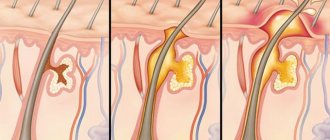
A boil on the face is a purulent formation caused by an anaerobic bacterium - Staphylococcus aureus. Most often, treatment is carried out surgically within the hospital.
Photo 1 - Furuncle on the face
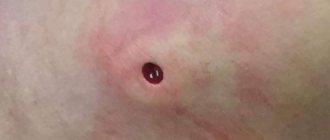
Self-medicating and trying to get rid of an abscess on your own is fraught with unpleasant consequences.
Photo 2 - It is not recommended to open the boil yourself
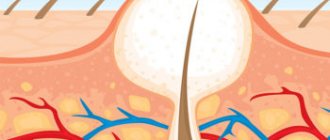
In addition, opening an abscess without anesthesia is sometimes difficult due to the patient's high sensitivity to pain.
Photo 3 - The boil is opened under anesthesia
Indications
The greatest danger is represented by purulent formations that appear on the mucous membrane of the vestibule of the nose and on the area of the face limited by the nasolabial folds. Such boils are often complicated, due to the peculiarities of the blood supply to these areas. The risk of complications increases many times after attempts at squeezing and improper treatment at home.
Indications for contacting the clinic are also the following cases:
- temperature increase;
- severe, unbearable pain;
- location of the boil on the face, in the nasal or ear canal;
- large boil size (more than 5 mm);
- there are signs of the inflammatory process spreading to neighboring areas: a second boil appears not far from the first, the skin around the formation is hyperemic, and stripes have appeared on it.
It is imperative to consult a doctor if a boil appears in a small child. Professional medical care is also needed for those who suffer from serious illnesses that require constant use of medications.
In other cases, it is also better not to experiment with health. It is difficult for an untrained person to properly remove and treat a boil after opening. Infectious agents remaining in the wound can provoke repeated suppuration and other complications.
Why does a boil break out?
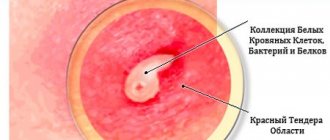
At the initial stage of the disease, a pustule forms at the mouth of the follicle. It contains leukocytes, fibrin clots, and pathogenic flora. With the development of the inflammatory process, staphylococci move, multiply freely and release exotoxins. Infiltration and tissue necrosis form. The affected areas melt, creating pus in the boil.
The body tries to localize the process, forming an infiltration shaft. Under conditions of constant elevated temperature and humidity, staphylococcus continues to multiply in the hair follicle. But the follicle with a boil has strictly defined anatomical dimensions; the shaft restrains the spread of infection to neighboring tissues. The volume of the hair follicle is not enough for a large number of pathogenic organisms. The appearance of a white cone means that the abscess is ripe.
The surface of the skin over the affected follicle is not protected; it becomes thinner under the pressure of purulent formations from the inside. It melts and bursts easily. The opening of the boil occurs. Pus should come out of the formed canal freely. The last part to come off is the necrotic core.
Contraindications
There are practically no restrictions for surgical removal of a boil. In case of acute infectious diseases or severe depletion of the body, the autopsy can be postponed until the patient recovers. However, if the boil is painful or threatens to spread to nearby areas, your doctor may decide to remove it. Resection of the boil is done with caution in cases of poor blood clotting or active tuberculosis.
Possible complications
A boil is a formation caused by the pathological activity of infectious agents, therefore its contents contain a large number of microorganisms. The flow of pus upon opening contributes to the spread of bacteria and infection of adjacent areas of the skin. If you try to squeeze out the boil yourself, you can provoke the formation of new purulent processes in neighboring hair follicles.
The development of several boils at the same time can lead to their fusion. Extensive purulent formations form on the skin - abscess, carbuncle, phlegmon. The regular formation of several boils is called chronic recurrent furunculosis. This disease brings physical suffering to the patient and leaves cosmetic defects in the form of scars.
The spread of the purulent process to nearby lymph nodes and blood vessels leads to the development of lymphadenitis, phlebitis, and thrombophlebitis. The penetration of infectious agents from the abscess into the bloodstream causes sepsis.
The likelihood of dangerous complications is highest if purulent formations are located on the face. In the absence of adequate treatment, such processes are fraught with inflammation of the membranes and the formation of brain abscesses.
Symptoms of furunculosis
There are several stages in the development of boils, each of which has its own characteristic symptoms. The boil goes through 3 stages:
- Stage of development of infiltration - hardening is noted around the hair follicle, the skin turns red, a person experiences a tingling sensation and slight pain in the inflamed area. Gradually, the infiltrate takes on a rounded shape, which increases in size, nearby tissues swell greatly and the skin becomes very painful.
- The stage of suppuration and necrosis occurs 3 days after the onset of infiltrate development. At this time, the neoplasm has a diameter of approximately 1-3 cm and a boil core forms in its center. With the development of the purulent head, the neoplasm acquires a cone-like shape. During this period, the pain becomes unbearable, the person’s temperature may rise, and symptoms of intoxication appear. With mechanical impact or with careful treatment, the opening of chiria occurs. A huge amount of pus is released from the wound, sometimes with blood. After this, a green new formation emerges, it is called a plug or rod. Once the plug is removed, the inflammation will gradually subside and the pain will subside.
- Healing stage - within 2-3 days after removing the rod, the crater of the boil becomes scarred, initially it is blue-red, gradually becoming white. In general, the development cycle of a boil on the skin takes 8 days.
A boil can develop anywhere on the patient’s skin where there is hair; the formation of an abscess is never noted, on the soles and palms.
According to the degree of development, acute and chronic forms are noted. The acute form is characterized by the formation of a large number of boils in different places, and the chronic form is caused by the development of single neoplasms with a short interval of time. As a rule, exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease is observed with a decrease in immunity and mechanical damage to the skin.
Preparation
Only a fully mature boil can be opened. In order to speed up this process, it is necessary to regularly treat the inflamed area with Vishnevsky or ichthyol ointment and make compresses.
Warm, damp lotions on the boil accelerate blood circulation, which promotes rapid ripening. They are done 3-4 times a day, applying a compress for 10-15 minutes. Vishnevsky ointment, applied to several layers of gauze and applied to the diseased area, helps well. For small boils, this therapy can help get rid of it without surgery.
Before using ointments and other medications, you should consult your doctor. Vishnevsky ointment is contraindicated for atheroma, lipoma, hidradenitis and many other formations on the skin. If the patient makes a mistake and does not have a boil, such compresses can only do harm.
Treatment at home
Self-treatment and opening of an abscess is only permissible as an emergency measure in the absence of access to qualified medical care! Errors during the procedure can lead to serious complications and death.
Removing the core of the boil is permissible if it has broken through on its own and the wound is free of pus. Maturation without any intervention occurs 2 weeks after the appearance of the first symptoms. If the procedure is carried out before this date, then there is a possibility of infection entering the blood. And this in turn will lead to sepsis and death. Attempts to squeeze out a boil can lead to similar consequences.
To remove the necrotic rod you will need: a needle, chlorhexidine solution, bandage, antiseptic bandage.
The sequence of actions is as follows:
- Treat the needle, boil and the skin around it with an antiseptic.
- Carefully hook the needle into the plug covering the abscess and, without touching its edges, pull out the rod.
- After removal, treat the wound with chlorhexidine.
- Apply a bandage with antiseptic ointment.
Sometimes it is possible to pull out only the upper part of the rod. In this case, you need to wait until the purulent contents are completely released.
How is the operation performed?
The opening of the boil is carried out in the surgery department on an outpatient basis. Most patients do not require hospitalization, except in severe cases (large boils on the face or neck). The procedure is performed by a surgeon. In cases where the purulent formation is located on the face or neck, it is preferable to contact a maxillofacial surgeon or dental surgeon.
The technique for performing an operation to open a boil includes the following steps:
- Local anesthesia is performed by injection of Lidocaine or Novocaine;
- to release the accumulated pus, you need to make a small incision;
- through the incision, using a special instrument, the doctor pulls out a hard rod, around which the purulent process occurs;
- after removing the rod, a sterile rubber tube (drainage) is inserted into the cavity, which is necessary to prevent early healing of the wound until the remaining pus is completely evacuated (removed after 24 hours);
- then the cavity is treated with an antiseptic solution (hydrogen peroxide);
- a sterile sticker is applied (to prevent dissemination, it is not recommended to apply circular dressings).
What to do when opening a boil
If the boil has broken through, you need to make sure that the hard part - the rod - comes out and cleaning occurs. With an open wound, be sure to follow the rules of antiseptics. It is important to prevent the spread of infection from the opened abscess to adjacent healthy areas of the skin.
Treatment
After the boil has broken through, the purulent liquid masses and the stem that have come out should be removed. This is done using a gauze napkin. It is advisable to work with gloves. Moderate pressure on the area of the opened boil is allowed. This will allow the pus to drain freely.
If blood is released after squeezing, then the wound has been cleaned and the rod has come out. In this case, it is treated with hydrogen peroxide. The drug is applied directly to the opened abscess. Several antiseptic procedures may be required. This will prevent the development of relapse of the disease and prevent the formation of a new rod.
In addition to hydrogen peroxide, the following means can be used to treat a boil after the contents have been released:
- Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin;
- furatsilin solution;
- Betadine.
Do not use brilliant green solution or iodine to treat a wound from an opened boil. They contain alcohol and can cause a chemical burn to the wound surface.
Dressing
A gauze swab with an antibacterial and healing ointment is applied to a clean wound from an open abscess with a protruded rod. The dressings are changed according to the instructions for the medicine or the doctor’s recommendations. The best drugs are Vishnevsky's liniment, Levomekol, tetracycline ointment.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
They are applied in a dense layer, filling the resulting crater from the boil after the rod, and covered with a gauze cloth. Fix with a plaster or bandage. When changing the dressing, the remaining ointment is removed using a cotton swab.
Then the wound is cleaned using hydrogen peroxide and other liquid antiseptics. Apply ointment for external use and cover with a bandage. Compresses, lotions, and treatment with folk remedies are not used after the rod comes out.
If the boil is extensive and the doctor opened it and installed drainage in the postoperative wound, then dressings are carried out in the hospital. To do this, the patient must come to change the bandage on the appointed day. The first procedure is one day after the surgical procedure, then as prescribed by the doctor.
Further care and healing
Subsequent recommendations are to comply with hygiene standards and prevent infection of the wound surface after the white formation and rod have come out. The use of wound healing drugs is indicated as prescribed by a doctor.
In addition to the fact that it is necessary to heal the area after the boil has opened and the rod has come out, you need to keep the wound surface clean, avoid injury from clothing or other objects, and do not rip off the scab yourself. Epithelization takes place within the time frame established by the body. It is impossible to significantly speed it up.
Healing process
To accelerate tissue regeneration and prevent scar formation during the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to continue treatment. The complex of therapeutic measures includes the mandatory use of local remedies. In case of a high probability of complications, the doctor prescribes antibiotics to prevent relapses and spread of the inflammatory-infectious process.
After removal, the boil should be treated with healing bactericidal ointments, changing the sticker daily. The most effective ointments are Levomekol, Solcoseryl, synthomycin (1%), white mercury (2%), and tetracycline. Hypertonic sodium chloride solution helps well. When changing the sticker, the skin surrounding the cavity is treated with camphor or salicylic alcohol 2%.
To speed up healing, it is recommended to apply dry heat to the affected area. To do this, use a heating pad or UHF. Wet warming compresses, which help during the period of boil maturation, are contraindicated after opening.
Physiotherapy during the healing process (UVR, laser therapy, ultrasound therapy) additionally disinfects the wound and prevents the formation of scars at the site of the boil cavity.
You can sign up for an operation to open a boil at the clinics presented on the website. The price of the service ranges from 3-4.5 thousand rubles. Despite the rather high cost of the procedure, if a boil forms, it is necessary to seek medical help to prevent the negative consequences of the purulent process.
Complications after removal of chiria and how to deal with them
After opening the abscess at home, it is necessary to maintain hygiene of the area of the ulcer and adhere to the medical treatment plan. If the wound from the boil does not heal for a long time, pus oozes, swelling and temperature occur, it is necessary to exclude factors that contribute to the formation of new boils. Blackness in the wound can lead to bacteremia and sepsis.
To speed up healing after opening, it is necessary to treat with an antiseptic and apply bandages with ointments. At first, you should not wet the boil wound; take a shower carefully. Give up alcohol, stick to proper nutrition.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Why are unexploded ulcers dangerous?
If the disease drags on and the suppuration does not clear up after 10-12 days, you need to seek help from a surgeon. There is a danger that the infection can enter the blood and internal organs of a person. As a result of a purulent formation that cannot come out, problems such as blood poisoning and purulent meningitis often develop. The main danger of an unbursted abscess is that its causative agent easily involves surrounding tissues in the inflammatory process. For example, boils on the hands can provoke diseases such as lymphadenitis or lymphangitis.
Sometimes the compaction freezes in development and turns into a hard lump that is unable to break through. In such cases, the surgeon makes an incision to remove the frozen boil.