Many have heard scary stories about the terrible, all-consuming human papillomavirus, which affects nine out of ten people around the world. Also, more than one person knows about the danger of this virus and the possibility of developing negative consequences. Even if this is your first time encountering this problem, it is better to learn about this virus in more detail.
Condoms are used as protection against HPV
As you know, many diseases are transmitted due to such a natural human need as sex. This does not mean at all that you should stop having sex. But everyone wants to be as healthy as possible, so let’s try to figure it out: “Does a condom protect against HPV?”
What is papilloma and why is everyone so worried?
Human papillomavirus is a disease that has been known to doctors for a long time. However, recently it has attracted close attention from doctors and scientists.
A number of studies have found that HPV has a direct relationship with the development of cervical cancer. This virus was found in ninety percent of cases in biopsies taken from cancer tumors. This is why doctors around the world are concerned about the spread of this disease.
According to statistics, seventy percent of the world's population are infected with the human papillomavirus. It is worth noting that most women are affected by this disease. The virus is transmitted exclusively from person to person.
The popularity of anal sex has led to the fact that papillomas are increasingly found on the skin in the anal area and on the rectal mucosa. Even newborns are not immune from infection: infection occurs during labor and manifests itself in the form of a huge number of condylomas in the larynx.
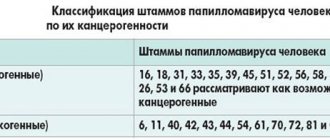
To date, more than a hundred types of HPV have been discovered. Of these, forty can cause damage to the genital organs and anal area in men and women. Doctors divide the disease into three groups:
- Non-oncogenic (diseases of types 1, 2, 3, 5).
- Low oncogenic risk (diseases of types 6, 11, 42, 43, 44).
- Highly oncogenic (diseases of the 16th, 18th, 31st, 33rd, 35th, 39th, 45th, 51st, 52nd, 56th, 58th, 59th , 68 types).
Highly oncogenic HPV types 16 and 18 are found in seventy percent of detected cases, of which type 16 leads to cancer in almost fifty percent of cases.
As the virus enters the human body, it tends to enter the lower layer of tissue covering the surface of the body cavity. The area of transition from the stratified squamous epithelium of the cervix to the columnar epithelium is considered to be the most prone to infection zone.
In the affected area, the virus can exist in several possible forms - benign (that is, the virus is located outside the human chromosome) and malignant (the DNA of the virus becomes one of the parts of the human genome and causes tissue degeneration). The latent period can last from a couple of weeks to several years.
It is worth noting that in ninety percent of cases the body will get rid of this virus on its own. Duration – from six months to a year. However, if the recipient has any infectious or somatic diseases, as well as a weakened immune system, the disease enters the stage of clinical manifestation.
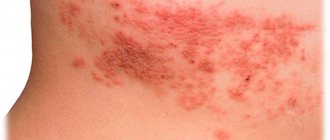
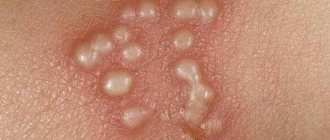
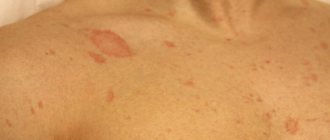
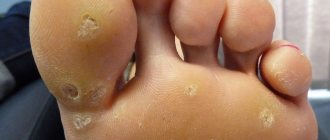
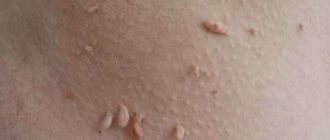
These manifestations can appear in the form of genital warts (they are also called anogenital warts). They can be either single or multiple. Warts are located on the labia, mucous membrane of the vaginal vestibule and on the head of the penis. It's easy to spot them. However, cancer (cervical cancer) can only be detected through screening.
You can provoke the appearance of HPV yourself. If at least one of the points below applies to you, then you are at risk.
- Active sexual life before adulthood.
- Long-term use of oral hormonal contraceptives.
- Presence of gynecological and general chronic diseases.
- Constant stress.
- Avitaminosis.
- Weak immune system, susceptibility to frequent colds.
- Traumatic birth.
- Frequent change of sexual partners.
- Smoking and drinking alcohol.
Behavior of HPV in the body
During the penetration of the papilloma virus into the cells of the body, a healthy structure is transformed. For a long period the disease does not manifest itself in any way. The person’s well-being does not change. Subsequently, various stages of dysplasia occur (pre-cancer form). In the “advanced” stage, mutated DNA changes tissue, which can result in cancer.
“Sleeping” virus and the reasons for its “awakening”
Having penetrated the epidermis, the virus “attracts” cells of the immune system. In most cases, defenses win. From the moment it enters the body, the infection is “frozen” and remains in incubation mode for a long time (sometimes years). The disease “wait” for suitable conditions, and then a “breakthrough” occurs. A weakened immune system can increase the likelihood of the disease occurring. Long-term illnesses, regular stress, physical overexertion are factors that can provoke a “surge.” Hormonal changes in women due to pregnancy or menopause also contribute to the manifestation of a hidden disease.
Stages of progression and symptoms
The main task of every infected person is not to miss the visible symptoms. Exacerbation of HPV goes through three periods of development:
- First stage. Small flesh-colored lumps appear on the human body. The area of distribution is the entire body (from head to heels).
- Second stage: the growths move to a new level - papillomas, the diameter of which is about 7 mm.
- Third "stage". Inflammation and bleeding of condylomas appear.
The external manifestation of papillomavirus indicates the “height” of the disease.
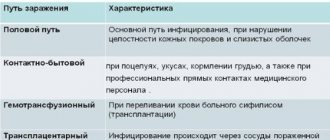
How is human papillomavirus transmitted?
Transmission of the virus can occur in several ways. Below we will look at the most common of them.
Sexual transmission of the virus
Most often, infection occurs during sexual contact. It does not matter in what form it takes place: anal, vaginal or oral. Even if your partner has no external signs of the human papillomavirus, this is not a guarantee of his health.
Even if you have been faithful to one partner all your life, this is not insurance against infection. Symptoms may develop several years after sex and by the infected person.
Vertical method of infection
The vertical mode of infection occurs from mother to child. Most infants who have been diagnosed with human papillomavirus acquired it during passage through the mother's birth canal.
There is also a hematogenous route, when the disease is transmitted through the placenta. Caesarean section is not 100% insurance against transmission of papillomavirus to a newborn.
Household transmission of the virus
According to doctors, infection through household means is possible, although with less risk than through sexual contact. The virus can be transmitted through the use of toilet and hygiene items, and even by touch.
Can children get sick?
The strains of the virus that cause the growth of genital warts are transmitted only through sexual contact. Children cannot become infected from their parents. By carefully observing personal hygiene rules, the risks of infection are minimized.
Parents can protect their child by getting the HPV vaccine. Today there is a vaccine that allows you to obtain immunity against the most dangerous oncogenic strains (virus types 16, 18). You can be vaccinated against them before engaging in sexual activity, at the age of 9 years. The vaccination scheme involves three vaccinations: the first is done on the day of treatment, the second – two months later, the third – six months later. After vaccination, the body begins to produce antibodies that can suppress HPV activity throughout life. Vaccination is carried out in specialized medical centers.
Is it possible to escape from papilloma, how to protect yourself?
Use a condom during sexual intercourse. Oral sex also requires protection: when doing cunnilingus, it would not be superfluous to use a latex napkin.
To protect yourself from this disaster, follow a basic list of recommendations.
- First of all, wash your hands or treat them with antiseptic as often as possible. Remember that the human papillomavirus is transmitted through the slightest microcracks in human skin.
- Get yourself a separate towel that only you will use.
- Do not use public brooms in bathhouses.
- Go only to trusted beauty salons; do not hesitate to ask the master for a health book before carrying out the procedure. Also, during a manicure or pedicure, make sure that the master always wears disposable gloves. All tools must be unpacked with you.
- Always wash your underwear after purchasing.
- Try not to drink from the same bottle with strangers.
Preventive measures
To prevent the appearance of genital warts, you should:
- Avoid sex with someone who has HPV.
- Use condoms. They do not guarantee 100% safety, but they reduce the risk of infection.
- Give up promiscuity and have a reliable sexual partner.
- Get checked regularly.
- Strengthen the immune system: give up bad habits, do daily exercises, walk in the fresh air, try to avoid stress, eat right.
If this does happen, treatment methods
Before starting treatment for a disease, you need to find out its symptoms. Below we present the main symptoms that may indicate the presence of a disease in the human body.
- The appearance of warts near the genital areas.
- Irregular menstrual cycle.
- Vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Constant fatigue, severe weight loss, lack of appetite.
- Unpleasant odor from the vagina and the appearance of uncharacteristic discharge.
There is currently no effective way to get rid of HPV. World specialists in the field of treatment of this disease provide sufficient arguments in favor of the use of immunomodulators in the case of treating manifestations of HPV. It can help with the appearance of flat papillomas and genital warts, as well as HPV-associated cancer.
However, a distinction must be made between treatment and attempts to control the virus. This method is most often used in Russia and the CIS countries, despite the fact that drugs are also produced abroad. It is worth noting that the above method does not guarantee a 100% result.
But conditions caused by the human papillomavirus can be treated. It is carried out using surgical methods, for example, laser, radioknife, liquid nitrogen or weak electric current.
Benign condylomas and papillomas can also be removed. This is due not only to the aesthetic side of the issue, but also to reducing the risk of transmitting the virus to your sexual partner.
Many, when they find out that they are carriers of the papilloma virus, decide to refuse treatment. This is due to the fact that it is impossible to completely get rid of the disease, which creates in a person the illusion of doom. However, the situation cannot be left to chance. Even benign papillomas and condylomas can cause cervical cancer.
Wart removal can only be done in a clinical setting. You should not trust advertisements for drugs that promise to remove tumors at home. This can be dangerous and lead to serious consequences. Also, you should not rely on traditional medicine.
Restoring intimate life after destruction
Immediately after surgery to remove condylomas (growths on the genitals), a wound forms at the site of removal. Sexual contact can easily lead to any infection .
Therefore, the resumption of sexual activity depends on the size and method of removal of papillomas:
- after electrocoagulation - after 14 days;
- after laser - 10-15 days;
- after radiosurgery - after 14-21 days;
- after cryodestruction - after 15-30 days;
- after surgery - the healing process is individual, sex is possible after restoration of the epithelium.
Important! For six months after treatment, doctors recommend using condoms for any type of sexual intercourse.
After removal of condylomas, sexual intercourse may cause pain as a result of:
- The appearance of a scar at the site of the removed growth. A scar may occur after exposure to lasers, radio waves, or surgery.
- Relapse of the disease, the appearance of new growths due to improper treatment.
Is vaccination guaranteed protection?
Today there are two vaccines that protect against human papillomavirus types 16 and 18. It is these forms of the disease that cause cervical cancer in seventy percent of cases.
Also, these vaccines can provide a shield against some other less common types of papillomavirus. One of the available vaccines protects against HPV types 6 and 11, which cause anogenital warts.
According to the results of clinical studies, vaccines are absolutely safe for humans. In addition, they are effective in countering and preventing HPV viruses types 16 and 18.
Vaccination should be carried out before the first sexual contact. The World Health Organization recommends vaccination for all girls aged 9-13 years.
It is worth noting that vaccines used to prevent HPV cannot affect the treatment of cancer. Vaccination against human papillomavirus does not replace screening for cervical cancer.
Thus, we can conclude that vaccination is not a 100% guarantee against the disease, but additional protection can reduce the likelihood of infection significantly.
Precautions to avoid getting infected
The papilloma virus is so common that becoming infected with it is not particularly difficult. Following certain recommendations will reduce the likelihood of disease transmission:
- use exclusively personal hygiene items;
- check compliance with sanitary standards during salon procedures and gynecological examinations;
- do not walk barefoot in public places;
- exclude contact with papillomas in another person.
The main recommendation for people who are sexually active is to have a regular lover. Based on the fact that HPV is transmitted from partner to partner through a condom, only this condition can guarantee safety.
Another way to avoid infection is vaccination. There are 3 HPV vaccines. Quadvalent Gardasil - from 16, 18, 6, 11 types. 9-valent Gardasil - from 16, 18, 6, 11 and 5 highly carcinogenic strains. Cervarix - from types 16 and 18. Vaccination occurs in 3 stages, after which the vaccination can be considered complete.
HPV is transmitted to a partner. It is important for people suffering from this disease to understand that they can easily become infected with papillomavirus. To avoid such a situation, it is necessary to identify the development of infection and begin treatment.
Main modes of sexual transmission
The virus is found in all biological fluids of the human body, so even when using a condom, infection can occur. In the active phase and during its external manifestations, the virus is transmitted:
- upon contact with mucous membranes (during arousal and secretion of lubricant from partners, with sperm);
- with any type of sexual contact (vaginal, oral, anal);
- when kissing (through saliva);
- upon contact with the skin, if there is damage or microtrauma.
Return to contents
Planning a pregnancy
A pregnant woman diagnosed with genital papillomavirus can infect her baby during childbirth. This happens rarely, but the consequences of infection are always very serious. When infected, papillomas begin to grow in infected children within a year on the larynx or trachea, which over time can close the entire lumen of the respiratory organs.
RRP (recurrent respiratory papillomatosis) is a disease that is potentially life-threatening to a newborn. It can only be treated surgically. In case of severe infection, about one hundred operations may be performed over the entire period of therapy. Only in a third of patients does radical treatment help achieve stable remission. In most cases, treatment with antiviral drugs and immunomodulators is carried out to prevent relapses. For small children this is a big burden. That is why it is so important to undergo a full examination even at the stage of pregnancy planning. If genital warts are detected, remove them and make an appointment with an immunologist to correct the immune system.