Growth on the wall of the throat
Growths on the wall of the throat can have different origins, and some of them are indeed quite dangerous formations.
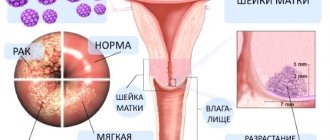
So, such a condition is a good reason to visit a doctor. For example, carcinomas mainly affect the back wall of the pharynx and tonsils, although they can also occur on the soft palate. Dangerous Sarcomas are located on the lateral walls of the pharynx and tonsils, and lymphoepitheliomas cover the pharyngeal lymphadenoid ring.
Malignant formations in the oropharynx are observed mainly in elderly patients, however, sarcomas can especially affect young people and even children.
Symptoms of the growth
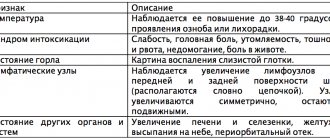
The onset of malignant growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma is usually not accompanied by any special signs, and the initial symptoms may be a feeling of awkwardness when swallowing, fullness and other unpleasant sensations that occur when eating. At the second stage, spontaneous pain in the throat occurs, radiating to the ear and jaw, increased pain when swallowing, and a change in the timbre of the voice. Then the tumor continues to grow, and the pain becomes stronger, saliva and phlegm already include streaks of blood, and a putrid odor from the mouth is felt. The severity of the symptoms depends on the location of the tumor. Some patients develop cervical lymphatic metastases.
Of the sarcomas, the pharynx most often affects lymphosarcoma, which is considered a disease of the young. Most often, lymphosarcoma is observed on the pharyngeal lymphadenoid ring.
At the same time, the affected tonsil is enlarged already at an early stage, it has a nodular surface and a very soft consistency. It is easy to notice by its bright color with a bluish tint. Some types of lymphosarcoma ulcerate very early.
Lymphosarcoma leads early to regional metastases. Sometimes lymphosarcoma affects both tonsils. In this case, you should rather think about leukemia or general lymphosarcomatosis.
Types of benign throat tumors
A benign tumor of the throat originates from various tissue structures. These structures can be nerve endings and nerve trunks, blood vessels, lymphatic channels, connective tissue, cartilage, glandular components of the mucous membranes, etc. Tumors of the larynx can be congenital or acquired.
Most often in otolaryngology the following types of benign tumors are diagnosed:
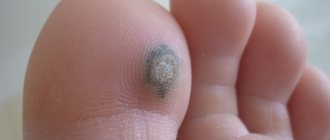
- laryngeal fibroma - single tumors of connective tissue origin, ranging in size from 0.5 to 1.5 cm, usually spherical in shape, located in the upper part or free edge of the vocal fold.
The surface of laryngeal fibromas, photos of which can be seen below, is smooth, gray in color, if there are many blood vessels in the structure of the neoplasm, it will be red in color:
- Laryngeal papilloma is a hollow single, less often multiple, mushroom-shaped growth with a wide base. Tumors of this type have a finely lobulated structure and are very similar to cauliflower.
Papillomas in the throat, photos of which are presented below, are whitish or pinkish in color:
If the neoplasm is very intensively supplied with blood, the color will be dark red. Typically, papillomas in the throat are localized on the vocal folds; sometimes the process can spread to the trachea, epiglottis and subglottic region;
- polyps are a separate type of fibroids; in their structure, in addition to connective tissue fibers, there are cellular elements and fluid. They can reach the size of a large pea, have a wide base, a thick stalk and a less dense consistency than fibroids. Polyps are most often localized in the anterior part of the vocal folds.
- angiomas are single tumors of vascular origin, in most cases congenital. Hemangioma of the larynx, consisting of vessels, is red in color, and can grow into neighboring tissues. Lymphangioma of the larynx is a tumor of the lymphatic vessels, is yellowish in color and is not prone to proliferation.
Less common are chondromas of cartilage tissue, cysts, lipomas (fat formations) and neuromas (nerve tumors).
Pharyngitis
However, the cause of some formations in the throat can also be pharyngitis, which is a chronic or acute inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa.
It is difficult to independently diagnose pharyngitis, although the disease has some characteristic signs. For example, pain when swallowing is typical, when swallowing saliva is more painful than food. The temperature with pharyngitis is slightly elevated. The voice quickly gets tired, and changes in its timbre are noticeable. Pharyngitis is usually accompanied by a runny nose. This combination of symptoms requires mandatory treatment.
The doctor can already notice a growth on the wall of the throat ; these are individual follicles in the form of red grains, and the entire pharynx is covered with purulent mucous secretion. Chronic hypertrophic pharyngitis is characterized by enlarged groups of follicles on the posterior wall.
Symptoms and diagnosis of benign throat tumors
The most common and main complaint of patients who have benign laryngeal tumors is a change in voice, which in the presence of such tumors in the throat becomes hoarse or hoarse.
If the detected tumors have a long stalk, then among the symptoms there is also frequent coughing, and voice changes are intermittent. In the case when the neoplasm is localized in the area of the vocal cords, thereby interfering with their closure, aphonia is observed, i.e. complete absence of voice. Large formations often cause difficulty breathing and even cause asphyxia.
Most often, small laryngeal tumors are asymptomatic, do not interfere with the closure of the vocal cords, and are accidentally discovered when examining a person for another disease. Diagnosis of laryngeal tumors is carried out by an otolaryngologist; it includes procedures such as laryngoscopy, endoscopic biopsy and subsequent histological examination.
Treatment of malignancy
Treatment of a growth on the wall of the throat is pointless without eliminating its causes. And we should not forget about weakened immunity.
First of all, you should gargle with a decoction of medicinal herbs, which can have an anti-inflammatory effect. These include sage, chamomile, calendula, eucalyptus, but pharmacies also sell infusions specially formulated for rinsing. In addition, do not forget to take medications prescribed by your doctor.
Acute bacterial pharyngitis is treated with antibiotics, mainly penicillin, and the entire course must be completed very carefully and completely. In this case, you should take means to restore microflora and vitamins.
Viral pharyngitis is treated symptomatically, and again, herbal decoctions are used. They also gargle with warm antiseptic solutions, for example, furatsilin and iodinol, every half hour to an hour. Your doctor should prescribe immunomodulators to you.
source
Treatment of hemangiomas and lymphangiomas of the larynx
Tumors of vascular origin (hemanginomas and lymphangiomas) are removed in several ways, and the choice of method depends on how widespread the tumor is, as well as the nature and intensity of its growth. Local hemangiomas, characterized by exophytic growth, are first excised, and then anti-relapse treatment of the affected area is carried out using laser irradiation, diathermocoagulation or cryotherapy. In case of endophytic growth and widespread nature of hemangiomas, the method of sclerosis or occlusion of the vessels feeding the tumor is used.
Treatment of papillomas in the larynx is the most difficult task. Surgical intervention in the treatment of papillomas in the throat consists of excision of areas of the mucous membrane that are changed as a result of the proliferation of papillomas. It is carried out using a special surgical microscope, which allows you to accurately identify the boundaries of diseased and healthy tissues.
If you have questions for your doctor, please ask them on the consultation page. To do this, click on the button:
Causes of white growths in the throat and treatment methods
Various tumors in the throat can spontaneously appear and disappear, like warts. Some growths are malignant. If you have a white growth in your throat, it could be caused by bacteria or fungi living in your mouth. If the outgrowths are formed from the epithelial tissue of the throat, then the cause may be genetic malfunctions in the body. In any case, such a formation in the throat cannot be ignored, since the possibility of a malignant tumor cannot be excluded.
Benign tumors of the larynx: types, symptoms and treatment
Benign tumors of the larynx quite often cause the development of stenosis, persistent cough and difficulty breathing. These neoplasms are characterized by slow growth, non-invasive course, absence of ulceration and metastases. Symptoms of a benign tumor of the larynx may not be observed, so its discovery sometimes comes as a complete surprise to a person and a reason for worry. According to medical statistics, they most often occur in men.
Prevention
For preventive purposes, it is necessary to promptly treat any diseases of the oral cavity, nasopharynx and sinuses. The transition of an acute infectious process into a chronic one should not be allowed.
If a white coating appears on the throat or white lumps on the tonsils, you can use rinses with medicated antiseptic solutions or folk remedies. It is recommended to chew propolis or use a tincture of this rinse. It is useful to drink tea with lemon, chew a slice of lemon along with the peel, and also use onion-honey syrup. Aloe juice is indispensable in the prevention of growths in the throat. It is also an immunomodulator and strengthens the body's defenses.
source
Causes
Before treating a growth in the throat, it is necessary to identify the causes of its appearance. Many people do not know why the growths appear and whether the disease is contagious.
Factors provoking the disease are:
- contacts with infected patients;
- use of personal belongings of people with HPV;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- frequent colds;
- hormonal imbalance;
- alcohol abuse;
- long history of smoking;
- regular use of hormonal drugs and contraceptives;
- frequent use of antibacterial drugs;
- violations of oral hygiene;
- infectious diseases;
- diseases of the nasopharynx;
- papillomas in the nose;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- dietary disorders;
- papillomas on the face;
- allergic reactions;
- chronic stress;
- papillomas in the mouth and on the oral mucosa;
- functional disorders of the nervous system;
- damage to the oral mucosa during pregnancy;
- visiting baths and saunas;
- papillomas on the lips;
- laryngeal papillomas in children appear when passing through the birth canal if the mother is infected;
- use of tracheotomy.
The appearance of growths in the throat should be a reason to contact a dermatologist, allergist or oncologist.
Yellow bumps on the throat
Pimples in the throat can scare anyone. The formation of inflamed or purulent tubercles indicates that it is time to go to the doctor and find out what’s wrong. The main reason for their appearance in this area, as doctors note, is infections. A rash is not an independent disease; it is a frequent companion to ENT diseases.
Rashes that affect the throat come in different shades, sizes, and differ in location. Sometimes they cause pain, soreness, and a feeling of discomfort, but sometimes they give no sensation at all. Why do tubercles appear, what diseases are they characteristic of?
Pimples in the throat are one of the signs (not mandatory) of these viral infections, along with a dry cough, rhinitis, general malaise, and fever.
Scarlet fever
The causative agent of the disease is group A streptococcus.
In a child (children aged two to ten years are most often affected), purple pimples in the throat can be a symptom of this acute infectious, contagious disease. Its causative agent is group A streptococcus, a “representative” of the type of bacteria that is most virulent for humans. When it gets on the mucous membrane, it produces the poison erythrotoxin, which spreads throughout the body with the blood, destroys red blood cells, causes general intoxication, dilation of small vessels and, as a result, the appearance of characteristic rashes on the epidermis and mucous membranes.
Allergy
Such a reaction of the immune system to any irritant is characterized by red pimples in the throat, or more precisely, on its mucous membrane. This happens quite often. This nature of small formations is indicated by the absence of signs of infection (fever, general malaise).
In adults, the appearance of pustules with this disease is extremely rare; in young patients, on the contrary, it is common. In addition to a swollen throat, fever and headache, the disease is characterized by yellow and white spots on the tonsils.
Sometimes in a child, such a symptom becomes a “load” for this type of fungal infection of the throat. The location of the tubercles in this case is the posterior wall (soft palate), palatine arches, and pharynx.
It is distinguished by the appearance of red “dots” on the inside of the cheeks and gums. Quite rarely they sprinkle on the throat. It is believed that stomatitis is a specific reaction of our immune system, the result of an “attack” of leukocytes on molecules unrecognized by the body.
Establishing diagnosis
Only a specialist can determine the cause of pimples in the throat.
A patient who is faced with acne in the mouth, on the palate, or tonsils must understand that it is necessary to find out what causes their appearance. It is better not to resort to self-medication even in simple cases.
The doctor will help you understand where the pimple in the throat or its “scattering” came from by analyzing other complaints (runny nose, fever, etc.), examining the mucous membranes and the back wall of the throat.
Additional studies are also prescribed:
a general clinical blood test, which helps to obtain information about the presence of infection, inflammatory processes, possible allergies; swabs and smears from the nasopharynx and tonsils. The collected samples are mainly used to isolate viral agents.
Drug therapy
The selection of medications that can cure that same “pimple in the throat” depends on the etiology of the disease that caused it:
For bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed (plus probiotics - to maintain the normal state of intestinal microflora), for viruses - antiviral agents. Symptomatic treatment consists of the use of antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, antihistamine drugs. Gargling with antiseptic solutions is used.
In addition, the patient may be asked to adhere to bed rest, consume soft foods that are not capable of causing additional harm to the throat, and drink warm fluids frequently and generously.
Traditional medicine does not always work in a situation with a pimple in the throat.
The best centuries-old recipes (inhalations, infusions) to help with sore throat:
Traditional methods of treatment additionally help in treating the disease. Mix medicinal chamomile flowers, eucalyptus leaves, linden blossom. Pour a tablespoon of raw material with just boiled water and leave for 15 minutes - half an hour. Mix Kalanchoe or aloe juice with warm water (1:1).
The resulting drugs are used for rinsing five times a day.
For inhalation it is recommended to use:
A mixture of herbs (sage, chamomile, mint). Pour two tablespoons of water into a liter of water, boil a little, then let the broth cool a little and breathe the steam over the saucepan for five to ten minutes. In this case, the head must be covered with a towel or sheet. Propolis. Add a tablespoon of bee glue to a liter of boiling water. The time allotted for inhalation is the same 5-10 minutes.
When using steam inhalations, be careful not to burn your upper respiratory tract. If your body temperature is above 37.2°C, doctors recommend abstaining from them.
Throat diseases are widespread among both children and adult patients - there is a fairly comprehensive classification that systematizes all types of oropharyngeal diseases known to specialists.
Which of them cause pimples in the throat?
People who, before consulting a doctor, conducted an independent examination of the pharynx and tonsils and discovered a suspicious rash on the surface of the mucous membrane may complain about their presence.
A similar symptom is present in various forms of pharyngitis and tonsillitis, but to clarify the diagnosis it is necessary to identify other characteristic signs.
A change in the relief of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and tonsils, the appearance of tubercles on its surface is an alarming sign, which is usually accompanied by a sore throat of varying severity. Why do pimples occur in the throat and what diseases do they indicate? Formations resembling pimples can be represented by:
rash; inflamed follicles.
One way or another, a rash in the throat, which can be mistaken for acne, is a sign of an inflammatory process provoked by viruses or bacteria.
There are different reasons why they can be detected during an examination:
Acute pharyngitis. Follicular tonsillitis. Herpangina.
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharynx, and tonsillitis or tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils. Most often, the palatine tonsils are affected, in which case they speak of classic or banal tonsillitis. One of its forms is called follicular, since the main symptom is the accumulation of pus in the follicles of the tonsils.
The nature of inflammation affects the color of pimples in the throat. For example, with a bacterial etiology of the disease, a purulent process occurs, and the formations in the throat acquire a whitish, yellowish tint.
This sign is also confirmed by laboratory tests - if they are carried out. With a viral infection, the rash is usually red.
It is important to pay attention to the number of elements of the rash. If there is only one tubercle or the number of pimples does not exceed 3–5 units, then we are most likely talking about a mild form of a viral infection, which is not accompanied by a pronounced deterioration in the general condition of the patient.
The type of pathogen, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient’s body (in particular, the strength of the immune system, the severity of immune reactivity) determine the course of the disease. At the same time, rashes resembling pimples are only part of the clinical picture, although assessing their appearance, quantity and area of localization can help in clarifying the diagnosis.
It occurs in patients of all age groups; the lymphoid tissue of the posterior pharyngeal wall is involved in the pathological process. The causative agents of acute pharyngitis are respiratory viruses (adenoviruses, etc.), bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci).
Pimples on the back of the throat with pharyngitis look like millet grains; they have a bright red color, slightly raised above the surface of the swollen and reddened mucous membrane. In addition to pimples, you can see:
redness and swelling of the lateral ridges; redness and swelling of the uvula.
If acute pharyngitis develops in an infant, it usually occurs in combination with inflammation of the nasal mucosa (rhinitis) as nasopharyngitis. At the same time, all the changes described above remain, and pimples in the throat are complemented by swelling and redness of the soft palate, on which pimples and other rash-like formations may also appear.
Follicular tonsillitis is an acute infectious and inflammatory process. Various types of streptococci and staphylococci are of greatest importance in the development of this disease; the causes of occurrence are the entry of the pathogen into the body by airborne droplets or through autoinfection in the presence of a chronic focus of infection in the oropharynx.
The follicular form of tonsillitis is characterized by the presence on the palatine tonsils:
swelling; redness; pus-filled follicles.
The follicle looks like a white pimple in the throat; due to the presence of purulent exudate, it acquires a yellowish tint. In general, follicles can look like rounded islands, millet grains, pimples or pimples.
Experts compare the tonsils in follicular tonsillitis to the “starry sky”, since festering follicles appear through the mucous membrane, standing out against the background of redness and swelling.
Pimples in the throat with follicular sore throat gradually increase in size and can open on their own. In this case, the patient's saliva will contain a slight admixture of pus. If follicular tonsillitis occurs in isolation, pathological changes are localized only within the palatine tonsils, but with tonsillopharyngitis, pimples also appear on the back wall of the pharynx.
It is important to know that changes in the palatine tonsils do not always coincide - in some patients, upon examination, signs of follicular tonsillitis are noticeable on one side, and catarrhal or lacunar on the other.
Therefore, pimples can be located only on the right or left, combined with redness, loosening of the tonsils, the presence of yellowish and whitish deposits on their surface, and inflammation of the back wall of the pharynx.
Herpangina is sometimes also called coxsackievirus tonsillitis because it is caused by enteroviruses, coxsackieviruses and ECHO viruses. The elements of the rash that the patient mistakes for pimples are nodules or papules, which are red in color and appear from the first hours of the disease. They are localized:
on the tonsils; on the palatine arches; on the tongue; on the soft palate.
Each such red pimple in the throat soon turns into a bubble, or vesicle. The color of the vesicles matches the color of the nodules, so upon examination you can see red elements against the background of the hyperemic mucous membrane of the affected anatomical areas. Moreover, in some cases, a rash appears with normal coloring of the underlying areas of the mucous membrane - then red blisters and pimples stand out even more clearly.
Pimples with herpangina do not merge, but erosions can form in their place - defects in the mucous membrane, which often bleed and are painful. With herpangina, they heal without the formation of secondary changes.
Herpangina must be differentiated from herpetic stomatitis, the rash in which can also spread to the back wall of the pharynx and palatine tonsils. Herpetic stomatitis is caused by the herpes simplex virus. With this disease, grouped small blisters filled with serous contents form on the mucous membrane. They have a yellowish tint and also spread to the skin around the lips and nose, where they usually soon crust over.
If the patient complains of a sore throat and notices pimples on the mucous membrane, you should consult a doctor - antibiotic therapy may be required. But even if antibiotics are not prescribed after examination by a specialist, many other treatment options are used aimed at quickly and effectively alleviating the patient’s condition.
Such an unpleasant phenomenon as pimples in the throat rarely goes unnoticed. In normal condition, our mucous membrane has a uniform pink color. With infectious and colds, the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat and pharynx not only become inflamed and become red, but also pimples appear in the throat. Let's take a closer look at the causes of pimples in the throat and methods of treatment.
The appearance of white pimples is associated with:
follicular form of tonsillitis; chronic respiratory diseases; stomatitis; abscess; infections of viral and bacterial origin.
Children are especially predisposed to this. A white pimple in the throat may appear after an acute viral illness. For example, if a child has chickenpox, then pustules and rashes cover not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat.
There are many throat diseases that have such common symptoms as a rash of white pimples in the throat, pustules. This occurs with follicular, herpetic, sore throats. The history of follicular tonsillitis is an inflammatory process of bacterial origin. During a medical examination of the mucous membrane of the throat, the follicles or lymph nodes look like pimples. Abscesses with follicular sore throat rarely appear. Pimples are localized on the back wall of the throat. They are all white, about the size of a pin's head. The course of the disease is associated with fever, intoxication and headache. There is acute pain in the throat, redness of the mucous membrane, enlarged tonsils, blisters, and ulcers. With angina, complications may arise: rheumatism, disruption of the heart muscle, renal colic.
Inflammatory diseases can provoke allergic reactions and attacks of bronchial asthma. With herpetic sore throats, pustules appear in the form of pimples on the palate and back wall of the pharynx; they are called vesicles. The cause of the disease is enteroviruses. There are forms of sore throat that appear due to staphylococcus and streptococcus. Then pimples appear on the throat.
Another disease with similar symptoms is enteroviral pharyngitis. Transmitted by airborne droplets. The disease causes high fever, delays in swallowing, vomiting, and granules on the mucous membranes of the throat. Swallowing food is very difficult. The entire back wall of the throat is covered with small pimples. Most often, children suffer from antiviral pharyngitis, less often adults.
A throat abscess is a purulent disease. An abscess forms on the tonsils, pharynx and palatine arches after suffering purulent otitis or tonsillitis. The causative agents of abscesses are: streptococci, Klebsiella and Escherichia coli.
Abscesses with pharyngitis occur as a complication of acute respiratory viral infections or colds. When the disease occurs, the throat and tonsils are covered with pimples and watery blisters. Pustules form on these pimples. After treatment they disappear, but in some cases the tonsils remain enlarged for several weeks after the illness. If, despite treatment, symptoms persist, then you should consult a doctor. This may be due to chronic granulosa pharyngitis. The formation of ulcers is promoted by reduced immunity, lack of vitamins and microelements, constant hypothermia, and bacterial infections. Purulent processes are accompanied by fever, pain, increased salivation and bad breath. On the outside of the neck, at the site of the internal lesion, the skin turns red and swelling forms.
With stomatitis, the mucous membranes of the mouth are affected. Yellow and gray erosive wounds form on the gums, the inside of the lips and the soft palate. Single and grouped foci of the disease appear, which are accompanied by an increase in temperature. The cause of the disease may be the herpes virus. A sign of the disease are bubbles in the throat. They occur in acute and severe forms of the disease. The course of the disease is similar to all viral diseases: fever, weakness and malaise.
The use of antibiotics helps to eliminate pimples in the throat with pharyngitis. Chronic disease of the larynx - granulosa pharyngitis - requires complex treatment. In this case, immunostimulants, antibiotics and physiotherapeutic procedures are used.
Purulent abscess formations in the throat require surgical intervention. After removal of the abscess, complex treatment with antibiotics and detoxification agents is used. If the analysis of purulent discharge reveals candidiasis bacteria, then antifungal therapy is used. Doctors recommend bed rest, plenty of warm drinks and a balanced diet. In addition to drug therapy, rinsing with a solution of sea salt, baking soda and iodine is prescribed. Gargling should be done at least 10 times a day: this will relieve inflammation of the throat mucosa. After this, an infusion of calendula flowers is used for rinsing. Doctors recommend taking furatsilin solution sold in pharmacies. You can also prepare it yourself at home. To do this, dissolve 2 tablets of furatsilin in 0.5 ml of boiling water.
The same solution can be prepared based on streptocide. Both of these drugs have an antiseptic effect. Doctors recommend gargling with such solutions until recovery. The drug Lugol cleanses the throat mucosa well. The mixture contains iodine; it is an allergen, so people prone to allergic reactions are not recommended to use the drug.
For tonsillitis and tonsillitis, complex treatment is carried out, which helps remove white pimples from the tonsils. In this case, take a complex of vitamins, anti-inflammatory and hyposensitizing drugs. Modern medicine widely uses laser and ultraviolet treatment and physiotherapeutic procedures. If after treatment the disease often relapses, pimples and pustules appear, then surgical intervention is prescribed. In modern medicine, this operation is performed using laser surgery.
In the treatment of acute forms of herpetic stomatitis, antiviral agents (Acyclovir) and a complex of vitamins and microelements that stimulate the immune system are used.
source
White lumps in the throat on the tonsils and tonsils: what is it and how to treat it
The presence of white lumps in the throat with an unpleasant odor is a characteristic symptom of inflammation of the tonsils , which is of a viral or bacterial nature. Most often, this symptom indicates chronic tonsillitis (tonsillitis). Usually a person does not even suspect the presence of pus balls in the throat until they begin to “come out” along with sputum when coughing or sneezing.
Causes of benign tumors of the larynx
The development of congenital tumors of the larynx is associated with the presence of a genetic predisposition, as well as with the impact of teratogenic factors on the unborn baby. Such factors include infectious diseases of the mother (measles, rubella, viral hepatitis, mycoplasmosis, HIV, syphilis), radiation exposure, and taking embryotoxic medications during pregnancy.
The reasons for the development of acquired benign tumors of the larynx include various disorders of the immune system, the presence of herpes infection or adenoviruses in the body, past influenza and measles, chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis or laryngitis, as well as adenoids. Also, the formation of tumors can be caused by prolonged, systematic inhalation of irritating substances, such as tobacco smoke or fine dust.
Whitish lumps in the tonsils with tonsillitis
Exacerbation of chronic or the onset of acute tonsillitis can be recognized by the following signs:
- bad breath, a sour taste in the mouth;
- there is an increase in body temperature;
- periodically painful sensations occur during eating and swallowing;
- pain appears in the throat, head, and cervical region.
Why do purulent plugs form and what do they consist of?
Photo: this is what white lumps on the tonsils look like
Many people believe that the white things in the throat and tonsils are just small pieces of food that have begun to rot and give off a rotten smell. Residues of food are indeed present in these formations, but basically calcified miniature balls consist of dead bacteria that entered the body along with air, and leukocytes, aimed at fighting them by the human immune system.
Microorganisms that cause inflammation in the tonsils produce hydrogen sulfide. They need this substance to protect against oxidative processes and subsequent destruction of DNA; it also emits the aroma of rotten eggs, due to which the patient’s mouth begins to smell bad.
The “culprits” for the formation of yellow and white lumps on the tonsils
There are several types of microorganisms that cause a whitish coating to form on the tonsils, which gradually turns into miniature pebbles. It can be:
- Streptococci. A bacterial infection causes symptoms such as frequent vomiting, fever, abdominal pain, swollen lymph nodes, and a rash.
- Epstein-Barr virus, which causes infectious mononucleosis, can also cause white, hard lumps in the mouth that have a foul odor. The presence of the disease is indicated by the following signs: high body temperature, enlarged tonsils and pain in the larynx. In advanced cases, clots of pus may be released.
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV-1), leading to the development of oral herpes. Most often, the disease can be recognized by the presence of sores on the lips. Simultaneously with the appearance of bubbles on the outer surface of the lip, a whitish or yellowish coating may form on the mucous membranes of the tonsils, which later transforms into stones.
Other causes of stones in the tonsils
In most cases, the cause of the formation of whitish plugs on the tonsils that have an unpleasant odor is chronic tonsillitis. But she is not the only one possible. White lumps on the tonsils can be found with the following diseases:
- Chronic sinusitis. With this disease, thick whitish or yellow mucus is produced, which accumulates in the larynx area. Clots of mucus become the culprits of the unpleasant odor from the mouth and lead to a strong cough with sputum, which may contain miniature whitish balls. Depending on the results of laboratory tests, the patient is prescribed one of the following drugs:
- Clarithromycin.
- Amoxicillin.
- Cefoperazone.
- Augmentin.
- Products with a disinfecting effect. The most popular are Chlorhexidine and Dioxidine. You can also rinse your mouth with herbal infusions (sage, chamomile).
- During the period of exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs: Panadol, Nurofen. Sometimes doctors advise taking homeopathic remedies. The most popular - Tonsilton - has no side effects and is recommended for the treatment of tonsillitis in children.
- Taking vitamin complexes. The inflammatory process affects the entire body, but the immune system is particularly damaged. To get rid of dizziness, poor health and improve the functioning of the immune system, you need to diversify your diet and take vitamins, the composition of which is replete with basic micro and macroelements, useful substances necessary for the normal functioning of all organs and systems.
To treat an advanced disease, several drugs that have an antibacterial effect may be prescribed at once.
To effectively get rid of white lumps that appear on the tonsils due to chronic tonsillitis, it is necessary to combine antibiotics with the following drugs:
Physiotherapeutic treatments
In addition to taking medications and gargling, it is recommended to undergo a course of physiotherapeutic procedures. Their type and duration are determined by the attending ENT doctor. The following types of physiotherapy are distinguished:
- ultrasonic;
- microwave therapy;
- UHF;
- laser irradiation.
Local therapy
Quite often, experts prescribe medications for resorption (Septolete or Hexalize) and recommend taking a course of procedures for washing the lacunae of the tonsils. This manipulation is extremely difficult to do at home without experience, so it is better to take a course from a doctor.
Traditionally, the otolaryngologist prescribes 10–15 procedures; for rinsing, the specialist uses a copper-silver solution, which has a disinfecting effect.
In advanced forms of tonsillitis, even after several courses of traditional drug treatment, lumps with or without pus continue to appear on the tonsils. For some patients, the doctor may suggest removal of the tonsils. After a surgical procedure called tonsillectomy, the patient will no longer be bothered by tonsil plugs.
What does throat cancer look like: photos taken in operating rooms
Cancer pathology, regardless of which part it develops in, poses a mortal threat to a sick person. Very often, death occurs due to the fact that the disease is diagnosed too late and treatment is not carried out in a timely manner.
About the disease
Throat cancer - also called laryngeal cancer, these are multiple neoplasms, malignant in nature and formed from the mucous cells of the organ. It is aggressive in nature, grows quickly and just as quickly affects neighboring sections.
Metastasizes already at the initial stages of tumor development. It has several types, depending on the area of localization of the anomaly and is most often a consequence of chronic nicotine addiction. In the later stages, it is practically incurable and is accompanied by severe symptoms.
Location
The disease is classified based on the location of development of the pathology. The same factor determines the degree of its severity and the intensity of symptoms. The following types of throat cancer are distinguished.
Below the vocal cords
Photo of a tumor under the vocal cords
Refers to anomalies of the lower part of the organ. Evaluated according to the following criteria:
- the tumor is minimal, varies within 1 – it is still reversible and does not pose a mortal threat;
- the tumor grows 2-3 times , partially affects the vocal folds, complicating their mobility;
- the malignant formation is limited to the specified zone , while its size is critical, and its structure changes qualitatively;
- the anomaly begins to rise higher , grows into the external sections and almost completely covers the tracheal area.
Middle part of the larynx
The tumor develops in the area of the vocal cords. Characterized by the following parameters:
- the size of the malignant formation is minimal, no more than 15 mm . The anomaly slightly affects the vocal cords, sometimes reaching the anterior commissures, but does not interfere with their mobility. It causes virtually no discomfort. It can develop within the boundaries of one fold, or it can affect both;
- the pathology increases several times and reaches the size of a nut . It begins to interfere with the full functioning of the larynx, partially blocking its vestibule;
- education is growing, but is still located within a given area;
- the tumor gradually grows into all deep cartilaginous layers and leaves the organ. Its parameters in this case are catastrophic for this section of the throat;
- the pathology overlaps the artery and mediastinum and passes into the intervertebral zone.
Photo: localization of tumors
Supraglottic part of the larynx
It affects the upper part of the organ, located slightly above the vocal cords. It is very difficult to diagnose, since outwardly it is no different from ordinary sore throat, therefore treatment is prescribed accordingly. The clinical picture is almost erased.
Described by the following parameters:
- size up to 2 cm in diameter . It belongs to small tumors, and fits in one anatomical part, and does not interfere with the mobility of the vocal folds;
- formations are multiple , also not too large in size, but they already affect several segments of the larynx, sometimes partially affecting the fossae of the organ, the lingual base, and the posterior walls of the pyriform recess;
- the tumor reaches impressive parameters - up to 10 cm in diameter and partially fixes the vocal folds, often grows into the posterior region of the cricoid cartilage, provoking the appearance of minute erosions of the thyroid gland;
- the pathology completely grows across the entire width of the thyroid cartilage , its size is no longer controlled. The tumor begins to leave the supraglottic area;
- with pronounced growth, the formations descend down into the vertebral zone and put pressure on the carotid artery.
View at different stages
Photo: changes at each stage (from 1 to 4)
Stage 1
This stage of development of a malignant tumor is considered initial. There are no external manifestations of the disease. However, upon careful visual examination of the laryngeal region, one can notice some atypical manifestations, similar to inflammatory infectious lesions, accompanied by enlarged tonsils.
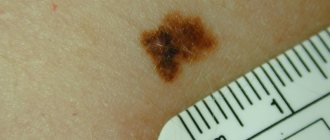
The color of the pathology is also similar to the manifestations of angina - pronounced redness of the mucous membrane, swelling of the surrounding seal, soft tissues of the mucosa. The maximum size of the tumor is about 3 cm.
If a tumor develops in the laryngeal area, it is easier to diagnose it by visual examination than in cases where the pathology is localized in the upper or lower parts of the organ. In this situation, visibility is somewhat limited, which, given the relatively small size of the anomaly, does not make it possible to study it in more detail.
The structural content of the affected tissues is still almost identical to healthy ones, despite the fact that the cells are already subject to mutation processes.
If we examine the pathology under multiple magnification, we can observe that its surface is dotted with multiple papilloma-shaped islands, consisting of the squamous epithelium of a group of highly differentiated organisms.
Despite the slow growth, the disease is characterized by a significant inflammatory reaction of the soft tissues, as a result of which they gradually change their hue to whitish.
This feature of an early throat tumor is similar to purulent infectious manifestations and interferes with the objective diagnosis of the disease due to the confusion of primary symptoms.
Stage 2
At the second stage, oncology behaves more actively, and external signs are quite obvious. It becomes more mobile, growing into the sections that are located next to the larynx.
The function of the vocal folds is impaired, which makes the voice hoarse and blocks the full passage of air flow into the patient’s body.
At this stage, the pathology, which has developed unilaterally, moves to the second half of the organ, taking up more and more space. At the same time, its external manifestation changes qualitatively - from whitish, the shade of the compaction becomes abnormally purple, the structure becomes denser, and the internal tissues are irreversibly damaged.
Photo of the second stage
The size of the formation reaches impressive proportions; it is not only clearly visible visually, but also causes serious discomfort to the patient, complicating the functioning of the respiratory and digestive systems.
The laryngeal lumen, gradually narrowing, reaches a critical point. The tumor is still under control and does not leave the territorial limits.
Stage 3
The photo clearly shows that at the moment when the oncological processes occurring in the affected area reach the third stage, the pathology, which has too little space to grow and develop, begins to grow deep into the throat , and also spreads to the tissues surrounding it.
Gradually “conquering” larger and larger territories, it produces single or multiple metastases. It becomes extremely difficult for a person to breathe, speak, and eat. The symptoms of the disease at this stage are quite difficult to tolerate, the pain syndrome is significant and poorly controlled, and attacks of suffocation often occur.
Since the formation has completely affected all parts of the throat, it becomes immobilized, which does not interfere with maintaining active growth processes.
The surface of the compaction is distinguished by visible tuberosity, infiltrative growth and a large number of blood vessels protruding very close to the surface layer of the tumor.
The pathology has clear shapes and boundaries; endophytic cancer cells quickly affect all internal tissues of the throat. Often multiple erosive lesions appear on the organ mucosa, emitting a putrid odor.
Often at this stage, the pathology affects the base of the tongue - in such a situation the prognosis will be extremely unfavorable, and the clinical picture of the disease is aggravated by concomitant manifestations.
This stage of development of the type of cancer in question is extremely severe, practically cannot be treated and leaves very little chance of five-year survival, even after surgery to remove it.
Stage 4
This stage of the pathology is the most critical and is considered final. The patient is inoperable, all methods of therapy are ineffective.
The neoplasm is very large, spreads to adjacent tissues, affects almost the entire throat, and often comes out , exposing the tissues of the oral mucosa and the outer skin of the face to processes of cancer mutation, forcing epithelial cells to divide abnormally.
Since the tumor development zone is located close to the brain, and with active growth the compaction very quickly reaches its boundaries, then at this stage irreversible processes of brain activity begin quite quickly, its activity decreases, and the organ itself is quickly affected by metastases.
As a rule, by this time, all three sections of the throat discussed earlier are completely affected. The structure of the pathology is greatly modified - the tissues mostly consist of fat cells, characterized by increased friability.
They practically do not retain elasticity and have a shade that goes from bright purple to dark, in places almost black, color. In those fragments where the tone of the anomaly is completely dark, the processes of tissue decay and cell necrosis have already begun.
Photo of stage 4 outside and inside
There are no longer any blood ducts here, cancer cells are dividing tens of times faster than what happens in stages 1-2. Almost always, at the fourth stage of development of the disease, the neoplasms are multiple in nature; the weight of a single tumor can reach several kilograms.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
stoprak.info
Inflammation of the tonsils in a child: nuances
Photo: white lumps on a child’s tonsils
A child's body is more susceptible to developing diseases of the throat and oral cavity than an adult. With tonsillitis, the baby often behaves restlessly, cries a lot and cannot sleep at night. In addition, the child’s body temperature periodically rises.
In children, white growths and stones in the throat area appear due to the development of diseases such as:
Parents whose children often suffer from sore throat are advised to always have a special medical device called a nebulizer on hand. It is used for inhalation at home. You should not hope that the unfortunate lumps will come out on their own.
Treatment of papillomas and laryngeal fibromas in children and adults
Regardless of the presence or absence of symptoms of the disease, benign throat tumors are subject to exclusively surgical treatment. Thus, when treating laryngeal fibromas and small polyps, their tumors are removed endoscopically using laryngeal forceps or a special loop. The operation is usually performed under local anesthesia, but general anesthesia is also possible.
Isolated laryngeal papillomas, photos of which are shown below, are removed in a similar way:
Small cysts are excised along with the membrane. If their size is significant, a puncture is first made and their contents are sucked out, and then the walls of the cyst are removed. To avoid relapse, cryotherapy of the throat is performed.
Limited laryngeal papillomas in children and adults can be removed by cryo- and laser destruction or diathermocoagulation. To prevent relapses, any surgical treatment must be accompanied by immunomodulatory therapy and antiviral drugs.