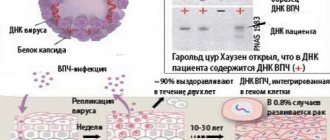
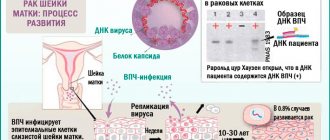
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a type of DNA virus that belongs to the papovirus family. Intracellular parasites not only lead to the development of benign skin formations (warts, papillomas, condylomas), but also have pronounced oncogenic activity. Human papillomavirus infection is a source of many troubles, ranging from aesthetic ones to the threat of degeneration into a malignant tumor.
HPV infection is dangerous due to the degeneration of cells into malignant neoplasms
The main problems from an epidemiological point of view are the colossal percentage of carriage (according to some sources - up to 90% of people) and transmission through physical contact, including sexual contact. The most unpleasant are the primary manifestations associated with damage to the anogenital zone, which occur, on average, in 1% of the sexually active population.
Features of HPV
About forty types of the virus out of 100 cause damage to the genitals.
All types of papillomavirus differ in genetic characteristics, but the principle of their action on the body is the same:
- penetrating into cells, they insert their genetic material into them and begin to reproduce
- condylomas and papillomas begin to appear at the site of pathogen penetration
- after some time, the tumors degenerate into malignant forms
Due to the fact that medicine does not stand still, diagnostic methods are constantly being improved.
Doctors were able to detect DNA of type 16 human papillomavirus in malignant neoplasms in the male genital area.
Based on the data obtained, HPV 16 is classified as a virus with high oncogenic activity.
It is believed that the pathogen can provoke the development of cancer of the penis, scrotum and anus in men.
Routes of infection and development of the virus
- Contact and household. Infection with the virus occurs through the use of shared towels, shaving machines, etc.
- Sexual. The virus is transmitted through sexual contact. The risk of infection remains quite high even when using condoms.
Once HPV enters the human body, it penetrates into the spinous cells of the epithelium. The areas of skin at the border with the mucous membranes are particularly affected. Penetrating into the cell, the viral DNA is released from the shell and penetrates the nucleus, where it is integrated into the human genome near the division center.
Further, HPV may not make itself felt for a long time until factors arise that stimulate cell division.
Simultaneously with the signal carrying information about cell reproduction, viral DNA is read, which ends with a non-stop repetition of cell division.
Externally, this process can be observed in the form of the growth of condyloma or the formation of a malignant tumor .
How can you become infected with HPV 16?
Like all types of HPV, type 16 viruses are transmitted through skin-to-skin contact with a sick person.
For men, the main routes of infection are:
- unprotected sex
- intimate caresses
- use of personal hygiene items for the patient
It is reassuring that the epithelial cells of the skin are more resistant to pathogenic flora than the mucous membranes.
But the contagiousness of the virus is so high that even with one-time sex with a sick person you can become infected with HPV.
Especially if there are microscopic abrasions and cracks on the mucous membrane or skin.
HPV 16 is also transmitted to healthy men from sick partners during non-traditional forms of sex.
Symptoms of human papillomavirus
HPV types 16 and 18 provoke the appearance of condylomas in the anogenital area, and especially on the penis, which dramatically affects a man’s sex life.
Note! In addition to the formation of a cosmetic defect, genital papillomas can cause discomfort during sexual intercourse for both the man himself and his partner.
The condylomas themselves are small, cone-shaped or thread-like formations 1–2 mm in height. Their color is the same as the surrounding skin or slightly darker.
HPV type 16
Most often, this papillomavirus affects the glans penis and anus. In this case, condylomas are located either on the mucous membrane itself, or on its border with the skin epithelium.
Due to the specificity of its localization, the virus in rare cases leads to the development of Queyrat erythroplasia . Keir's erythroplasia is a flat, red lesion with a shiny or velvety surface. This lesion is located directly on the head of the penis. In 30% of cases, Keir's erythroplasia develops into squamous cell carcinoma, which is accompanied by the appearance of ulcerations and crust formation.
Pay attention! Most often, the disease affects older people, but the risk of development remains in younger men.
HPV type 18
Unlike papillomas of the virus type 16, type 18 often directly affects the skin of the perineum, scrotum, penis, and inner upper thighs.
Photo 2: Condylomas, as a rule, are located singly or in small groups; rarely, plaques form from the fusion of several genital warts. Source: flickr (EncinoMan)
A number of authors believe that oncogenic HPV types, including 18, lead to the development of Bowen's disease. It manifests itself in the form of an irregularly shaped red spot or plaque. On the surface of the formation there are small scales that separate painlessly and without bleeding. The size of the lesion can be from 8 to 120 mm; nodules or small papillomas are sometimes located along its contour.
At its core, Bowen's disease is the initial stage of carcinoma . In the absence of treatment, carcinoma develops directly in 11–80% of cases.
How does HPV 16 manifest?
The appearance of the first signs of HPV 16 infection in men is not unusual.
Symptoms and signs of the disease on the skin and mucous membranes do not appear immediately.
The incubation period lasts from one to several months.
There are cases when the first symptoms of the disease appear several years after infection.
This may be due to the fact that the infection occurs in a latent form.
Signs of infection include the following:
- formation of papillomas on the penis, which can be localized on the glans, coronary sulcus or foreskin
- the surface of the growths is smooth, the color is flesh or pink
- neoplasms rise above the surface of the mucous membrane or skin
- papillomas and condylomas are painless
- growths are often single, the transverse size is 1 mm or more
What types of condylomas appear in the anogenital zone?
Growths that are localized on the mucous membrane are called genital warts.
When papillomas are localized on the scrotum, the growths resemble a wart in appearance.
Localized on the mucous membrane, condylomas take on the appearance of cauliflower or cockscomb.
Neoplasms grow slowly and cause almost no discomfort to their owner.
When condylomas are localized in the urethra, disturbances in urination and ejaculation are observed, since the growths block the path for urine and sperm to exit.
If measures are not taken, the condylomas will grow and increase in size.
A secondary infection can join them and provoke an inflammatory process.
The moment of malignancy can occur at any time and, often, the degeneration of neoplasms occurs unnoticed.
Signs of malignancy of papillomas and condylomas may be accompanied by the following transformations:
- rapid growth of growths
- the formation of scales, peeling of the surface of the neoplasm, which was initially smooth
- formation of ulcerations
- bleeding
In the presence of papillomavirus type 16, these symptoms often indicate the degeneration of neoplasms into squamous cell carcinoma.
If the patient does not consult a doctor and treatment is not prescribed, then manifestations of a progressive tumor will begin very quickly.
With the development of the pathological process, the inguinal lymph nodes will enlarge and tissue disintegration will begin at the site of the tumor.
As a result, secondary infection will occur.
It is important to understand that in the early stages of the development of the disease, when the process is still benign, it cannot be visually determined that the pathogen is HPV 16.
What to do if a man has tumors in the genital or anal area?
It is necessary to be examined immediately to determine the type of pathogen.
If HPV 16 is detected, immediately undergo a course of therapy to prevent dire consequences.
Often people do not know which doctor to contact in such cases.
To undergo further examination and receive treatment, you should contact a venereologist or dermatologist.
Types of papillomavirus
HPV DNA type in men is widespread. Papillomavirus can be of different types. This disease has a large number of varieties. Some types of HPV cause cancer.
To correctly determine the type of problem, you need to seek help from a medical center. This disease should not be taken lightly. Cancer develops quickly.
If it is not detected in a timely manner, the death of the patient may occur.
The type can only be determined in a laboratory. For this reason, you should visit a specialist at the first signs of skin damage.
Characteristics of the pathology
HPV DNA affects the body at the cellular level. Pathology begins its development in the cell membrane.
The disease is caused by microorganisms that are an intermediate form between fungi and viruses. A distinctive feature of papillomavirus is its ability to function outside the cell membrane.
The virus survives only in the cell itself. This microbe causes changes in the cell's DNA. It changes its structure. The cell acquires atypical properties. Some cells exhibit a binucleate form.
This indicates oncological changes in tissues.
HPV is not able to live in environmental conditions. If it hits the air, it dies instantly. This affects the characteristics of infection with this infection. The virus enters the body only upon contact with damaged mucous tissue. For this reason, the main route of infection with HPV DNA is through unprotected sex.
Infection occurs from a carrier to a healthy person. Many carriers are unaware of the presence of this infection. The acute form develops only under the influence of certain factors. Some types of HPV can become active in a man’s body only after several months.
HPV type DNA influences the development of various negative processes on the skin. Such diseases can also cause cancer. Cancer is characteristic of such types of HPV as: 31, 16 and 18. The remaining types can be classified as conditionally oncological and non-cancerous forms. For a man, these types are dangerous. They affect not only the formation of oncology, but also reproductive function.
Why is papillomavirus dangerous?
HPV DNA type causes a variety of health problems. Since the main route of transmission is sexual, complications arise in the intimate area. In men, papillomavirus can cause diseases such as:
- Prostate cancer;
- Kidney and bladder problems;
- Changes in the gonads;
- Oncological lesions of the skin.
For men, the HPV DNA type is dangerous precisely because of its complications. Often the disease affects the gonads due to the peculiarities of their structure. Papillomavirus occurs in tissues that have an epithelial layer. These organs include the prostate gland and testicles.
The male prostate gland performs several functions. Its main effect is to produce fluid for sperm. It also forms part of the male sex hormones – androgens. The virus penetrates the glandular layer of the prostate and causes changes in the cells.
They become unusual for this tissue. HPV type DNA causes changes in cell structure. She begins to actively reproduce. A small tumor forms in the organ. In this case, the first symptoms of the HPV DNA type are similar to prostate adenoma.
HPV type DNA also affects the function of the paired sex glands - the testes. In this case, the microorganism penetrates the testicular cavity and has a negative effect on the condition of sperm. When sperm are infected with a virus, their production is disrupted.
In the sperm of such a man, a large number of atypical germ cells are found that do not have the properties of healthy sperm. The germ cells acquire an abnormal shape and lose the ability to fertilize an egg.
The patient is diagnosed with infertility.
The microorganism also affects the male urinary system. When infected with HPV DNA of the bladder type, the microorganism invades the mucous layer. In this case, areas of tissue appear that are covered with small growths.
This area is incapable of natural contraction. There are problems emptying the bladder. At the same time, various inclusions can be found in a man’s urine. You should be wary if you find bloody inclusions in the liquid.
They may indicate cancerous development of the disease.
Problems can also appear in the renal pelvis. Against the background of infection with HPV type DNA, areas of tissue appear in the pelvis where the epithelial layer ceases to function. The epithelial layer of the pelvis consists of many papillae. Papillomovirus causes the replacement of part of the papillae with neoplasms.
The kidneys stop absorbing substances from the urine. Various inflammatory pathologies appear. In men, pyelonephritis or cystitis often occurs against the background of HPV DNA type. Since the microorganism penetrates the genitourinary system during sexual intercourse, it causes changes in the skin of the penis.
First of all, the tissue of the foreskin and glans is affected. The foreskin consists of a large number of epithelial cells. The virus settles on the inside of the flesh and causes disruption in the structure of the epithelial layer. Various rashes appear on the foreskin.
In this case, it is necessary to undergo additional examination to determine the characteristics of the disease.
Causes of papillomavirus
Many people have HPV DNA in their bodies. There are two forms of the disease: carriage or latent form, active virus.
When carried, the patient does not know about the presence of the microorganism. There are no external signs of the disease. In the acute form, the patient experiences a variety of symptoms.
The causes of HPV type DNA infection vary. The main infection occurs through sexual contact. Friction of the mucous membrane can be accompanied by the occurrence of microdamages. Through the surface of the wound, the microorganism penetrates into the tissues of a healthy person. This is how infection occurs.
But there are other negative factors that can cause the virus to transition from an inactive form to an active stage. In this case, a man often experiences the following processes:
- Decreased protective function;
- Nervous overstrain;
- Hormonal imbalances.
Often the microorganism is activated due to a sharp decrease in the protective properties of the body. The human immune system acts as a barrier.
A healthy person has special bodies in the blood that have a detrimental effect on pathogens. Under the influence of various factors, the number of these bodies can sharply decrease.
Protective properties are lost. The virus is not attacked by the body and can function freely.
Most men have jobs that involve constant stress. Against the background of constant worries, disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system occur. She begins to perform her function inadequately. Because of this, changes occur in the tissues. They depend on the amount of oxygen supplied. Against the background of stress, tissue trophism decreases. They create ideal conditions for the reproduction of HPV type DNA.
One of the negative factors is a disruption in the hormonal system. The male hormonal system plays a major role in the formation of sexual function. When the amount of hormones in the body is disrupted, a malfunction occurs. It is accompanied by the activation of various pathological processes. If a person is considered a carrier, the virus can suddenly become active.
You should know that HPV type DNA is not transmitted through everyday contact. Human infection does not occur through the use of other people's personal hygiene products. The microorganism does not survive in the environment.
Diagnostic measures
To determine the type of HPV DNA, several tests are required. The main study is carried out on the basis of scraping or biopsy. Scraping is carried out on tissues that have changed their cytological structure.
During the study, the specialist determines the presence of additional inclusions in the cell body. HPV type DNA can be detected by detecting whitish inclusions around the nucleus. Other changes in the cell may also be detected.
Thus, HPV type 16 DNA is characterized by the presence of two or more nuclei.
A small part of the tumor is taken for a biopsy. She is undergoing cytological examination. The specialist determines the presence of atypical cells.
Diagnostics is also carried out using other samples. The study is carried out on the blood and secretory fluid of a man. It is necessary to establish in the blood the presence of antibodies that the body needs to fight the microbe. An accumulation of antibodies is also observed in the secretion.
It is also necessary to establish what changes have occurred in the DNA of the cell. This can be done using PCR. This procedure allows you to detect the pathogen even at an early stage of infection.
Diagnosis of HPV 16
The appearance of anogenital neoplasms in men should be a reason to consult a doctor.
You need to undergo an examination and find out the type of papillomavirus.
For diagnostic purposes, the following types of tests are performed.
A cytology smear from the urethra will determine the presence of changes in cells under the influence of the virus.
It takes several days to complete the analysis.
The result has digital indicators:
- 1 - indicates the absence of pathogens in the biomaterial
- 2 – indicates the presence of inflammation of some cells
- 3 – shows a dubious result. In this case, additional examination of the patient is necessary.
- 4 or 5 – indicates the presence of HPV
Histological examination is used to confirm or refute the presence of an oncological process.
A small fragment of tissue taken from the affected area is examined as a biomaterial.
The next stage of diagnostic measures is PCR diagnostics.
A smear is taken for examination.
The analysis is prepared quickly and can be ready on the same day, or, in extreme cases, the next day.
The technique is highly accurate if all requirements for the study are met.
Using PCR, not only the presence of pathogen DNA in the biomaterial is determined, but also its quantity.
If there is no virus, this will be written on the form.
If the pathogen is present, the concentration will be indicated.
It happens that there are growths, but the analysis does not show the presence of a pathogen.
This is explained by the fact that the body’s immune defense has already coped with the infection, and neoplasms appeared earlier.
In this case, they must be removed.
✔ The Digene test also allows you to calculate the amount of genome of viral particles in a biomaterial. The technique is characterized by high sensitivity and accuracy.
Symptomatic picture
In order to recognize the disease in time and begin proper treatment, you should know the signs of the presence of infection in the body and what manifestations to pay attention to.
The main symptoms of the presence of papillomavirus in the body are visible changes in the external epithelium in the form of warts and papillomas. There are several types of growths on the genitals.
- Warts are rough, round growths that are brown or burgundy in color.
- Papillomas have a smooth surface, irregular shape, dark brown color. The presence of a large number of papules on the body is evidence that the virus has been in the body for a long time.
- Condylomas are growths that form on the genital organ. They have an irregular shape and color varies from light pink to dark brown. When neglected, they provoke a tumor
The disease will not begin to appear immediately. The incubation period ranges from several weeks to six months, after which a period of exacerbation begins - the formation of skin growths. How HPV manifests itself during unprotected sexual intercourse:
- over the entire surface of the penis, in the groin and perineum, which occurs upon contact with infection;
- during anal intercourse, the anus becomes infected both inside and outside;
- When engaging in oral sex, condylomas begin to form in the oral cavity.
Condylomas are contagious through close contact. They are dangerous: they can be damaged when putting on clothes or strong friction when walking.
PCR diagnostics of HPV 16 with concentration
This is one of the most common methods for detecting oncogenic types of HPV.
What does the concentration of pathogens indicate?
This is an indicator of the viral load.
- If the amount of viral DNA is less than 3 per hundred thousand cells, then we are talking about a low concentration of the virus in the body
- If more than 3, but less than 5, then such a quantitative indicator has clinical significance
- A reading of more than 5 indicates a high viral load
What indicators are used to prescribe treatment? Therapy is indicated in the presence of high levels.
At what concentration of the virus is treatment not prescribed?
If the concentration of pathogen DNA is low, wait-and-see tactics can be used.
If the HPV 16 titer is low, then in 20% of cases the virus can be eliminated spontaneously.
Oncocytology for HPV 16
This is one of the most reliable methods for diagnosing malignant neoplasms.
Carrying out this technique is justified if it is necessary to work out the tactics of treating a patient.
The study allows you to determine the presence of malignancy of cells.
There are simple and liquid oncocytology.
- In the first case, the biomaterial is applied to a glass slide and analyzed.
- In the second case, the biomaterial is placed in a special solution, then centrifuged, and then examined.
Liquid oncocytology is considered to be more reliable.
The technique is used for early diagnosis of cancer.
Immunogram for HPV 16
This type of study for diagnosing papillomavirus type 16 is important if it is necessary to establish how long ago the patient was infected.
If the infection is fresh, then IgA and IgM are detected; in the presence of a pathology that lasts for several months, then IgG predominates.
To carry out the analysis, blood is taken from a vein.
The study is carried out to determine the parameters of the body's immune status.
Features of treatment of HPV type 16 in men
Due to the fact that papillomavirus type 16 has a high oncogenic risk, all patients with a confirmed diagnosis of HPV are subject to treatment.
Therapy is mandatory even in the presence of low concentrations of pathogenic microflora, especially with large tumors localized in the urethral area.
There are several approaches to treatment:
- removal of growths on the skin and mucous membranes
- the use of conservative treatment, including the prescription of systemic and local drugs
- combination therapy. In this case, the tumors are removed followed by the use of medications.
The latter option for HPV therapy is considered more effective. During and after treatment it will be necessary to take tests to avoid relapses.
The entire therapy process is carried out on an outpatient basis.
The tactics of diagnosis and treatment for HIV boils down to the fact that the patient is simultaneously observed by a venereologist and an infectious disease specialist.
People infected with HIV are at greater risk of contracting HPV due to decreased immune defenses.
Therapy and preventive measures
It happens that anogenital warts and other pathological changes caused by the papilloma virus go away on their own, without any treatment. However, in most cases, treatment of visible changes requires medical intervention. Venereologists recommend for this:
- Do cryotherapy (freezing warts).
- Use creams and solutions against warts.
- Perform laser removal of visible changes.
- Perform electrocoagulation and radio wave therapy of pathological growths.
- Use surgical treatment.
In cases of precancerous conditions and detected malignancy, more radical surgical treatment is performed, which is often recommended to be done with radiation or chemotherapy.
Surgery is recommended with radiation or chemotherapy if the condition is precancerous.
Unfortunately, no modern antiviral drug (Isoprinosine, Condilin, etc.) can guarantee complete elimination of the papilloma virus, and the virus continues to live even after their use. Therefore, preventing infection with human papillomavirus remains a more effective means of combating HPV than treating it. You can exclude the cause of infection in the following ways:
- Use a contact method of contraception (condom).
- Be selective in choosing sexual partners.
- Be faithful to your sexual partner.
Methods for removing external manifestations of HPV 16 and their effectiveness
Previously, it was believed that removal of papillomas and condylomas guaranteed the complete destruction of the papillomavirus.
In fact, this is not entirely true; pathogens are removed along with the growths, but HPV remains in the body and continues to destroy it.
Various surgical techniques are used to remove growths:
- cauterization of growths with liquid nitrogen;
- laser therapy;
- radio wave treatment;
- excision of the tumor with a scalpel.
To remove papillomas and condylomas when affected by HPV type 16, the use of a scalpel is considered more effective.
If this type of papillomavirus was previously confirmed, then after excision of the growth an oncocytological study of the removed tissue should be performed.
Excision with a scalpel is the most optimal option for obtaining biomaterial for testing for the presence of a cancerous tumor.
How to recognize the type of virus yourself
It is impossible to reliably determine, without laboratory tests, which type of papillomavirus caused the growth of condylomas in a particular case. However, this can be suggested with a certain probability based on clinical manifestations:
- HPV type 16 often affects the glans penis and the skin next to it, the anus area. The number of condylomas is quite large in comparison with the affected area (from 5 to 15 in one area of skin); sometimes confluent plaques form due to the close proximity of papillomas. The appearance of Queyra's erythroplasia is the only reliable sign of the presence of HPV type 16, but it develops extremely rarely.
- HPV type 18 most often affects the epithelium of the skin, weakly affecting or not affecting the head and anal area at all. Pointed warts are located at a sufficient distance from each other, their total number rarely exceeds 20 pieces. The development of Bowen's disease is not a characteristic feature, because its development may be facilitated by other types of virus.
The final diagnosis is established only after testing for the presence of types of papillomavirus.
How to treat HPV 16
To date, there is no medicine that can completely destroy the virus.
But it is possible to stop the proliferation of pathogenic flora and prevent infection of new cells.
Areas affected by growths can be removed using modern methods of excision of tumors.
Medicines used to treat HPV type 16 in men and women can be divided into groups:
- Drugs that have a cytotoxic effect cause disruption of mitosis. Serve for local effect on the skin (it is better not to use on the mucous membranes of the genitals).
- Means for chemical destruction. Also used locally, they serve to destroy tissues affected by papillomavirus. When using, you must be careful, as the effect of the drug on the skin may cause scars.
- Antiviral drugs. They contribute to the disruption of viral DNA synthesis and also stimulate local immunity. Cream and injections can be used. Antiviral treatment should be one of the components of complex therapy, since monotherapy may not produce any effect.
- Immunological drugs. Used to enhance the immune response, thereby reducing the duration of therapy.
- Prescription of antiseptics. They act effectively locally against concomitant infections; they have little effect on the virus itself.
- Vaccination.
Therapy must be strictly individual.
The regimen and duration of drug treatment is determined by the doctor.
Two weeks after the end of the course, the patient is asked to take control tests.
Etiology of the disease
HPV type 16 infection in men affects the outer epithelial cells and inner mucous membranes. There are 2 types of papillomas.
Infections by the papilloma virus of internal organs are rare and may be a congenital or hereditary pathology. The virus is dangerous due to its ability to integrate DNA into the chromosome at the cellular level. It will exist in the form of a micro-inclusion.
A type of dermotropic papillomas is unfavorable; the infection provokes cell changes, leading to gene mutation. The consequence of the processes is uncontrolled divisions, leading to the formation of cancer cells.
HPV DNA suppresses the immune system of cells, destroying their ability to resist viral infections and tumor activity.
Review of antiviral drugs for HPV 16
Before prescribing an antiviral drug to a patient, the doctor must decide whether there is a need for their use.
Cycloferon, Panavir and Viferon are prescribed strictly according to indications, the mechanisms of action of which are similar.
✔ Viferon
The drug is used in the form of a gel, ointment or suppositories, depending on the location of the growths.
Has an immunomodulatory effect.
Viferon is prescribed to prevent relapses of viral infection.
✔ Panavir
The drug is prescribed in the form of injections or gel.
The drug is of plant origin. it has antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects.
The use of Panavir is very convenient, it is well tolerated and does not produce side effects even with prolonged use.
✔ Cycloferon
This is a powerful antiviral and immunomodulatory drug.
Release form: ointment, tablets, solution.
If necessary, any form of the drug can be used.
How is the effectiveness of HPV 16 treatment monitored?
After removal of the tumors, you will need to be observed by a specialist for some time.
When and by whom are control tests prescribed?
During the course of therapy and at the end of treatment, the attending physician prescribes tests to determine the effectiveness of the drugs.
How often and what types of examinations should the patient undergo?
Over the course of several months, the patient must undergo a series of tests:
- Take an immunogram. What indicators are used to evaluate results? The analysis should show a gradual decrease in the concentration of specific antibodies.
- Daijin test or PCR to determine the viral DNA titer.
- Control smears after treatment.
All of the above examinations are necessary to ensure that oncological complications do not develop.
If tests after the course do not show the patient’s complete recovery, the doctor will most likely prescribe re-treatment.
Treatment methods
It is worth emphasizing that the papilloma virus itself cannot be eliminated from the body. All treatment methods are aimed at indirectly suppressing it, restoring normal functioning of the immune system and eliminating emerging skin lesions.
The following methods are used to remove condylomas and papillomas:
- Cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen;
- Radio wave destruction;
- Laser destruction;
- Diathermocoagulation;
- Removal using chemicals.
All these methods are quite effective; the doctor makes the choice based on the examination results and available equipment.
It is highly not recommended to use traditional methods and remove formations at home. This can lead to injury and chemical burns. In addition, without tests, it is impossible to unambiguously determine the nature of the tumors, so the consequences can be even more dire.
As already mentioned, treatment for HPV must be comprehensive. For this purpose, antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy is used.
Drugs such as Isoprinosine, Grosprinosin, Imiquimod, Panavir and others help suppress the papilloma virus. Various interferon-based drugs (injections, tablets, suppositories, ointments) are prescribed as immunomodulators.
In addition, the attending physician may recommend a vitamin-mineral complex and herbal remedies (tincture of echinacea, ginseng, lemongrass, rose hips) to increase the body's defenses.
In which institutions is HPV treated?
HPV belongs to the group of sexually transmitted diseases, so patients infected with papillomavirus are treated by a venereologist.
To undergo diagnosis and treatment, you must go to a skin and venereal disease clinic, but a visit to a private doctor is not excluded.
Why is HPV 16 dangerous for men?
Human papillomavirus infection poses a danger to any person, regardless of gender.
When infected with HPV type 16, the following may develop:
- cancerous and precancerous lesions of the anal area
- cancer of the head of the penis
- papillomavirus infection can have a negative effect on potency
- erectile dysfunction, ejaculation
- infertility
Side effects and complications of treatment
The most common complication is the use of vaccination. Among the most common complaints:
- pain at the injection site during vaccination;
- headache
Prevention of complications
Since the percentage of complete cure for HPV tends to zero, the best preventive measure would be to monitor tumors in order to prevent the development of cancer.
The formation of malignant tumors in almost 100% of cases is associated with papillomavirus type 16.