Human papillomavirus
Most often, growths in the genital area appear due to HPV. The disease is transmitted mainly through sexual contact. There is also the possibility of intrauterine infection or when visiting public baths, swimming pools, and toilets. The virus enters the body and remains there until favorable conditions arise for its development. The pathogen is activated when immunity decreases. This happens for the following reasons:
- previous viral or infectious diseases;
- avitaminosis;
- taking antibacterial and hormonal drugs;
- avitaminosis;
- stress;
- STD;
- pregnancy;
- hypothermia.
Human papillomavirus infection, when the body’s protective properties are weakened, deforms the cells, after which flesh-colored or pink neoplasms appear on the skin and mucous membranes. Most often they are localized on the labia, clitoris, walls and vestibule of the vagina.
The growths look different. These can be genital warts, round pedunculated warts, cauliflower-shaped or scallop-shaped skin folds. There are usually no associated symptoms. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by itching, burning, bleeding, and discomfort during sexual intercourse. There is no drug treatment for HPV, but it is necessary to remove papillomas. There are oncogenic forms of the virus that cause cervical cancer. Condylomas are removed by excision, laser or cauterization.
Benign tumors of the vagina
Fibroma, myoma, vaginal lipoma
True benign tumors of the vagina include fibroids, myomas, fibromyomas, and lipomas.
The growth of benign vaginal tumors is based on the proliferation of connective (fibroma), smooth muscle (fibroids), and less commonly adipose (lipoma) tissue. True tumors are localized under the mucous membrane of the vaginal wall; may look like a single node with a wide base or a long leg; less often they are in the nature of multiple nodules. Clinically, vaginal tumors can manifest themselves as nagging or contact pain, foreign body sensation, discomfort during sexual intercourse, and disturbances in defecation and urination. Torsion of the leg or hemorrhage in the vaginal tumor tissue may be accompanied by necrotization, inflammation or suppuration. In rare cases, malignancy of benign vaginal tumors is observed.
True vaginal tumors are detected during a gynecological examination. During bimanual examination, a tumor associated with the vaginal wall is palpated, having clear boundaries, dense consistency, and limited mobility. When examined in the speculum, a node is found located in the area of the anterior wall, on a broad base or pedicle under the unchanged vaginal mucosa. The size of true vaginal tumors can reach a chicken egg. During transvaginal ultrasound, a solid structure of vaginal tumors is visualized, with average or reduced echogenicity, similar to uterine fibroids.
For asymptomatic vaginal tumors, they can be monitored dynamically. If there is a tendency to growth or clinical symptoms, vaginal tumors are removed surgically: they are peeled off from the submucosal layer within the bed or the stalk is cut off. The operation is often performed through a transvaginal approach; Deeply located vaginal tumors can be removed using abdominal wall transsection. The morphological form of the vaginal tumor is determined during histological examination of the specimen.
Papillomas (condylomas) of the vagina
Papillomas (condylomas) are tumors of the integumentary epithelium that look like papillary growths on the vaginal mucosa. Papillomas are a manifestation of a common human papillomavirus infection. They have exophytic growth, have a thin stalk or a wide base. Papillomas can manifest as itching, burning in the vagina, contact bleeding due to trauma, and unusual discharge. Papillomatous tumors of the vagina in some cases undergo decay or malignancy.
Diagnosis of papillomas includes cytological examination of a smear, colposcopy, biopsy of a vaginal tumor with histological examination, PCR determination of HPV with typing of non-oncogenic and oncogenic strains.
Removal of vaginal papillomas is strictly necessary and can be done with medication, liquid nitrogen, laser, electrocoagulation, plasma coagulation, surgical scalpel, or radio wave method. After removal of papillomas, immunomodulatory therapy is prescribed.
Vaginal hemangioma
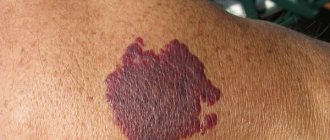
Hemangiomas are vascular tumors of the vagina with a soft consistency. Based on their structure, capillary and cavernous hemangiomas are distinguished. Having arisen on the vaginal mucosa, hemangiomas can spread to the cervical canal and into the uterine cavity. In some cases, ulceration and necrosis of vascular tumors of the vagina are noted.
Vaginal hemangiomas often manifest themselves as contact bleeding due to trauma. When a vascular tumor of the vagina spreads to the internal genitalia, a clinic of hyperpolymenorrhea may occur.
During a gynecological examination, a vaginal hemangioma appears as a red, purple or bluish spot rising above the mucosa. Local swelling of the mucous membrane, loosening of the integumentary epithelium, and engorgement of folds are noted. During colposcopy, attention is drawn to the presence of an extensive network of anastomosing, and in some areas, varicose vessels.
Non-progressive, non-ulcerating, vascular tumors of the vagina that do not disrupt the ovarian-menstrual cycle can be left under observation. With a progressive clinical picture, vaginal hemangiomas can be removed surgically, using cryotherapy, electrocoagulation, or sclerotherapy.
Bartholinitis
Growths at the entrance to the vagina occur due to inflammation of the Bartholin gland. It is located in the vestibule of the vulva and is responsible for the secretion of natural lubrication. The cause of the disease is weakened immunity, infections, including STDs, and vaginal dysbiosis.
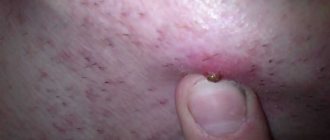
The growth looks like a dense bright red ball on the border of the upper and middle third of the labia majora. When suppuration occurs, a white dot appears in the center of the formation. Spontaneous opening of the inflammation with the release of pus is possible. The process begins with swelling and redness in the genital area. Then severe pain occurs and body temperature rises. The seal interferes with normal walking and prevents sexual intercourse. Nearby lymph nodes become enlarged.
Treatment consists of taking antibacterial drugs, analgesics, and sulfonamides. If an abscess appears, the abscess is opened and the contents are sucked out. Patients are also prescribed physical therapy. If left untreated, the disease enters the chronic stage. Bartholin's gland stops secreting secretions, the mucous membrane dries out, and cracks appear. Pathogenic microorganisms enter damaged areas, and the process is aggravated by concomitant infections. The disease is most dangerous during pregnancy, as there is a serious risk of infection of the fetus.
Treatment
If the causative agent of infection is identified, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a course of antibacterial therapy. Each patient is individually selected a drug, its dose and the duration of treatment is determined. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use only medications registered in the Russian Federation, which are effective and have a minimal range of side effects. Complex therapy for vaginal polyps includes hormonal drugs. They are necessary to eliminate hormonal imbalance. Endocrinologists select the necessary medications after receiving the results of a study of the level of hubbub.
An endoscope is used to remove a polyp from the vagina. Separation of the neoplasm from the vaginal wall is carried out using the following methods:
- Electrocoagulation – endoloops “anneal” the polyp by applying electric current to it. The method is characterized by high efficiency, minimal blood loss, low risk of infection, and rapid healing of the wound surface;
- Cryodestruction is the destruction of tissue when treating a polyp with liquid nitrogen. The method is effective and leads to rapid restoration of the vaginal mucosa. Thanks to the professionalism of the doctors at the Yusupov Hospital, the surrounding tissues are not damaged during the procedure;
- Chemical cauterization - applying chemicals to the surface of the polyp that destroy the tumor;
- Mechanical curettage is rarely used, since after excision of the polyp with a scalpel, a wound surface remains that can become infected, the vaginal mucosa takes a long time to recover, and there is a high risk of relapse of the disease.
At the Yusupov Hospital, gynecologists remove vaginal polyps using a laser beam. Laser exposure can quickly and effectively relieve a woman of the disease and promotes rapid restoration of the vaginal mucosa. After the laser removal of a vaginal polyp, the patient can begin her duties the next day. The risk of relapse of the disease is minimal. To make an appointment with an oncologist-gynecologist, call the contact center of the Yusupov Hospital.
Growths near the vaginal opening
Treating a Vaginal Infection – What You Should Know
When infectious treatment is carried out after a gynecological examination, it must be accompanied by the restoration of lactobacilli - the intimate bacterial flora.
Treatment is carried out as follows:
- Taking medications that destroy inflammatory agents;
- Prescribing gynecological probiotics for women in oral or vaginal form, containing lactic acid and promoting faster renewal of the bacterial flora of the vagina;
- The use of moisturizing preparations that prevent mechanical damage to the vagina and promote faster renewal of the bacterial flora.
Treating a Vaginal Infection
Important Prevention Measures:
- Washing with special intimate hygiene preparations under running water. When choosing a liquid, you should pay attention to the composition. It must contain natural ingredients, lactic acid and must have appropriately low pH values: from 4.5 to 5.5;
- Using your own separate towel for intimate areas – it is important to change it frequently;
- Use your own bath accessories - sponges, razors. In this case, it is also worth remembering about frequent replacement;
- Consumption of pickles and dairy products that contain lactic acid bacteria;
- Washing from the labia to the anus - thanks to this, intestinal bacteria are not transferred to the vaginal environment;
- Wearing underwear made of natural, breathable materials;
- Frequent change of linen;
- Wearing loose trousers made of natural materials;
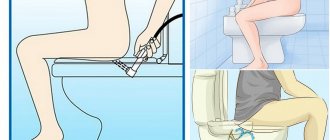
- Safe use of public toilets - you cannot sit down without a special cardboard seat;
- Taking baths for no more than 15 minutes;
- If you are prone to frequent infections, you should use special probiotic tampons during menstruation;
- Protection during intimate contacts.
These measures are worth remembering not only during a vaginal infection, but also during everyday life, as they reduce the risk of infection.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Syphilis
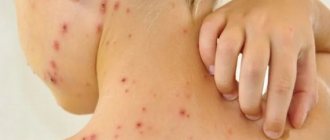
Another cause of growths near the entrance to the vagina. An infectious disease that is classified as sexually transmitted, but it can also be transmitted through blood. The domestic route of infection is extremely rare. This requires close contact with a third-stage syphilitic person who has open ulcers and gummas. The rash with syphilis has a characteristic difference - it spreads throughout the body with the progression of the disease.
The causative agent is Treponema pallidum. The incubation period lasts 3-6 weeks from the moment of infection. After this period, a hard chancre appears at the site of penetration of the bacterium. The surface of the neoplasm is smooth, dark red in color. The growth does not bleed or hurt and is usually localized on the wall of the vulva, near the vagina or labia. Secondary syphilis occurs 6-7 weeks after the appearance of chancre. Various rashes spread throughout the body. The patient's hair falls out, bones are destroyed, vision and brain activity are impaired.
In the absence of adequate treatment, the disease enters the third stage. Soft tumors spread throughout the body, turning into scars. The patient simply rots alive. Fortunately, in the modern world there is little chance of starting the process to such an extent. Syphilis is treated with antibiotics, bismuth derivatives and arsenic derivatives. Therapy of all sexual partners of the patient over the past three or 12 months is also necessary, depending on the stage of the disease.
Symptoms of vaginal cancer
With vaginal cancer, a woman complains of pain and leucorrhoea. Bloody vaginal discharge due to cancer is observed in 58–67% of patients. In 5–13% of patients the disease is asymptomatic. Quite often, the course of the disease is characterized by a combination of several symptoms. In 16% of patients, gynecologists find a cancerous tumor in the vagina by chance during a routine examination.
The clinical picture of vaginal cancer is quite polymorphic. This determines certain features and difficulties of diagnosis. They are detected when analyzing symptoms at various stages of the disease. If the frequency of bloody or mucous discharge from the vagina that is white or yellowish in color does not depend on the stage of the pathological process, then the proportion of pain syndrome increases significantly according to the degree of spread of the neoplasm. The presence of pain in a patient with a vaginal tumor indicates that the cancer process has spread beyond the organ. Most often, carcinoma is accidentally detected in the early stages of tumor development.
With a careful gynecological examination, diagnosing vaginal cancer is not difficult. During a speculum examination, gynecologists carefully examine the vaginal vaults, not forgetting that most malignant neoplasms of the vagina, especially in the early stages of development, are localized in its upper third. Tumors of the vagina belong to the “visual” localization. A reliable diagnosis is provided by cytological examination, colposcopy and biopsy. These diagnostic procedures are performed sequentially.
Where can I get a biopsy of a vaginal tumor in Moscow? At the Oncology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, doctors professionally perform targeted biopsies of suspicious areas and send the material for histological examination. It allows you to confirm or exclude a malignant tumor with high accuracy (up to 95%). To clarify the extent of spread of the tumor process in the Yusupov Hospital, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic and abdominal organs;
- Cystoscopy;
- Sigmoidoscopy;
- Radioisotope renography;
- Chest X-ray;
- Isotopic study of skeletal bones.
High-tech examination methods, which include magnetic resonance, computed tomography and positron emission tomography using the radiopharmaceutical drug fluorodeoxyglucose, are very informative, but, given their cost, are not mandatory. In vaginal cancer, magnetic resonance imaging is useful in diagnosing regional lymph node metastases, but MRI characteristics of the primary vaginal tumor are nonspecific.
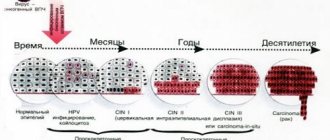
To plan treatment and follow-up of patients at the Yusupov Hospital, a comprehensive diagnosis of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is carried out using the following methods:
- Cytological - allows you to identify specific cells that are characteristic of HPV infection;
- Extended colposcopy after treating the vaginal mucosa with a solution of acetic acid;
- Molecular - determination of HPV DNA in the cells and tissues of the genital organs (polymerase chain reaction).
Using a comprehensive step-by-step approach to diagnosing vaginal cancer allows gynecologists at the Yusupov Hospital to quickly establish an accurate diagnosis and develop a treatment regimen. All cases of vaginal tumors that are difficult to diagnose and treat are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category.
Other reasons
Growths sometimes appear for reasons that do not pose any particular harm to health:
- cysts;
- polyps;
- shellfish
These defects are not accompanied by alarming symptoms and are not accompanied by discomfort. Nevertheless, it is recommended to remove them, since with strong magnification such neoplasms block the birth canal and interfere with conception. If growths appear at the entrance to the vagina, you need to visit a gynecologist or venereologist. Only timely medical care will help avoid dire consequences.
Treatment of vaginal growths and diagnosis
It is impossible to delay the treatment of formations in the vagina. The earlier removal techniques are applied, the greater the likelihood of avoiding developmental pathologies. Fixing the problem yourself is fraught with negative consequences. The method of curing the disease is prescribed only by a gynecologist who has a clear clinical picture. To establish it, diagnostics are prescribed. The table describes the main methods for diagnosing the disease.
| Method | Description |
| Visual inspection | Conducted by a gynecologist along with an oral survey of the patient for symptomatic manifestations. The walls of the vagina and uterus (colposcopy) and the anus area (anoscopy) are examined. |
| PCR diagnostics | The type of HPV, quantity and effect on the body is determined, which can be done by scraping from the affected area of skin |
| ELISA | The presence and reaction of antibodies to the virus are checked |
| Cytological and histological | Cells and tissues of nodular formations are examined using a microscope |
| Oncocytology | The presence of cancer cells is determined using a smear from the cervical area and the cervical canal area |
Having complete information about the type and type of growth around the vagina or on its walls, the treatment method is determined.
To treat condylomas, you cannot do without antiviral tablets.
Drug treatment
To get rid of condylomas using a conservative method, antiviral drugs are used. Popular medications among consumers are Alpizarin, Lykopid or Podophyllotoxin. When prescribing such medications, the doctor takes into account the patient’s age, health status and individual sensitivity to the components. In combination with antiviral drugs, drugs to stimulate the immune system are prescribed: Cycloferon, Galavit, Immunofan. "Galaderm" is an ointment with restorative and healing properties that is applied directly to the growth.
Hardware treatment
Gynecologists recommend using hardware methods for getting rid of vaginal condylomas. Such treatment is not as long as medication, not as traumatic as a conventional operation, which is performed by a surgeon with complete excision of the condyloma, and, if necessary, with nearby tissues. Hardware techniques reduce the risk of relapse and leave no scars. It is carried out in combination with immune therapy under the supervision of a physician. The table provides descriptions of hardware methods.
| Hardware treatment method | Description |
| Laser therapy | Drying and removing the growth using a laser. Used for large diameter build-up |
| Cryodestruction | Freezing with liquid nitrogen. The procedure takes place in several stages |
| Radio wave destruction | Removes using radio waves, leaves no scars |
| Electrocoagulation | Getting rid of condylomas using elevated temperature. Skin restoration course - 14 days |
It is rational to treat extensive or aggressive neoplasms in the vagina using hardware methods.
The choice of hardware treatment technique is based on the wishes of the patient and the doctor’s recommendations. Only specialized clinics perform such procedures. You should not go to a cosmetology salon because of the risk of encountering unprofessionals. The rehabilitation course does not last long; during this period you should abstain from sexual activity. Recurrence of condylomas in the vagina means that HPV remains in the woman’s body and repeated intervention is required.
Growths in the vagina: drugs and treatment regimens
For different pathologies, different treatments are used.
In most cases, growths in the vagina can be removed using conservative therapy.
For herpes, acyclovir is prescribed.
For nonspecific inflammations or bacterial STDs - antibiotics.
For pediculosis pubis, treatment with permethrin is prescribed.
For some viral diseases, such as molluscum contagiosum and condylomas, there are no specific drugs.
Therefore, treatment regimens consisting of immunomodulators and general antiviral drugs are used.
They help reduce the viral load.
As a result, there is a possibility that the growths will disappear.
Although in most cases they have to be removed by laser or electrocoagulation.
Then immunomodulators are prescribed only to prevent the re-formation of rash elements.
Should my partner be treated?
Most growths in the vagina appear as a result of infectious causes.
It could be herpes, papillomavirus, molluscum contagiosum, etc.
Therefore, in such cases, the sexual partner most likely has the same disease.
He needs to be treated at the same time as the woman.
Otherwise, re-infection will likely occur in the future.
And then all the results of treatment will go down the drain.
In some cases, there is no need to treat your partner.
After all, growths can be caused by mechanical injuries, allergies, burns, and nonspecific inflammations.
Such pathologies are not contagious.
Similar diseases are unlikely to be detected in a partner.
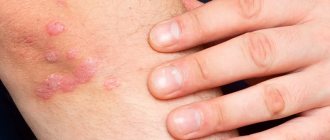
Genital herpes near the vagina
Genital herpes is an infection that is sexually transmitted.
It causes the appearance of growths in the vagina, the causes of which are viral infections of the skin and mucous membranes.
Bubbles containing clear liquid appear.
The pathology is accompanied by burning and other unpleasant sensations in the problem area.
General intoxication symptoms often occur.
A woman's body temperature increases.
Symptoms of genital herpes go away even without treatment.
Although this takes one and a half to two times longer than when receiving adequate antiviral therapy.
Such growths in the vagina are especially dangerous during pregnancy.
Because herpes is one of the most unfavorable viruses for the fetus.
It often causes spontaneous abortions or congenital deformities.
If herpes is detected during pregnancy, the woman must be treated.
This is necessary to prevent infection of the fetus.