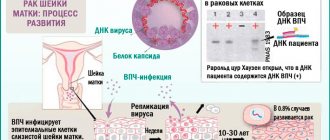
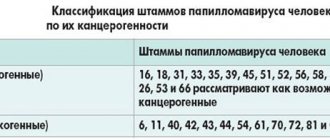
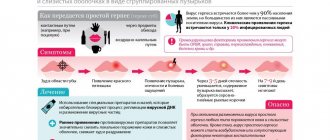
As is known, the majority of mature sexually active people (more than 70%) are infected with HPV. The clinical picture of the disease is characterized by damage to epithelial tissue - skin, mucous membranes. Before the appearance of clinical signs - papillomas/papillomatosis, condylomas, warts, it is impossible to detect the presence of the virus in the body using standard diagnostic methods - it may not manifest itself for a long time. But HPV PCR as a test is used not only to confirm the presence of the virus, but also to determine whether it belongs to a specific type (more than 100 of them have been found). This is important for determining the likelihood of malignancy of papillomas and condylomas, since the virus has 3 oncogenicity groups: low risk - types 6, 11; middle – 31, 33, 35 types; high – 16, 18 types.
Indications for use
The need for diagnosis by PCR for HPV arises in the following cases:
- Contact with people who already have a positive PCR reaction to the human papillomavirus - unprotected sexual intercourse, independent childbirth of an infected mother (possible infection of the child), use of shared personal hygiene items (towels, washcloths), close skin contact.
- The presence of formations such as papillomas/condylomas on the genital organs – the patient is referred for PCR by a gynecologist/urologist in order to diagnose human papillomavirus infection, that is, to detect HPV and determine its oncogenicity.
- Screening studies for early detection.
Preventive actions
It is impossible to exclude the possibility of HPV infection, but there are rules that will minimize the risks:
- Adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
- Treat diseases in a timely manner, especially those occurring in acute and chronic forms.
- It is recommended to begin sexual activity no earlier than 18 years of age. By this time, representatives of the fair sex have formed a protective coating in the vagina, otherwise any infection will quickly penetrate the body.
- After sex with an untested partner, use antiseptic medications and perform hygiene procedures.
- Do not have promiscuous sex. Even protected sex does not guarantee safety.
Preventive procedures also include regular examinations by a gynecologist and urologist. Regular examination will allow timely detection of structural changes and initiation of treatment.
HPV is a fairly common pathology that has different effects on the human body; it is impossible to protect yourself from it. To protect yourself, you must follow all the rules of prevention and be regularly examined by competent specialists.
Pros and cons of analysis
PCR diagnosis of HPV is often used by gynecologists, urologists, and dermatovenerologists. What is a PCR test?
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) - increasing the number of certain DNA sections in biological material to identify them, is used in the diagnosis of infectious and genetic diseases, examination for hidden infections, and determination of kinship.
Pros:
- High level of specificity.
- High speed of execution, since the process is automated - you don’t have to wait weeks for results.
- One sample of biomaterial can be used to diagnose several diseases - the reliability of the analysis remains high.
- High level of sensitivity – detection of the infectious agent even at low concentrations in the material, which helps to begin specific prevention.
Minuses:
- The risk of a false positive result is that the analysis was not done in a timely manner, for example, the material was taken immediately after treatment, when the infection was eliminated, but dead cells still remained. The PCR method does not distinguish dead cells from living ones.
- Risk of a false negative result – the cause is process violations:
- Improper storage and transportation of biomaterial.
- Failure to comply with the rules for maintaining sample sterility.
- Expired/poor quality reagents.
The choice of technique is made by the attending physician
Is it possible to do HPV without genotyping?
Of course, such an analysis can be done.
It is also quite informative.
HPV genotyping costs are higher, and such costs are not always necessary.
In any case, as a result of the test, the type will be determined or not, the doctor will find out whether the HCV papillomavirus is present in the body.
If it is present, and if it is present in high concentrations, in any case the patient must:
- treatment;
- dynamic observation.
And this is necessary, regardless of the specific type of virus detected.
Types of analysis
There are 4 types of papillomavirus testing using the PCR method. The choice of technique is made by the attending physician.
Research methods:
- Qualitative - this method of PCR detects HPV; the virus strain is not determined.
- Genotyping is a more in-depth analysis of HPV, that is, strain identification.
- The combined method, which includes a polymerase chain reaction and has a narrow focus, is aimed at finding the 16th strain.
- Quantitative – determines the number of viral bodies.
Genotyping of papillomaviruses
Genotyping of papillomaviruses is carried out to predict the dynamics of the disease. The purpose of HPV typing is not only to find the virus - it is important to identify the strain. If several strains are found, the prognosis is considered unfavorable, and the likelihood of persistent infection is high. Used to monitor the effectiveness of antiviral therapy . It is also possible to determine whether a positive result of a qualitative analysis is a consequence of residual DNA of the pathogen after treatment or a new infection (a new type will be identified, different from the one that was determined before treatment). The result is formulated as in the qualitative method.
Qualitative way
Determining the presence of HPV without identifying any strain is important in the initial diagnosis. The results are formulated as “detected”/“not detected”.
Quantification and combined method
Quantitative analysis - counting the content of viral bodies in biological material (number of viruses per 100,000 cells). This type of testing is used to determine the severity of the process and prescribe therapy. The essence is to determine the number of HPV in 100 thousand cellular units of biomaterial (scraping). Less than 3 – the virus content is low, more than 5 – high (the likelihood of malignancy is increased).
A combined method (combines qualitative and quantitative) is a targeted search for strain 16, which is highly oncogenic. Used in situations where the doctor suspects the presence of a high-risk virus. The results of the study are worded “not detected,” “strain 16 detected,” “HPV detected, including strain 16.”
VKR screening is a mass routine diagnosis for papillomavirus for the purpose of early detection
Diagnostic methods
After contacting a specialist, confirmation of the diagnosis begins, and then its typing. Treatments include:
- examination of lesions, external belonging to the types of papillomas;
- colposcopy for women, before this a smear must be taken;
- diagnostic methods at the molecular biological level;
- cytological examination;
- histological examinations after taking a biopsy;
- General tests of blood, urine, secretions.
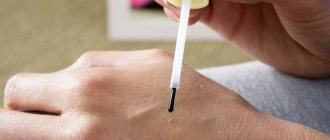
The diagnosis of HPV itself usually does not cause difficulties, as formations can be detected either independently or during a doctor’s examination. To verify the viral basis of neoplasms on the body and organs, smears and scrapings are prescribed for PCR.
VKR screening – what is it and how is it carried out?
VKR screening is a mass routine diagnosis for papillomavirus for the purpose of early detection. The study on HPV HCR in women involves persons over 25 years of age (according to some data - from 21 years old / 3 years after the start of sexual activity; with strong sexual activity, a large number of partners - from 18 years old). It is recommended to undergo medical examination once every 3 years. During the event, high-risk viruses are identified that pose a danger because they can cause the development of cervical cancer. Determination of DNA concentration for HPV of high oncogenic risk is carried out using the PCR method.
Screening steps:
- Papanicolaou cytology smear (PAP test). To carry out the test, material is taken from the cervical canal (transformation zone - the place of transition of the columnar epithelium to the stratified squamous epithelium) during the examination, which is applied to glass / in a container with a special liquid (then the smear is taken with a brush). Then, after staining, the material is examined under a microscope for the presence of atypical cells; if they are present, the test is positive. The method is also called cytological.
- PCR – determination of the presence of a virus. The reaction is carried out for those who have a positive Pap test result. For research, you can use smear material, blood, and urine.
- Extended screening - determination of the type and quantity of HPV with a high risk of oncogenicity (Dajin test - number of viral bodies per 100 thousand cells: up to 3 - low concentration, 3-5 - medium, more than 5 - high).
The material is collected as for a PAP test.
Rules for preparing for the test
2 days before the event you need to abstain from sex
- 2 days before the procedure, you need to abstain from sex, taking any medications, douching, vaginal suppositories, and pills.
- A PCR smear is taken in the first phase of the cycle, after menstruation.
- During periods of exacerbation of chronic infectious pathologies, after taking antibiotics, material is not collected.
Rules for donating blood/urine:
- Blood - donated from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach; a few days before the test, allergens (chocolate, citrus fruits, etc.) are excluded from the diet.
- Urine – for HPV PCR analysis, you need to take morning urine on an empty stomach (last meal 8 hours ago) into a sterile container. The container must be delivered to the laboratory within 4 hours after collecting the material.
How to give to men and women
For research it is possible to use almost any human biomaterial - blood, urine, smear, scraping. The rules for donating blood and urine are no different for men and women.
The method of taking a smear differs:
- How to take a test for a woman - scraping is done with a brush, in a circular forward movement from the urethra/vagina/cervical canal.
- For a man, scraping with a brush is done from the head of the penis and the urethra.
Before taking a smear, you must ensure that personal hygiene is observed.
Decoding the results
The interpretation of the results obtained depends on the method used:
- Qualitative – presence/absence – “detected”/“not detected”.
- Genotyping - detection of a specific strain - “detected” / “not detected”.
- Combined – detection of strain 16 – “not detected”, “strain 16 detected”, “HPV detected, including strain 16”.
- Quantitative:
Calculation of the number of viral bodies per 100 thousand cells of biomaterial (scraping):
- <3 – low content (low risk of cancer)
- 3-5 – average
- >5 – high (high probability of cancer)
What to do if dangerous types of HPV are identified?
The risk of detecting dangerous types of HPV in an individual person is low.
In most people, no variant of this virus is detected at all.
If the patient is infected, then with a high probability it is a harmless type of HPV.
Low-oncogenic varieties are much more common.
If you are unlucky and have been diagnosed with highly oncogenic HPV, you need to look at its quantity.
If it is small, no treatment is required.
Most likely, your body has already begun to get rid of the virus, and soon it will no longer be detected.
It's worse if its concentration is high.
In this case, the following is necessary:
- additional tests;
- treatment;
- dynamic observation.
A smear is taken from the patient for oncocytology.
Most often, this study is carried out not after HPV genotyping, but simultaneously with this test.
Based on the results of these two tests, a decision can be made about the need for colposcopy.
It is needed to identify areas of altered epithelium (precancerous processes).
In turn, the results of colposcopy (examination of the cervix) may require a biopsy.
This is a procedure in which a piece of tissue is taken and sent for histological examination.
Based on its results, both a malignant tumor and a precancerous process of stages 1-3 can be diagnosed.
Stage 1 is reversible, while stages 2-3 require cauterization to prevent cancer.
But precancerous processes develop very slowly.
If antiviral treatment is carried out in time, the virus disappears from the body and the cervical epithelium is restored.
Patients must be monitored.
They are tested every six months to assess whether the concentration of the virus is increasing or decreasing.
To eliminate it, antiviral and immunomodulating drugs are used.
Treatment methods
Antiviral drugs are used to treat HPV
- Surgical – removal of papillomas, condylomas, warts:
- Laser (laser destruction/coagulation).
- Radio wave radiation.
- With an electric knife.
- Cauterization of warts with liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction).
- The use of locally acting agents to necrotize pathological elements - verrucacid, supercelandine, podophyllotoxin 0.5%. After surgical treatment, antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs are prescribed.
- Antiviral drugs – Isoprinosine, Viferon, Panavir, Genferon, Kipferon.
- Strengthening the immune system – Immunal, Polyoxidonium, Galavit.
Antiviral and immunostimulants are available in the form of tablets and suppositories. The duration of the course is determined by the attending physician, usually 10-14 days, extended if necessary.
In case of ulceration/inflammation of formations, anti-inflammatory treatment is carried out - treatment with antiseptics (for example, chlorhexidine, miramistin), antibiotics, antiviral ointments. Severely inflamed papilloma is best removed surgically.
It is possible to use traditional methods of treatment after consultation with your doctor. Traditional methods of treatment have 2 directions:
- Removal of formations. Externally use celandine tincture, dandelion juice/raw potatoes - lubricate twice a day. The papilloma disappears after about 1.5-2 months.
- Strengthening the immune system - can be carried out throughout the disease. Recommend:
- Decoctions – spruce needles/onions with the addition of honey.
- Teas – rosehip, lemon balm, fireweed, mint, linden blossom, coriander.
- Dried fruits - a mixture of walnuts, dried apricots, raisins, lemon and honey.
Features of examination in women
During the examination, the woman takes a scraping from the cervix. This option is the most preferable and provides much more complete information than scrapings from the vagina or urethra. In order to take scrapings in this place, use a special brush.
It is placed in the woman’s cervical canal, collecting the material necessary for research with its bristles. Then fingerprints are made with the instrument and sent for examination. The brush is often replaced with a universal probe. The analysis does not cause the woman any pain. Not carried out during critical days.