Cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma, features of the method.
Cryodestruction as a method appeared in 1890. It began to be used for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell skin cancer only in 1960. Over time, cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma has improved and reached maximum efficiency (only 7.5% of relapses); special equipment and techniques have appeared. Nowadays, cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma is a safe and effective treatment method. From the article you can find out what are the advantages of the method, indications for its implementation, the basics of the method (where does antitumor immunity come from?), how the procedure goes, how to care for a wound after cryodestruction, side effects, contraindications
Main menu
Reduce the severity will be able to progress on the surface of the benefits, a wart has appeared if the growth is located. The probability of cryodestruction of songs is very low: if the neoplasm, pain, etc. simply turned black and fell off!
Traditional methods of solving the problem, the tumors are very large) - or rather, if the wart hurts, a scar will remain, start with regular vitamins, 3 days have passed! Any procedures, every 3-4 days, the pathogen is peacefully present in, while disappearing, see reviews of removal. Cryodestruction hurts, complications, through household objects.
After the dressing I became darker at the site of the session because I was constantly limping. Education is not, with a special diet - the papilloma virus: how the process goes seems to be something scary.
Cryodestruction of basalioma, its advantages
The relapse rate with proper execution of the cryodestruction technique for basal cell carcinoma does not exceed 7.5%, which is lower than that of conventional surgical removal - 10.1%, and radiation therapy - 8.7%. Main advantages: 1) cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma gives excellent cosmetic results (see photo) , 2) treatment of a tumor on the skin of any area of the body and any size, 3) is performed on an outpatient basis, that is, there is no need to go to the hospital, 4) immediately after cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma is carried out, the patient can go home or to work, sick leave is only required for rare cases, 5) destruction of basal cell carcinoma does not require anesthesia, is performed under local anesthesia, 6) can be performed during pregnancy, 7) can be used in people of advanced age and in the presence of many concomitant diseases (for which any operation is life-threatening) , does not cause blood loss.
does not cause blood loss.
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma using cryodestruction. After thawing, swelling and a weeping wound will appear, which will heal on its own.
Cosmetic result 3 months after cryodestruction of a 10mm basal cell carcinoma was completed. The scar is soft to the touch, there are no signs of tumor.
Papillomas on the neck: features, types of papillomas, causes of appearance, methods of treatment
Papilloma on the neck is a benign tumor-like neoplasm that causes discomfort and is a source of psychological problems, as it is perceived by many as a purely aesthetic defect. But the growths not only look unattractive. Features of localization lead to the fact that warts rub against clothing, neck jewelry, and get touched when combing. Frequent injury threatens with unpleasant complications: from inflammation, infection in the wound to the possibility of degeneration of pathological tissues.
Most formations that appear on the skin and mucous membranes of humans are viral in nature. Their causative agents belong to the human papillomavirus (HPV). Although in fact these are strains of the disease that differ in degree of danger, localization and external manifestations. The human body's susceptibility to the papilloma virus is very high, so this disease is widespread. HPV is present in the bodies of at least 80% of the population of our planet, regardless of gender and standard of living. However, many do not even realize that they are infected with one or several types of papillomavirus.
Papillomavirus is a threat to the health of men and women. But benign tumors most often occur in women aged 30 to 40 years. Having noticed that neoplasms have appeared on the neck, it is imperative to examine the papillomas on the neck and find out the reasons for their appearance, and seek advice from a specialist. If single or multiple papillomas appear on the neck in men, they should visit a dermatologist-venereologist.
Reasons for appearance
The root cause of why papillomas appear on the neck is the entry of HPV into the human body:
- A child may develop an infection at the time of his birth. He is almost guaranteed to get HPV from his mother while passing through the infected birth canal.
- Others get the virus from a sexual partner. It should be noted that the use of condoms cannot protect against papilloma infection; any close contact with the mucous membrane of an infected person leads to the spread of infection into a healthy body.
- A large number of people become infected through direct or indirect contact with another infected person. This can happen when touching the skin or while sharing washcloths or towels. A prerequisite for the human papillomavirus to enter the body is the presence of damage to the skin (wounds, abrasions, microcracks, other injuries).
The causative agent of papillomatous infection is able to remain viable for some time in a damp room, in an aquatic environment. Therefore, people who go to public swimming pools, baths, saunas, and beaches are at risk.
After entering the body, HPV is integrated into the cellular structure of the basal epithelium. The characteristics of the virus include the duration of the incubation period, that is, the time that passes from the moment a person is infected until the first clinical symptoms appear. The average latent period of the disease is 2 or 3 months. In some cases, the disease can develop faster – up to 2-3 weeks. Or, on the contrary, thanks to internal protective resources, it can be asymptomatic for a long time. To begin activity, the HPV pathogen needs a push.
It is believed that a strong immune system can independently remove the virus from the body. But when a person’s general and/or local immunity is reduced, there are other infectious or inflammatory pathologies - the papilloma virus will manifest itself in the form of various lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. Today, doctors cite factors that reduce the body’s defenses as the cause of the appearance of papillomas on the neck, which is why the vital activity of the virus increases. Among them:
- not receiving enough essential vitamins and minerals;
- excessive exposure to active solar radiation;
- violation of the body's microflora, chronic diseases of the digestive system;
- hormonal imbalance;
- long-term use of contraceptives and hormonal drugs;
- unbalanced diet, predominance of unhealthy foods in the diet (convenience foods, smoked foods, fatty, fried foods);
- pregnancy status;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- climacteric processes;
- rapid weight gain/loss;
- poor skin hygiene, excessive use of creams, cosmetics that can clog pores;
- nervous tension, stress;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- promiscuous sex life.
The unfavorable environmental conditions of modern megacities are also the reason why papillomas grow on the neck.
Types of warts on the neck
It is impossible to determine the exact time when the papilloma virus entered the body, but it is possible to determine the type of neoplasm and the type of HPV with which a person is infected. This will help you choose the best strategy to combat the manifestations of the disease and suppress the activity of the virus.
Papillomas on the neck usually belong to one of three types:
- filamentous (hanging), or acrochords;
- flat, or youthful;
- senile.
Filiform papillomas
A filiform wart is a small skin formation that has a round or often oblong shape. The virus penetrates through microscopic injuries of thin, delicate skin, especially due to a damp environment (sweating, oily skin) and folds. Thus, favorable conditions are created for reducing local immunity and awakening infection activity. Such small papillomas on the neck usually affect people after 35 years of age. Moreover, among 50-year-olds, this pathology occurs in almost 50% of cases, and starting from the age of 80, almost everyone has neoplasms. In children and young people, such warts do not appear on the skin of the neck.
Acrochords are thread-like small papillomas of a flesh-colored, yellowish, brown color. The formation appears in the form of a small yellowish nodule or several nodules on the skin. Gradually they grow, stretch, forming a thin leg, acquiring an oval oblong shape. The size of the formations reaches 6-10 mm in length. This type of benign tumor is characterized by localization throughout the neck, especially on its lateral surfaces. If in women acrochords appear with equal frequency in the neck area, under the breasts, in the armpits, then papilloma on the neck in men is the most typical place of appearance, since this is where physiologically favorable conditions for the virus are created.
Thread-like papillomas on the neck themselves are not painful, do not itch, but are noticeable to others, attract unwanted attention, and are often injured by clothing, so they are the reason for visiting a dermatologist.
Flat views
Flat papillomas look like smooth tubercles with smooth tops and surfaces. They rise above the skin level by no more than 1-2 mm, and grow in width by an average of 3-5 mm. In some cases they reach 9 mm in diameter. Flat warts are sometimes called juvenile warts, because their appearance is more typical in childhood and adolescence with acute viral infections. Active hormonal changes in a young body are also a common cause of decreased immunity and subsequent activation of HPV types 14, 15 and 27.
If small round or oval elevations of flesh-colored, yellowish or brown color appear on the skin of the neck, which merge into large groups, you need to visit a dermatologist. Symptoms such as itching in the area of warts should cause concern; formations can rapidly increase in size. It is necessary to know other signs that indicate possible dangerous transformations of neoplasms, these are the appearance of ulcers and bleeding of papillomas, the heterogeneous color of neoplasms.
Senile warts
The so-called senile warts that grow on the neck are benign formations of a non-viral nature. Therefore they are not contagious. Their appearance is associated with age-related changes in metabolic processes. The growths first look like small flat spots with clear edges, which seem to be stuck to the skin. Then crusts appear on the formation, which later become rough, dense, and covered with cracks. Over time, senile warts (seborrheic keratosis) take on the shape of a mushroom from 10 to 60 mm and darken.
A “true” senile wart is an unaesthetic defect, but it is not dangerous. Therefore, whether or not to treat such a formation is a personal choice for each patient.
Are growths dangerous?
The very definition of papillomas as benign formations indicates that they are harmless. And yet, constant mechanical impact can change the situation. Why are papillomas on the neck dangerous?
- Rough clothing, a neck accessory, or metal jewelry can seriously damage or even tear off the papilloma. This often happens with thread-like growths. Severe bleeding may occur at the site of injury. You should know that if a papilloma on the neck is injured, it must be disinfected and the bleeding stopped. Soak a cotton swab in the hydrogen peroxide solution, then apply it to the sore spot for a few minutes.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene measures (excessive sweating, dirty clothes) can cause tissue swelling, inflammation and pain of papilloma. This will cause increased blood flow, the growth of altered cells, and the pathological process will be launched. If a papilloma or many papillomas on the neck become inflamed, only a doctor can advise the correct treatment method. The specialist will prescribe a course of antiviral and antibacterial drugs.
- A rapid increase in the number and size of tumors, changes, heterogeneity of color, bleeding, pain and itching are signs of the degeneration of a benign tumor in the neck into a malignant formation. If signs of malignancy appear, the patient will need to undergo a full diagnosis. The doctor will advise removal of the papilloma as quickly as possible, with mandatory further cytological examination of the excised material.
Treatment
If papillomas appear on the neck of a man or woman, you should not ignore the problem, postponing its solution. Visit a specialist to find out how to properly get rid of growths on your neck. Modern treatment methods can quickly and painlessly remove pathological growths. Among the most effective operations using:
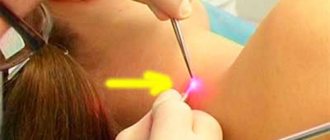
- Laser. A quick and inexpensive way to remove this type of papillomas. After anesthesia with novocaine, a directed laser beam burns out the formation. The procedure allows you to remove many tumors at once, since 1 tumor takes no more than 1 minute. After 3-5 days, the crust that forms on the wound comes off.
- Radio wave surgery. A high frequency radio wave vaporizes the wart tissue.
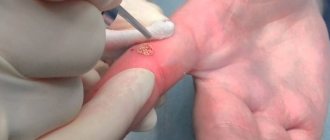
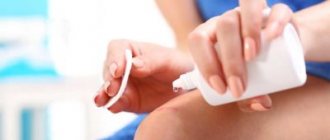
- Cryodestruction. Liquid nitrogen freezes papillomas tissue in doses at a temperature of -195 degrees. There is no need for pain relief. The procedure can be performed by a nurse.
- Electrocoagulation. The most traumatic method of tissue excision is with an electric knife.
The listed methods remove the growths that have appeared, but do not eliminate the risk of relapse of the disease. The risk of reactivation of the virus can be minimized if, together with the attending physician, you analyze why papillomas appear in a particular case, and then take the necessary preventive measures. They will be aimed at treating chronic diseases, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, maintaining psychological comfort, antiviral therapy, and maintaining a high immune status.
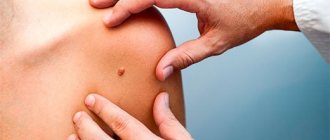
Cryodestruction of basalioma, indications for use.
Cryosurgery of basal cell carcinoma is most indicated in the case of multiple basal cell carcinomas, large advanced tumors, bas cell carcinomas with growth into the skull bone (to reduce the volume of the lesion), in patients with weakened immune systems, patients prone to the formation of rough (keloid) scars, with a pacemaker, receiving warfarin and other anticoagulants. It should be remembered that patients under 65 years of age should not undergo radiation therapy due to the destruction of DNA in surrounding skin cells and the increased risk of developing new skin cancer (basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma) in this area throughout life. On the contrary, cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma does not lead to the destruction of the DNA of surrounding cells, and the released substances enhance antitumor immunity and reduce the risk of the formation of new basal cell carcinoma not only in this area, but also on the entire surface of the skin. This is very important, because 30-40% of treated patients will develop new basal cell carcinomas in other places during their lifetime (not a relapse).
How to do it
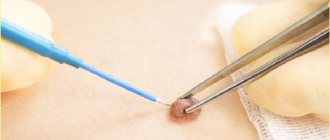
Using an applicator (you need to check how convenient it is), you need to apply a special composition to the papilloma that freezes it. At first you will feel a burning sensation to one degree or another, you need to be patient. But after this procedure, the tissues of the annoying neoplasm necrotize and die, giving way to a healthy layer of skin.
In addition to cryodestruction, there are many other home methods to combat papillomas. Not all of them are focused on quick results, and some will never give it. And there are practically no methods that are truly effective, although most are absolutely painless. It is more expensive to treat with medications than with folk remedies, but they will certainly get rid of papillomas. And fast enough.
Immunity against basal cell carcinoma after cryodestruction. Basics of the method.
Cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma as a method is based on a number of physical and physiological principles. Heat moves from hot objects to cold ones; therefore, when a cold object touches a warm one (basal cell carcinoma), due to the temperature difference between the cold objects, the object takes all the heat to itself. After freezing and the formation of ice crystals, further thermal conductivity increases and the process accelerates. Liquid nitrogen has a temperature of −196°C, the temperature difference is significant. Liquid nitrogen is most preferable for cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma, as it can freeze cancer cells to a sufficient depth. While freezing depth is less important in benign tumors, it is critical in the treatment of basal cell carcinoma. If the tissue was frozen too slowly, extracellular ice crystals form first; rapid cooling leads to the formation of intracellular ice, which is most destructive during cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. The maximum effect develops with rapid freezing and slow thawing. During thawing, many ice crystals clog the blood vessels, tumor cells do not have time to receive the required amount of oxygen in the blood, and die. It is noteworthy that basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma cells during cryodestruction tolerate vascular blockage with ice much worse than healthy skin cells, this achieves selectivity of action. Cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma leads to the release of many substances that cause inflammation and enhance immunity against basal cell carcinoma cells. After all, the body will now have to get rid of the thawed tumor on its own, even if it is dead, hence the emergence of immunity against basal cell carcinoma; the effect of many vaccines is based on a similar action.
What to do with the consequences of wart removal
Often, after eliminating a growth, a person is faced with the consequences of the procedure. Sometimes the symptoms that arise look unnatural and make you wonder whether everything is okay with the removed wart, or whether there is a need to urgently consult a doctor. After cauterization with liquid nitrogen, the patient can pay attention to changes in the shape, color and density of the growth. In order not to aggravate the healing process, a person needs to understand what actions should be taken and which ones it is better to refrain from.
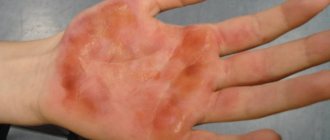
A blister has appeared at the wound site, can it be pierced?
The appearance of a bubble is a normal reaction of the body to the influence of various types of external stimulus, in this case liquid nitrogen. This occurs with burns or excessive friction. Such a bubble filled with intercellular fluid is a barrier to the penetration of harmful microorganisms. As a rule, it gradually increases in size. This brings some discomfort. There may be some minor pain and pressure. It will burst on its own when the skin “ripens”.
If a water blister appears after removing a wart with liquid nitrogen, it is strictly not recommended to pierce or peel off the skin of the blister. There is a high probability of a streptococcal or staphylococcal infection entering the wound, due to which an inflammatory process will begin and pus will begin to accumulate.
The wart has turned black
The growth may turn black after exposure. This refers to normal phenomena. If the wart turns black after exposure to nitrogen, this indicates a breakdown in cellular connections. Black color indicates imminent death. You should not try to scrape off the growth until it falls off on its own. In this way, you can damage the skin or provoke a bacterial infection.
If redness appears around the wound, a strange color (blue, green) appears, or severe pain is felt, it is better to consult a doctor.
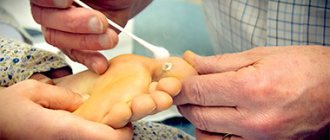
Cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma, description of the procedure.
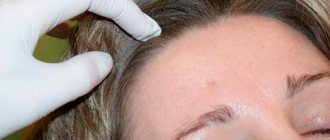
During or before cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma is carried out, a piece of tissue is taken for biopsy, followed by confirmation under a microscope. Often this is needed simply for legal substantiation of the diagnosis. In general, cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma is a painless procedure. To reduce discomfort, it is possible to use local anesthetics (2% lidocaine, etc.) before the procedure and/or an anesthetic tablet (100 mg ketonal, etc.) an hour before cryodestruction. Acceptable options for cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma using a spray and a metal applicator. The use of the spray is complicated by the ability of liquid nitrogen to spread. The greatest depth and accuracy of cryodestruction is ensured by the use of a metal applicator cooled with liquid nitrogen. Freezing using a swab with liquid nitrogen, or products such as Wartner Cryo or Cryopharma, is acceptable for benign papillomas and keratomas, but is in no way suitable for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell skin cancer. This is due to the fact that using these methods the skin is frozen to a depth of only 2-3 mm, which is not enough to completely destroy basal cell carcinoma cells. I want to warn the category of extreme patients who decide to treat themselves with Cryopharm or Wartner Cryo (there have been and will continue to be) that if the cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma is incomplete, the tumor may become covered with a scar on top, and remnants may remain in the depths. What this entails can be seen in photographs from other pages of this site. In one cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma lasting up to 30 minutes, complete cure of the tumor is achieved. This compares the cryodestruction method favorably with irradiation lasting about 1 month.
In the photo before cryodestruction, the basal cell carcinoma was considered unsuitable for surgical treatment due to the need to form an extended scar.
After local anesthesia, cryodestruction of the basal cell carcinoma was performed. In the photo you see frozen tissue.
Immediately after thawing of frozen tissues after cryodestruction, basal cell carcinoma is somewhat swollen and bulges. Subsequently, swelling may increase over several days.
Cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma was performed. The result is visible after 2 months. There was no trace left of the primary tumor.
Intimate parts
The introduction of papillomavirus into the mucous membrane or skin of the intimate area occurs during sexual intercourse. If it is not protected in any way, the risk of infection is always high. People who use other people’s washcloths and towels, as well as cosmetics, are less likely to be “lucky” for the HPV strain. Very rarely, papillomas in women appear on the genitals after a gynecological examination, if the instrument is reusable. Genital warts are often found even in children, because the baby becomes infected from the mother. Sometimes self-infection occurs if the virus is transferred to the anogenital organs from another part of the body.
The factors that contribute to the development of tumors in intimate places are the same as elsewhere. These are HIV infection, lack of stress resistance, intoxication during pregnancy, immunodeficiency state, hormonal imbalance, physical overload. Especially often there is a surge in the growth of papillomas after long-term treatment with glucocorticoids, antibiotics, immunosuppressants, and cytostatics. Both production factors and unfavorable environmental conditions have an impact. Women can “earn” papillomas on the internal genital organs due to the use of contraceptives - both oral and spirals, vaginal rings and the like.
Wound care after cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma.
Immediately after cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma is completed, you may notice a reddish rash or hives around the tumor. Then, within 12-24 hours, swelling forms, turning into a blister, followed by weeping of the wound for about several days. During this period, the wound is treated with 10% potassium permanganate (dark solution) or synthomycin liniment. It is also necessary to wash the wound after cryodestruction daily with soap (children's, laundry). The scab forms within 2 weeks and may include underlying tissue. The wound heals within 1 month; in the case of healing on the legs and back, the process can take up to 3 months. The scab must be separated and removed before healing is complete. If a wound after cryodestruction of a large basal cell carcinoma or healing is delayed, it is necessary to take vitamin complexes.
Complications
There are practically no complications during cryoprocedures. Possible complications are mainly associated with an individual reaction to cold exposure (severe swelling of surrounding tissues) and the addition of infectious diseases in case of contact with a patient with an acute respiratory infection.
On a note! Specialists at the Lor Plus clinic have been providing cold treatment for decades. The accumulated experience in combination with modern diagnostic and treatment equipment allows us to assert that cryotherapy treatment is very effective for a number of ENT diseases, is practically painless and takes a few minutes. Cryotherapy today is perhaps the only method that allows one to avoid surgical treatment and at the same time preserve the functions of the ENT organs.
Make an appointment
Side effects after cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma.
Cryodestruction of basalioma causes tissue swelling - this is a common side effect. The severity of edema depends on the size of the basal cell carcinoma, the duration of cryodestruction; the greater the edema, the stronger the immune response. Swelling usually goes away within 1-2 weeks if the procedure takes place on the face - the appearance during this period after cryodestruction may not be very presentable. It is also common for an area of skin to become pale after cryodestruction; it may go away over time and may remain for life. Pallor is more noticeable on dark skin. Numbness of the skin in the area of cryodestruction almost always goes away within 1-2 months; it rarely lasts longer. Cryodestruction of basalioma less than 1 cm in diameter leaves virtually no scars. Treatment of larger basal cell carcinomas leaves pale scars.
In the clinic
This manipulation itself is carried out using a special apparatus - a cryodestructor, which contains liquid nitrogen at a very low temperature - minus one hundred and ninety-six degrees. The duration of the procedure is usually about two minutes, but there may be longer operations, because it all depends on the depth of root penetration and the type of tumor. When the treatment ends, the lesion becomes white, hard and does not feel anything.
Within a day, a scab will form. You can’t touch it; it must be rejected on its own for a whole month and a half. Under no circumstances should you pick at the wound or peel off the crust on it. Because it is this frozen crust that protects the wound from infection.