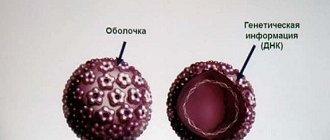
According to official statistics, from 80 to 90% people are exposed to the human papillomavirus throughout their lives. It usually manifests itself in the form of neoplasms located on the skin or mucous membranes of the patient. Most types of the virus are harmless, but among them there are those that have pronounced carcinogenic properties. Therefore, patients who have learned about their diagnosis need to be diagnosed with the type of HPV, for which different types of testing are offered.
HPV symptoms
The content of the article
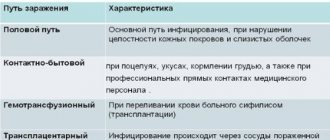
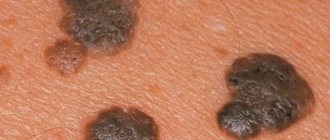
HPV infection can occur in different ways. Very often these are accidental HPV infections that either show no symptoms or produce temporary symptoms that are not very bothersome and harmless, such as warts on the skin.
Warts on the skin
If infection with the human papillomavirus HPV is not overcome spontaneously by the body within several months (up to two years), then it is a chronic infection. Chronic infections can lead to serious consequences, including the development of cancer of the penis (in men), cervical cancer (in women), or head and throat cancer (regardless of gender).
What do the results mean?
Briefly, but we will talk about each below.
False positive
A positive test result for HPV infection does not always mean the presence of the disease. There are also false positive results that need to be double-checked.
Referential meaning
The reference results of the analysis cannot be considered as the only correct ones. These indicators imply the overall value obtained by the laboratory during the study of a specific sample of the population.
For example:
- pregnant women;
- young people aged 20-35 years;
- nulliparous girls, etc.
The results of analyzes of these categories of citizens are necessary in order to obtain the average total indicator of the relative norm.
Thus, a quantitative analysis for HPV is performed. An average value of 3–5 Lg implies questionable results. They were collected based on an assessment of a specific sample of HPV virus carriers.
REFERENCE: Therefore, the concepts of normal are vague, because they may differ depending on age, concomitant diseases and characteristics of the body.
Most often, it is necessary to give importance only to the qualitative result of the study, which shows the presence of the virus. If a non-oncogenic HPV type is detected, its concentration should be assumed to be insignificant.
If the study is positive?
If the HPV test is positive, it means the virus is present in the body. Don't worry.
REFERENCE: According to statistics, 7 out of 10 people are carriers of the papilloma virus.
Many people are not even aware of their illness and live happily for many years. Symptoms of the pathology become active only during a period of weakening of the immune system.
Depending on the general clinical picture of the disease and the type of pathogen identified, the doctor prescribes treatment. Most often it includes:
- antiviral therapy;
- methods of tumor destruction;
- therapy to strengthen the immune system.
At 56, 16, 31, 18 and other cancer-dangerous strains
If strains of infection with an increased oncogenic risk are detected, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment. Therapy should be aimed at restoring immunity and eliminating formations.
Important!
Cancer-dangerous strains of the virus are the most destructive to women's health. They can cause the development of malignant neoplasms in the cervix.
Therefore, it is imperative to undergo additional diagnostic testing for the presence of dysplasia or erosion. To identify malignant changes in cells, a histological examination of the tissue should be performed.
For benign strains
Non-oncogenic types of HPV virus do not lead to cell mutation. They can only pose a threat if the papillomas are damaged or scratched by clothing items.
An infection can get into the wound, which will cause a secondary inflammatory process. Damaged neoplasm cells will begin to rapidly spread to healthy “neighbors.”
Benign strains of HPV can manifest as:
- warts of various shapes and types;
- condylomas;
- “Butcher’s warts” are red growths that look like open wounds.
It happens that the test for HPV is positive, but there are no clinical manifestations of the virus (warts, condylomas, etc.). This may indicate that the person is only a carrier of the infection.
If papillomavirus DNA is not detected
If the results of the analysis showed that no human papillomavirus DNA was detected, it means that there is no infection in the patient’s body.
Important!
But a negative result does not always indicate the absence of the virus.
If there is a small concentration of infection in the body, then the human immune system is able to independently suppress its activity.
But with a weakened immune system, the virus can begin to “act”. Therefore, you should not neglect repeated examinations. Often they are the ones who detect the presence of the disease.
HPV infection, how to protect yourself?
HPV infection occurs through direct contact, mainly through any type of sexual contact. Most people become infected with HPV soon after becoming sexually active. Thus, the main method of preventing HPV infection is to avoid risky sexual behavior, especially with multiple partners.
Using condoms reduces the risk of contracting the virus. It is equally important to wash your hands before and after using the toilet. This reduces the risk of transmitting HPV from a hand that might touch an infected person or contaminated objects in the intimate area. In addition, remember that you cannot use the same items (towels, sponges) for intimate hygiene.
Using condoms reduces the risk of contracting the HPV virus
Prevention of the virus is also important, namely testing for the presence of human papillomavirus in the body.
Infection with HPV belonging to the group of high- or low-oncogenic HPV is an indication for further, regularly repeated preventive examinations. The average time from HPV infection to the development of cervical cancer is approximately 13 years, so early changes can be recognized during this time, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
There are laboratory methods that can confirm that the cancer process has already begun, even if there are no obvious symptoms yet.
How to prepare
Preparation for women involves advance refusal of:
- sexual intercourse (at least 2 days);
- vaginal suppositories, tampons;
- intimate hygiene products with bactericidal properties;
- douching;
- colposcopy;
- vaginal ultrasound.
The study is recommended to be carried out no earlier than 5 days after the end of menstruation and no later than 5 days before their start, that is, approximately in the middle of the cycle. Before taking the test, it is necessary to replace washing in the bathroom with taking a shower. If the patient has inflammatory processes, diagnosis is carried out only after treatment. During pregnancy, diagnostics are possible. The procedure is safe for both the fetus and the expectant mother.
A man should also refuse sexual contact 1-2 days before taking the test . Before collecting the biomaterial, a man should not urinate for about 2 hours , since the analysis is taken directly from the urethra. And on the eve of the study, you should also avoid taking a bath and using products with antiseptic properties.
The exception for anyone being tested is the use of topical antibacterial agents. After taking a course of antibiotics, the patient needs a month to recover. Only after this will it be possible to conduct a test that adequately assesses the presence of papillomavirus. On the day of the examination, the patient should not wash himself before the procedure.
Compliance with these rules will ensure reliable testing results and eliminate possible errors in the analyzes.
HPV treatment
There is no universal effective method for treating infections caused by all types of HPV (human papillomavirus). Treatment is usually immunomodulatory and consists of supporting the body in a way that increases its resistance and helps it cope with the virus.
Some types of human papillomavirus, such as those that cause common skin warts, are susceptible to the use of certain dermatological medications. In other cases, it is very difficult or even impossible to completely get rid of the virus from the body. Disease caused by viruses is treated in the hope that the number of viruses in the body will significantly decrease after the outbreak is eliminated.
For neoplastic diseases, surgical treatment is combined with radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy
Types of tests
Today, there are several types of testing designed to identify the virus and identify strains. Among these are:
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It is a test that helps detect the presence of infection and monitor viral concentrations.
- Digen test. It operates using the hybrid capture method. Based on the differentiation of papillomavirus according to the risk of developing oncology. Rarely used as a single test, it is usually used in conjunction with other research methods.
- PAP test. A Papanicolaou test is similar to a classic cytological examination. It is aimed at tracking atypical cells in the epithelium, which can be used to determine the presence of malignant processes in the body.
To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out the procedure for collecting biological material from the patient in accordance with the standards.
Otherwise, the analysis may be false negative (which is quite common) or false positive (which is less common).
HPV in men
HPV causes many diseases. Malignant neoplasms of the head and neck are among the most dangerous in men. Most male infections are asymptomatic until the disease progresses.
Infections associated with HPV variants that cause:
- Warts in the respiratory tract and cancer of the mouth, salivary glands, conjunctiva, larynx, esophagus and anal cancer.
- In the genital area, condylomas acuminata, flat condylomas, giant condylomas, and penile cancer may appear.
Men at risk of contracting HPV have the following characteristics:
- many sexual partners;
- decreased immunity;
- smoking;
- lesions in the genital area or around the anus;
- chronic inflammation of the urethra and glans penis;
- other symptoms of HPV infection. HPV in women
HPV is most often referred to as cervical cancer. Indeed, long-term follow-up shows that almost 100% of diagnosed cases of this cancer are associated with infection with highly oncogenic variants of the HPV virus. HPV also causes vulvovaginal cancer in women. Regardless, women are also at risk for all other diseases caused by the HPV family of viruses.
Cervical cancer
Risk factors for HPV infection in women:
- onset of sexual activity at a young age;
- multiple sexual partners;
- decreased immunity;
- smoking;
- other sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea, chlamydia and herpes simplex;
- number of children born and young age with first child;
- chronic infections or skin lesions of intimate organs.
Recommendations
Global recommendations on HPV vaccinations differ. According to American practice, the optimal time for vaccination is 11-12 years, that is, before the onset of sexual activity. Moreover, it is recommended to vaccinate both boys and girls.
Girls will be vaccinated against infection with a dangerous type of HPV. Vaccinated boys, firstly, will receive protection from certain types of cancer, and, secondly, will not be able to become carriers of the virus and infect their partners. This will help contribute to herd immunity.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that only girls aged 9-14 years be vaccinated. However, this recommendation is likely due to economic rather than epidemiological reasons.
Life in the hospital. Helping people.
It has long been believed that HPV vaccination is justified before the age of 27 years. However, evidence has since emerged that HPV vaccination is effective and safe for women aged 25-45 years.
Even if a woman already has the HPV virus, it still makes sense to get vaccinated. Vaccination will protect against other types of HPV, but will not accelerate or complicate the disease that already exists.
HPV vaccine
There is no vaccine to protect against all types of HPV. However, there are vaccines that are effective in preventing infections with high-oncogenic and low-oncogenic variants.
The factor that stimulates the body to produce antibodies against HPV are not live or inactivated viruses, but elements of the viral “shell” obtained by gene recombination that do not contain its DNA code, so it should be emphasized that the vaccine cannot cause the disease.
It is especially recommended to vaccinate girls and young women who have not yet become sexually active. However, it is also beneficial to vaccinate women at a later stage.
HPV vaccine
Vaccination of men is not of great importance, but it is also desirable because it breaks the chain of transmission of infection.
DNA test for HPV
HPV can be divided into two types:
- low-risk groups (HPV) 6, 11;
- and highly carcinogenic (high risk): HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58 and 59.
Types 16 and 18, as well as 31, 33, 45, are responsible for the development of cervical cancer. Type 16 causes more than half of squamous cell carcinomas. Genetic tests that detect HPV infection help prevent and treat infections.
A positive test result indicates the presence of the virus. The test result also includes information about the type of virus detected. A negative result means that none of the HPV types tested were detected.
HPV research
In the case of a female test, medical staff take a smear from the cervix during a routine gynecological visit. The smear is sent to the laboratory. The study of human papillomaviruses in women covers the widest range of the 28 HPV types tested (6, 11, 16, 18, 26, 31, 33, 35, 39, 40, 42, 43, 44, 45, 51, 52, 53. 54, 56, 58, 59, 61, 66, 68, 69, 70, 73, 82).
Cervical smear
In the case of a male patient test, genetic testing material is taken from the urethra. The study of human papillomavirus in men includes 28 types of HPV (6, 11, 16, 18, 26, 31, 33, 35, 39, 40, 42, 43, 44, 45, 51, 52, 53, 54, 56, 58 , 59, 61, 66, 68, 69, 70, 73, 82).
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method
The HPV PCR method makes it possible to detect several types of the virus in one procedure.
PCR diagnostics is a test that determines the DNA of sexually transmitted diseases in biological media. Material for screening in women is taken from the cervical canal, vagina or urethra, in men - from the urethra. In addition, the analysis can be carried out on the basis of semen or the first portion of morning urine. The advantages of this method of diagnosing HPV:
- fairly high reliability of the results;
- a variety of biological material can be used for diagnosis;
- quick receipt of examination results;
- the ability to detect several HPV genotypes from one material;
- availability.
hpv for men
Oral lesions such as papillomas, condylomata acuminata, focal epithelial hyperplasia, or common warts may be associated with the presence of HPV in the oral cavity. If suspected, an HPV test or oral test should be performed. Undiagnosed and untreated, the virus can cause cancer of the mouth and throat.
The genetic test covers both low- and high-risk viruses - a total of 28 types of HPV (6, 11, 16, 18, 26, 31, 33, 35, 39, 40, 42, 43, 44, 45, 51, 52, 53 , 54, 56, 58, 59, 61, 66, 68, 69, 70, 73, 82). If the result is positive, the patient will require long-term observation and treatment.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter