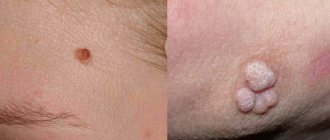
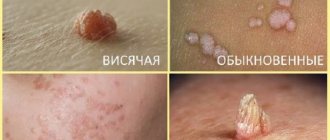
Anogenital, or genital, neoplasms differ from other types of warts in their appearance, symptoms and location. Growths appear in men and women for different reasons. Some types of them can provoke a malignant tumor. Therefore, if a wart appears in intimate places, it is recommended to consult a venereologist.
Factors in the appearance of benign neoplasms
Growths on the reproductive organs appear due to the human papillomavirus - HPV. The disease is characterized by a long incubation period, and warts appear when a person's immune system is weakened. Papillomatosis should be treated in combination with enhancing immunity.
There are several reasons for the appearance of benign growths in intimate places:
- infectious diseases that are sexually transmitted - herpes, gonorrhea, chlamydia,
- promiscuous sex life,
- vaginal dysbiosis,
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals - vitamin deficiency,
- period of bearing a child.
With one sexual intercourse with a partner who is sick with HPV, the risk of infection is only 60%; if sexual intercourse is constant, the result of infection is one hundred percent. The virus enters the body, then penetrates the skin cells of the intimate area, and there it rapidly grows and divides. An inconspicuous neoplasm appears on the skin, which gradually increases in size.
Routes of infection
The papillomatosis virus, which causes intimate warts, is most often transmitted through sexual contact. The likelihood of infection increases several times if there are microcracks and scratches on the mucous membranes and skin. At the same time, even those who always use a condom during sexual intercourse are at risk of infection, since this protective agent does not cover all areas where condylomas may be present.
It has been proven that neoplasms in intimate areas can also appear due to infection through domestic means - when visiting public baths, saunas, gyms, and swimming pools. HPV can remain in the environment for some time, and if the skin or mucous membranes come into contact with an infected household item, the virus can enter the body.
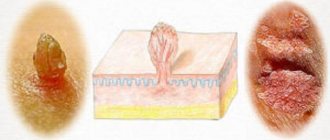
How do papillomas appear in intimate areas?
Papilloma can be called by other terms, for example, acrochord or filiform wart. In any case, the symptoms of the tumor are no different. Papilloma develops from the appearance of a small nodule, then gradually grows to the formation of a thin stalk. Very often the growth stretches out and turns into an oval, rarely remains round. Such features help to recognize papilloma. There are many types of HPV, and the course of the disease in women and men has many differences:
Symptoms in men.
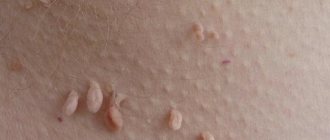
Often, papillomatosis in men does not give any manifestations, but in case of HPV infection, the disease is accompanied by the appearance of numerous warts on the head of the penis and its shaft, on the mucous membrane of the foreskin, scrotum, perineum and at the entrance to the anus. Such neoplasms are called genital warts, the appearance of which is similar to inconspicuous flesh-colored tubercles.
HPV infection can cause Bowen's disease, in which velvety plaques of a characteristic red color appear on the penis, which can progress to invasive oncology. New growths that are yellowish, pink or white indicate bowenoid papulosis.
Benign growths on an intimate place in men cause a lot of unpleasant sensations; the most popular are considered to be unbearable itching and burning, as well as discomfort between the legs. If the lesion is located inside the urethra, urination is impaired.
Symptoms of papillomas in women
If a man is able to independently detect the problem, then in the case of a woman this is not always possible. To detect an HPV infection, you need to undergo an examination by a gynecologist.
The primary reason for visiting a doctor should be the following symptoms:
- copious discharge,
- severe itching and burning,
- slight bleeding after intercourse.
On the female genital organs, papilloma can be located:
- on the clitoris,
- cervix,
- labia minora,
- in the vaginal area,
- in the cervical canal,
- on the pubic part,
- in the anus area.
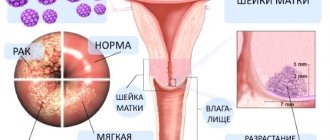
Upon examination, pointed neoplasms can be noticed immediately, while condylomas growing inward, that is, deep into the skin, are much more difficult to notice. In the case of pointed growths formed on the cervix or uterine canal, the prognosis is unfavorable and the risk of developing cancer increases.
Are warts a harbinger of cancer?
It is known that HPV can cause malignant tumors and is the most important cause of cervical cancer. But warts are, by definition, benign growths. Anogenital warts in 95% of cases are caused by non-oncogenic HPV types 6 and 11. Oncogenic HPV types are sometimes found in them (16, 18), but their role in the appearance of warts has not been proven.
Sometimes warts can hide the danger of cancer. Precancerous and cancerous lesions can literally develop on them. Occasionally, malignant tumors are mistaken for warts. Signs of cancerous lesions may include bleeding, ulceration, and inflammation (redness and swelling). In such cases, urgent contact with a specialist is required.
Rare types of oncologically dangerous warts
Giant Buschke-Levenstein condyloma looks like many papillomas merging on one base. This is a malignant formation that requires surgical treatment.
Bowenoid papulosis. It is caused by oncogenic HPV and appears as reddish-brown spots with a velvety surface. May develop malignantly.
Diagnosis of the disease
To prescribe accurate therapy, a thorough diagnosis is carried out. A dermatologist or gynecologist can easily make a diagnosis even with a visual examination.
Diagnosis in women is more difficult than in men. A gynecologist examines a woman's genitals using a speculum to rule out or detect tumors in the vagina or cervix. A special PAP test is also performed, which detects the presence of atypical cells, and, if necessary, colposcopy.
More informative and reliable is the polymerase chain reaction, or PCR for short, which can be used to detect not only the presence of a viral infection in the human body, but also to determine the severity of the disease. To exclude malignant degeneration of papilloma, a histological examination is performed - a biopsy.
Reviews of methods of treating papillomas
Based on patient reviews, you can determine how to treat papillomas in intimate places and which method is better:
- Conservative treatment: using special ointments and tablets, patients noted the effectiveness of therapy. After a couple of months, the tumors disappeared. This method is considered the most gentle and accessible.
- Laser treatment: patients noted the speed, painlessness and effectiveness of the procedure. The recovery period passed quickly. But in some cases there have been cases of relapse.
- Cryodestruction: in general, patients were satisfied with the result. During cauterization, pain and discomfort were noted. Disadvantages included a long healing process and the need to repeat the procedure.
- Radio waves: patients noted the high effectiveness of the procedure. The entire removal process takes no more than 10 minutes. Wounds must be treated with antiseptics until healing. Gentle but expensive treatment. After excision surgery, relapses are possible.
- Folk remedies do not cause pain, but require a long course of therapy. In some cases, patients had to seek medical help because medicinal prescriptions did not cope with the treatment, and the disease progressed.
Modern methods of treating benign growths on human intimate places
Under no circumstances should you use the method of removing a wart by bandaging its stem in order to avoid unpleasant consequences. Treatment begins only after the doctor has confirmed the diagnosis, since in nature there are several types of human papillomaviruses that affect intimate parts, and it is impossible to independently determine the type of infection.
Hardware therapy
The most popular treatment is considered to be hardware removal of papillomas in intimate places, which includes:
- removal of the growth using a laser, which is carried out at the stage of exacerbation of the disease (the good thing about this method is that it leaves no scars, and the procedure itself is quick and painless),
- freezing papillomas using liquid nitrogen, in other words – cryotherapy (this method is not carried out in the vagina or cervix, it is used only on visible areas of the skin),
- removal of papillomas using radio waves using the Surgitron apparatus, which affects only growths in intimate places, without affecting healthy tissue,
- electrical destruction (implies removal of papillomas in intimate places using an electric knife in combination with vascular coagulation),
- removal of growths using surgery, which is carried out under local anesthesia using a scalpel,
- burning out papillomas using electric current.
Drug intervention
It should be remembered that there is no single approach to treating this disease, only complex therapy that a doctor can select. If there are a lot of papillomas in intimate places, then immunostimulating and antiviral medications, as well as cytostatics, are prescribed.
To boost the human immune system, the following is prescribed:
- Viferon,
- Cycloferon,
- Genferon and others.
The following means are used to cauterize warts:
- Feresol is an oil solution with a phenol odor. The product is applied to the growth within 10-30 minutes, depending on the size of the papilloma. The procedure is carried out no more than once a week with great care, without cauterizing papillomas on the penis, labia and vagina.
- Super celandine - this preparation contains a mixture of alkalis. The product is applied to the tumor for five days, gradually the papilloma will disappear. Before use, the skin around the growth should be treated with baby cream.
- Solkovagin and Condilin are safe remedies for the treatment of vaginal warts, growths on the cervix and head of the penis.
- Solcoderm is a concentrated preparation for the removal of warts on the pubis, groin and scrotum. Before use, the skin is treated with baby cream or zinc ointment to avoid burns and scars.
The use of all of the above drugs is unacceptable before consulting a specialist. After all, some of them can harm not only the skin of intimate places, but also their mucous membranes. For the delicate skin of intimate organs, it is advisable to use ointments and creams, which are available at all pharmacies.
The most popular are considered to be:
- Oxolinic ointment is used in the complex treatment of benign growths on intimate organs. Oxolin has an antiviral and antiherpetic effect on warts. Apply the ointment 3 times a day from two weeks to several months.
- Stefalin is a popular remedy that contains only plant materials.
- Chinese drug San fen zhong - eliminates growths and germs.
Prevention measures
The development of papilloma can be prevented by having one sexual partner. The onset of sexual activity should not be too early (it is recommended to start having sex no earlier than 18 years of age). Having a condom will help reduce the likelihood of contracting papilloma.
There is also a vaccine against cervical papilloma. Vaccination is carried out before the onset of sexual activity and in the absence of HPV. If you have a disease, the vaccine will not help. In general, the effectiveness of vaccination has not been tested, because It has been used recently.
Unfortunately, uterine papilloma is common today. Vaccination is seen as an effective way to prevent such health problems in women.
The procedure is effective against HPV strains 16 and 18. They are the cause of neoplasms on the cervix in 80% of cases. The vaccine does not cause any harm to health. Girls should be vaccinated between the ages of 9 and 12, before they become sexually active.
Vaccination is carried out in 3 stages:
- on a day agreed with the doctor;
- after two months;
- in another 6 months.
Temporary contraindications are exacerbation of any chronic process, increased temperature. The vaccine is administered intramuscularly and will not be a traumatic experience, but will only protect against a dangerous pathology.
Since papilloma viruses, which cause the growth of tumors, are transmitted primarily through sexual contact, infection can be prevented by following a number of recommendations.
Among them:
- refusal of casual sexual contacts;
- use of barrier contraceptives (you can also become infected when using a condom, but the risks are much less);
- timely treatment of genital warts in the early stages;
- refusal of self-medication;
- exclusion of sexual intercourse until the end of the treatment course;
- simultaneous treatment of the sexual partner.
Following these simple rules significantly reduces the likelihood of HPV infection and relapses after treatment.
In addition, there is a vaccine against the four most dangerous types of sexually transmitted HPV.
But vaccination is recommended before the start of intimate life.
If there is an infection in the body, it is important to support the immune system, which, when functioning normally, is able to cope with the virus on its own.
To do this you need:
- take vitamin complexes;
- exercise;
- eat well;
- maintain a sleep-wake schedule;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- avoid physical fatigue and stress;
- treat other diseases in a timely manner.
Nonspecific methods of preventing human papillomavirus infection include a good state of immunity, preventing the appearance of microcracks on the skin, their rapid elimination, and maintaining personal hygiene.
It must be remembered that having only one sexual partner reduces the risk of transmitting the virus.
Specific methods of prevention include vaccination. It is recommended that the vaccine be administered before the age of sexual activity, since this drug cannot remove the virus that has already entered the body.
ethnoscience
A benign growth on a person’s intimate parts can be cured not only with hardware or medication, but also with the help of an unconventional approach. At home, papillomas on the genitals are treated with the following means:
- Celandine juice - apply to the affected areas twice a day for several weeks until the wart completely disappears.
- Potato juice helps to cope with papillomatosis on the labia minora, pubic area, and groin. Both internal and external use are allowed. Potato juice is drunk half an hour before meals for several months. Potato lotions are applied to the labia minora and pubis. Potato juice is used to wipe papillomas on the clitoris of the vulva and on the frenulum of the male genital organ.
- Garlic based ointment. Papillomas on the penis and labia can be cured by garlic gruel, which is made by passing several cloves of garlic through a garlic press and adding a small amount of any cream to the mixture. The pulp is spread on gauze and fixed to the papillomas with a patch for five hours, then washed off with warm water.
Features of the course of the disease in men
Immediately after infection, a small rash may appear. Then the growths transform into tubercles. In some cases, they are observed on the foreskin of the penis. Neoplasms can be either single or multiple. If it was not possible to figure out in time how to get rid of papillomas in intimate places, then their number can increase to hundreds.
In men, formations are localized in the scrotum and on the penis. In the worst case, the growths can “settle” inside the foreskin, affecting the frenulum, coronal groove or glans. Gradually they will cover the groin area, which can cause significant discomfort and pain to the person. In the wounds formed due to injury, inflammation can occur, worsening the general condition of the body.
Possible complications
Papillomas on the penis or labia can cause a number of complications, which include:
- decreased human immune system,
- frequent respiratory diseases,
- inflammation of the respiratory tract,
- relapses.
A more severe form of complication is considered to be the degeneration of a benign growth on intimate organs into a malignant form. Pointed papillomas are diagnosed by doctors as the initial stage of oncology. It is best to get rid of such growths immediately - this is the only way to preserve the health of the sexual organ and its integrity. Men are prone to cancer not only in the penis area, but also in the anus.
Visiting a doctor, diagnosis, treatment
The discovery of warts or condylomas is a reason to go to the doctor. It is difficult to predict what the doctor will do. Russian recommendations provide for a bunch of tests: for the presence of HPV and determination of its genotype, morphological examination of warts, testing for other sexually transmitted infections. Many Western sources do not recommend this, since it does not affect treatment tactics.
Anogenital warts are treated with surgical (excision, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation) and medicinal methods (medicines are applied directly to the affected area). Unfortunately, the likelihood of wart recurrence is high. Over time, they are rediscovered in at least 30% of patients. This may occur due to the circulation of an old human papillomavirus infection in the blood or due to re-infection.
Preventive measures
Papillomas on the penis and labia are classified as sexually transmitted HPV infections, therefore, in order to avoid the appearance of such growths on the genitals, you should definitely use contraception.
To reduce the risk of disease, doctors recommend:
- Do not use other people's washcloths or towels.
- Maintain proper intimate hygiene.
- If you suspect genital warts, visit a doctor immediately.
- Constantly boost your immune system.
Are rashes dangerous?
Genital warts in intimate places may not bother the patient for a long time, but this does not mean that they do not pose any health hazard. Such skin neoplasms can degenerate into malignant tumors and provoke cancer of the penis or cervix, since some types of HPV are viruses of high oncogenic risk.
If warts appear in the urethra, this often leads to a deterioration in the outflow of urine and its stagnation, which subsequently causes an inflammatory process in the kidneys and bladder.
The development of condylomas on the genitals and injury to skin growths is fraught with the addition of a bacterial infection and the formation of a purulent focus. In the worst case, this can lead to blood poisoning - sepsis.
Causes
Warts appear as a result of damage to the human body by the papilloma virus; infection with this virus occurs through sexual contact through small cracks in the skin and mucous membranes.
The reasons for the growth of warts in the intimate area are:
- lack of personal hygiene;
- promiscuity;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- lack of protective contraceptive measures;
- earlier onset of sexual relations.
Reference!
It can take a long time, sometimes even years, from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first signs. People at risk:
- having concomitant infections - thrush, herpes, gonorrhea, syphilis;
- with chronic pathologies of the immune system;
- often exposed to stress, eating poorly, getting little rest;
- having dysbiosis of the microflora of the genital mucosa;
- taking hormonal medications for a long time.
Symptoms
Warts that arise in the pubic area are distinguished by the fact that their symptoms are vague and largely depend on the location of the formations.
- When there is damage to the pubic area in representatives of the stronger sex, in addition to the unattractive appearance, you may notice a burning sensation and pain; in women, the phenomenon is accompanied by itching.
- When the vagina is affected, women may experience unpleasant painful sensations during sexual intercourse, as well as mild tingling and “lumbago”, mainly during menstrual periods.
- If the papilloma is damaged, there is a possibility of significant bleeding and unpleasant painful sensations.
- If condylomas develop in the area of the urethra, there is a possibility of disturbances in the outflow of urinary fluid.
- If papillomas infections penetrate the tissue, they emit an unpleasant odor.
Despite the blurry picture, identifying pubic warts is quite simple.
Is the disease contagious?
Genital warts are contagious. According to some statistics, infection with the virus during sex occurs in 46-67% of cases.
Infection with the virus occurs through unprotected sexual contact, during childbirth and, in rare cases, at home. After this, the first clinical symptoms appear after a long period of time, and the infected person does not know for a long time that he is a carrier of HPV. The incubation period can range from a few weeks to 8 months - usually around 2-3 months. Sometimes the latent presence of the virus in tissues can last for several years.
The following factors can contribute to infection:
- frequent change of partners;
- sexual intercourse unprotected by barrier contraception;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- sexually transmitted infections (herpes, ureaplasmosis, thrush, chlamydia, etc.);
- disturbances of the normal microflora of the vagina;
- reduced immunity (frequent stress, poor nutrition, etc.);
- diabetes;
- pregnancy period;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules in public saunas, swimming pools, etc.;
- using other people's towels and other hygiene products.
Infection occurs in areas exposed to microtrauma or friction. The virus can multiply for a long time in the surface layer of the mucous membranes or epidermis and subsequently manifests itself in the form of an exophytic (external) or endophytic (internal) form. In the latter case, the patient learns about the disease only when examined by a doctor.