especially if they experience other symptoms, as this may signal a serious illness.
Keep reading to learn more about this type of rash and what treatments are available.
What does it look like?
The most distinctive feature of a maculopapular rash is the pattern of macula and papules. A macula is a small, flat, red area of discoloration, while a papule is a small, red, raised lesion.
As a result, the maculopapular rash appears as red bumps on a red background. People with darker skin may not notice the flat red patch.
Maculopapular rash can appear on any part of the body depending on the underlying cause. It may also spread to other areas. The rash usually lasts from 2 to 21 days.
Chronic maculopapular rash can last more than 8 weeks.
Zika virus rash
Scarlet fever
Zika virus rash
Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP)
measles
Maculopapular
When a maculopapular rash occurs, papules with a dense consistency appear on the surface of the skin. They are distinguished by their significant size, so the diameter exceeds 1 cm.
The rashes can have different shades. Flesh-colored, burgundy and purple growths are often observed.
The rash appears quickly.
Depending on the causes of the disease, the location of the papules may vary. A distinctive feature is a viral infection of the body. In case of an allergic reaction, bacterial or fungal infection, or immunodeficiency, the rash appears mainly on the hands and feet.
Maculopapular rash can be caused by various factors. Among them are:
- measles, rubella and other infectious diseases;
- enterovirus;
- adenovirus;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- sudden exanthema;
- allergies to food irritants, medications, streptococcus, staphylococcus toxins;
- damage by bacteria and fungus;
- helminthiasis
Most often, the rash does not cause itchy skin. But if the reason lies in an allergic reaction, this symptom often appears.
The rashes are localized in the area:
- faces;
- limbs;
- lower back.
Most often the elbows and knees are affected. The boundaries of the rash are clear, and a symmetrical pattern is visible.
In the central zone, darkening of the papule is observed. The edges of the neoplasm have a bright red tint. The rashes are large in size, up to 1 cm. When papules merge, large lesions are formed.
The appearance of such a rash can be caused by:
- lupus erythematosus;
- atopic dermatitis;
- syphilis;
- rosacea;
- allergic reaction;
- trichinosis;
- vasculitis;
- scabies;
- diathesis.
The nature of the rashes of the disease differs slightly. Therefore, this symptom can be used to make the correct diagnosis.
Other symptoms
A maculopapular rash may cause itching at the site of the bumps.
It may also cause other symptoms associated with infections and immune reactions, such as:
- difficulty breathing
- dry skin
- fever
- headache
- muscle pain
- vomit
Anyone experiencing other symptoms should see a doctor immediately because infections that cause maculopapular rash can be dangerous and can spread to other people.
Differential diagnosis
Assessing the type of rash alone may not be enough to make an accurate diagnosis. The doctor takes into account:
- The presence of a combination with rashes of other clinical manifestations, in particular, respiratory symptoms, enlarged lymph nodes, fever, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, etc.
- The nature of the rashes, the time frame for their appearance, the preferential areas of localization, the symmetry of the elements of the rash, the tendency to merge, as well as the number of rashes. An important role is played by the analysis of the patient’s subjective sensations, including discomfort, itching and burning.
- Duration and evolution of rashes. In particular, under different pathological conditions, the rash declines in different ways, and over time it usually disappears without a trace.
- Patient’s medical history, presence of contacts with other people (suspected spread of infection), etc.
Usually, only a visual examination and history is sufficient to determine the probable root cause of a maculopapular rash. In some cases, there is a need to conduct additional diagnostic studies.
Loading…
What are the reasons?
The following can cause a maculopapular rash:
Infection
Several bacterial and viral infections are known to cause maculopapular rash. People will experience other symptoms, including those listed above.
Some infections associated with maculopapular rash:
- Ebola virus
- diseases of the hands, feet and mouth
- hepatitis B
- hepatitis C
- herpes
- HIV
- measles
- scarlet fever
- Zika virus
Allergic reaction
An allergic reaction occurs when the body mistakenly identifies a substance (allergen) as a threat to the body. A maculopapular rash may be a symptom of an allergic reaction.
Other allergy symptoms include:
- labored breathing
- dizziness
- hives
- increased heart rate
- abdominal pain
- swelling
Response to treatment
Some people experience an allergic reaction to prescribed or over-the-counter (over-the-counter) medications. The rash usually occurs within 7 to 28 days after taking the drug.
Some studies reported that the antibiotic amoxicillin caused a maculopapular rash in 70% of people treated for a viral infection, especially Epstein-Barr virus.
Other drugs that have been associated with maculopapular rash include:
- allopurinol (Zyloprim)
- angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
- anticonvulsants
- beta-lactam antibiotics
- hypoglycemic drugs
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- sulfonamides
- thiazide diuretics
However, a reaction can occur in response to almost any medication.
Clinical manifestations
Rashes on the body (exanthema) can be a consequence of many skin diseases described below.
Measles
During measles, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- 1. Fever.
- 2. Intoxication.
- 3. Cough, runny nose.
- 4. Conjunctivitis.
- 5. Facial swelling.
- 6. Hyperemia of the sclera.
As the disease progresses, maculopapular rashes appear on the human body. Elements arise behind the ears, then affect the head and neck, and upper chest. On the second day, the patient’s entire torso is covered with a characteristic rash. The spots are brightly colored and tend to merge. The rash disappears first from the body, then from the face and finally from the areas behind the ears.
Molluscum contagiosum
A characteristic symptom of molluscum contagiosum is nodules on the skin. Papular rashes in children appear on the face, trunk and limbs. In adults, it affects the genitals, thighs and lower abdomen. The blisters are flesh-colored, dense, but soften after a few days. The pimple has a dimple in the center, which, when pressed, releases a curd-like mass. Both the child and the adult experience severe itching.
Smallpox
With chickenpox, maculopapular rashes occur at the initial stage of the disease. Gradually, the erythema turns into a vesicular form.
Initially, the spots appear on the scalp, then localize throughout the body, affecting the mucous membranes.
Scabies
Scabies is caused by the scabies mite, which affects a person if personal hygiene rules are not followed. The patient is bothered by severe itching, then a papular-vesicular rash appears. Visually you can notice scabies and scratches. The spots are localized between the fingers, on the palms, the extensor side of the elbows, the umbilical part of the body, buttocks, thighs, and genitals.
Scabies can be atypical. In this case, there is no papular rash, but the patient is bothered by unbearable itching.
Lichen planus
Lichen planus is a chronic pathology of toxic origin. Pink-violet spots with a flaky surface appear on the skin and mucous membranes. At an advanced stage of the disease, the elements merge with each other. Typical localization sites:
- 1. Extensor surface of the leg, forearm.
- 2. Armpits.
- 3. Groin.
After the spots disappear, persistent pigmentation remains on the affected area.
Syphilis
Syphilis is characterized by the appearance of round-shaped spots - dense, elastic, brown in color, with a flaky surface. The elements can be located on any part of the body, mainly on the genitals, soles, and face. Upon palpation, a person feels pain.
Types of rash with syphilis:
- 1. Coin-shaped.
- 2. Psoriasiform.
- 3. Seborrheic.
- 4. Condyloma lata.
HIV
In AIDS, a papular rash is an important early clinical sign. Due to immunodeficiency, symptoms are atypical of the usual picture of the disease.
Characteristic features of skin tumors associated with HIV:
- 1. Nodes up to 0.5 cm in diameter, burgundy in color, spherical in shape.
- 2. Papules are single, without a tendency to merge.
- 3. The patient feels unbearable itching.
- 4. Locations: upper body, neck, arms, legs, head.
Papular urticaria
In children, a papular rash is initially localized on the legs and back, then moves to other areas of the skin.
Characteristic symptoms:
- 1. Acanthosis or redness of the skin.
- 2. The presence of red-brown papules with a diameter of 0.5-1 cm.
- 3. The presence of severe itching.
- 4. Horny and roughening of the skin.
If the rash is caused by an infectious disease, characteristic signs appear:
- 1. Intoxication: high fever, general malaise, nausea and vomiting, migraine and others.
- 2. Cyclicity of the flow.
Infectious papular rash in children spreads hematogenously or by contact. This is due to the rapid proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms on the skin and their introduction into the blood.
complications
The underlying cause may lead to complications.
For example, complications associated with an allergic or drug reaction include the risk of anaphylaxis, a medical emergency that can be fatal.
Various viral and bacterial infections can cause complications. For example, the Zika virus can lead to:
- microcephaly (smaller head size) in infants
- Guillain-Barré syndrome, a neurological disorder
What other skin rashes are there due to coronavirus?
In addition, in a study published April 30 in the journal JAMA Dermatology, doctors identified two more types of skin rashes that can occur with coronavirus:
- Petechiae (small purple, red or brown spots due to capillary bleeding);
- Scaly rash Digitate Papulosquamous.
In addition, dermatologists from Bulgaria say that a rash on the skin (in particular on the hands) may not be associated with the coronavirus, but with increased hygiene measures and the use of antiseptics.
How is it diagnosed?
To diagnose the cause of a maculopapular rash, a doctor will ask a person about their general condition and history of medical conditions and allergies. They will ask where the rash started on the body and when it started.
The doctor will also ask:
- any medications the person is taking
- presence of other symptoms
- recent travel to areas where viral infections are common
The doctor will then perform a physical examination. They may order blood tests or urine tests to check for infection. Sometimes they may take a small sample of the rash (biopsy) to examine under a microscope.
If the rash gets worse or doesn't resolve with treatment, the doctor will likely refer the person to a dermatologist (skin doctor).
Maculopapular rash
This type of rash occurs as a result of the body’s reaction to the influence of various pathogenic factors of external or internal etiology. Maculopapular rash refers to papules of various colors appearing on the skin (ranging from burgundy and deep red to pale pink), which protrude somewhat above the entire skin surface.
- On the face, in particular on the eyelids and areas around the mouth.
- On the limbs.
- On the chest and neck.
As a rule, a maculopapular rash does not provoke severe skin irritation or obsessive itching. This condition is characterized by a positive prognosis - most often it goes away quite quickly, leaving no marks on the skin.
treatment
Treatment for maculopapular rash depends on the underlying cause:
Infection
The doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics for the bacterial infection. But antibiotics do not work for viral infections.
Sometimes the virus will have to run its course. People can manage symptoms with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers.
However, more serious viruses such as HIV will require a treatment program, which may include antiviral drugs.
Allergic reaction
The best way to treat allergies is to discover and avoid the allergen. Antihistamines, topical creams, and cold compresses may relieve symptoms in cases of allergen exposure.
Response to treatment
If a drug reaction causes a rash, you may need to stop taking the medication. Your doctor may suggest alternative treatments.
People should not stop using the medicine without talking to their doctor first.
Relief from itching
To relieve the itching caused by a maculopapular rash, your doctor may recommend over-the-counter antihistamines or hydrocortisone cream. Stronger versions of these drugs are available by prescription.
It is important to see a doctor before treating a maculopapular rash at home so they can determine the underlying cause.
Types of papules
Papular urticaria consists of neoplasms of various types. They differ in size and nature of the lesion.
- Miliary rashes are the smallest neoplasms. They are characterized by a cone-shaped shape. Most often, the rash is localized in the area of the hair follicles.
- The diameter of lenticular papules does not exceed 5 mm. A feature of this type of neoplasm is the varied form of rashes.
- Numular papules are the largest (up to 2 cm). When flat, small rashes merge, a large affected area is formed.
The rash affects different layers of the skin. Depending on this, papules have localization:
- epidermal;
- dermal;
- epidermo-dermal.
In affected areas, the skin changes color. After the rash goes away, no scars or scars remain on the surface.
A person may experience papular urticaria in different ways. The types of rash differ in:
- localization;
- symmetry and asymmetry of the pattern;
- the presence or absence of itching;
- color;
- intensity of damage;
- provoking factor.
Takeaway
The outlook for people with maculopapular rash depends on the underlying cause. Sometimes a rash is a symptom of a drug reaction or an allergic reaction. Avoiding the trigger can clear up the rash and prevent recurrence.
A maculopapular rash caused by a virus will usually clear up once the infection goes away. However, some diseases are more serious than others and can cause serious complications. Some, such as HIV, have no cure but can be treated with appropriate treatments.
People with the rash should see their doctor, who can provide a more accurate prognosis based on their diagnosis.
Trophic changes in facial tissues
Such manifestations can occur in patients who are on a ventilator and lie on their stomach for a long time.
At the same time, scientists say: it cannot be said that the above rashes appear solely due to coronavirus. This can also be an allergy to drugs used during the treatment of coronavirus.
Spanish doctors previously described the symptom as “coronavirus fingers.”
In appearance, this pathology is similar to frostbite or injury, although patients deny such damage.
Scientists from Italy and Spain also named a rash on the legs as one of the symptoms of coronavirus infection, calling it “Covid foot.”