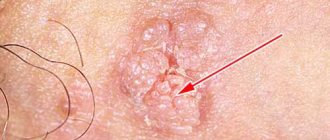
Genital perianal condylomas are a viral disease that occurs when a patient is infected with the human papillomavirus. Exophytic fibroepithelial growths appear on the skin around the anus. In ICD 10, condylomas of the perianal area are coded A63.0. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital take an individual approach to the treatment of each patient who suffers from perianal condylomas.
For small tumors, local therapy with antiviral drugs is carried out. If the patient has a compromised immune status, he is consulted by an immunologist and prescribed systemic immunomodulators. In the presence of large condylomas, various methods of their destruction are used. If there are multiple condylomas of the perianal area, surgeons at the proctology department remove them surgically. After treatment, patients are under the supervision of doctors at the Yusupov Hospital. The issue of treatment of patients with recurrent perianal condylomas is discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council with the participation of professors, doctors of medical sciences, and doctors of the highest category.
Vulvar condylomas: how does infection occur?
Papillomavirus enters the body from an infected person, and several types of this virus can be “received” at the same time.
Once in the body, the virus penetrates epithelial cells.
The favorite zone is the junction of the flat and cylindrical layer of cells.
There it can exist in two forms: episomal and introsomal.
- Episomal form - the virus is in the cell, but is not integrated into the genetic material (chromosomes). This is a benign form of the existence of HPV, when there is an incubation period for vulvar condylomas. Its duration is very variable: from several weeks to decades. In addition, the virus can be eliminated from the body on its own without leading to the development of the disease.
- Introsomal form - the virus is located inside the cellular genome; this is a more malignant version of the infection.
With the active reproduction of HPV, a change in the growth and development of epithelial cells begins.
Namely, their uncontrolled division, which leads to tissue proliferation with the formation of genital warts.
Location of vulvar condylomas in women: labia minora, frenulum and clitoris area of the vulva, anus area.
Less commonly found on the labia majora, in the perineum, inguinal folds, on the walls of the vagina and cervix.
The last two options can only be detected by a doctor during an examination.
Possible complications
Timely diagnosis plays the main role in the success of treatment of the disease. If you ignore the symptoms of the disease, the risk that the process of changing the disease to a malignant form will begin. In this case, the patient may develop malignant tumors, as well as squamous cell carcinoma.
Patients with this disease should be regularly monitored by their doctor. The specialist carefully monitors the patient’s general condition, as well as his body’s reaction to the chosen treatment method. Constant monitoring of the patient's condition is important to protect against relapse and complications.
Unfortunately, even after radical removal of the lesions, the possibility of relapse still remains high. For this reason, the patient is obliged to follow preventive measures: use antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs prescribed by a doctor.
Condylomatosis is a disease that is quite dangerous for the human body. If you pay attention to its symptoms in time and begin proper treatment, the patient’s condition will soon return to normal.
Methods of infection with vulvar condylomas
- Sexual contact with a partner who has HPV in his body. Even using a condom will not protect against infection.
- Through any biological fluids in direct contact: blood, urine, vaginal discharge, semen.
- A child can become infected during childbirth from an infected mother.
- Since viral particles are very small, the likelihood of household infection is high. Sharing hygiene products (razors, washcloths), towels can lead to the virus entering the body. Although it is quite difficult to prove the domestic route of infection.
There are 4 ways the virus can develop when it enters the body and causes genital warts to appear:
- Self-regression, even in the absence of treatment. This often happens when the disease manifests itself during pregnancy, and after childbirth the condylomas disappear. Such regression is observed in 18% of patients.
- Process stabilization. The existing growths remain in the same quantity and have unchanged sizes for a long time (more than 2 years).
- Intensive reproduction of condylomas, their proliferation, increase in size, appearance of new elements. This form of the disease requires active systemic treatment and surgical removal of condylomas.
- Malignant degeneration with frequent trauma and inflammation (although the risk of malignancy with condylomas is low).
The state of the body's immune system plays an important role in the clinical manifestation of HPV.
There are a number of external and internal factors that serve as a favorable background for the development of the disease.
- A state of pregnancy, and often lactation, when a woman is forced to limit her diet due to allergic rashes in the child.
- Long-term chronic stress conditions.
- Injuries, inflammation and mechanical damage to the vulvar mucosa.
- Any acute and chronic pathology of the reproductive system (STI, nonspecific colpitis, endometriosis, etc.).
- Numerous sexual contacts lead to a weakening of local immunity due to the constantly changing microflora.
- Long-term use of medications from any group. Particularly dangerous in this regard are long-term use of antibiotics, cytostatics, antitumor drugs, and antidepressants.
- Frequent recurrent acute infections of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory organs.
- Chronic pathology of the endocrine, urinary, cardiovascular and other systems.
- Prolonged hypothermia and excessive passion for tanning/solarium.
- Vitamin deficiency (an important role is played by vitamins C, A, beta-carotene and folic acid).
- The issue of the effect of combined oral contraception on the appearance of genital warts is being debated. There are individual statements from patients that they developed vulvar condylomas after Yarina, Regulon and other contraceptives used for more than a year. But long-term multicenter studies conducted in Europe suggest that even long-term use of contraceptives does not affect the incidence of genital condylomatosis. Vulvar condylomas are not even mentioned in the instructions for use as one of the possible complications.
Types of papillomas
Experts also identify the following forms of human papillomas:
- Vulgar papilloma. This formation is a small lump - about 1 mm in diameter. Its keratinized part protrudes above the skin border. This type of papilloma does not have a stalk. The formation can form on any part of the body, but most often spreads to the fingers or knees.
- Plantar papilloma. In this case, a rough formation forms on the sole of the feet, is not large in size, and has an unusual protruding rim. Most often it forms in single quantities, but can provoke the formation of daughter growths near the main papilloma. This formation leads to unpleasant sensations during movement, and most often goes away on its own without outside help. In order not to confuse a papilloma with a callus, it is important to remember that calluses have a smoother surface and also have a characteristic pattern on them.
- Flat papilloma is a flat-shaped lump. Can be a polygon. The color almost matches the skin. Such a lesion can occur on any part of the body, but is most often localized on the face and hands. Provokes pain, redness, burning and inflammatory processes in the affected area of the body.
- Filiform papilloma. Typically appears in patients aged 40 to 50 years. The location of distribution is the area of the eyes, neck, groin and armpits. At the beginning of development, the growth is a protrusion of yellow color and small size. After some time, the formation turns into a thread-like, elastic and elongated papilloma. Filiform papilloma requires mandatory treatment.
What can vulvar condylomas be confused with?
With the active development of the process, the shape of condylomas is quite typical for this disease.
But in the early stages, when the pathological elements are still small and there are few of them, other diseases can be assumed:
- herpes infection;
- allergic rashes;
- nonspecific pustular lesions;
- flat warts;
- lipomas;
- manifestations of secondary syphilis.
The most dangerous disease, which is very similar to genital warts, is verrucous invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
Bibliography
1. Human papillomavirus infection of the urogenital tract of women (epidemiology, clinical and pathogenetic features, diagnostic methods, treatment, prevention). Information and methodological manual / Folyak E. V., Sokolova T. M., Makarov K. Yu., Yakimova A. V., Mukhamedshina V. R., Usova A. V. - 2010. 2. Errors in oncogynecological practice / Vishnevskaya E. E., Bokhman Ya. V. - 1994. 3. Human papillomavirus infection - clinical picture, diagnosis, treatment / Dolgopolova I. A. // Pediatric pharmacology - 2007 - T. 4, No. 1.
Source
Vulvar condylomas with HIV
The human immunodeficiency virus leads to a weakening of general immunity.
As a result, all bacteria and viruses that are in an inactive state in the body are activated.
After fungal infections, vulvar condylomas are the second most common in the presence of HIV in the body.
The peculiarity of condylomas in immunodeficiency is their active reproduction, a rapid increase in the number of rashes, and a tendency to merge.
Infection as a result of the addition of secondary bacterial flora is also possible.
Vulvar condylomas with HIV are difficult to treat.
The danger of oncology with vulvar condylomas is associated with two reasons:
- A general and local decrease in immunity, against the background of which condylomas have developed, is in itself dangerous in terms of the development of oncological pathology.
- Localization of formations in the genital area contributes to traumatization by underwear, as well as during sexual intercourse. As a result, inflammation develops, and against this background, malignant degeneration of cells is possible.
Causes
The main route of transmission of papillomavirus is sexual. Of course, it is possible to become infected through household means, but it is extremely rare. This is due to the fact that for the virus to spread through household contact, several factors must be present simultaneously: decreased immunity, insufficient hygiene, and a living pathogenic microorganism in the external environment.
In contrast, sexual contact creates an optimal environment for the virus:
- humidity;
- friction;
- microtraumas;
- The pathogen gets on the skin, and it does not need to survive in the external environment.
Even protected sexual contact does not guarantee the absence of infection. For example, if one of the partners has a tumor on the pubis or on the root of the penis, it cannot be covered with any condom. Thus, a healthy person becomes infected.
Provoking factors
As mentioned above, HPV can remain latent for a long time. The following circumstances can provoke the growth of condylomas:
- weakened immunity;
- various chronic diseases;
- irregular sleep and wakefulness patterns;
- unhealthy food abuse;
- other sexually transmitted infections;
- microcracks or injury to areas of usual localization;
- disruptions in the endocrine system;
- hypothermia/overheating;
- clothing that restricts movement and rubs the body.
It happens that the growth of genital warts is associated with the use of contraceptives. For example, a drug taken by Yarina without undergoing a hormone test can cause a hormonal surge. That is, incorrectly selected drugs weaken the body, provoking the activation of HPV.
Important!
Before taking birth control contraceptives, you should undergo a full examination.
Vulvar condylomas, where to go
If you have suspicious rashes in the genital area, you can consult an obstetrician-gynecologist or dermatovenerologist.
A visit to a gynecologist will help rule out nonspecific inflammation and other possible sexually transmitted infections.
A dermatovenerologist will make a differential diagnosis between genital warts and skin pathology of another origin.
Which doctor treats vulvar condylomas when they are detected?
If the diagnosis has already been established, treatment can be prescribed by both an obstetrician-gynecologist and dermatovenerologist, and an infectious disease specialist.
Description
These are benign tumors of the female genital organs associated with infection of an oncogenic virus. The disease can be asymptomatic escritis or manifest in the vulva, vagina, or cervix. Visible growths are usually accompanied by bleeding and itching. The diagnosis is established based on the results of a clinical examination, colposcopy, cytological and DNA analysis. Complex treatment includes immunotherapy, the use of cytostatic drugs, and destructive methods.
Vulvar condylomas: diagnosis
There are a number of sequential steps that help establish a diagnosis.
- Examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist or dermatovenerologist on a gynecological chair. At the same time, the appearance, quantity, size and location of pathological elements are described in detail. Condylomas are also supported by their painlessness when pressed with a spatula.
- Carrying out simple and extended colposcopy and vulvoscopy (examination using a microscope). It is important not to miss viral lesions on the cervix, which may accompany condylomas.
- Carrying out an oncocytological smear. Allows you to detect atypical cells and other signs of viral damage in the cervical canal.
- Biopsy and histological examination - if the clinical picture is unclear and it is impossible to differentiate condyloma and malignant neoplasm. Histology can also be performed after removal of pathological lesions.
- PCR for HPV in genital warts allows us to identify the genetic material of the papillomavirus, determine its type and degree of oncogenicity. This is one of the most reliable and reliable examination methods, which is quickly and painlessly carried out by doctors at our dermatovenerological dispensary.
- A serological test is a study of blood from a vein for the presence of antibody proteins, which are produced by the body in response to the virus entering the cells. Antibodies of type M can be detected even before the onset of clinical symptoms. Thus, the examination can show how long the body has been affected by the virus, but does not provide information about the concentration of HPV, the type of virus and the degree of its oncogenicity.
- The Digene test (daijin test for vulvar condylomas) is a relatively new, simple and reliable research method that detects a clinically significant level of papillomavirus. Those. it determines the concentration of the virus that can lead to the development of cancer.
Also, in the presence of vulvar condylomas, tests for other sexually transmitted infections, which can often exist in parallel with the virus, may be recommended.
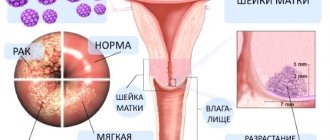
Classification
Condylomas are classified according to various criteria. Depending on the clinical course, a distinction is made between clinical, subclinical and latent forms of infection. Due to the localization of pathological changes, condylomatosis of the cervix, vulva and vagina occurs (damage is often observed due to the proliferation of various areas). Depending on the clinical signs and appearance, genital warts can be divided into two types: This is the predominant form of the disease. Clearly visible growths of various shapes (pointed, papillary, papuloid) protruding from the mucous membrane were found. The growths are rarely malignant (with the exception of giant warts - giant warts of Buschke-Levenshtein), and the area of the external genitalia is most often affected. The formations are located in the thickness of the epithelium, usually they do not rise above the surface, they are invisible without the use of instrumental methods. There are flat and inverted (penetrating deep into the stroma, cervical glands) condylomas. Endophytic forms are most often associated with dysplasia, cancer and are mainly observed in the cervical and vaginal regions. In addition to these types, some doctors distinguish condylomatous vaginitis and cervicitis. These forms are characterized by focal lines without clear boundaries or widespread epithelial lesions throughout the anatomical region (vulva, vagina, or cervix). Sometimes they can be identified without special imaging tools, such as small pointed growths against a background of edematous mucosa over its entire surface.
Treatment of vulvar condylomas
When small single growths appear, many patients are in no hurry to see a doctor and practice home treatment for vulvar condylomas.
And although official medicine does not confirm the effectiveness of such therapy, you can find many reviews of positive experiences with the use of certain herbs.
- Celandine . This plant is well known to many. Used to remove a variety of skin tumors. To treat condylomas, an alcoholic tincture of this herb is used, which has bactericidal properties due to the isoquinoline alkaloids it contains. It is quite labor-intensive to prepare the tincture yourself; it is better to purchase a medicine made from celandine in a pharmacy chain. The affected areas must be treated carefully, without affecting healthy tissue.
- Potato juice. Unpeeled but well-washed potatoes should be grated on a fine grater and the juice squeezed out through cheesecloth. It must be taken orally for at least 2 months.
- The leaves of pinnate Kalanchoe are also used in the fight against condylomas. They must be thoroughly crushed until a paste forms, applied to the pathological growth and fixed. The dressing with fresh pulp is changed after 4-5 hours.
- In the unofficial literature there are also a few references to the treatment of genital warts using red wine, plum pulp, as well as many medicinal herbs , but the effectiveness of such treatment methods is extremely unlikely.
In addition to alternative medicine, medications are used to remove condylomas, the regimens of which are quite complex.
They are signed individually for 2-6 months.
In the presence of long-term persistent condylomas of the vulva, an immunogram may be prescribed and immunological treatment may be carried out.
It consists of prescribing tablets, intramuscular and intravenous injections, vaginal and rectal suppositories to stimulate one’s own immunity.
Is sex acceptable during treatment for vulvar warts?
Since treatment of the virus takes a long time and none of the therapeutic regimens is more than 80% effective, there are no restrictions on sexual intercourse.
But this only applies to connections with a permanent partner.
If a change of sexual partner occurs during treatment, infection with a different strain of the virus or other STIs is possible, which will significantly worsen the prognosis of the therapy.
Tests after treatment of vulvar condylomas are taken no earlier than 6 months after the end of the course of therapy.
Prevention measures
Personal prevention will consist of protecting the skin and mucous membranes of the genitourinary system, careful treatment of the disease, and abstaining from sexual intercourse for some time. Also, to prevent the development of vulvar condylomatosis, it is important to get rid of all existing diseases that can create conditions for the spread of infection.
If necessary, during treatment therapy, the treating specialist changes the method of treatment, the drug or adds additional therapy; in each specific case, the method will be selected individually. Observation at the dispensary is also important in order to avoid the development of a relapse of the disease and prevent its degeneration into the form of a tumor.
Features of papilloma infection
The main features of papilloma infection include:
- decreased immunity;
- condylomas grow and resemble cauliflower in appearance;
- causes discomfort during sexual activity (if condylomas form on the penis and vagina);
- If the growths are injured, infection and suppuration may occur.
Condylomas are neoplasms that can develop into malignant tumors.
Symptoms
Small genital warts cause almost no discomfort, and there are almost no symptoms. The appearance of certain omens has a strictly individual nature for any person. In the primary phases, the disease may not manifest itself at all.
The progression of the disease is indicated by the appearance of a rash similar to nodes. As a rule, in the female part of the population, the place of manifestation of this disease is the labia, cervix and vagina. Men can find it on the glans penis and scrotum. In the oral cavity and in the anal area, condylomas are found in any gender.
Women are characterized by certain symptoms:
- uncomfortable sensations at the site of the rash;
- feeling of a foreign object;
- increased humidity at the site of formation;
- the disease is accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
Men have the following characteristics:
- walking and physical activity increase discomfort;
- mild pain in the stomach;
- sharp pain appears during sex;
- painful sensations during urination.
When the form is severe, the disease is accompanied by intoxication, migraines, and increased body temperature.
You can relieve certain symptoms at home, but first, you need to consult a specialist.
What tests are needed?
If a woman notices neoplasms, it is necessary to consult a specialist to establish a correct and accurate diagnosis.
- A cytological smear helps to find an atypical cellular form in the uterus. If the age is over thirty years, then a screening test is recommended; it is carried out in combination with a smear and determines the necessary information about the virus. For girls under thirty years of age, this procedure is prescribed if the smear results are positive. If atypical cells are found, additional treatment is prescribed.
- There are no screening tests for men; a physical examination method is used for them. This examination includes an external examination of the genital organ and anus. Experts recommend that men who practice homosexual relations undergo periodic anal smears at least once a year.
- More often than not, a physical examination is sufficient to correctly make this diagnosis. A special substance changes the color of the growths and highlights them for better detection. A weak solution of acetic acid is also used to detect the disease; a strong burning sensation and discomfort will be felt in the infected areas.
Who should I contact?
A general practitioner or family doctor can diagnose the disease. But for successful treatment, you need to seek help from a gynecologist, urologist or dermatologist.