Types of HPV testing
There are several types of tests to determine HPV.
Some require blood sampling, others require mucous secretions. None of the tests are painful. For reliable analysis, it is important for patients to comply with the following conditions:
- Do not carry out the procedure for collecting material for analysis while taking antibiotics or antiviral drugs. Treatment must be completed one week before the test
- Do not use vaginal medications for a week if material for analysis is to be taken from the vagina
- Abstain from sexual intercourse 2 days before the procedure
- 2 days before the procedure, transvaginal ultrasound or colposcopy should not be performed
- Women should take tests no earlier than 5 days after the end of menstruation, preferably in the first half of the cycle
Additional conditions for preparing for the procedure (if necessary) are communicated by the specialist who refers you for tests.
PCR analysis
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) - analysis is a study of biological fluid for the presence of human papillomavirus DNA in it. You can examine blood, epithelial scrapings or mucosal surfaces.
PCR analysis for HPV is a reliable and quick way to detect the presence of papillomavirus and determine its genotype. The polymerase chain reaction shows the presence of the virus, even if it is isolated in a single quantity.
A negative PCR test result is normal.
HPV genotyping
The analysis is carried out to find out which group of viruses the identified virus belongs to. All papillomaviruses are divided into groups according to similar genotypes - into phylogenetic groups. The most dangerous groups: A9; A6-A7; A8.
HPV genotyping is the determination of the genotype of the virus. For each type of virus, a study is carried out in groups, then an individual determination of the genotype.
Genotyping allows you to:
- track infection over time
- determine tumorigenicity
- detect multiple viruses
Note! HPV genotyping is especially important against the background of identified cervical dysplasia, since it allows us to determine the chronic type of infection
Blood test for HPV
Diagnosis by blood for HPV is carried out for preventive purposes or in case of suspected infection, when there are no visible manifestations.
HPV smear
A smear for HPV is a scraping of the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, vagina, vulva (for women) and urethral mucus (for men), taken by scraping.
To ensure reliable results, the patient must:
- Men - do not urinate two hours before the procedure
- Women should not douche on the day of the procedure.
If necessary, analyze scrapings of the epithelium of the anus, smears from the oral cavity, and throat. Analysis technique – PCR test.
Daijin test
The Daijin test is an internationally recognized type of HPV test that determines the presence of the virus and its oncogenicity. An analysis is carried out for the purpose of preventing and diagnosing uterine cancer. For analysis, a scraping is taken from the surface of the cervix.
- low-oncogenic virus - test No. 395
- highly oncogenic type of virus is determined by test No. 394
The test result is interpreted as:
- negative – result below 3 units.
- doubtful – from 3 to 5 units.
- positive – above 5 units.
Important! In young women, even with a positive high value of the Daijin test, a repeat test is prescribed after 9 months, without immediately making a final diagnosis. In older patients, a positive test No. 394 is a possible indicator of a persistent oncogenic virus, which is an indicator for further examination of the patient for oncopathology. https://www.youtube.com/embed/zcMhqo-cscc
Features of HPV analysis in women
For women, the scraping is performed by a gynecologist on a gynecological chair. The procedure is painless and no different from a regular preventive examination. A cervical smear is performed with a special brush. The most informative is scraping from the site of visible tissue damage. At the same time, a cytology analysis is taken.
Note! Women under 30 years of age are tested for HPV, but the diagnosis is not made, but observed over time. In most cases, a young body copes with infection on its own
Features of analysis in men
For men, the procedure is performed by a urologist, a scraping is taken from the urethra, from the head of the penis. In case of asymptomatic infection, HPV can be detected by a PCR test, which shows moderately and highly oncogenic papillomaviruses.
Indications for use
The need for diagnosis by PCR for HPV arises in the following cases:
- Contact with people who already have a positive PCR reaction to the human papillomavirus - unprotected sexual intercourse, independent childbirth of an infected mother (possible infection of the child), use of shared personal hygiene items (towels, washcloths), close skin contact.
- The presence of formations such as papillomas/condylomas on the genital organs—the patient is referred for PCR by a gynecologist/urologist in order to diagnose human papillomavirus infection, that is, to detect HPV and determine its oncogenicity.
- Screening studies for early detection.
Existing types of diagnostics
If signs of HPV activity are detected on the body, the doctor may refer you for an examination to identify the fact of infection with the virus and determine its specific type. In addition, it is recommended to be tested for human papillomavirus infection for women planning a pregnancy, as well as if they have problems with bearing a fetus. In this case, the diagnosis is carried out on both partners, since if one of them has an infection, it is possible with a very high degree of probability to talk about the disease in the other.
Clinical laboratories use several methods to diagnose HPV, determine its type and assess the damage caused to the body. Of these it is worth highlighting:
- colposcopic examination;
- cytological diagnostics;
- histological examination;
- PCR test.
Colposcopy method
This type of examination is prescribed to women with suspected condylomas on the cervix. During this procedure, the doctor examines the mucous membranes in the vaginal area using a special microscope. Thanks to the multiple magnification of this device, you can notice the smallest formations. During an extended study, special reagents are also used to treat mucous tissues. Thanks to them, it is possible to identify pathological changes at the cellular level.
Cytological examination
To perform this procedure to test for HPV, a smear containing epithelial cells is taken from women. The sample is examined under a microscope. In this case, the main goal is the possible identification of modified cells indicating the presence of a viral infection.
This method is quite simple and does not require large financial costs. However, its main disadvantage is the high risk of obtaining false negative results. The conclusion is issued after 5-7 days. In this case, a digital code is indicated on the form: 1 indicates the absence of affected cells, 2 indicates the presence of altered cells due to the inflammatory process, 3 indicates a questionable result, and numbers 4 and 5 indicate the presence of a viral infection.
Histological analysis
This study is prescribed as an additional method after colposcopy. It is also called a biopsy. During the procedure, a specialist takes a sample of the tissue being examined and transfers it to the laboratory for examination, where it is carefully examined under a microscope to assess the condition of the affected cells.
The use of histological examination makes it possible to determine the nature of the growth, qualifying it as a condyloma or a tumor. The test result is usually released after three days. In most cases, the patient is then sent for a PCR test to identify a specific strain of the virus.
Carrying out a PCR test
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) research is one of the most informative diagnostic methods that allows you to detect viral DNA even at very low concentrations in the blood. The accuracy of this test for detecting HPV is approximately 100%. But the correctness of the result may be affected by the correctness of the test technique, and therefore you should very carefully choose a laboratory in which all the standards of this study are strictly observed.
Thanks to PCR, it is possible to determine the exact amount of virus present in the biomaterial. If no infection is detected, it will be reported as a negative result. If HPV is present, the laboratory indicates its concentration for every 100 thousand cells. If the number of genomic equivalents (Lg):
- less than 3 - indicates an extremely low concentration of the virus in the biomaterial;
- from 3 to 5 - indicates the presence of a clinically significant amount of infection;
- more than 5 indicates a high viral load.
What is polymerase chain reaction
The fundamental point is the repeated doubling of a section of DNA with enzymes using artificial conditions. The result of the analysis is the production of the amount of DNA necessary to compare the standards with the detected fragments. The process of increasing the number of copies of DNA is called amplification. PCR is often used to detect HPV.
The method has wide application in biology and medicine. This includes diagnosing infectious and hereditary diseases, establishing paternity, introducing mutations, cloning existing genes and creating new ones. The table shows a list of diseases diagnosed using this method.
| Sphere of diseases | Disease |
| Clinic of infectious and viral diseases. | Salmonellosis, diphtheria, hepatitis B, C, G, HIV. |
| Practice of urology and gynecology. | Herpes, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, HPV. |
| Pulmonology. | Tuberculosis, pneumonia. |
| Gastroenterology. | Helicobacteriosis. |
| Hematology. | Cytomegalovirus infections, oncoviruses. |
PCR was invented by American scientist and Nobel laureate Kary Mullis in 1983.
Screening procedure
The examination of a woman begins with a routine appointment with a gynecologist. He conducts an examination, collects anamnesis, and inquires about complaints. At this stage, condylomas and papillomas can be detected.
During the examination, the doctor takes a smear for HPV PCR and a smear for cytology (Papanicolaou test, Pap test). Below we will take a closer look at the essence of these studies. If the PCR result is positive and changes in the epithelium of the cervix are detected, the woman is sent for colposcopy - an instrumental examination to assess the condition of the cervix. You can read about this study below.
Important! Since HPV is transmitted sexually, if the test result is positive, the gynecologist will advise the woman’s partner to visit a urologist or dermatovenerologist for an examination and get tested
What does a PAP test show?
The method of examining cervical smears for the presence of pathologically altered cells was invented by a Greek doctor named Papanikolaou back in the 30s of the 20th century. And today it remains the leading method of screening studies to identify precancerous conditions of cervical cancer and PVI infection. As mentioned earlier, WHO recommends that healthy women undergo it every three years.
It is believed that, on average, a persistent human papillomavirus infection caused by a highly oncogenic strain can develop into cancer in 10-15 years. Therefore, regular examinations protect the health and life of women.
Smears from the vaginal vault, surface of the cervix and cervical canal are taken with special instruments and applied to a glass slide. This material is then treated with a special compound so that the cells do not dry out or become deformed, and is stained using the Papanicolaou method. The stained glasses are sent to the laboratory for analysis.
Under a microscope, a specialist examines cells, analyzing their shape and size. Based on the results of this study, a conclusion is given that classifies the obtained material into one of five classes.
Table 1 provides a description of the cytological classes:
| Class 1 | Normal, no atypical cells. |
| Class 2 | There are cells that are changed as a result of inflammation of the mucous membrane, an inflammatory process occurs, for example, caused by an STD. After treatment, the smear usually returns to normal. |
| Class 3 | There are single atypical cells; the diagnosis needs to be clarified using other studies or the test repeated after 4 months. |
| Class 4 | Clearly altered cells were found, which gives reason to suspect a precancerous condition or cancer. |
| Class 5 | A large number of changed cells were recorded. |
In the last three cases, the woman will be sent for further in-depth examination; in class 2, the smear will need to be taken again after treatment of the cervical inflammation.
During papillomavirus infection, among the atypical cells, koilocytes (cells with an atypical light zone around the nucleus and numerous vacuoles are present in the cytoplasm) and dyskeratocytes (elements with an unusually large nucleus) are found.
Preparation and cost of the study
The Pap test gives the best results if it is performed immediately after menstruation. 48 hours before the test you need to avoid sexual intercourse. You cannot use medications for insertion into the vagina (suppositories, spermicidal contraceptives), or douching.
If there are signs of infection (itching, discharge), they must first be treated, then a test should be performed. The examination itself is completely painless and lasts only a few minutes along with the examination.
A Pap test is done free of charge (according to the compulsory medical insurance policy) in any gynecology, but if you want to get the most accurate results, you can do thin-layer liquid cytology (a more advanced method) in a private clinic. The approximate price in Moscow clinics is 1,500 rubles.
Features of the development of HPV 18 in the female body
Patients encountering the disease for the first time are wondering: HPV 18 in women: what is it, how to get rid of the scourge. The nature of the development of the pathology is unique, since it may not appear immediately, but long after the virus has settled in the body.
Usually it is in a latent state, and when the immune system is weakened, the disease progresses. During the period of active reproduction, multiple growths in the form of warts and papillomas appear on the surface of the epidermis. In medicine, a large number of varieties of the virus are isolated.
It is important to know! Papillomavirus type 18 belongs to a group with high oncogenicity, and the cervical area becomes vulnerable in women. Over time, the risk of infection decreases, so cases of infection are common among young and middle-aged people.
HPV (human papillomavirus) are viruses divided into groups and types. A total of 120 of them are known. The types in women (16-56) and in men pose a particular danger to the body, as they can cause serious illness and death. Viruses are transmitted mainly through sexual contact. A person is least likely to become infected through wounds and microcracks.
Once in the body, the papillomavirus produces special substances that facilitate penetration through the intercellular substance and further passage into the basal cells of the dermis. There he lingers. As soon as the papillomavirus DNA enters the human cell nucleus, it begins to rebuild. Before entering the nucleus, no changes harmful to the body occur.
Along with the restructuring process, the cell changes its own DNA and pathogenic growth and reproduction begins. As soon as the processes of change begin, the cells grow and multiply in disorder, which is why neoplasms (condylomas and papillomas) appear on the skin and mucous membranes of the human body, which at first they may be indistinguishable from the natural color of the skin.
Women are most susceptible to the disease; papillomavirus causes diseases associated with the reproductive system, including oncology. The risk of infection is especially high at the beginning of sexual activity. Promiscuous sexual intercourse, neglect of contraceptives - all this can lead to the development of HPV.
Much less often, infections occur through dirty medical devices or during procedures (including cosmetic ones). HPV has an incubation period - usually 15-20 years.
Papillomavirus is divided in most cases into types, including:
- Type 16 – the most dangerous for women; if it enters the body, the risk of genital cancer is the highest;
- Type 18 – also dangerous, causing the appearance of condylomas when it enters a cell;
- Types 31-33 are also oncogenic, more typical when Bowen’s disease occurs and are located in the scaly layer of the epidermis.
- Types 51-56 – medium-high risk of oncology, the disease develops only in an environment favorable for the virus (for example, with reduced immunity).
The latter types are also capable of causing mutations in the female organs, and are the cause of infertility and menstrual irregularities.
Oncogenic classification is the division of papilloma virus types into several large groups, indicating the degree of their danger. This is done in order to have a clear idea of which strains of the virus are dangerous for causing serious diseases and which are not.
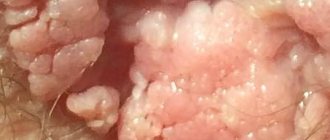
The first external signs of the disease appear in the form of one or more warts. Depending on how weakened a person’s immune system is, the number of growths can reach several hundred. This disease is called papillomatosis.
In women, the HPV virus can cause cervical cancer. According to statistics, people suffering from this type of cancer have genital condylomas in 8 out of 10 cases. It is these skin growths that are the main problem that threatens the lives of the beautiful half of humanity.
This virus leaves its “products of activity” not only on the internal genital organs. Often condylomas appear in the oral cavity, as well as on the labia and clitoris. When you notice the first symptoms, you should not delay diagnosis. The sooner an infected person consults a doctor, the greater the chance of quickly overcoming the disease.
The epithelium of the genital organs, as well as the skin of the abdomen and chest, stretches, forming microdamages. In people infected with HPV, growths appear in such places. If such a problem arises during pregnancy, it should be solved in the first two trimesters. Otherwise, there may be complications during childbirth.
HPV may be responsible for causing cancer in different parts of the human body
How to identify the HPV virus
In order to prevent fatal developments, it is necessary to be tested for HPV from time to time.
If suspicious foci are identified, no matter where - on the cervix in women or on the head of the penis in men, it is necessary to identify the type of pathogen (there may be several of them) and determine the number of virions. Quantitative analysis of HPV also helps to make a forecast for malignancy (degeneration of the formation into cancer) - the more copies of the oncogenic HPV type in the sample, the higher the risk. Quantitative analysis of HPV also helps to make a forecast for malignancy (degeneration of the formation into cancer) - the more copies of the oncogenic HPV type in the sample, the higher the risk
Quantitative analysis of HPV also helps to make a forecast for malignancy (degeneration of the formation into cancer) - the more copies of the oncogenic HPV type in the sample, the higher the risk.
In modern dermatovenerology, it may be recommended to undergo several types of analyzes and tests:
- Cytology. This microscopy of cells from a suspicious lesion can find signs of cancer. Not suitable for identifying the type of viruses or early diagnosis at the stage of precancerous phenomena.
- Colposcopy with treatment of the lesion with acetic acid and Lugol's solution. Allows you to accurately determine the boundaries of the lesion.
- PCR analysis for HPV. An excellent molecular genetic method, which we will look at a little below.
- Serological tests. They are not very informative for clinical practice; they are more often used to conduct epidemiological studies on HPV.
Throughout the civilized world, a key role in the diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection is given to molecular genetic methods - PCR, Digene test.
Polymerase chain reaction
PCR is a polymerase chain reaction - a type of analysis used to find unique DNA fragments of STD pathogens in biological material.
The method is based on the fact that, with the help of a special apparatus and a set of reagents, individual unique sections of the viral genome are detected in the diagnostic material.
Thus, using PCR analysis, it is possible to distinguish the type of HPV 16 from the type of HPV 18, and by switching the equipment to real-time mode, we obtain a quantitative count of detected pathogens.
The technique has very high sensitivity and specificity.
A positive result can be obtained even if there are only 40 virions in the sample.
Usually the diagnostic material is a smear or scraping from the lesion.
The sample for PCR for HPV is taken from the urethra in men, and from the urethra, vagina, and cervical canal in women.
In addition, sperm (seminal fluid) or the first portion of urine can serve as biological material for PCR.
For the last analysis, you need to take three glasses and make sure that a third of the urine from one urination ends up in each glass.
The contents of the first glass will be the first portion of urine.
A sample is taken from the urethra using a sterile, disposable probe.
In order to take a smear, a probe is inserted into the urethra 2-4 centimeters in men, and 0.5-1.5 centimeters in women.
PCR smear testing for HPV is prepared within 24 hours.
Preparation for HPV PCR analysis:
- 1. Do not visit the toilet for 2-3 hours before taking tests. Urine does not have an antiseptic effect, but the stream will wash away pathogens from the surface of the urethral mucosa. Because of this, a false negative test result is possible.
- 2.Do not take antibiotics a month before the test.
- 3.Do not wash your face or douche the day before the test.
- 4.PCR analysis must be taken before menstruation or three days after its end.
- 5.For three days you must avoid sexual intercourse.
- 6.Do not use vaginal suppositories, pills and contraceptives (Fraatex, Polygynax and others).
Venous blood can also be examined.
The analysis is taken on an empty stomach in the laboratory from the ulnar vein.
True, equipment and reagents for analysis are not cheap, and therefore not every laboratory, even in Moscow, can afford to conduct such tests for HPV.
hpv screening methods
Content
Content
There are, however, some negative aspects in carrying out PCR diagnostics. The main one is the possibility of obtaining a false positive result. This happens if treatment has already been carried out, the infection has been defeated, but dead cells still remain inside the tissues. Cell renewal takes time.
If the analysis is carried out earlier than 2-3 months, PCR may show a positive result, in fact mistaking already dead cells for living ones. The method does not distinguish between them; it is aimed at searching for viral DNA, which can be found even in already dead cells. All this leads to a false positive result. This situation can be avoided if you take the test within the time limit established by your doctor.
There is also a risk of a false negative result. In this case, the patient cannot influence the quality of the diagnosis in any way, since a false negative analysis is a miscalculation of the laboratory. It may occur if:
- the collected material was improperly transported and stored;
- sterility is compromised and other microorganisms get into the samples obtained;
- the reagents were unsuitable.
In order to exclude the possibility of obtaining a false negative result, it is necessary to choose a trusted laboratory with qualified personnel.
For early detection of HPV of high oncogenic risk in the body, modern highly sensitive research methods are used. Polymerase chain reaction Daigeon test oncocytology is the gold standard in the diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection. The listed studies are prescribed to patients for the following indications:
- Women over 30 years of age have a high risk of becoming infected with HPV. Unreliable sexual partners and their frequent changes are the main causes of infection. In men, papillomavirus rarely causes malignant processes of the urogenital tract. It is mainly the female half of the population that suffers. About 5,000 women are diagnosed with cervical cancer every year. It is recommended to take a Papanicolaou smear once a year in order to promptly detect degeneration of the cervical epithelium.
- The presence of warts on the body is a reason for a detailed examination of the body.
Polymerase chain reaction is a highly sensitive quantitative method for studying papillomatosis. Screening requires a scraping from the cervical canal in women and a smear from the urethra in men.
To obtain the result, specific enzymes are used that produce multiple copies of the DNA of viruses from the test tube. Laboratory assistants compare the resulting fragments with samples from their database. The patient receives a conclusion about the concentration and genotype of the virus.
The positive aspects of the method include:
- To test for the presence of HPV, a smear is suitable.
- The method detects the presence of a virus even with a small number of DNA molecules in the material being tested.
- The analysis is capable of identifying several pathogens at once.
- A person receives results 7 hours after submitting the biomaterial.
Among the negative aspects of this study are:
- The method requires highly qualified personnel and compliance with all requirements when working with the device. Minimal violations of technology can lead to false results.
- Screening does not show the type of papillomavirus. We cannot talk about the risk of developing cancer.
To get an accurate result, proper preparation for the study is necessary:
- Before the procedure, abstain from sexual intercourse for 1 week.
- Douching is not allowed.
- Diagnosis is not carried out during menstruation.
The attending physician interprets the results.
Several methods are used to treat infection. In each specific case, the doctor pays attention to the effectiveness of the therapeutic approach and its tolerability by the patient, and the frequency of relapses.
The use of medications is considered fundamental in initial therapy. It is appropriate to prescribe antiviral agents and agents that enhance the functioning of the immune system.
The following drugs have proven themselves to be quite effective:
- "Viferon" suppositories or gel.
- "Isoprinosine" in tablets, solution for injection.
- "Galavit" suppositories.
- "Panavir".
These drugs have a general strengthening effect, but they do not completely eliminate existing pathogens. The treatment regimen is determined by the doctor. In cases of high risk of malignant tumors, therapy is supplemented with cytostatic drugs.
It is important to know! Patients with such a diagnosis should be treated comprehensively. To eliminate unpleasant symptoms and live a normal life, medication alone is not enough.
When infected tissues and a severe form of the disease appear, invasive methods are used:
- Electrocoagulation.
- Cryodestruction.
- Cauterization.
- Laser excision.
- Radio wave removal.
- Surgery (to remove large growths).
What is the main method for diagnosing the corresponding neoplastic changes?
Cytological examination by Papanicolaou of a scraping (smear) from the cervical canal (the so-called PAP test, PAP).
This is one of the fundamental screening measures in gynecology.
Cytological signs of HPV infection:
- koilocytosis - the appearance of koilocyte cells characteristically changed under the influence of the virus, having one/several dark volumetric nuclei of irregular shape and with a perinuclear light zone, vacuoles;
- dyskeratosis - the appearance of small superficial keratocyte cells with dark nuclei and specific cytoplasm.
When identifying cellular changes, the following are indicated:
- colposcopy with simultaneous implementation of tests with acetic acid and Lugol's solution;
- histological examination - examination of a tissue sample under a microscope.
Signs of HPV during colposcopy are:
- uneven absorption of Lugol's solution;
- pearly surface, white staining of the epithelium in a test with acetic acid (acetowhite epithelium);
- outgrowths, etc.
PCR typing is used to determine the specific type of virus.
Importance of screening
All people need to undergo HPV screening after 25-30 years of age regularly every 5-7 years. Women, as a risk group, can do this more often. In men, infection with the papilloma virus occurs in the same way as in women; the number of infected men is no less. But due to the structural features of the urogenital canal, the disease is asymptomatic in representatives of the stronger half of humanity, so they are carriers of HPV without even knowing it.
Women are recommended to start by visiting a gynecologist. The doctor will take a swab from the cervical canal to determine HPV. Further, if the result is positive, other tests are performed. They may prescribe a colposcopy, during which the doctor examines the mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina using a colposcope - a binocular with a lighting device. Using colposcopy, you can see areas of the mucosa affected by HPV.
If you find condylomas on any part of the body, especially on the face and genital area, you should consult a doctor for advice. This applies to pregnant women, whose immunity weakens due to increased stress on the body, and the virus does not keep itself waiting. If the problem is not addressed early, complications may occur during childbirth.
It is important to conduct screening studies to identify the presence of HPV in the body and its susceptibility to malignancy. Screening is carried out before the age of 30, and if there are positive results, you will need to undergo the test again. And in the future, even after completing a course of therapy, you will need to regularly visit a doctor for diagnostics, approximately three times a year.
VKR screening – what is it and how is it carried out?
VKR screening is a mass routine diagnosis for papillomavirus for the purpose of early detection. The study on HPV HCR in women involves persons over 25 years of age (according to some data - from 21 years old / 3 years after the start of sexual activity; with strong sexual activity, a large number of partners - from 18 years old). It is recommended to undergo medical examination once every 3 years. During the event, high-risk viruses are identified that pose a danger because they can cause the development of cervical cancer. Determination of DNA concentration for HPV of high oncogenic risk is carried out using the PCR method.
Screening steps:
- Papanicolaou cytology smear (PAP test). To carry out the test, material is taken from the cervical canal (transformation zone - the place of transition of the columnar epithelium to the stratified squamous epithelium) during the examination, which is applied to glass / in a container with a special liquid (then the smear is taken with a brush). Then, after staining, the material is examined under a microscope for the presence of atypical cells; if they are present, the test is positive. The method is also called cytological.
- PCR – determination of the presence of a virus. The reaction is carried out for those who have a positive Pap test result. For research, you can use smear material, blood, and urine.
- Extended screening - determination of the type and quantity of HPV with a high risk of oncogenicity (Dajin test - number of viral bodies per 100 thousand cells: up to 3 - low concentration, 3-5 - medium, more than 5 - high).
The material is collected as for a PAP test.
Rules for preparing for the test
2 days before the event you need to abstain from sex
- 2 days before the procedure, you need to abstain from sex, taking any medications, douching, vaginal suppositories, and pills.
- A PCR smear is taken in the first phase of the cycle, after menstruation.
- During periods of exacerbation of chronic infectious pathologies, after taking antibiotics, material is not collected.
Rules for donating blood/urine:
- Blood - donated from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach; a few days before the test, allergens (chocolate, citrus fruits, etc.) are excluded from the diet.
- Urine – for HPV PCR analysis, you need to take morning urine on an empty stomach (last meal 8 hours ago) into a sterile container. The container must be delivered to the laboratory within 4 hours after collecting the material.
How to give to men and women
The method of taking a smear differs:
- How to take a test for a woman - scraping is done with a brush, in a circular forward movement from the urethra/vagina/cervical canal.
- For a man, scraping with a brush is done from the head of the penis and the urethra.
Before taking a smear, you must ensure that personal hygiene is observed.
Decoding the results
The interpretation of the results obtained depends on the method used:
- Qualitative – presence/absence – “detected”/“not detected”.
- Genotyping - detection of a specific strain - “detected” / “not detected”.
- Combined – detection of strain 16 – “not detected”, “strain 16 detected”, “HPV detected, including strain 16”.
- Quantitative:
Calculation of the number of viral bodies per 100 thousand cells of biomaterial (scraping):
- <3 – low content (low risk of cancer)
- 3-5 – average
- >5 – high (high probability of cancer)
Causes of papilloma virus infection
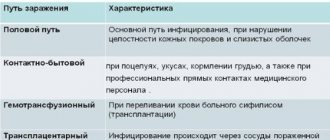
HPV is transmitted in different ways. You can become infected tactilely, directly from the patient or from his personal belongings. Viral microorganisms can remain on the surface of any objects, but without a person they die after a while. People who have visited public places are often infected with HPV. There are a large number of them. You can become infected through a handrail in public transport, swimming in a pool, taking a shower, etc. There are many ways to catch the virus. What is most interesting is that infection and progression of the virus in the body occurs asymptomatically.
External signs appear only during periods of malfunction of the immune system or when the integrity of the skin is compromised. At such moments, the papilloma virus activates its cells and new growths appear on the skin. Such growths have a benign structure, but some types of them can, when exposed to certain factors, transform into malignant tumors.
What is Digene HPV test?
Currently, a widely used method for diagnosing HPV is the Digene HPV test.
Gynecological examination technique
was developed by Digene Diagnostics (Murex) and is based on the binding of viral DNA to an RNA probe.
To conduct a Digene test
, any material obtained during a gynecological examination is used - scraping of cells of the cervical canal, vagina, urethra, vagina;
slides for cytological examination, biopsy of the cervical mucosa.
Otherwise, this diagnostic development is called the “hybrid capture method” and its essence is that it is possible to identify specific DNA fragments of the human papillomavirus by conducting differentiated diagnostics between 2 groups of virus genotypes - high and low oncogenic risk. However, there is little definition of type - Digen test
makes it possible to detect the concentration of the virus in the tissues of the cervix, which can serve as a very important prognostic sign.
Digen test
has become very widespread due to its reliability and ease of implementation. In addition, it increases the sensitivity of the Pap test (oncocytology smear) - it is not for nothing that the Digene test is recommended if the results of the Papanicolaou test give a false positive or questionable result. Currently, the combined Digene HPV test and cytological examination of the cervix is the “gold standard” for diagnosing precancerous and cancerous changes in the cervix in women over 30 years of age.
Digen test
is the only method for diagnosing high-oncogenic risk human papillomavirus that has received approval and permission for use by the US Food and Drug Administration. The methodology was also approved by the Federal Service of the Russian Federation for Surveillance in Healthcare and Social Development.
If the result is positive after the Digen test, it is recommended to repeat the test after 6-9 months. With a double positive result of the Digen test, we can talk about the persistence of the human papillomavirus - the long-term presence of the human papillomavirus in the body. This condition is dangerous due to the possibility of transition to precancerous and cancerous diseases of the cervix. Negative Digen test
in women over 30 years of age, a repeat examination is required after a year.
Etiology of the disease
Anyone can become infected with HPV using public transport, public places where the carrier was located, and cleaning was not carried out. The virus can remain on objects for some time, but without a person it soon dies.
Most people become infected with it in public places, and everything happens quickly and asymptomatically. The virus is activated only when the body is weakened or the skin is damaged. It is at this time that growths appear on the skin. They are usually benign, but certain types can become malignant (turn into cancerous tumors).
First, single papillomas appear, which, as they develop and depending on the weakening of the immune system, grow and reach several hundred. This is called papillomatosis.
The human papillomavirus is divided into several types:
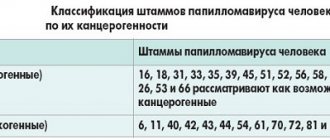
- Viruses of high oncogenicity. These include types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, 68, 73, 82. They have a high risk of carcinogenicity, causing precancerous conditions and cancer (in men it is cancer of the head of the penis and anogenital cancer, in women it is uterine cancer).
- Non-oncogenic. These are HPV types 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, which never cause cancer. They may appear as warts or disappear spontaneously.
- Viruses with low oncogenicity. These include types 6, 11, 42, 43, 44. These types rarely become malignant only under certain conditions. Such viruses are sexually transmitted and cause the growth of condylomas.
HPV treatment depending on type
HPV type (in women 16, 18 and some others can cause pathologies of the genital organs, as well as the bladder) provoke diseases depending on which group they belong to. Each type has its own treatment methods; therapy is especially necessary for the second and third groups.
HPV in these groups does not always mean oncology, but other serious health problems may arise. Even the slightest deterioration in health or the appearance of neoplasms should be a reason to visit the hospital for examination.
Diagnosis of HPV strains
HPV type in women (16 and others) and in men (it is believed that 31-33 are the most dangerous for the male body) can be diagnosed using different methods. However, diagnosis of certain strains is rarely sought. Most often, people come to the doctor to remove tumors, since they bring discomfort and aesthetic disgust.
But when growths appear, you should be examined and tested - further development of the virus seriously threatens the body. It is recommended to carry out diagnostics immediately. People with the HPV virus are referred to a urologist, gynecologist, cosmetologist and venereologist.
Manifestation of papillomavirus type 18 activity in men
The most dangerous types for both women and men are types 13 to 33, as they increase the risk of cancer. Types 51-56 are also considered dangerous, although not as aggressive, but this does not mean that if you have the papillomas virus, you don’t have to worry about your health.
There are several types of tests to detect the HPV virus. Some of them show only the presence or absence of the virus in the body, while others also reveal the amount of each type of HPV. The choice of one or another diagnostic method is determined by the gynecologist.
HPV is transmitted sexually, and even contraception such as a condom cannot protect against it. It causes two types of diseases:
- pointed papillomas on the mucous membranes;
- cervical cancer.
However, not only highly oncogenic types of papillomavirus can contribute to the development of cancerous tumors. Eight out of ten women who are sexually active can become infected, but for most, the virus will disappear on its own over the next 1.5 years without treatment. Only a small percentage of women are at risk of developing cancer within a couple of decades.
The following factors also influence the development of cervical cancer:
- the presence of the BCR virus, the dangerous type and its quantity;
- weak immunity and health in general;
- chronic inflammatory processes of the genital organs.
Thus, it is possible to identify the lesion at the initial stage of precancer, which means treatment is simpler, easier and much more effective. This will help avoid consequences and complications. If no suspicious formations or lesions are found, then treatment will not be required. Periodic observation is possible. After some time, the body itself will destroy the virus.
Preparing for the tests is simple and does not cause any particular difficulties.
- 48 hours before taking a smear, you must exclude: sexual contact; the use of contraceptive creams, suppositories or other local contraceptives; use of tampons; vaginal douching, bathing.
- It is better to take smears no earlier than a month after a course of oral antibiotics, as well as 2 weeks after using local antibacterial drugs (for example, vaginal suppositories).
- On the day of the test, it is better not to use intimate hygiene products; it will be enough to wash with plain water.
- A smear is also not taken during menstruation or in the presence of inflammation, as well as the first two to three days after the end of menstruation.
- A distorted result can be obtained if you take a smear immediately after a vaginal examination, colposcopy, or ultrasound examination.