During the period of bearing a child, a woman often experiences various exacerbations of diseases due to reduced immunity. If the human papillomavirus is present in the body, pregnancy becomes a trigger for its activation.
Since papillomas are a viral disease, many women are concerned about their possible impact on the intrauterine development of the fetus and the course of pregnancy in general. If the tumors are not located on the genitals, then they do not pose any danger.
Therefore, at this time, women often discover various neoplasms that were not there before. The immune defense, which cannot cope with its work, releases the human papillomavirus infection, which was previously in a latent (hidden) form.
Causes of papillomas in expectant mothers
If papillomas appear during pregnancy, this is due to a decrease in the production of immune cells. The phenomenon is physiological in nature and is not considered a pathology.
The woman’s immune system initially perceives the fetus as a foreign body and tries to get rid of it by synthesizing an increased amount of immunoglobulins. If this process is not stopped, bearing a fetus becomes impossible. Therefore, under the influence of certain hormones, the body is forced to reduce the level of antibody production, which leads to a decrease in the body’s resistance and the appearance of papillomas during pregnancy.
However, this is not the only factor that provokes the activation of HPV. Other reasons for the appearance of formations include:
- changes in the functioning of the endocrine glands;
- relapses of chronic pathologies;
- severe hypothermia or overheating;
- deterioration of the liver and kidneys due to the increased load on them associated with the neutralization of toxins and waste products of the fetus.
The growth of papillomas during pregnancy can be provoked by:
- mechanical or chemical damage to existing tumors;
- UV radiation;
- stress;
- excessive emotional stress.
If the papilloma has grown significantly during pregnancy, then you should donate blood and feces for the presence of helminths, since the toxins secreted by parasites inhibit the functioning of the immune and nervous systems, and complicate the functioning of the digestive organs and kidneys.
To find out the causes of papillomas and develop treatment, you should contact a dermatologist at the first signs of the appearance of these formations.
Safe Treatment Methods
The growths do not interfere with the course of pregnancy and often disappear after childbirth. Removal using various methods will not affect the situation; the papilloma may pop up in another area of the skin.
It is advisable to undergo HPV treatment when planning a pregnancy. It will relieve you from unnecessary worries while carrying a child. You can get vaccinated against human papillomavirus before you become sexually active.
Only topical medications are prescribed.
Pharmacy drugs
Drug treatment during pregnancy involves the use of ointments, gels, solutions that remove growths, and drugs that stimulate the immune system. These include:
| Name | Action | Mode of application |
| Kipferon | Suppositories for rectal and vaginal administration. Helps cope with condylomas in the vagina. The action is aimed at increasing immunity, eliminating papillomavirus. The drug has anti-inflammatory properties. | Suppositories are inserted into the vagina, 1-2 pieces (depending on symptoms), 2 times a day. Therapy lasts about 10 days. |
| Galavit | Suppositories designed to combat the HPV virus. The drug has an anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating effect that changes virus cells. | Take one suppository once a day for 10 days, then one suppository every other day. A full course of therapy requires 25 suppositories. |
| Viferon | Available in the form of suppositories and ointments. Helps cope with growths in the vagina, stimulates the immune system, controls formations, thanks to its antiviral properties. | One suppository is administered rectally. The course is about 10 days. The ointment is applied to the affected area of the skin, mucous membrane or vagina. Apply a thin layer of ointment to the formation 4 times a day for 5 days. Take a break for 5 days, repeat the course again. |
| Infagel | A drug for the treatment of viral diseases, has anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating, antitumor effects. Suppresses the growth of infection, provokes drying out and detachment of the wart. | The product is applied to the damaged area of the skin or mucous membrane. Wait until it dries completely and a protective film forms. Use twice a day for 5 days. |
| Solcoderm | The solution for removing papillomas, due to the action of acids, causes the growth to dry out and fall off. | It is recommended that the treatment procedure be carried out by a doctor. Application should be spot-on due to the high risk of burning healthy skin. After the fourth procedure, the result will become noticeable, the papilloma will begin to peel off. |
Pharmaceutical drugs are used only after a doctor's prescription.
Minimally invasive removal methods
When papillomas appear in places subject to mechanical stress, and condylomas prone to rapid growth, it is recommended to remove the elements using surgical methods. Indications for getting rid of growths are: bloody, purulent discharge from the surface of papillomas, itching, burning, discoloration, peeling.
Popular:
| Method name | Description |
| Cryodestruction | A method of removing growth using liquid nitrogen, which has a freezing effect. |
| Laser therapy | A painless, gentle method of getting rid of growths using a laser. Leaves no marks or scars. Removal is possible in hard-to-reach places, mucous membranes and vagina. There is no risk of bleeding; the edges of the tissue are burned. |
Other hardware methods: DEC and Surgitron are not used during pregnancy. After removal of the formations, it is recommended to increase immunity to prevent relapse and the appearance of new growths in other parts of the body.
Locations
Papillomas during pregnancy are formed mainly:
- in the area of the inguinal or axillary folds;
- under or between the mammary glands;
- on the face and neck.
If papillomas appear on the nipples during pregnancy, you need to discuss with your doctor the advisability of removing them in order to avoid damage while the baby is breastfeeding.
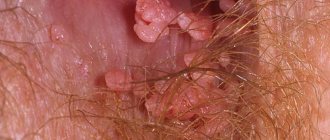
The appearance of pointed papillomas on the mucous membranes of the genital organs is caused by a change in acidity in the vagina and an increase in the amount of discharge.
What is the danger
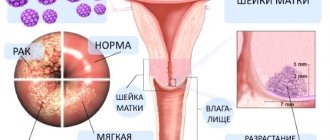
Papillomas are caused by different strains of papillomavirus, which determine their oncogenic potential. This indicator indicates how dangerous the pathogen is and whether the likelihood of malignant degeneration of the tumor is high.
If the papillomavirus during pregnancy caused the appearance of neoplasms in the vagina, cervix or external genitalia, then damage to them during childbirth can provoke inflammation, dysplasia of the mucous membranes and the proliferation of cancer cells.
Sometimes severe growth of tumors in the genital area makes natural childbirth impossible. Then the doctor prescribes a caesarean section.
The risk of a child becoming infected with HPV is high during passage through the birth canal and when sucking on the mother's breast, which has papillomas. If a woman is a virus carrier, then infection of the fetus through the placenta does not occur. The pathogen is also not transmitted through breast milk.
HPV types 16 and 18
Papillomaviruses types 16 and 18 have the greatest propensity for cancerous degeneration. Activation of these strains of human papillomavirus during pregnancy provokes changes in the cervix, during which transformation of the cytoplasm and organic inclusions of epithelial cells occurs. This pathology is called neoplasia and is a precursor to cancer.
Knowing how HPV affects pregnancy, a woman should be tested for the presence of the pathogen and its typing before conceiving a child.
If papillomavirus type 16 or 18 is detected, it is necessary to undergo a course of antiviral therapy, and if a tumor is present, it must be surgically removed.
Complications of gestation
The papilloma virus does not have a detrimental effect on conception and the process of gestation if the woman’s immune system is functioning satisfactorily. However, a sharp and significant decrease in the production of immune cells can cause the destruction of embryonic cells at the earliest stages of their formation, causing spontaneous abortion.
The appearance of papillomas on the body during later stages of pregnancy of such neoplasms does not affect the health of the child, but indicates disturbances in the endocrine or immune systems of the mother.
By eliminating the causes of the formation of papillomas at the stage of pregnancy planning, a woman will be able to prevent the negative consequences of their development and avoid complications. To do this, you need to be tested for the presence of HPV in the body and determine its strains. If a pathogen with a high oncogenic coefficient is identified, the doctor prescribes a biopsy of the affected tissue with histological examination.
If signs of neoplasia are detected, then treatment is carried out with pharmacological drugs and surgical methods, and antiviral and hormonal therapy is prescribed. The specialist also recommends removing genital warts on the genitals and breasts, since such manipulations are undesirable during pregnancy.
Consequences for the child
The human papillomavirus during pregnancy is not capable of exerting a pathogenic effect on the fetus while it is in the uterine cavity. In rare cases, papillomatosis of the vocal cords and respiratory organs becomes a consequence for the fetus. Infection occurs when a child inhales prematurely. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of papillomas in the larynx, which gradually spread to the trachea and bronchi. This causes difficulty breathing, and with severe growth - asphyxia.
Infection of a child can occur during birth if there are epithelial growths on the reproductive organs.
The most severe consequences for the baby are caused by the initial entry of HPV into the mother’s body during pregnancy. A woman’s strong immune system begins to intensively produce protective antibodies, which can provoke fetal rejection or developmental abnormalities. With weakened immunity, the active pathogen is able to penetrate the placental barrier, causing infection of the fetus and disruption of its development.
Effect on the pregnant woman and fetus
Externally, HPV manifests itself in 2 forms:
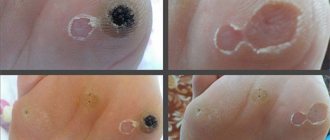
- papillomas - growths located on the skin; papillomas grow in colonies
- condylomas are neoplasms localized in the anogenital area. Genital condylomas are flesh-colored
During pregnancy, existing tumors begin to progress in size, and new growths actively join them. They are usually painless to the touch, but cause some discomfort at the location.
The cause of papillomas is the action of a virus, but not every type of growth is potentially dangerous for the woman and fetus. Common skin growths located on the neck, arms, face, etc. are not capable of causing the development of cancer and affecting the health of the unborn child.
Condylomas, especially those that grow actively during pregnancy, should cause concern. They can become injured and bleed, which can lead to infection in the body. In addition, during pregnancy, vaginal discharge becomes a common occurrence, which is a fertile environment for the proliferation of infections.
Papillomavirus does not pose an immediate threat to the fetus, since it does not live in the blood, but in epithelial cells.
This means that the baby cannot become infected in utero, but there is a risk of infection if the fetus passes through the natural birth canal.
However, this phenomenon is typical only for children of pregnant women who have been diagnosed with genital warts. In this case, a cesarean section can be performed during childbirth, which significantly reduces the risk of transmission of the virus to the fetus.
If the child was nevertheless infected during childbirth, there is a high probability of developing laryngeal papillomatosis. This is a disease characterized by the appearance of multiple growths in the larynx.
The disease is characterized by frequent relapses and can lead to breathing problems, including the development of asphyxia. However, laryngeal papillomatosis is quite rare and is considered a curable disease.
Differential diagnosis
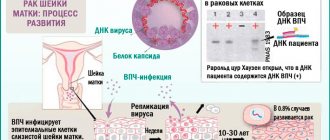
Papillomas in pregnant women on the cervix are detected mainly during registration, when a gynecological examination is performed by a doctor. After this, the specialist prescribes additional studies to determine the strain of the virus using polymerase chain reaction. This diagnosis of HPV accurately establishes the type of pathogen and its oncogenic activity, which makes it possible to predetermine the pattern of development of papillomatosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Some modern clinics offer a more accurate diagnostic method - the hybrid capture method, for which a scraping is taken from the cervix. This test not only performs HPV typing, but also determines the viral load.
If neoplasms on a woman’s genital organs are caused by HPV types 16 or 18, then she must be additionally prescribed:
- smear from the mucous membrane of the cervix for cytological examination;
- colposcopy;
- biopsy of cervical tissue.
Possible complications
The most dangerous types of HPV are 16 and 18, which cause cervical cancer in women. The appearance of HPV during pregnancy can pose a threat to the health of not only the woman, but also her baby if the papillomas are located in the uterus and on the walls of the vagina.
During the birth process, the child may take a breath prematurely, and with it, an infection will enter the child’s body through the respiratory tract. In most cases, the immune defense of newborns copes with the virus. But some babies may develop a rare disease - laryngeal papillomatosis. Thus, complications will be dangerous for the baby.
It is allowed to give birth if there are formations in the genital area. But if the papillomas are too large and cannot be cured, doctors will suggest another method - a caesarean section. This decision will protect the mother and child from HPV entering his body.
However, papillomas can be located in other places on the skin. If they are not in the uterine cervix and vagina, then they do not pose any danger to the fetus, and there will be no complications for the pregnant woman.
If a woman has the opportunity to recover from the virus before pregnancy, this should definitely be done. Some strains in advanced form lead to adverse consequences. But a baby needs a healthy mother for full development.
The main danger of HPV in a pregnant woman is that in the event of a decrease in immune defense in combination with other viral infections, there is a risk of exacerbation of old or the appearance of new diseases. This can lead to pregnancy complications and health problems for the fetus. Such patients need to pay attention to enhanced measures to strengthen the immune system and follow a gentle regimen.
In addition, papillomas in pregnant women can provoke the development of other infectious diseases, for example, thrush - candidiasis, which, in turn, can be transmitted to the fetus.
Important!
Monitoring a woman’s health status, especially before childbirth, will make it possible to prevent many problems with the birth and development of a child.
Indications for consultation with other specialists
If a patient is diagnosed with human papillomavirus during pregnancy, which poses a high oncogenic risk, she is referred to an oncologist. After conducting the necessary tests for HPV, the doctor predicts the development of the disease and prescribes treatment.
If there are growths on the cervix that can be damaged or come off when the fetus is delivered, the woman is sent for a consultation with a surgeon. After inspection and assessment of the danger, the specialist decides on the advisability of their removal.
Routes of transmission of the virus
HPV, which affects the genitals, is transmitted sexually through any form of intimacy.
But this method of transmission should not be considered as the only one. All it takes is contact of the affected area with the skin or mucous membrane, which probably has microcracks. Do not forget that wounds can also appear during sexual intercourse.
Thus, it is believed that there is a risk of contracting the virus during a kiss if one of the partners has formations in the oral cavity.
Many people mistakenly believe that if there was no direct intercourse, then there is no need to think about the virus. This statement is absolutely incorrect, since simple close contact is enough to transmit HPV. All of the above suggests that a permanent partner, means of protection or virginity do not yet indicate the absence of infection in the body.
Related article:
Papillomas on the cervix in women - how to treat?
The household method of transmission of HPV is due to the fact that the virus continues its life outside the human body for about 3 hours. Foci of infection can accumulate on linen, towels, and wet surfaces.
However, not all types of strains can be discussed when indicating this method. This does not apply to anal-genital types.
In autonomous conditions, HPV does not spread throughout the human body. It gives manifestations in the area where it was brought. But there is such a thing as self-infection.
When shaving, for example, a person may accidentally touch a fresh wound with the affected area. To avoid this phenomenon, you should constantly avoid contact with papillomas.
Until recently, the possibility of infecting the fetus with a virus during pregnancy was completely excluded. If a newborn was diagnosed with papillomavirus infection, the only explanation was the possibility of contact with the mother’s genitals during childbirth.
Today, doctors fully accept the transmission of HPV through the placenta. After the virus was discovered in children born by cesarean section, the method by which the virus is transmitted from mother to child has been officially confirmed.
Is it possible to remove papilloma during pregnancy?
Gynecologists insist on removing papillomas from pregnant women in isolated cases when the risk of malignant tumor degeneration or infection of the fetus exceeds the negative consequences of surgical intervention.
If the neoplasms are not injured by clothing, do not change in appearance and do not become inflamed, then HPV treatment during pregnancy is not worthwhile. An exception may be small pedunculated papillomas, which are removed without prior administration of anesthesia or frozen.
Why should drug treatment be postponed?
When asked whether HPV can be cured in a pregnant woman, doctors give an unequivocal negative answer, since the papillomavirus, once it enters the body, is not removed from it. But with the help of medications, it is possible to suppress the activity of the pathogen and prevent the growth of tumors.
Antiviral therapy is not carried out during pregnancy, as it can provoke abnormalities in the development of the fetus, cause fading or premature birth. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend testing for the presence of papillomavirus before conceiving a child.
Experts do not recommend surgical removal of papillomas during pregnancy, explaining this for the following reasons:
- the need to use anesthesia;
- stress factor;
- the likelihood of bleeding in the postoperative period;
- increasing the likelihood of malignant degeneration.
Treatment of papillomas in pregnant women should also be postponed because of the possibility of self-destruction of growths after childbirth, when the body’s immune status is completely restored.
Folk remedies are unacceptable
Removing papillomas during pregnancy using celandine juice, potato pulp or garlic is not prohibited. But their independent use can cause tumor growth and its malignant transformation against the background of a decrease in the level of general immunity. Remember that all folk remedies are designed for the average person, but not for a pregnant woman. Therefore, it is necessary to clearly understand that only a qualified specialist should treat papillomas during pregnancy.
What removal of papillomas during pregnancy is allowed?
There is no clear answer to the question of whether papillomas can be removed during pregnancy. It all depends on the type of virus, the location of the growth, the resistance of the expectant mother’s body and other factors. Removal of papillomas during pregnancy is carried out only after agreement with the gynecologist and in case of risk of injury or malignant degeneration.
Removal of papillomas during pregnancy should be carried out only in a clinical setting where sterility is ensured and there is the possibility of providing first aid in case of unforeseen complications.
Acceptable removal methods include:
- excision of the tumor using a scalpel;
- laser destruction;
- cryodestruction;
- radio wave method.
It is impossible to say for sure whether it is possible to remove papillomas for pregnant women using electrocoagulation. Despite the absence of direct contraindications, this method does not exclude the possibility of relapses, therefore it is used extremely rarely.
HPV types 16 and 18 during pregnancy
These strains are considered the most dangerous, especially if a woman is infected with both. They are largely responsible for the occurrence of cancer. When these types of papillomavirus are detected, constant monitoring by a doctor and regular diagnosis of the viral load on the body are mandatory.
During pregnancy, HPV passes from a latent phase to an active one. This can be tracked not only by the increasing number of tumors, but also with the help of special diagnostics that reflect the viral load.
The higher this indicator, the faster the development of oncology awaits the patient without surgical intervention.
Planning a pregnancy
Many women at the stage of planning to conceive a child are concerned about whether it is possible to get pregnant with HPV, whether complications will arise during pregnancy and childbirth, and how safe it is for the baby. Pregnancy with HPV can only be a problem if there are genital papillomas caused by an oncogenically active type of virus, or if the mother is initially infected during pregnancy.
Therefore, before becoming pregnant, it is worth being examined by a gynecologist and dermatologist for the presence of HPV, and also learn about possible complications that may arise during pregnancy.
If types of virus are detected that can cause cancerous degeneration of the affected tissues, it is necessary:
- undergo antiviral treatment;
- increase immune defense with the help of pharmacological drugs and folk remedies;
- in case of excessive growth of papillomas or their degeneration, excise the neoplasms.
Features of localization and symptoms
Some strains have no symptoms, but many appear as a rash on the body of different shades, with a rough surface that differs from a nevus. The growths can be flat or convex, located on a stalk or hanging down. Papilloma does not cause pain, itching, burning, or redness if it is not at risk of frequent damage.
Favorite places for infection to appear are the facial, cervical area, armpits, intimate area (areas subject to damage). The neck is rubbed by the collar, the chest, armpits are rubbed by the bra, and the intimate area is rubbed by underwear.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
During the period of bearing a child, growths appear on the chest, nipple halo, and intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland may appear. The growth does not interfere, does not pose a danger, and resolves after childbirth. You can get rid of it using pharmaceutical drugs or modern removal methods.
In cases of genital papillomavirus infection, there is no danger to the child in the womb. The fruit is protected. Vaginal growths are dangerous for the baby during birth. Upon examination, the gynecologist may recommend removing the formation or undergoing a course of drug therapy after childbirth. Condylomas are not removed at any time; the doctor may decide, based on the totality of medical indications, to prescribe a cesarean section in order to avoid infection of the child. You can get rid of formations after childbirth.
Is it possible to prevent the manifestations of HPV?
There is no specific prevention of rashes during pregnancy. There are general preventive measures to prevent infection with papillomavirus:
- abstaining from casual sex;
- refusal to use alcohol, tobacco and psychotropic drugs;
- introducing into the daily diet a sufficient amount of fresh vegetables and fruits, fish oil, foods containing fiber, vitamin drinks, infusions of medicinal plants;
- visiting only those beauty salons where instruments are aseptically processed;
- avoiding the use of other people's clothes, shoes, hygiene products;
- preventing diseases from becoming chronic, that is, their timely treatment.
However, even if you strictly observe the rules of hygiene, you cannot exclude HPV infection through household contact. Therefore, you should undergo regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist and undergo tests.
Prevention
It is possible to prevent the appearance of papillomavirus in a pregnant woman, but not completely. There are a number of ways to reduce risks:
- Do not gain excess body weight.
- Do not wear tight clothes that irritate the skin.
- Strengthen immunity.
- Provide protection against colds and the penetration of other viruses and infections into the body.
- Get medical examinations regularly.
However, all these methods do not provide a full guarantee of protection - no one is immune from the appearance of papillomas.
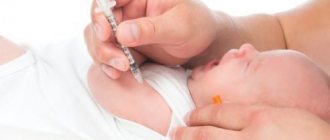
There is no specific treatment for HPV in the world yet. However, a vaccine is now available that prevents infection by the most dangerous types of papillomavirus. It's called Gardasil.
You can purchase the medicine in 60 countries around the world, including Russia. However, vaccination will only help for preventive purposes and not for treatment. The vaccine helps protect against the four most dangerous types of HPV.
It is rational to vaccinate before the conditions of infection appear, that is, before the onset of sexual activity. Young women are recommended to get vaccinated between the ages of 17 and 26 years.