Symptoms and first signs of the disease
Even after entering the human body, human papilloma viruses may not manifest themselves at first. When immunity decreases, the virus is activated and begins to multiply. At this stage, clinical manifestations appear.
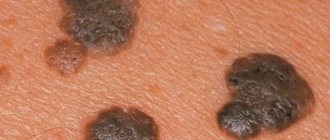
When infected with HPV of low oncogenic risk, patients are most often concerned about visual discomfort associated with the appearance of warts on any part of the skin and mucous membranes. These formations in the anogenital area have a special name - genital warts or anogenital warts. They are often accompanied by itchy skin. As a rule, these formations are of various shades of brown, have an uneven surface, and may be on a narrow base (leg).
Appearance of skin warts
A distinctive feature of warts and condylomas is rapid and multicentric growth. The presence of single warts on the skin and mucous membranes is an indirect sign of HPV infection and requires diagnosis.
Most infections caused by highly oncogenic types of HPV are asymptomatic. Only a general decrease in immunity is possible. Often the virus can only be detected after swab collection. However, the prolonged presence of an oncogenic type of virus leads to the development of precancerous pathologies, which, without appropriate therapy, degenerate into a malignant process. It is well known that in the early stages of the disease, cervical cancer is practically asymptomatic, and specific manifestations (discharge and irregular bleeding, pain in the back, pelvis, legs; unilateral swelling of the legs) occur when the process is widespread.
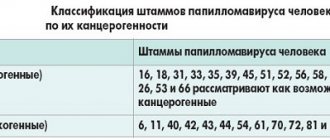
Viruses of high oncogenic risk - HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 50, 59, 64, 68, 70. The most studied and aggressive are types 16 and 18; these HPVs in women cause up to 70% of all cases of precancerous conditions and cervical cancer.
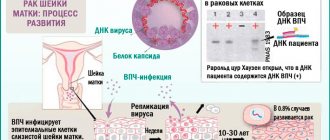
Research results and transcript
The results are issued on special forms and are indicated by a digital code.
| Type of study | Decoding |
| Cytology |
|
| PCR, Digene test |
|
The above tests give an idea of the presence of HPV in the body. To check for other sexually transmitted diseases, other tests are prescribed.
Your doctor will help you decipher the test results. The table is for reference only.
Diagnosis of HPV in women
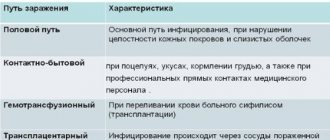
The polymerase chain reaction method, the so-called PCR, can reliably identify a specific type of papilloma virus. For analysis, a vaginal smear into a test tube with a special medium is sufficient. PCR is a simple but highly sensitive method.
A positive test for HPV 16 and 18 is associated with a higher risk of malignancy.
Eppendorf tube for collecting material for HPV testing
It is important to understand that changes in the cervix are often not visible to the naked eye, so it is necessary to use special additional examination methods, such as colposcopy and smears from the cervix and cervical canal.
Colposcopy is an examination of the cervical mucosa using a special device - a colposcope.
In this case, 2 tests are carried out:
- Acetic Acid Test - test with acetic acid solution
- Schiller's test - treatment of the surface of the cervix with Lugol's iodine solution.
Based on the data obtained, a satisfactory or unsatisfactory colposcopic picture is judged. This test is performed using a special Papanicolaou stain, which is why it is often referred to as a PAP test.
Detection of a pathological type of smear and an unsatisfactory colposcopic picture are indications for a biopsy of suspicious lesions.
Pap smear staining
Types of HPV tests
In modern medicine there are several effective examinations for human papillomavirus. With their help, you can determine the presence of infection and find out the type of HPV. The patient is referred for testing for papillomavirus by the attending physician, a dermatologist, gynecologist or urologist.
The most common HPV tests are:
- colposcopy;
- histological diagnosis;
- cytological examination;
- amplification and non-amplification test;
- detection of antibodies to HPV.
Colposcopy is prescribed to women to detect papillomas localized in the cervix. Diagnosis is considered simple and is carried out using special equipment - a microscope. The doctor examines the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix. Colposcopy allows you to examine organs at multiple magnification. The duration of the procedure varies from 10 to 30 minutes. The doctor hands over the results 10-15 minutes after the examination.
Histological diagnosis is almost always prescribed in conjunction with cytological tests. This test examines a small biopsy sample - a small piece of tissue. The biomaterial is placed under a microscope and the affected cells are assessed. Histological techniques allow one to determine whether a tumor is malignant or benign. The duration of the manipulation takes no more than 15 minutes. The patient can receive the results 2-3 days after the examination. Most often, after histology, the patient is sent for a non-amplification test or PCR study.
To conduct a cytological examination, the doctor collects biomaterial. A smear of skin cells is taken as a sample. The resulting material is examined under a microscope. With this analysis, you can see modified cells and tissues that indicate HPV. The technique is simple and not expensive, but at the same time it quite often shows a false negative result. The result form is given to the patient after 4-6 days.
The amplification test in modern traditional medicine is considered accurate because it shows the type of infection and its oncogenicity. The sample is taken from the urinary canal or vaginal mucosa. This analysis is often prescribed by a gynecologist in conjunction with cytological diagnostics.
PCR analysis is used to determine the oncogenicity of a growth or papilloma. The biomaterial is urine, blood plasma, a smear from the mucous surface or amniotic fluid. The accuracy of the survey is close to one hundred percent. Human papillomavirus can be detected even with a small concentration of infection in the blood. With the correct collection of biomaterial and accurate interpretation of the results, it is possible to know for sure whether there is HPV or not just 1-2 days after the manipulation.
Some patients are surprised when the test result is “positive”, but there are no condylomas on the body. This indicates that there is an infection in the body, but the immune system is restraining it in every possible way. Doctors recommend that if the result is “positive,” you undergo a course of treatment, and if there are papillomas, remove them using a laser or other methods.
Prevention and treatment
The issue of preventing human papillomavirus is currently being actively discussed.
Patients often ask, is there a vaccine for cervical cancer?
In fact, there is no such vaccine. There is no treatment for the papilloma virus that would completely remove the virus from the human body. Only the result of the virus’s impact on the body’s cells can be treated. Regimen containing antiviral drugs and immunomodulators are used. The papillomas themselves can be removed surgically: by radio wave techniques, laser coagulation, and also by methods of chemical destruction.
All these types of therapy are actively used on the basis of the National Medical Research Center for Oncology named after N.N. Petrova after a thorough examination, examination and individual selection of treatment by highly qualified specialists. Undergoing therapy in a non-specialized institution may result in the spread of the virus to surrounding tissues damaged during the removal of the affected areas.
Antiviral therapy for human papillomavirus infection
No special treatment has been developed. Therefore, the patient is prescribed antiviral drugs that stimulate the immune system:
- Medicines that block the reproduction of the virus and activate the immune system. Effective drugs are Isoprinosine and Inosiplex.
- Interferons. Medicines provide antiviral effects and help improve immunity. In addition, they have an antitumor effect. Such drugs are “Intron-A”, “Alpha-interferon”, “Genferon”.
- Drugs that activate the body’s production of its own interferons. Medicines “Cycloferon” and “Amiksin” may be recommended.
- Medicines that prevent the proliferation of cells affected by the virus. Excellent drugs are Podophyllin, Condilin, Podophyllotoxin.
However, none of the drugs listed above can completely cure the infection.
Vaccines against human papillomavirus
There are currently 2 recommended vaccines in use. It is considered optimal to vaccinate girls before they become sexually active.
Since 2006, the Gardasil vaccine has been used (Fig. 4). This is a quadrivalent vaccine, i.e. it is directed against HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18.
The recommended course of vaccination consists of 3 doses and is carried out according to the following scheme: first dose - on the appointed day; the second - 2 months after the first; the third - 6 months after the first. Carrying out the full course leads to the formation of stable immunity in 99% of vaccinated people for a period of at least 36 months in all age groups. Children and adolescents, as well as young women aged 9 to 26 years, are subject to vaccination.
Another vaccine is Cervarix. Created in 2007 for the prevention of diseases caused by human papilloma viruses types 16 and 18. A full course of vaccination according to the 0–1–6 month schedule leads to the formation of specific immunity in 100% of vaccinated individuals 18 months after the last dose of the vaccine in age groups from 10 to 25 years. The need for revaccination has not yet been established.
Vaccines against human papillomavirus a) Gardasil b) Cervarix
In a number of regions of the Russian Federation, patients are vaccinated free of charge, while in others vaccination is carried out on a commercial basis.
How the analysis is carried out
To conduct a quantitative analysis for HPV, the following materials can be used:
- Capillary blood (from a finger). A fairly common method for collecting biological material. It is very often used when conducting several tests aimed at identifying other infections and biochemical blood parameters.
- Scrapings from skin or mucous membranes. An absolutely painless technique in which the upper layers of the epithelium are carefully removed with a cotton swab or a special spatula. The material is collected from the affected area, which increases the information content of the method.
- Tissue biopsies. Very often, especially if the development of a malignant neoplasm is suspected, a special diagnostic procedure is performed - a biopsy. In this case, a part of the affected tissue is taken, after which it is examined under a microscope and, if the clinical case requires it, laboratory diagnostics for the presence of viral DNA or specific tumor proteins.
The trend of modern medicine is the desire for maximum painlessness of procedures. In this regard, diagnostic techniques that can work with scrapings of the epithelial surface have become most widespread. In some cases, capillary blood sampling is used. Biopsy is used only in extreme, difficult to diagnose cases.
Diagnosis and determination of HPV types are resorted to in cases where papillomas affect the genital organs (especially the cervix), suspicions arise about the possible development of malignant tumors from previously benign growths, or massive papilloma infection, prone to frequent relapses.
Before taking the tests, you should undergo certain preparation:
- Do not take antifungal, antimicrobial or antiviral agents within 12 hours before the procedure.
- On the day before the test, take a shower, wash, and clean the area being examined of hair.
- Refrain from sexual intercourse for 2 – 3 days before the diagnostic procedure.
Dynamic observation
Today, cervical cancer screening in the Russian Federation is regulated by Order No. 572n of the Ministry of Health: preventive examinations with cytological screening are carried out at least once a year. PCR testing of vaginal discharge for the presence of human papillomavirus is not prescribed as part of a preventive medical examination. However, according to international standards, HPV detection is an important and integral factor in the prognosis of cervical diseases. Initial HPV testing is recommended, as is cytological screening of the cervical epithelium. The screening interval for patients with a normal cytology test result and a negative HPV test ranges from 1 to 3 years.
How to prepare for a smear test
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
A smear is a safe procedure that does not cause any inconvenience. The test is performed during a routine gynecological examination.
The doctor dilates the vagina using a speculum and makes a scraping with a special instrument. For analysis, a cervical cytological brush resembling a brush is used. Previously, a Volkmann spoon was used for these purposes. With the use of new instruments, the procedure is painless; the patient may feel only slight discomfort, which lasts a few seconds.
Diagnostics can be carried out in any medical institution that has the appropriate license. For timely diagnosis, it is recommended to be checked by a gynecologist and have a scraping tested for HPV at least once a year.
Preparing for an HPV smear in women:
- 2 days before going to the doctor, avoid sexual intercourse, douche, and do not use cosmetics for intimate hygiene.
- Before the procedure, take a shower without using hygiene products.
- The test is not performed during menstruation. Perform scraping in the first days after the end of menstruation.
- After the manipulation, thoroughly wash the skin of the intimate areas and take a shower. To avoid infecting your partner, sexual intercourse is not recommended until the test results are known.
- If the patient is taking medications, he must inform the doctor about this.
Disadvantages of the method
There are, however, some negative aspects in carrying out PCR diagnostics. The main one is the possibility of obtaining a false positive result. This happens if treatment has already been carried out, the infection has been defeated, but dead cells still remain inside the tissues. Cell renewal takes time.
If the analysis is carried out earlier than 2-3 months, PCR may show a positive result, in fact mistaking already dead cells for living ones. The method does not distinguish between them; it is aimed at searching for viral DNA, which can be found even in already dead cells. All this leads to a false positive result. This situation can be avoided if you take the test within the time limit established by your doctor.
There is also a risk of a false negative result. In this case, the patient cannot influence the quality of the diagnosis in any way, since a false negative analysis is a miscalculation of the laboratory. It may occur if:
- the collected material was improperly transported and stored;
- sterility is compromised and other microorganisms get into the samples obtained;
- the reagents were unsuitable.
In order to exclude the possibility of obtaining a false negative result, it is necessary to choose a trusted laboratory with qualified personnel.