December 5, 2020
Most infections are caused by streptococci and staphylococci. They live in the environment, inhabiting the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, and genitals. In 9–12% of cases, inflammation is provoked by corynebacteria, leprosy bacilli, tuberculosis, and campylobacter.
Healthy skin keeps germs out. This is prevented by the structure of the epidermis, the pH of sweat and sebum, and the antiseptic properties of the secretion of the sebaceous glands. When protection is violated, pustular rashes occur.
Causes
The occurrence of an infectious pathology always involves the presence of a corresponding pathogen. They are bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. Depending on the type of pathogen, the clinical picture of a particular disease will differ.
Common Causative Agents of Skin Infections:
- Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus – scarlet fever, erysipelas.
- The herpes virus is herpes zoster.
- Rubella, measles, and chickenpox viruses that cause corresponding diseases with severe skin damage.
- Fungi of the genus Candida – candidiasis.
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a specific skin lesion.
- Human papillomavirus – warts.
- Staphylococci and streptococci - sycosis (skin lesions under the nose), pyoderma, folliculitis - inflammation of the hair follicle.
- Fungi – trichophytosis, microsporia.
- Mycobacterium leprosy - leprosy.
The mechanism of human infection is based on physical contact with the carrier. Transmission of microorganisms can occur by airborne droplets (measles, rubella, chickenpox). The chance of developing a corresponding skin lesion directly depends on the following factors:
- The aggressiveness and amount of the pathogen that has entered the human body.
- Reactivity of the patient's body. If a person is healthy and has a strong immune system, then the risk of getting sick is reduced. As the pathology progresses, it progresses more mildly.
- Presence of concomitant diseases.
In addition to these reasons, an important role is played by the influence of external factors on a person, which can increase the risk of developing pathology:
- Ignoring personal hygiene rules.
- Frequent trauma to the skin. Mine workers, lumberjacks, and doctors are at risk.
- Poor nutrition.
- Congenital or acquired immunodeficiency.
- Frequent fluctuations in air temperature.
- Excessive exposure to sunlight.
An arbitrary combination of these factors affects the activity of the pathology and its prognosis. Depending on the pathogen, appropriate treatment is selected to stabilize the patient’s condition.
Neglecting bandages
If you think it's a good idea to let your skin breathe after initially treating any microtrauma, think again. By not covering the wound with a bandage, you expose the skin to infection. New cells must migrate to the appropriate areas for the wound to heal faster. By covering it with a bandage, you make this process easier and faster. The best way to help prevent infection is to apply an ointment to the wound, which you should always have in your home. If you haven't visited a doctor, then at least keep Vaseline in your medicine cabinet. As you know, it prevents the wound from drying out and scabs forming, and accordingly, it heals faster.
General symptoms
Skin infections are a group of diseases that primarily affect the human dermis and epidermis. The clinical picture directly depends on the localization of the process with the progression of characteristic symptoms.
General signs:
- Redness of the skin.
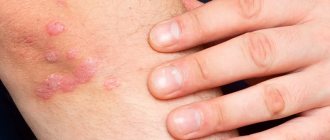
- The appearance of pathological elements of different shapes and sizes. It all depends on the specific pathogen. The nature of the rash is one of the important elements for the differential diagnosis of various infectious diseases.
- Itching or pain in the affected area of the epidermis.
- Local increase in body temperature.
- General deterioration of a person's condition.
In severe forms of diseases that occur with damage to the skin, other body structures - internal organs - are drawn into the process. Symptoms can be supplemented by a person’s nervousness and the progression of dyspeptic disorders - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
A common sign of skin infections is fever, which can vary in nature. This symptom is optional (optional) and occurs in severe forms of pathology with massive penetration of the pathogen into the human blood.
Additional signs:
- Formation of a film or plaque on the surface of pathological skin elements.
- Retraction of lymphatic ducts or nodes into the process with their soreness and enlargement.
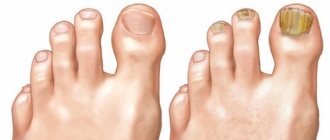
- Thinning, hair loss or damaged nail plates that become uneven and gradually deteriorate.
- The appearance of dark spots on the body.
- Sleep rhythm disturbance.
General symptoms are further aggravated in the presence of concomitant diseases and disorders that increase the activity of the pathogen. Children and older people suffer more severely from bacterial and viral lesions of the body.
Types of Skin Infections
There are three main groups of viruses:
- Infections caused by the herpetic virus: herpes zoster, herpes, chickenpox.
- The cause of infections of the second group is poxvirus. It causes molluscum contagiosum, vaccinia and false cowpox.
- The third group includes skin diseases that are caused by 3 viruses - polyoma, papilloma and vacuolinating virus. Manifestations of these viruses are genital and plantar condylomas, flat and vulgar warts.
Major diseases
Infectious skin diseases are a large group of pathologies, including different variants of the problem. Some of them are encountered more often in practice, others less frequently. Below we will describe the main diseases that require special attention from the patient and the doctor.
Leprosy
Leprosy or leprosy is a relatively uncommon chronic infectious disease of the human body, which occurs due to the activity of the corresponding microbacteria. It is transmitted only through prolonged and close contact with an infected person.
Erysipelas
Erysipelas is an acute skin lesion caused by hemolytic streptococcus, which manifests itself with a pronounced clinical picture with redness of the epidermis, fever and pain.
Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic form of skin disease, which is accompanied by local dilation of blood vessels in the epidermis with the formation of characteristic rosacea. In this case, infection often acts as a provoking factor for the disease.
Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is one of the childhood infections that is caused by streptococcus and occurs with a syndrome of general intoxication of the body, fever and a characteristic rash that spreads throughout the patient’s body.
Erythrasma
Erythrasma is a bacterial infection of the stratum corneum of the epidermis, which occurs in natural folds - under the breasts in women, in the scrotum area in men. Less commonly, the axillary fossa is affected.
What pathologies does a dermatologist treat?
Dermatologists at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences successfully treat diseases caused by:
- viral infections (warts, condylomas, herpes, molluscum contagiosum, etc.);
- bacterial infections (impetigo, pyoderma, etc.);
- fungal infections (mycosis of smooth skin, candidiasis, onychomycosis, favus, pityriasis versicolor, etc.);
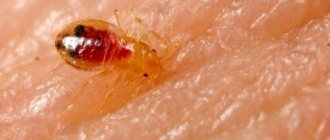
- skin damage by parasites (scabies, pediculosis).
They will help you get rid of any non-infectious pathologies associated with skin, nails and hair problems: psoriasis, eczema, acne, atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, rosacea. Benign formations (keratomas, papillomas, etc.) are removed.
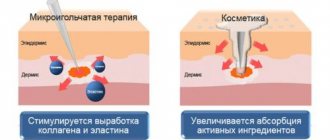
Cosmetic procedures help restore and improve the condition of the skin. To prevent negative changes, a dermatologist can recommend special diets and effective cosmetics to maintain the elasticity and healthy appearance of the skin.
Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a dermatovenerologist 2500 Repeat appointment (examination, consultation) with a dermatovenereologist 2000
+7 (495) 320-43-41
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pathology influences the correct selection of therapy. To determine the root cause of a particular disease, doctors carry out:
- Analysis of the patient's complaints and medical history.
- General examination of the skin and pathological elements.
- Clinical blood test.
If necessary, an additional microscopic examination of scrapings from the affected areas of the epidermis is carried out to verify the pathogen. An auxiliary laboratory method remains the study of blood for the presence of antibodies to the corresponding bacteria - serological analysis.
To establish the sensitivity of microorganisms to individual drugs, an antibiogram is performed. It allows you to accurately select a medication that will affect a specific pathogen.
To verify the presence of viral invasion, polymerase chain reaction is additionally used, a diagnostic method that allows the detection of pathogen DNA or RNA particles in the patient’s blood.
Principles of treatment
Therapy for infectious diseases is divided into three large groups:
- Etiotropic – involves the destruction of the causative agent of the problem.
- Pathogenetic – based on neutralizing the main points of the corresponding process.
- Symptomatic or supportive – involves minimizing the patient’s negative feelings without affecting the source of the problem.
When identifying a specific pathogen, specific medications must be used. If the cause of the pathology is bacteria, then doctors use antimicrobial agents (tetracycline ointment and others), viruses - antivirals and stimulants of the immune system (interferons, acyclovir), fungi - fungicides (fluconazole).
The speed of elimination of concomitant symptoms depends on correctly selected etiotropic therapy. The destruction of the pathogen automatically breaks the pathological process, which is accompanied by damage to the skin and other organs in the human body.
To speed up the process, auxiliary medications are used, which significantly increase the effectiveness of antibiotics and other groups of substances. The most popular remain glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone).
This group of hormonal drugs is used in moderate and severe cases to support the body and speed up recovery. Improper use of steroids is fraught with the progression of a number of complications and adverse reactions.
The following groups of medications are prescribed as symptomatic therapy:
- Antihistamines - Tavegil, Suprastin, Diazolin. The drugs help reduce the activity of itching and partially reduce the severity of the inflammatory process.
- Immunomodulators - Viferon, Arbidol and others. The drugs are used to enhance the activity of endogenous defense mechanisms.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – ibuprofen, paracetamol, acetylsalicylic acid. Prescribed to combat fever and pain.
To improve the condition of the skin, in rare cases, a variety of moisturizing creams are used. Their prescription should be carried out only after consultation with the attending physician due to the risk of worsening symptoms if used inappropriately.
Prevention
It is always easier to prevent the development of a disease than to deal with its consequences. To prevent any infectious process, there are several simple tips:
- Eliminating or minimizing contact with an infectious person. If it is impossible to completely limit communication, you should use a mask and not make physical contact to prevent the transmission of microorganisms.
- Nonspecific enhancement of the resistance of the immune system. We are talking about proper nutrition and sleep, regular proper stabbing.
- Vaccination. Specialized prophylaxis has been developed for a small number of skin infections (measles), but should be used whenever possible.
- Minimizing skin trauma.
- Timely consultation with a doctor if characteristic symptoms occur with the selection of adequate therapy.
Sometimes infections are transmitted from pets - trichophytosis. In this case, disease prevention involves avoiding contact with cats or dogs.
Infectious diseases are a common problem that can be managed. The main thing is to see a doctor on time and not delay with proper treatment.