Rash on the scrotum: photo and list of possible causes
Rash on the testicles in men is varied and appears for many reasons. Before sounding the alarm, you should pay attention to the type of rash and accompanying symptoms. In some cases, this phenomenon is safe or easily treated at home. But sometimes you can’t do without medical help.
When not to worry
In some cases, rashes can be dealt with on your own. The main thing is to accurately determine the cause of the problem. If in doubt, it is better to consult a doctor.
Allergy
An allergic reaction in the scrotum area usually occurs to hygiene products or the fabric of panties. If itching and burning appear, small red or pink pimples form, the source of the allergens should be identified and eliminated from everyday life.
It is advisable to choose underwear made from natural fabrics, wash with soap and shower gel without dyes or strong fragrances. For shaving, it is recommended to use a special foam, and not the one applied to the face.
To relieve unpleasant symptoms, you can take an antihistamine.
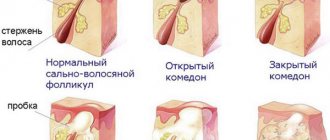
Fordyce granules
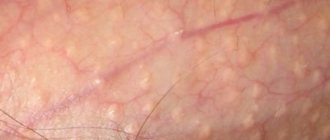
A white rash on the testicles appears due to blockage of the sebaceous glands. This happens if the glands are located close to the skin and their ducts are narrowed. The problem usually occurs during adolescence, when sebum is actively produced due to hormonal fluctuations.
Pimples usually do not exceed 2 mm in diameter and barely protrude above the surface of the epidermis. There is no physical discomfort. Fordyce granules are not a disease and do not require treatment. For reasons of aesthetics, they can be removed, but the harm from the intervention is much greater than the benefit.
In addition, the rash will soon appear again.
Molluscum contagiosum
Although it is a disease, it does not pose a danger to life and health. Appears when infected with a virus. Transmission occurs predominantly during close physical contact. Hemispherical growths with a pit at the top appear on the skin.
When pressed, a white plug comes out of the recess. There is no physical discomfort. The rash disappears on its own within 3-6 months.
Treatment with antiviral drugs is indicated for people with weakened immune systems, as well as in cases where the growths are constantly rubbed and injured by underwear and clothing.
Pseudofolliculitis
A red rash on the testicles may be a sign of skin inflammation due to ingrown hairs. If the shaft grows in the wrong direction, a bump will form around the hair follicle.
A loop or the tip of a hair sticks out of it. There is slight pain when touched. Ingrown rods must be pulled out using a thoroughly disinfected needle or tweezers.
The skin should also be treated with an antiseptic before and after the procedure.
Rash on the testicles in men photo
Often, a rash in the scrotum area is caused by diseases. In this case, you cannot do it on your own. You should seek medical help.
Papillomatosis
A disease caused by the human papillomavirus. With this pathology, soft growths appear in the genital area on a thin stalk or flat base. When they grow, they look like cauliflower. Discomfort is caused only by rubbing underwear or during sexual intercourse.
If such rashes are detected, you should get tested to determine the type of HPV. If it turns out that the virus has a high risk of oncogenicity, the growths must be removed. Removal is also indicated if they are damaged regularly. It is impossible to get rid of HPV forever.
But a well-chosen course of antiviral drugs and strengthening the immune system will help put the pathogen into hibernation for a long time.
Folliculitis
A rash on the scrotum may be a sign of inflammation of the hair follicle under the influence of streptococci or staphylococci. In this case, the area around the hair becomes inflamed and festers, becoming painful. You can't squeeze pimples.
This threatens to worsen the situation. The lesions should be treated with antiseptics and antibacterial ointments prescribed by a dermatologist should be applied. If the abscess grows, you should consult a surgeon.
The doctor will open the boil and clean out its contents.
Herpes
Genital herpes is a viral disease. Characterized by the formation of watery blisters. The rash is accompanied by itching and burning. After opening the elements of the rash, erosions and spots remain. Treatment consists of the use of antiviral ointments and tablets.
Scabies
Dermatitis caused by scabies mites. The parasite often enters the body through close physical contact, so the first symptoms in adults usually appear in the groin area.
Scabies rashes appear as white, black and red dots and blisters. Characteristic passages may appear - grayish winding lines about 1 cm in length. The unbearable itching intensifies in the evening and at night.
Pathology is treated with special ointments applied to the entire body except the face and head.
Pediculosis pubis
Lice infestation. Insects bite through the skin, leaving small bruises on it. Usually parasites can be easily seen among the hair. They cause severe itching, which intensifies after water procedures. Patients are prescribed ointments and sprays with insecticides. The most effective method of getting rid of lice is complete depilation of the groin area.
Athlete's inguinal
A fungal disease characterized by the appearance of red or pink spots with a flaky surface. The affected areas grow and merge.
The formed lesion is a ring with healthy skin in the center, covered with nodules and blisters along the outer edge. The affected epidermis becomes wet and itchy.
Treatment consists of using drying and antifungal ointments and antiseptic surface treatment.
Testicular rashes in men can be dangerous. Although in some cases medical attention is not required, it is still worth visiting a dermatologist. There are always exceptions, and in each specific case, even a seemingly safe condition can turn into complications.
Source: https://andrologiya.com/syp-na-moshonke.html
Sores on the testicles in men, what is it?
Sores may also be found on both the genitals and elsewhere on the body (such as the mouth and throat).
Common Causes
Male genital ulcers can have many different causes. The most common are STDs (sexually transmitted diseases). For example, such as:
- genital herpes simplex (infection caused by the herpes simplex virus there are two main types of the disease: type 2 more often and type 1 less often. Infection with genital herpes is possible through sexual contact in the mouth, vagina and rectum. People with symptoms of the disease are most contagious But more often, infection comes from people with an asymptomatic course of the disease.
Transmission of infection during pregnancy from a sick mother to the fetus is also possible. Other methods of infection are less likely. This virus is neurotrophic and neuroinvasive, i.e., after infection it migrates into the nervous system.
It is especially dangerous for people with weakened immune systems - those infected with HIV and those who have recently undergone organ transplant surgery, since their immune system is suppressed);
- syphilis (a systemic chronic infectious venereal disease with damage to the mucous membranes, skin, bones, internal organs, nervous system, with a sequential change in stages of the disease, caused by bacteria from the order of spirochetes, the species Treponema pallidum or pallid treponema subspecies pallidum, belonging to the genus Treponema of the Spirochaetaceae family Syphilis is sexually transmitted. Women and men are affected equally, mainly of reproductive age);
- chancroid (or chancroid, venereal ulcer - a classic venereal infectious disease, sexually transmitted. The causative agent is the bacterium Haemophilus ducreyi. The disease is widespread - in Africa, Central and South America, in Russia it is extremely rare.
The incubation period in men is often 2-3 days, in rare cases it reaches 2-3 weeks. In women it is longer: up to 2-3 weeks.
A few days after sexual intercourse with an infected partner, a small red spot appears on the genitals, which begins to increase in size over time);
- inguinal granuloma (or Donovanosis, granuloma venereum - an infectious disease from the bacteria Calymmatobacterium granulomatis, which until recently was called Donovania granulomatis; a low-contagious destructive bacterial chronic progressive infection. The causative agent in tissue sections is called “Donovan bodies”);
— lymphogranuloma venereum (or Durand-Nicolas-Favre disease) is a classic chronic disease that is usually transmitted sexually. The causative agents are invasive serovars L1, L2 and L3 Chlamydia trachomatis.
Lymphogranuloma venereum is characterized by damage to the femoral, inguinal, iliac and deep pelvic lymph nodes. Infection most often occurs through sexual contact, and much less often through household contact.
The disease begins with a vesicle or tubercle at the site of entry of the pathogen - usually on the genitals, where it can cause ulcers).
Other types of ulcers of the male genital organs can be caused by venereal warts, molluscum contagiosum, allergic reactions, Behçet's disease (Behçet's disease or Adamantiad-Behçet disease, Silk Road disease - an idiopathic inflammatory disease, systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology, characterized mainly by damage to the oral cavity , mucous membrane of the eyes, genitals and skin. Some people have a genetic predisposition to the development of this disease, which is proven by the identification of the HLA-B51 antigen in patients and violations of the gene that controls the synthesis of tumor necrosis factor; with Behçet's disease, systemic manifestations and damage to vessels of any size are possible - both arterial and venous beds. Also, this disease is characterized by a tendency to thrombosis) and H-infections, sexually transmitted infections.
Treatment and care at home
Avoid self-medication before visiting a doctor. Your doctor can notice the signs and symptoms and make a more accurate diagnosis.
The patient should avoid all sexual contact while he is undergoing a medical examination.
The patient should see a doctor if he has any unexplained genital sores or if new ones appear in other parts of the body.
The doctor will perform an examination, which should include examination of the genitals, pelvis, skin, lymph nodes, lips and throat.
The doctor may ask the patient questions about his medical history and symptoms, including:
- what hurts - for example, it is an ulcer, a blister, a hard nodule or pustules; - nature of pain; - is there any itching; - is there more than one pain; - where the ulcers are located; - at what time does it hurt; - when the patient first noticed the wound; - how long ago was the last pain; - Has the patient ever had similar pain in the past? — what are the patient’s sexual habits; - is there any discharge from the penis; — is there painful urination; - is there painful sexual intercourse?
- have a high fever, chills or enlarged lymph nodes.
Tests that can be done include:
- general or differential blood tests; - biopsy of a fragment of the affected skin or mucous membrane; - HIV test; - rapid plasma reagin test (or precipitation reaction with cardiolipin antigen, selection reaction for syphilis, microprecipitation reaction, rapid diagnosis of syphilis, anticardiolipin test - screening non-treponemal test that detects IgG and IgM antibodies to lipoid and lipoprotein-like material released from damaged cells of the patient syphilis). This test is recommended by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation for primary screening and monitoring the progress of syphilis treatment;
- test for sexually transmitted diseases.
Source: https://o-kak.ru/boljachki-na-jajcah-u-muzhchin-chto-jeto/
Pathogens
The culprits of white plaque on the eggs in men can be three types of microorganisms:
- Yeast-like fungi from the genus Candida, which are permanent residents of the mucous membranes and skin. Thrush is caused only by certain types of microorganisms. Often these are Candida albicans or Candida tropicalis - single-celled fungi with a round shape. When the disease starts, the infection affects the penis, urethra, and bladder. As a result, symptoms of cystitis appear - darkening of urine, burning, spotting, and a cheesy coating on the penis.
- Another type of yeast is Pityrosporum, which also lives on the surface of epithelial tissues. It causes pityriasis versicolor on the testicles. The rash is pale pink or dark brown, covered with a dense coating, peels, and is accompanied by itchy skin in the groin. More often, the growth of pathogenic flora is provoked by heat and increased sweating. Mostly teenagers and young men of puberty age suffer.
- Fungi from the genus Epidermophyton cause athlete's foot. Microbes can affect large skin folds, feet and nails. Pathogens destroy the epithelium, utilizing collagen fibers. Often, the infection spreads from the scrotum to the intergluteal fold and thighs, but the penis is rarely affected. It is easy to become infected with the disease in rooms with high humidity (baths, saunas, gyms, swimming pools). The growth of the fungus is promoted by excess sweat, excess weight, and diaper rash.
White coating on the eggs in men does not appear immediately after infection, but as the disease progresses. The incubation period ranges from 4 days to 2 months. The most common cause is thrush. It should be remembered that pathogenic fungi also reproduce from a man’s own microflora. With a weakened immune system, symptoms of the disease arise unexpectedly at any time.
Fungus on the scrotum: symptoms (PHOTOS) and treatment
Dermatologist of the highest category Inna Vladimirovna
29288
Update date: April 2020
One of the most common diseases in men is a fungus on the scrotum. If treatment is not started, the infection will spread to other parts of the intimate area. The skin folds and genitals are most susceptible to damage. Localized on the scrotum, the fungus causes severe discomfort, depriving a man of a normal sex life.
Why does the disease appear?
A pathogenic fungus can develop its active life activity in any part of the human body. In men, it most often occurs in the groin area, since ideal conditions are created for it here. The fungus successfully activates in places where there is high humidity and heat. This is how one can characterize the constant environment in the scrotal area.
Mycosis of the scrotum in most cases is diagnosed in men aged 20-60 years. This type of epidermophytosis is encountered by those who have a predisposition to this disease due to the following unfavorable factors:
- Severe sweating at the genital area;
- Working conditions that involve being in a hot room;
- Having excess body weight;
- Disturbance in the process of carbohydrate metabolism;
- Lack or insufficient compliance with the rules of personal hygiene in the genital area.
The fungus loves a moist and warm environment, so excessive sweating increases the risk.
Infection with the fungus occurs through household and contact routes. To get sick, it is enough to touch the scrotum to an infected surface. This often happens to men who like to regularly visit saunas, baths and other similar public places.
For a long time, the fungus in the scrotum area may not show itself. The following violations help speed up its activation:
- Decreased immune system;
- Diabetes;
- Hormonal disbalance;
- Cardiovascular diseases;
- Stress.
Heavy physical work also acts as a factor that accelerates the activation and proliferation of fungal microflora on the genitals and scrotum. Such a problem cannot be avoided by a person who neglects to regularly wash the intimate area and also constantly wears tight underwear made of synthetic materials.
Types of fungal infections
Doctors identify several types of mycotic pathogens that lead to infection of the scrotum. They are divided into groups presented in the table.
| Name | Description |
| Yeast fungus | If it is detected, genital candidiasis is diagnosed. With such a pathogen, not only the scrotum is affected, but also the penis and the genitourinary canal. |
| Fungus of the species Pityrosporum | Leads to the development of pityriasis versicolor. This form of lesion is the least common. Typically, the appearance of fungus is associated with hormonal problems and increased levels of testosterone in the body. |
| Epidermophytons | Because of them, a man suffers from dermatomycosis, which looks like lichen or athlete's foot in the groin. Typically, this disease affects people who lead an active lifestyle. |
All groups of fungi that infect the scrotum are characterized by similar symptoms. So it is possible to distinguish a certain type of pathogen only through laboratory analysis.
Symptoms
The disease causes itching and discomfort
Men who are concerned about their own health are interested in what signs of fungus in the intimate area. It is believed that this infection has the following symptoms, which appear in the scrotal area from the first days of infection:
- Severe itching at the site of the lesion, which begins to intensify without treatment;
- The skin in the groin area becomes covered with painful spots that are colored pink or red. They have clear outlines and are able to change with the course of the pathological process;
- Peeling of the skin, which leads to the appearance of cracks;
- Darkening and dehydration of the area of the scrotum that is not yet infected with the fungus;
- The skin on the testicles becomes wet and swollen due to increased sweating, if a man has a tendency to sweat.
If you do not start treatment or choose the wrong therapy, the affected area will gradually increase in size. Small rashes turn into one large spot that can reach the buttocks. It is possible that this area will become covered with blisters containing a rash and purulent discharge.
Diagnostic methods
The doctor will not be able to select an adequate treatment for the patient without knowing what kind of fungus is affecting his scrotum. Therefore, the patient initially needs to undergo diagnostics. During the appointment, the dermatologist should carefully examine the skin that has been infected with the fungus. Afterwards, he directs the patient to carry out the following diagnostic measures:
- Laboratory analysis of scrapings from the site of epithelial damage;
- Examination of the scrotum using a Wood's lamp, which can highlight problem spots;
- Balzer test, which uses iodine;
- Culture inoculation on active medium.
Only a complete and thorough diagnosis will help a specialist correctly identify the causative agent of the infection and select an effective treatment to combat it.
For effective treatment it is necessary to determine the type of fungus
Treatment
When the skin of the scrotum is affected by a fungus, patients are offered treatment, the action of which is aimed at destroying the infectious pathogen, restoring the damaged epithelium and increasing the body's defenses.
There are several effective methods of treating fungus on the scrotum, which can quickly and painlessly eliminate the signs of infection. They differ from each other in the method of application and the nature of the effect. For treatment to be effective, the patient must adhere to a number of rules and recommendations of the doctor:
- Medications with an antifungal effect should be applied only to those affected areas of the body that have previously been washed and dried with a towel;
- It is necessary to treat not only rashes, but also healthy areas that are located next to infected lesions;
- If within 10 days from the start of the treatment course neither the doctor nor the patient see obvious results of therapy, then other drugs will have to be selected;
- It is advisable to regularly wash hair that grows in the groin area with antifungal shampoo. Although it is usually recommended to get rid of them during treatment;
- Medications must be taken strictly according to instructions;
- The intimate area must be kept dry in order to deprive the fungus of the opportunity to feel comfortable in the place where it actively reproduces;
- Traditional therapy, which was suggested by a doctor, can be combined with traditional treatment if desired.
It is best to treat mycosis of the scrotum with pharmaceutical creams and ointments. No less useful are the tablets used to treat fungus. They affect pathogenic microflora and the human body from the inside.
The following medications show good results in the fight against fungus on the scrotum:
- "Triderm". Recommended for use in the treatment of dermatological diseases. This drug is not intended for the prevention of mycosis and other similar problems, as it contains potent components. Triderm is suitable for therapy under the supervision of a specialist. When it is abused, a person develops a habit, since the medicine belongs to the group of hormonal drugs;
- "Ketoconazole". The antifungal agent inhibits the synthesis of triglycerides, ergosterol and phospholipids. Due to this, the permeability of cell walls is lost and a mycostatic effect develops. The task of removing mycosis in the inguinal folds and on the scrotum in men is performed by the active component ketaconazole;
- "Miconazole". A fairly common drug in gynecology. It is also actively used in the treatment of the groin area in men, which was affected by a fungal infection. The active component miconazole nitrate is effective against most existing pathogens of this type. The ointment does not have the ability to penetrate into the deep layers of the skin, so its substances do not end up in the bloodstream.
There are other equally effective medications that successfully cope with the signs of fungus on the scrotum. It is strongly recommended that you trust their choice to an experienced specialist. Self-medication in such a situation may have no result. In addition, the wrong medication can cause harm to health.
Hormonal ointment is effective, but is addictive and has side effects
Prevention
Any man can face such an unpleasant disease as an infectious fungal infection of the scrotum. To prevent this, you must adhere to a number of simple rules regarding the prevention of the disease:
- Do not use soap to wash your intimate area. It is best to purchase special products for these purposes;
- You must shower or bathe daily. In hot weather, the frequency of water treatments should be increased;
- Don't forget to change your underwear daily. It should be washed at high temperature;
- Underwear must be made from natural fabric;
- It is worth protecting yourself from stressful situations and unnecessary emotional experiences;
- It is not advisable to exhaust yourself with increased physical activity. They should be moderate.
After treatment, it is necessary to boil all the man’s clothes, as fungal spores may remain on them, which will lead to re-infection. If possible, it is better to buy new underwear for him.
Methods for preventing fungus on the scrotum also include taking care of the immune system. It should be periodically strengthened so as not to deprive the body of its defenses.
Source: https://DermatologInfo.ru/gribok/lokalizatsiya-gribka/printsipy-lecheniya-gribka-na-moshonke/
What do spots on the scrotum in men mean?
Normally, the color of the scrotum should be slightly darker than the main shade of the skin of the body. As a man ages, the skin of his scrotum darkens. Pigment spots on the pubic area and on the scrotum in a man can appear for various reasons. If we consider non-infectious factors, these can be various systemic diseases:
- Disorder of the adrenal glands;
- Malfunctions of the endocrine and hormonal systems;
- Stressful situations and constant mental tension;
- Malfunctions of the reproductive system;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
In addition, the reasons for local changes in the color of the skin of the scrotum and the appearance of spots on the pubis or on the scrotum may be associated with the following reasons and factors:
- Reducing the amount of melanin in the body;
- Scars in the intimate area after injuries and operations;
- Regular rubbing of underwear against the skin;
- Reaction of chemicals on the skin in the groin and scrotum area.
Important: if a man discovers a sharply appearing spot on his pubis or scrotum of any shade, it is advisable to immediately consult a dermatologist. The marks can be either infectious, pathological, or non-hazardous in nature. The specialist examines the patient and, if necessary, sends him for diagnostics to other doctors (andrologist, infectious disease specialist, etc.).
Red spots on the scrotum
Erosion on the penis: causes, symptoms and treatment
Depending on the shade of the spots on the scrotum, the doctor identifies the pathology. Additional diagnostic methods include skin scraping, urethral smear, and general blood and urine tests. So, a red spot on the scrotum or pubic area may be a consequence of the following pathologies:
- Angiokeratoma. The pathology is characterized by the appearance on the skin of bright vascular purple or red marks with a smooth, almost glossy surface. Most often, this phenomenon is typical for fair-skinned men. Moreover, the marks will be brighter the older the person becomes. In some cases, a similar red spot may appear on the pubis or on the head of the penis.
- Fungal skin lesions. In this case, the spots are most often localized in the inguinal folds, only slightly affecting the skin of the scrotum. This clinical picture is characteristic of epidermopathy.
White spots on the scrotum
A white spot on the scrotum, one or more, may be a consequence of the following pathologies:
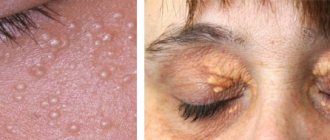
- Vitiligo. This type of pathology occurs due to a disruption in the production of melanocytes - special cells responsible for skin pigment. As a result, small or large white spots with a smooth surface may be observed on a man’s body (including in the intimate area). This phenomenon does not pose a danger to the body, but it is still worth seeing a doctor to confirm the diagnosis.
- Pityriasis alba. One of the pathological skin lesions. In most cases it is localized on the hands or face. But marks may also appear in the groin.
- Cyst. When small cysts form, small white spots may appear on the skin of the scrotum. They do not itch and do not bother the man in any way. But if the mark grows, it is better to see a doctor.
- Ingrown hairs. As a result of ingrown hair after shaving, the skin in this place can also change its shade to a paler one, which is regarded as a stain.
- Zhiroviki. They can also form on the skin of the scrotum, although very rarely. Often a man may be frightened by these formations, but they do not pose a threat to a person.
- Sexually transmitted diseases. Most often it is the herpes virus. The pathology requires urgent treatment, since in a chronic course it can periodically worsen.
- HPV is human papillomavirus. It is also transmitted sexually. As a result, a person may develop white spots on the skin, in the center of which condylomas or papillomas form.
Pink spots on the scrotum
Appointment with a urologist: preparation for examination, diagnosis and treatment measures
If we are talking about the formation of pink spots on the pubic area in men or on the scrotum, then most likely this is the result of the following pathologies:
- Diaper rash. As a result of prolonged wet mechanical action on the skin, for example, friction of clothing or skin folds, pink spots form. They are more likely to itch and bother you. They can progress without proper treatment. Even secondary infection is possible.
- Heat rash. It is often also called prickly heat. The rash may be localized, which suggests spots. Sufficient hygienic care and constant maintenance of the skin of the scrotum in dryness can get rid of this problem.
- Eczema. A skin pathology that can develop in men of any age as a reaction to external stimuli or stress.
- Allergy. This is the most common factor that leads to the formation of pink marks. Allergies can occur to water and detergents, to latex and synthetic underwear, to lubricants and medications, to food, and even to severe stress. You can get rid of such phenomena with the help of antihistamines.
Fungus on the scrotum: symptoms, treatment and diagnosis
16.05.2019
A disease such as a fungus can appear on any part of the body, as well as on internal organs.
On a man's body, a fungal infection can cover the scrotum, and for a man this is a big problem.
A fungus that appears on the scrotum is not a special type of infection, but it will cause panic in any man. In addition, he may misdiagnose himself and begin treating a non-existent disease.
You should not self-medicate; when the first signs appear, you should immediately visit a doctor. Only an experienced specialist will make the correct diagnosis based on test results and prescribe effective treatment. For it to help, you should follow all the doctor’s recommendations and take medications only according to the prescribed regimen.
Factors influencing the occurrence of the disease
The onset of the disease may be influenced by any of the following factors:
- Increased sweating, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. In other words, a humid and warm environment.
- Disturbance of the metabolic process in the body.
You can become infected through contact with an infection, that is, after sharing a washcloth or towel in public.
In addition, infection awaits a person in crowded places, such as a swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna, or hospital. In the latter case, the risk of disease is associated with the use of a hospital duck.
It is easy to determine the occurrence of an infection; spots appear on the scrotum that differ in color from normal skin. They have a yellowish tint. If you examine this area under a microscope, you can see that the testicle is covered with entire colonies of fungi.
Signs indicating the occurrence of a fungus
It is necessary to carefully examine this area of the body in men. The affected area becomes covered with pink spots, which later change color to yellow.
If timely treatment is not started, they will grow. The fungus can cover the entire scrotum, cover the groin and gradually affect the skin between the buttocks.
Can appear:
- Unbearable itching.
- Feeling pain.
- Peeling of the skin, which will cover the entire area and the egg as well.
After a certain time, the area affected by the fungal infection begins to turn red, and characteristic symptoms appear:
- Cracks form on the skin.
- These areas become dry and the protective properties are impaired.
- The skin begins to peel off not only in those places where there is a lesion, but also where healthy skin comes into contact with the affected area.
Treatment of the disease
When the first symptoms of a fungal infection appear on the scrotum, treatment should be started as soon as possible. But before that, you need to visit a doctor so that he makes the correct diagnosis.
It’s easy for an experienced specialist to do the following:
- Collecting the patient's medical history.
- Thorough visual inspection.
- Makes a scraping.
A scraping made in men at an “interesting” place will help make an accurate diagnosis, and then decide on the method of therapy.
Treatment of such a disease usually occurs with the use of complex therapy. To do this, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and medications for internal use (tablets, capsules), as well as topical medications (creams, ointments, gels). In addition, medications are prescribed that can boost and strengthen the immune system. All this must be strengthened by regular hygiene of intimate places.
It is important to understand that the entire course of therapy must be completed, even if the symptoms have disappeared. Some patients do not adhere to this advice and quit treatment at the first improvement. Such actions threaten new occurrences of the disease in men, and the fungus may become much more resistant to medications.
In general, the duration of treatment for the disease takes approximately two months. But in addition to treatment, you must adhere to some rules. For example, underwear should be made of natural material and be loose, that is, it should not tightly fit the groin area so that the scrotum does not sweat. Because humidity is a favorable environment for the proliferation of fungal spores.
Recommendation. You can avoid moisture and diaper rash in the scrotum by using talcum powder or powder, which have an antifungal effect.
Your doctor may prescribe fluconazole as a medication; this drug is most often used to treat fungus. In addition, it is effective against almost all types of infection.
The doctor also prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve redness in this area. If no ulcers or pustules appear during the development of the disease, you can treat the affected area with an iodine solution.
But you shouldn’t get too carried away, because you can get burned. Treatment in this method can be carried out as follows: for a week, iodine must be applied twice a day, and then an antifungal agent for another five days.
If the patient seeks help with an already advanced disease, medications are prescribed that can quickly relieve inflammation. Basically, these are ointments:
- Clotrimazole.
- Miconazole.
- Terbinafine.
How to carry out treatment correctly
During treatment of the disease in men, they need to follow certain recommendations, which will determine the outcome of treatment:
- Before applying antifungal ointment to the affected area, the scrotum and adjacent healthy area of skin should be washed with soap.
- The ointment should be applied to the area affected by the fungus and to healthy skin nearby.
- It is necessary to use medications after reading the instructions.
- If after fourteen days the fungus does not recede, contact the doctor again so that he changes the method of therapy.
- During treatment, you need to wear clean clothes and change bed linen every day.
- If the fungus affects not one area, but several that are not in contact, treat all foci of the disease, because it can eventually cover the entire skin.
If the disease is not treated, then over time, even if you have a normal level of immunity, it can develop into a chronic form, and will develop on the scrotum for several years.